Sleep is a universal experience that we all need to function properly, yet it remains one of the most mysterious aspects of human biology. Despite the fact that we spend roughly a third of our lives sleeping, we still know relatively little about what happens to our bodies and minds during this time. It is not just a period of rest – it is a time when our brains carry out critical processes that affect everything from our memory to our mood. In this article, we will explore the five stages of sleep that our bodies go through each night, and how they contribute to overall health and well-being. We will also discuss common sleep disorders and offer tips for improving the quality of your sleep.
The Basics of Sleep
Sleep is a natural and vital part of human life, but have you ever stopped to think about what happens when you sleep? Your body goes through a complex series of stages that are essential for your physical and mental health. Understanding the basics of sleep can help you get a better night’s rest and wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated. So, let’s take a deep dive into the fascinating world of sleep and explore what happens in our bodies when we drift off into slumber.
What is Sleep?
Sleep is a natural, recurring state of reduced consciousness where the body and brain are at rest. It is a vital activity that allows us to rest and recharge, both physically and mentally. During sleep, our brain processes and consolidates memories and performs various body functions, including repairing tissues and producing hormones.
The following table outlines the key characteristics of sleep:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced consciousness | Sleep is a state of lowered awareness where the brain is less responsive to external stimuli. |
| Inactivity | During sleep, our muscles are relaxed, and we are physically still. |
| Altered perception | Our perception of time and space is changed during sleep, and we may experience vivid dreams or nightmares. |
| Regulated by circadian rhythm | Sleep is controlled by our internal biological clock, which is influenced by various factors such as light exposure. |
| Vital for health and well-being | Adequate sleep is crucial for physical and mental functioning, and lack of sleep can have serious consequences. |
Sleep is a vital and complex process that is essential for physical and mental well-being. It is a natural state of reduced consciousness that allows the body and brain to rest and recharge. Sleep is regulated by our internal biological clock and influenced by various factors, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and quality of life.
The Importance of Sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial for overall health and wellbeing. Here are some of the key reasons why:
- Restoration: While we sleep, our bodies are hard at work repairing and restoring muscles, tissues, and other vital organs. This restoration process helps to keep us physically and mentally healthy, and is essential for maintaining a strong immune system.
- Memory consolidation: Sleep is also important for consolidating memories and allowing our brains to process and store information learned throughout the day.
- Mood regulation: Lack of sleep can have a negative impact on mood, leading to irritability, decreased ability to cope with stress, and other negative emotions.
- Improved concentration and productivity: When we get enough sleep, we are better able to focus, be productive, and make sound decisions. This is because sleep plays a critical role in restoring cognitive function.
- Reduced risk of chronic disease: Sleep has also been linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. This is because getting enough sleep can help regulate the hormones that control appetite and blood sugar levels, as well as reduce inflammation in the body.
- Increased energy: Finally, getting enough sleep can help increase energy levels and reduce fatigue. When we sleep, our bodies are able to store energy reserves that can be used throughout the day, keeping us feeling alert and focused.
Given all of these benefits, it’s clear that sleep is an essential part of our overall health and wellbeing. While it can be tempting to sacrifice sleep in order to get more done, it’s important to prioritize good sleep habits in order to ensure that we are functioning at our best both physically and mentally.
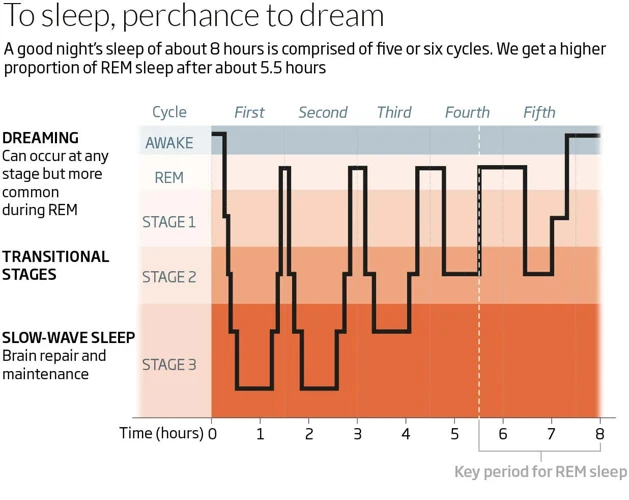
The Five Stages of Sleep
As we dive deeper into the world of sleep, it’s vital to understand the different stages of sleep that your brain and body go through during the night. These stages are divided into five distinct phases, each characterized by unique brain activity and patterns of bodily functions. Understanding these stages is crucial for achieving optimal sleep quality and promoting overall health and well-being. Let’s take a closer look at what each stage entails and what happens to the body during each phase.
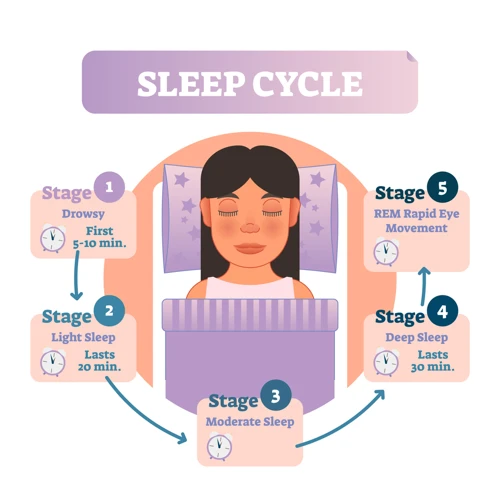
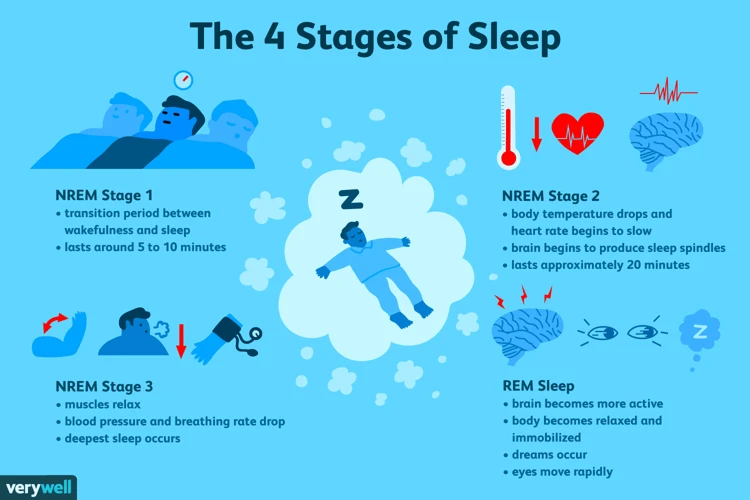
Stage 1 – Drowsiness
During Stage 1 of sleep, a person transitions from being fully awake to a relaxed state of drowsiness. This stage typically lasts around 5-10 minutes and is considered a light stage of sleep. During this stage, brain waves shift from the rapid, active state of wakefulness to slower, more relaxed patterns.
- Hallucinations: In this stage, it is common to experience brief hallucinations, such as seeing or hearing things that aren’t there.
- Hypnic jerks: It’s also common to experience hypnic jerks, which are involuntary muscle twitches that can briefly wake a person up.
- Decreased body temperature: As the body transitions into sleep, the body temperature drops slightly.
- Slow eye movements: During this stage, eye movements begin to slow down, and the muscles in the eyes start to relax.
- Easy to wake up: While it’s possible to be awakened during this stage, a person will likely feel groggy and disoriented upon waking up.
- Recharge: This stage of sleep allows the body and brain to recharge and prepare for the deeper stages of sleep to come.
While Stage 1 of sleep may only last a few minutes, it is an important stage in the sleep cycle as it sets the stage for the deeper stages of sleep.
Stage 2 – Light Sleep
During stage 2 of sleep, which typically occurs about 20 minutes after falling asleep, our brain waves slow down even further. This is a light sleep stage that accounts for about 50% of our total sleep time. During this stage, our body temperature and heart rate decrease, our muscles relax, and we become less aware of our surroundings.
During this stage, our brain also experiences brief bursts of rapid brain wave activity known as sleep spindles. These sleep spindles are believed to help with memory consolidation and strengthening neural connections.
One interesting feature of stage 2 sleep is the occurrence of what are known as K-complexes. K-complexes are single, large brain waves that occur in response to various stimuli, such as noises from the external environment. They are thought to play a role in protecting our sleep by suppressing our response to external stimuli that may disturb our sleep.
Stage 2 of sleep is a crucial stage that helps our body and brain rest and recover from the day’s activities. It prepares us for the deeper stages of sleep that are essential for physical and mental restoration.
Stage 3 – Deep Sleep
During Stage 3 of sleep, also known as deep sleep, the brain waves slow down even further. Delta waves, which are the slowest and largest brain waves, begin to dominate. This stage of sleep is essential for physical rejuvenation, as the body undergoes repair and cellular growth.
In fact, during deep sleep, growth hormone is released and tissues and muscles repair themselves. Immune system functioning is also boosted during this stage, as the body creates more immune cells to fight off infections and diseases.
One interesting aspect of deep sleep is that it’s harder to wake up from it. If woken up during this stage, a person may feel groggy and disoriented for a few minutes. However, it’s important to note that people don’t spend as much time in deep sleep as they do in earlier stages. It’s common for deep sleep to occur in the first half of the night, and as the night progresses, people tend to spend less time in deep sleep and more time in REM sleep.
Here is an overview of Stage 3 – Deep Sleep:
| Brain Waves: | Delta waves dominate |
|---|---|
| Description: | The brain waves slow down even further. Essential for physical rejuvenation, as the body undergoes repair and cellular growth. Growth hormone is released and tissues and muscles repair themselves. Immune system functioning is boosted. Harder to wake up from this stage. |
| Time Spent: | Occurs in the first half of the night, but people tend to spend less time in deep sleep as the night progresses. |
Deep sleep is a critical component of a healthy sleep cycle. Without enough deep sleep, the body is unable to repair and regenerate, which can lead to weakened immune system functioning, increased risk of illness, and overall decreased quality of life.
Stage 4 – Very Deep Sleep
During stage 4, also known as delta sleep, the brain produces a slow wave activity. This is the deepest stage of sleep, and it is the most difficult stage to wake up from. In this stage, the body has a reduced metabolic rate and the blood pressure drops, causing a decrease in the supply of blood and oxygen to the brain. The body’s tissues are repaired and restored and growth hormones are released.
Delta sleep occurs mostly in the first half of the night and is essential for feeling rested and rejuvenated the next day. A lack of delta sleep can lead to feeling tired and sluggish, with a decreased ability to concentrate and retain information.
Interestingly, children and teenagers experience more delta sleep than adults as it is crucial for their growth and development. As people age, the amount of delta sleep gradually decreases, leading to difficulties in falling and staying asleep.
The table below summarizes the characteristics of stage 4 or delta sleep:
| Stage | Brain Waves | Duration (in minutes) | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 4 (Delta Sleep) | Delta | 20-40 | Slow wave activity; very difficult to wake up from; reduced metabolic rate; decrease in blood pressure; tissue repair and growth hormone release |
Stage 4 is the deepest and most restorative stage of sleep. It is crucial for feeling rested and rejuvenated and plays a key role in growth and development. Ensuring a good amount of delta sleep by practicing healthy sleep habits is important for overall well-being.
REM Sleep – Rapid Eye Movement Sleep
During REM sleep, the body becomes very relaxed, almost paralyzed, while the brain is highly active. This stage is characterized by rapid eye movements and is known as Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep. REM sleep typically happens in bursts, with each burst lasting for 20-30 minutes.
REM sleep is essential for processing emotions and memories. During this stage, the brain consolidates memories and processes information received during the day. REM sleep also stimulates creativity and problem-solving abilities.
During REM sleep, heart rate and blood pressure increase, and breathing can become more irregular. This stage is also when individuals are most likely to have vivid dreams, sometimes causing them to physically react to the dream (such as kicking or talking in their sleep).
Below is a table summarizing the characteristics of each sleep stage:
| Sleep Stage | Brain Waves | Eye Movements | Body Position | Muscles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 – Drowsiness | Alpha waves and some theta waves | Slow rolling movements | Relaxed | Slightly relaxed |
| Stage 2 – Light Sleep | Theta waves and sleep spindles | Some movements | Relaxed | Relaxed |
| Stage 3 – Deep Sleep | Delta waves | No movement | Relaxed | Relaxed |
| Stage 4 – Very Deep Sleep | Delta waves | No movement | Relaxed | Greatly relaxed |
| REM Sleep – Rapid Eye Movement Sleep | Brain highly active | Rapid eye movements | Paralyzed/immobile | Relaxed |
It is important to cycle through all five stages of sleep in order to achieve restorative and restful sleep. Disruption of any stage of sleep can lead to poor sleep quality and negative health consequences.
Cycling Through Stages
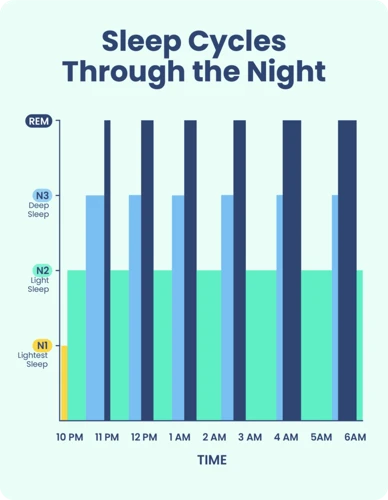
During a night’s sleep, an individual cycles through the five stages of sleep multiple times. Each cycle lasts around 90 minutes and consists of all five stages in order. It is important to note that the amount of time spent in each stage can vary throughout the night.
Stage 1 – Drowsiness: This stage is a transitional stage between wakefulness and sleep. It is characterized by the slowing down of brain waves and the feeling of drifting in and out of sleep.
Stage 2 – Light Sleep: During this stage, the body becomes more relaxed, and the heart rate and breathing slow down. Brain waves exhibited during this stage are slower and more rhythmic.
Stage 3 – Deep Sleep: Also known as slow-wave sleep, this stage is characterized by even slower brain waves, increased relaxation of the muscles, and a decrease in body temperature and heart rate.
Stage 4 – Very Deep Sleep: This is the deepest stage of sleep, during which the body is in a state of complete relaxation, and it becomes much harder to wake up. Brain waves during this stage are the slowest ones.
REM Sleep – Rapid Eye Movement Sleep: REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreams, and increased brain activity. During this stage, the body experiences increased heart rate and breathing, and the muscles become temporarily paralyzed.
After the completion of the REM stage, the cycle begins again with stage 1, and this cycle continues throughout the night. The length and frequency of each stage change during the night, with more time spent in the deep sleep stages during the first half of the night and more time spent in REM sleep during the later half.
It’s worth noting that the proportion of time spent in each stage changes as we age, with infants and young children spending more time in REM sleep than the other stages, while older adults tend to spend more time in the lighter stages of sleep.
How Much Sleep Do You Need?
Getting enough sleep is crucial for optimal health and wellbeing. But how much sleep do you actually need? The answer varies depending on your age, lifestyle, and individual needs.
According to the National Sleep Foundation, newborn babies need the most sleep, with recommended ranges of 14-17 hours per day. As children grow older, their necessary sleep time decreases. Toddlers require 11-14 hours of sleep, while preschoolers need 10-13 hours. School-aged children should aim for 9-11 hours, while teenagers require 8-10 hours.
For adults, the recommended amount of sleep is between 7-9 hours per night. However, some people may require as little as 6 hours or as much as 10 hours of sleep to feel rested.
It’s important to remember that quality of sleep also plays a role in how much sleep you need. If you frequently wake up throughout the night or suffer from sleep disorders, you may need more sleep than someone who sleeps more soundly.
Additionally, your lifestyle habits can also impact how much sleep you need. If you engage in physically demanding work or exercise, you may require more sleep for your body to properly recover. Similarly, if you’re consistently under high levels of stress, you may need more sleep to aid in mental and emotional recovery.
Ultimately, it’s up to you to determine how much sleep you need to function at your best. Keeping track of your sleep patterns and adjusting your routine as needed can help ensure that you’re getting the necessary amount of rest to maintain optimal health and wellbeing.
The Quality of Your Sleep Matters
The significance of getting a good night’s sleep cannot be overstated. Apart from feeling rejuvenated and refreshed when we wake up, sleep plays an essential role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. However, the quality of our sleep is just as important as the quantity of hours we spend sleeping. Poor sleep quality can lead to a range of physical and mental health issues, affecting our productivity and overall quality of life. In this section, we will highlight the benefits of good sleep quality as well as the consequences of poor sleep quality.
Benefits of Good Sleep Quality
Good sleep quality has numerous benefits for both physical and mental health. Here are some of the most significant benefits of getting a good night’s sleep:
| Physical Benefits | Mental Benefits |
|
|
Getting enough good-quality sleep is essential for maintaining good mental and physical health. It can help with weight management, reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, and boost athletic performance. Additionally, good sleep quality can improve mood, increase creativity, and enhance problem-solving skills. Make sure you are getting enough sleep to reap the many benefits that a good night’s rest can provide.
The Consequences of Poor Sleep Quality
Poor sleep quality can have a range of negative consequences on both our physical and mental health. Here are some of the most commonly observed effects of consistently inadequate sleep:
- Increased risk of obesity and chronic diseases: Lack of sleep has been linked to hormonal changes that can cause an increased appetite and decreased metabolism, leading to weight gain and obesity. Additionally, sleep-deprived individuals are at a higher risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
- Worsened cognitive function: Sleep is essential for the consolidation of memories and the ability to learn new information. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to impairments in attention, concentration, and problem-solving skills, making it difficult to perform daily tasks and work efficiently.
- Increased risk of depression and anxiety: Poor sleep quality has been shown to contribute to the development of mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. This is because sleep is essential for regulating emotions and mood, and a lack of sleep can lead to increased levels of stress and negative emotions.
- Decreased immune function: Sleep is critical for the functioning of the immune system, as it helps to produce cytokines and other immune cells that fight off infections and diseases. Chronic sleep deprivation can therefore lead to a weakened immune system and increased susceptibility to illness.
- Decreased libido: Hormonal imbalances caused by poor sleep quality can also lead to a decreased sex drive and reduced sexual function.
- Increased risk of accidents: Chronic sleep deprivation can impair reaction times, coordination, and decision-making abilities, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries at home or in the workplace.
It’s clear that getting good quality sleep is essential for our overall health and well-being, and consistently poor sleep can have a multitude of negative consequences. It’s important to take steps to improve our sleep habits and seek medical attention if we’re experiencing ongoing sleep problems.
Factors Affecting Sleep Quality
Our sleep quality is determined by multiple factors, ranging from environmental to lifestyle factors. These factors can greatly affect our ability to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night. It’s important to understand how these factors can impact our sleep quality and how we can make changes to improve it. Let’s dive into some of the common factors that can affect our sleep, and how we can work towards getting a more restful night’s sleep.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play an important role in the quality of one’s sleep. Here are some of the environmental factors that can affect your sleep:
- Noise: Excessive noise can be a major disturbance to your sleep. Loud noises such as traffic, construction, or even snoring can disrupt your sleep and cause you to wake up frequently throughout the night. Consider using earplugs or investing in a white noise machine to block out any unwanted noises.
- Temperature and humidity: The temperature and humidity in your room can have a significant impact on your sleep quality. Sleeping in a room that is too hot or too cold can interfere with your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. A temperature between 60 to 67 degrees Fahrenheit is considered optimal for quality sleep.
- Light: Light exposure can interfere with your sleep, particularly if it’s bright enough to affect your circadian rhythm. Invest in light-blocking curtains or an eye mask to make your sleeping environment as dark as possible. This can help you get a more restful night’s sleep.
- Bed and bedding: The quality of your bed and bedding can have a major impact on your sleep quality. If your mattress is too soft or too firm, it can lead to discomfort and pain that can interrupt your sleep. Investing in a high-quality mattress and bedding that cater to your needs can improve the quality of your sleep.
- Pets: While pets can be comforting to have around, they can also disrupt your sleep. Pets that move around a lot, make noise or need to go outside frequently can wake you up and disrupt your sleep. It may be helpful to train your pets to sleep in a separate space.
Addressing these environmental factors can improve the quality of your sleep significantly.
Lifestyle Factors
Our lifestyle choices directly impact the quality of our sleep. Here are some key lifestyle factors that can affect our sleep:
- Diet: Eating a heavy meal close to bedtime can disrupt sleep. On the other hand, going to bed hungry can also cause discomfort and make it harder to fall asleep. It’s important to find a balance and avoid eating heavy or spicy foods late at night.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can improve sleep quality. However, working out too close to bedtime can keep you awake. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per day, but avoid exercising within 2-3 hours of bedtime.
- Alcohol and caffeine consumption: Both caffeine and alcohol can disrupt sleep. While caffeine can make it difficult to fall asleep, alcohol can cause us to wake up during the night. It’s best to limit caffeine and alcohol consumption, especially in the evening.
- Smoking: Nicotine is a stimulant which can make it harder to fall asleep and disrupt sleep quality. Quitting smoking can improve your overall health as well as your sleep quality.
- Stress: High levels of stress can make it difficult to fall asleep and cause sleep disruptions. Develop relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation or yoga to help manage stress levels before bed.
By addressing these lifestyle factors, we can improve the quality of our sleep and enjoy its many benefits.
Tips for Better Sleep Quality

When it comes to getting a good night’s rest, there are several factors that can affect the quality of your sleep. Luckily, there are also a variety of strategies you can use to improve your sleep quality. From creating a sleep-conducive environment to managing stress levels, incorporating these tips into your nightly routine can help you wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most effective ways to enhance the quality of your sleep.
Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment
Creating a sleep-conducive environment is crucial for getting a good night’s sleep. Here are some tips on how to set up your sleeping space to ensure it’s comfortable and conducive to sleep:
- Keep the Room Dark: Exposure to light can suppress the production of the hormone melatonin, which helps regulate sleep. Consider using blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out light.
- Reduce Noise: If you live in a noisy area, consider using earplugs or a white noise machine to drown out external sounds.
- Make Sure Your Bed is Comfortable: Invest in a good quality mattress and pillows that support your sleeping position. Choose bedding made of soft, breathable material that feels comfortable against your skin.
- Keep the Room Cool: A cool temperature of around 60 to 67 degrees Fahrenheit (15 to 19 degrees Celsius) is ideal for sleeping. Consider using a fan or air conditioner to regulate the temperature.
- Avoid Clutter: A cluttered bedroom can cause added stress and anxiety, which can make it difficult to sleep. Keep your bedroom tidy and organized.
- Eliminate Electronic Distractions: Avoid using electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops or tablets in bed. The blue light emitted from these devices can interfere with your circadian rhythm and make it harder to fall asleep.
By creating a sleep-conducive environment, you can help set the stage for a good night’s rest. Taking steps to make sure your sleeping space is comfortable, cool, and free from distractions can lead to improved sleep quality and overall health.
Stick to Regular Sleep Schedule
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule is essential for improving the quality of your sleep. Our body loves routine, and maintaining a consistent sleep and wake-up time as much as possible can help regulate your internal clock. Here are some tips to help you stick to a regular sleep schedule:
- Set a consistent bedtime: Try to go to bed at the same time each night, even on weekends or days off.
- Create a bedtime routine: Establishing a relaxing pre-sleep routine, such as taking a warm bath or reading a book, can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
- Avoid naps: If possible, try to avoid daytime naps. They can disrupt your sleep schedule and make it harder to fall asleep at night.
- Avoid sleeping in: Try to wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Sleeping in too late can throw off your sleep schedule and make it harder to fall asleep the next night.
- Be patient: It can take a few weeks for your body to get used to a new sleep schedule. Stick to it and be patient, and eventually, it will become a habit.
By sticking to a regular sleep schedule, you can improve the quality of your sleep and wake up feeling refreshed and energized. So, try to make it a priority and see how much better you feel.
Limit Your Exposure to Screens Before Bed
It’s important to limit your exposure to screens before bed, as the blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with your natural sleep cycle. Here are some tips on how to do this:
- Avoid using electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops for at least an hour before bed. Instead, try reading a book or listening to calming music.
- If you must use electronic devices before bed, try using a blue light filter or wearing blue light blocking glasses.
- Avoid watching TV in bed, as this can disrupt your sleep cycle and make it harder to fall asleep.
- Don’t use your phone or tablet as an alarm clock. Instead, use a traditional alarm clock or a smartwatch that doesn’t emit blue light.
Remember, getting a good night’s sleep is crucial for your overall health and wellbeing. So, make sure you’re doing everything you can to limit your exposure to screens before bed, and create a relaxing environment that promotes restful sleep.
Relax Before Bed
It is important to relax before bed in order to fall asleep easily and stay asleep. Here are some tips for relaxing before bed:
| Tip | Description |
| Take a warm bath or shower | Warm water can help relax tense muscles and calm the mind |
| Practice relaxation techniques | Examples include deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualization exercises |
| Read a book or listen to calming music | A relaxing activity can help to shift the mind away from stressors and induce drowsiness |
| Use aromatherapy | Scents like lavender or chamomile can promote relaxation and help to induce sleep |
By incorporating relaxation techniques into your bedtime routine, you can help signal to your body and mind that it is time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Avoid stimulating activities like watching action-packed movies or having intense conversations before bed, as this can increase stress and make it harder to relax. Instead, focus on calming activities that will help you unwind and prepare for a restful night’s sleep.
Avoid Late-Night Eating and Drinking
One important factor that can greatly impact the quality of your sleep is your diet. Specifically, when you eat and drink before bedtime can have a significant effect on your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. Avoiding late-night eating and drinking is crucial for a good night’s sleep. Here are some tips to help you avoid consuming late-night snacks and beverages:
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine is a stimulant that can make it difficult to fall asleep, while alcohol may initially make you feel drowsy but can disrupt your sleep later in the night.
- Don’t eat heavy meals within 3 hours of bedtime: Digesting a heavy meal can take several hours, and can cause discomfort, making it difficult to sleep.
- Avoid spicy and acidic foods: These foods may cause heartburn and indigestion, which can disturb your sleep.
- Eliminate late-night snacks: Consuming sugar-laden or high-carb snacks before bed can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, leading to wakefulness during the night.
- Choose sleep-promoting foods: Some foods promote sleep, such as cherries, chamomile tea, and almonds. Incorporating these foods into your evening routine can help you fall asleep naturally.
By avoiding late-night eating and drinking, you can improve your chances of getting a restful night’s sleep. Try these tips and see if they make a difference in your sleep quality.
Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise has been shown to have numerous benefits for overall health, including improved sleep quality. Here are some tips for incorporating exercise into your routine to improve your sleep:
- Find the right time: It’s important to find a time that works best for you to exercise. Some people prefer to exercise first thing in the morning, while others find it helpful to exercise later in the day. Experiment with different times to find what works best for your schedule and your body.
- Choose the right type of exercise: Different types of exercise can have different effects on sleep. Aerobic exercise such as running or cycling can help improve overall sleep quality. Resistance training can also be beneficial for some people. However, it’s important to avoid intense exercise close to bedtime, as it can cause your body to be too energized to sleep.
- Don’t overdo it: While exercise can provide numerous benefits, it’s important not to overdo it. Excessive exercise can actually have a negative impact on sleep quality. It’s important to listen to your body and to gradually build up your exercise routine over time.
- Be consistent: Consistency is key when it comes to exercise and sleep. Aim to exercise at least three times per week, and try to keep a consistent schedule each day.
By incorporating regular exercise into your routine, you can improve your sleep quality and overall health. Remember to find the right type of exercise, be consistent, and listen to your body to achieve the best results.
Manage Stress Levels
One effective way to improve the quality of your sleep is by managing your stress levels. Stress can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep, which can result in poor sleep quality. There are many strategies you can use to reduce stress and promote relaxation before bed.
Meditation and Mindfulness: Practice meditation or mindfulness techniques to clear your mind of racing thoughts and reduce stress.
Deep Breathing: Take slow, deep breaths to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and relax each muscle group in your body to release tension and promote relaxation. This can be done while lying down in bed.
Aromatherapy: Use essential oils like lavender or chamomile to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Yoga or Stretching: Gentle stretching or practicing yoga can help release tension and promote relaxation.
In addition to these strategies, it is also important to identify and address the source of your stress. Consider talking to a therapist or counselor for additional support in managing stress and improving your overall sleep quality.
Common Sleep Disorders
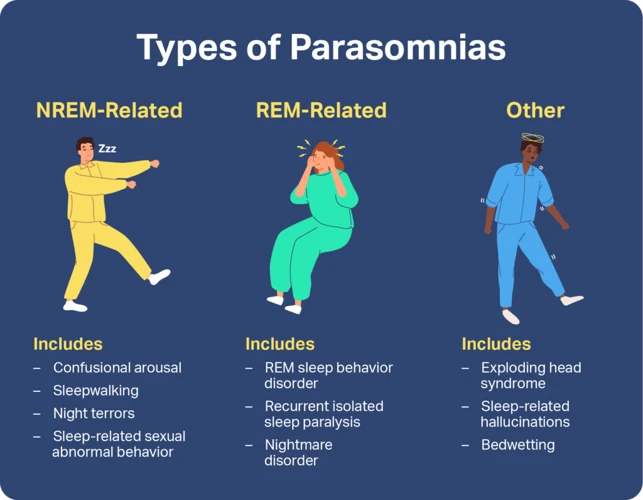
As much as we look forward to a good night’s sleep, it’s not always as restful as we hope it would be. Sometimes, we toss and turn all night, while other times we can’t seem to keep our eyes open during the day. This can be due to several sleep disorders, which can affect not only the quantity but also the quality of our sleep. In this section, we’ll delve into some of the most common sleep disorders that people experience and their symptoms. We’ll also discuss the possible causes and treatments for each disorder.
Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, even when a person has the opportunity to do so. People with insomnia often feel tired and irritable during the day, have trouble concentrating, and may experience mood swings. Insomnia can be a short-term issue or a chronic condition.
Symptoms of insomnia include trouble falling asleep, waking up frequently during the night, waking up too early and difficulty falling back asleep, feeling tired or not rested after a night’s sleep, and daytime sleepiness or fatigue.
Causes of insomnia
Insomnia can be caused by a variety of factors, including certain medical conditions, medications, lifestyle habits, and psychological issues. Some common causes of insomnia include:
| Medical conditions | Medications | Lifestyle habits | Psychological issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | Certain antidepressants | Consuming caffeine or alcohol | Stress and anxiety |
| Respiratory problems | Corticosteroids | Irregular sleep schedule | Depression |
| Neurological disorders | Stimulants like caffeine | Lack of exercise | Bipolar disorder |
| Gastrointestinal problems | Some blood pressure medications | Napping during the day | Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) |
Treatment for insomnia
Treatment for insomnia depends on the cause of the condition. In some cases, treating an underlying medical condition or adjusting medication can resolve the issue. Lifestyle changes, such as establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and regulating sleep schedule can also be effective.
In cases where insomnia persists despite these measures, a doctor may prescribe medications to help with sleep, such as sedatives or hypnotics. However, these medications can be habit-forming and may have side effects such as dizziness, confusion, or even worsen the quality of sleep.
It’s important to identify and address symptoms of insomnia early on to prevent the long-term negative effects on physical and mental health. Consult with a doctor if insomnia persists or has a significant impact on daily life.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea is a common sleep disorder where breathing is repeatedly stopped and started during sleep. This occurs when the muscles at the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open. The condition is more commonly found in people who are overweight or obese, but can also occur in people with narrow airways, enlarged tonsils or a family history of the condition.
Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea:
- Loud snoring
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Frequent waking up throughout the night to catch breath
- Morning headache
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
Obstructive sleep apnea can lead to a number of complications, including high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, stroke and diabetes. It can also cause poor quality of life due to fatigue and decreased productivity.
Treatment options for obstructive sleep apnea:
- Weight loss: for overweight individuals, losing weight can help reduce the severity of sleep apnea.
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP): a machine worn during sleep that delivers air pressure to keep the airway open.
- Oral appliances: devices that are fitted in the mouth to keep the airway open.
- Surgery: in some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove excess tissue from the throat or repair structural abnormalities in the airway.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have obstructive sleep apnea. A sleep study may be necessary to accurately diagnose the condition and determine the best course of treatment.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks. It affects approximately 1 in every 2,000 people in the United States, although the actual number may be higher as this condition is often misdiagnosed.
Symptoms of narcolepsy can include:
| Excessive daytime sleepiness | Feeling excessively tired during the day, which can impair daily activities |
| Cataplexy | Sudden loss of muscle tone, often triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or surprise |
| Hypnagogic hallucinations | Vivid, dream-like experiences that occur when falling asleep or waking up |
| Sleep paralysis | Temporary inability to move or speak when falling asleep or waking up |
The cause of narcolepsy is not entirely understood, but it is thought to involve an autoimmune reaction that targets the brain’s hypocretin-producing neurons, which help regulate sleep and wakefulness.
Currently, there is no cure for narcolepsy, but treatment can help alleviate symptoms. Medications such as stimulants and antidepressants may be prescribed to help with excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy. Lifestyle adjustments such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and avoiding alcohol and caffeine may also help manage symptoms.
It is important to see a doctor if you suspect you may have narcolepsy, as this condition can significantly impact daily life and increase the risk of accidents while driving or operating machinery. With proper treatment and management, however, many people with narcolepsy are able to lead normal, fulfilling lives.
Restless Leg Syndrome
Restless Leg Syndrome, also known as Willis-Ekbom disease, is a neurological disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs. This urge is typically accompanied by uncomfortable sensations such as itching, tingling, crawling, or burning that occur mainly in the legs. The symptoms of Restless Leg Syndrome usually worsen in the evening or at night, causing difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Here are some of the common features of Restless Leg Syndrome:
- Symptoms: As mentioned earlier, Restless Leg Syndrome is characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs that is accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. The urge to move the legs can be so strong that it causes difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to daytime fatigue or sleepiness.
- Causes: Although the exact cause of Restless Leg Syndrome is unknown, several factors are believed to contribute to its development, including genetics, iron deficiency, pregnancy, kidney failure, and certain medications.
- Treatment: The treatment of Restless Leg Syndrome typically involves medications that increase dopamine levels in the brain and promote better sleep. Some non-pharmacologic treatments such as regular exercise, good sleep hygiene, and avoiding certain medications can also help alleviate symptoms. In some cases, treating an underlying condition such as iron deficiency or kidney failure may help resolve the Restless Leg Syndrome.
- Impact: Restless Leg Syndrome can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to sleep deprivation, daytime fatigue, and mood disturbances. It can also affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities, including work and social interactions.
If you are experiencing symptoms of Restless Leg Syndrome, it is important to talk to your doctor to rule out any underlying conditions and receive appropriate treatment.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to pay attention to your sleeping patterns and seek medical advice if you experience persistent difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, or if you feel excessively sleepy during the day. If you notice any abrupt changes in your sleep patterns, such as sudden insomnia, frequent awakenings or episodes of snoring, it may be worth consulting a sleep specialist.
If you have other accompanying symptoms such as chest pain, heart palpitations, or shortness of breath during sleep, it could indicate a serious underlying medical condition, and you should consult a doctor immediately.
If you have been diagnosed with a sleep disorder and your current treatment is not relieving your symptoms, or if your symptoms worsen despite adhering to your treatment plan, it may be time to consult your healthcare provider.
It is important to remember that addressing sleep problems as soon as possible can help reduce your risk of developing chronic sleep disorders and their associated complications. So, if you are struggling with sleep on a regular basis, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the 5 stages of sleep and the factors affecting sleep quality can help individuals prioritize the importance of sleep in their lives. The stages of sleep range from light drowsiness to deep, restorative sleep, incorporating the important REM stage. It is critical to get an adequate amount of sleep each night to avoid the negative consequences of sleep deprivation, such as decreased productivity and increased risk of disease. Good sleep quality also requires a conducive sleep environment, regular sleep schedule, and healthy lifestyle habits such as exercise and stress management.
For those experiencing persistent sleep disturbances, it is important to consult a doctor to determine if a sleep disorder is present. Common sleep disorders, including insomnia, obstructive sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and Restless Leg Syndrome, have their own specific symptoms and treatments.
Incorporating healthy sleep habits into our daily lives can significantly improve our overall health and well-being. From better mental health to higher productivity, there is no end to the benefits of good quality sleep. So, let us all prioritize getting a good night’s sleep and wake up feeling refreshed and ready to take on the day.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many stages of sleep are there?
There are five stages of sleep.
What is REM sleep?
REM sleep is a stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movement and dreaming.
How much sleep do adults need?
Most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
What are the consequences of poor sleep quality?
Poor sleep quality can lead to daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and mood changes.
What are some environmental factors affecting sleep quality?
Noise, light, and temperature are some environmental factors that can affect sleep quality.
What lifestyle factors can affect sleep quality?
Factors like caffeine consumption, smoking, and alcohol consumption can impact sleep quality.
What is insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
What is obstructive sleep apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea is a sleep disorder marked by pauses in breathing during sleep.
How can exercise impact sleep quality?
Regular exercise can improve sleep quality and help with falling asleep more easily.
When should someone see a doctor for sleep concerns?
Someone should see a doctor if they are experiencing severe daytime fatigue, loud snoring, or difficulty staying asleep on a regular basis.