Millions of people around the world struggle with anxiety and nightmares, two seemingly different conditions that can actually be closely linked. While it’s no surprise that anxiety and stress can lead to poor sleep and vivid dreams, the connection between these experiences is still not fully understood. Scientists continue to explore the complex relationship between anxiety and nightmares, seeking to understand how the two influence each other and impact mental health. In this article, we will delve deeper into this connection, examining the causes, effects, and potential treatments for anxiety-related nightmares.
Definition of Anxiety and Nightmares
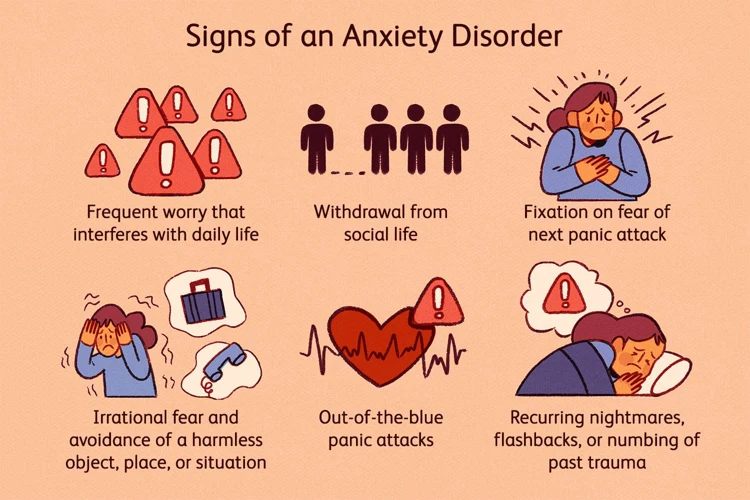
Anxiety is a feeling of unease, such as worry or fear, that can be mild or severe. It is a normal human emotion that can be triggered by stress, but for some people, anxiety can become chronic and persistent, interfering with daily life. Nightmares, on the other hand, are vivid and disturbing dreams that can be scary, sad, or anxious. They often wake a person up from sleep feeling frightened and disoriented.
Both anxiety and nightmares are common experiences, as nearly everyone will experience anxiety or a nightmare at some point in their lives. However, when these experiences become chronic and interfere with the ability to function and achieve restful sleep, they can have a negative impact on mental health and wellbeing.
Anxiety and nightmares are often linked, with anxiety being a common trigger for nightmares. This is because anxiety can cause the brain to become more active, leading to vivid and distressing dreams. In turn, nightmares can increase anxiety levels, creating a vicious cycle that can be difficult to break.
Understanding the definition of anxiety and nightmares is important because it provides insight into how these experiences can impact a person’s mental and emotional wellbeing. With a better understanding of these conditions, individuals can seek the appropriate support to reduce symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Prevalence of Anxiety Disorders and Nightmares
Anxiety disorders and nightmares are prevalent among the general population. Anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in the United States, affecting about 18.1% of the population every year. Women are more likely to experience anxiety disorders than men.
Nightmares, on the other hand, are experienced by around 50% of adults at some point in their lives, with women being more likely to have them than men. While nightmares are generally infrequent and short-lived, for some people, they can be a frequent occurrence that can severely affect their quality of life.
It is important to note that having anxiety does not necessarily mean that an individual will experience nightmares, and experiencing nightmares does not automatically point to an underlying anxiety disorder. However, research has found a significant link between anxiety and nightmares, with people with anxiety disorders being more likely to experience frequent nightmares than those without.
Additionally, certain types of anxiety disorders are more strongly associated with nightmares than others. For example, people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) often experience vivid and distressing dreams, which can be related to their traumatic experiences. Similarly, people with panic disorder may experience nightmares related to their fears of catastrophic events.
Both anxiety disorders and nightmares are prevalent among the population and are linked to each other in many cases. It is important for individuals who experience frequent nightmares or symptoms of anxiety to seek professional help, as these conditions can severely impact their mental health and quality of life.
Research linking Anxiety and Nightmares
Studies have confirmed a link between anxiety and nightmares. The American Psychological Association defines anxiety as an emotion characterized by feelings of tension, worried thoughts, and physical changes such as increased blood pressure. Similarly, nightmares can be defined as vivid and frightening dreams that occur during REM sleep.
Research has shown that anxiety disorders are closely associated with sleep disruption and nightmares. In a study conducted by the National Institutes of Health, it was found that people who suffer from anxiety disorders were more likely to have frequent and intense nightmares than those without the condition. Additionally, the study found that anxiety-related nightmares can contribute to the development of other mental health disorders, including depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Several other studies have confirmed the relationship between anxiety and nightmares. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Anxiety Disorders found that people with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) experienced more frequent and severe nightmares than those without the disorder. Another study carried out by the University of Pittsburgh indicated that post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) sufferers often experience intense and recurrent nightmares, which contribute significantly to their condition.
Additionally, research has revealed that the frequency and emotional intensity of nightmares increase as a person’s anxiety level rises. According to a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, people who experience high levels of anxiety are more likely to have nightmares and to experience them more frequently than individuals with lower levels of anxiety.
Research has confirmed a strong association between anxiety and nightmares. People who suffer from anxiety disorders are more likely to experience frequent and intense nightmares, which, in turn, can contribute to the development of other mental health disorders. Understanding the link between anxiety and nightmares can help identify potential treatment options and preventative measures to alleviate symptoms associated with both conditions.
Cause of Nightmares related to Anxiety

Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that can cause a great deal of distress and anxiety for the person experiencing them. While the exact cause of nightmares is still a topic of much debate in the scientific community, it is widely believed that anxiety plays a significant role in their occurrence.
The Role of Emotions in Dreaming: Dreams are believed to be closely tied to our emotional state. When we are feeling anxious or stressed during the day, these emotions can continue into our dreams at night. Dreams act as a processing mechanism for our emotions, and when we are feeling overwhelmed, our brains struggle to make sense of these feelings, resulting in nightmares.
The Fight or Flight Response: Anxiety triggers our body’s natural “fight or flight” response, activating our sympathetic nervous system and releasing adrenaline. This response is designed to help us react quickly and efficiently to perceived threats, but when it is activated during sleep, it can lead to nightmares. The adrenaline released during the fight or flight response can cause our heart rate and breathing to increase, further intensifying our dreams.
PTSD and Nightmares: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a condition that can result from experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. One of the hallmark symptoms of PTSD is regular nightmares about the traumatic event. These nightmares are thought to be caused by the brain’s attempts to process the trauma and can be particularly distressing for those experiencing them.
Anxiety is a major contributing factor to the occurrence of nightmares. While the exact cause of nightmares is still a topic of much scientific debate, the connection between anxiety and nightmares is well-established. By understanding the mechanisms that lead to nightmares, we can work towards preventing them and promoting better overall mental health.
The Role of Emotions in Dreaming
Dreams, including nightmares, are often influenced by emotions that individuals experience throughout the day. The role of emotions in dreaming is complex, and there are numerous theories about how emotions impact dream content. One theory is that emotions may affect the way memories are processed and consolidated during sleep, leading to the appearance of certain emotions in dreams.
Studies have suggested that highly emotional experiences, such as fear, anger, or sadness, may increase the frequency of nightmares. It is also believed that negative emotions can intensify the storyline of a dream and cause the dreamer to experience more vivid and realistic dreams than they would normally experience. Some researchers propose that this may be an evolutionary adaptation, allowing individuals to rehearse threatening scenarios and prepare for potential dangers.
On the other hand, positive emotions such as happiness, excitement, and love are less likely to produce nightmares. Instead, these emotions may lead to more pleasant dreams and a better overall sleep quality.
The role of emotions in dreaming is an area of ongoing research and controversy. However, it is clear that emotions can significantly impact the content and frequency of nightmares, which can in turn have negative effects on a person’s mental health and well-being. It is important to address the root causes of anxiety and try to reduce emotional stress in order to prevent anxiety-related nightmares.
The Fight or Flight Response
When a person experiences anxiety, their body enters into what is known as the “fight or flight” response. This is a natural response that has evolved over time to help us respond quickly to perceived threats, such as encountering a predator in the wild. During the fight or flight response, the body releases stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which can cause physical symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, sweating, and shallow breathing.
When these stress hormones are released, they can also affect the brain and the way we dream. Specifically, researchers have found that the amygdala, a part of the brain that helps regulate emotions, may be more active during both anxiety and dream states, leading to more vivid and intense dreams or nightmares.
This connection between anxiety and the fight or flight response may also be why nightmares can be more common during periods of high stress. For example, individuals who are experiencing a lot of stress at work or in their personal lives may be more likely to experience anxiety-related nightmares.
Interestingly, some researchers have also suggested that experiencing nightmares and other types of stressful dreams may actually be a way for our brains to process and cope with difficult emotions and experiences. By replaying these events in our minds, we may be able to better understand them and work through them on a subconscious level.
The fight or flight response is an important factor in understanding the relationship between anxiety and nightmares. By learning to manage our stress levels and address the root causes of anxiety, we may be able to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares over time.
PTSD and Nightmares
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop in people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. One of the major symptoms of PTSD is experiencing recurring nightmares related to the trauma. These nightmares can be so severe that they lead to fear of falling asleep and can even cause insomnia.
PTSD-related nightmares can be particularly distressing because they can feel incredibly real and vivid, as if the traumatic event is happening all over again. This can trigger intense emotions such as fear, anger, and sadness, which can cause physical symptoms such as sweating, rapid heart rate, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can cause further anxiety and stress, making it difficult for the person to fall back asleep even after the nightmare has ended.
The frequency and severity of nightmares in PTSD can vary depending on the individual and the nature of the traumatic event. However, research suggests that nightmares are a common symptom in those with PTSD. In fact, studies have shown that up to 80% of individuals with PTSD experience nightmares. Additionally, those who experience PTSD-related nightmares may also be at increased risk for other mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse disorders.
Fortunately, there are treatments available to help manage PTSD-related nightmares. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common form of therapy that is often used to address PTSD symptoms such as nightmares. This type of therapy helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to the trauma, which can help alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
In addition to therapy, medications such as antidepressants and prazosin (a blood pressure medication) have also been shown to be effective in reducing nightmares related to PTSD. However, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the most effective course of treatment for each individual.
PTSD-related nightmares can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health and quality of life. However, with proper treatment and support, it’s possible to manage and reduce the frequency and severity of these nightmares, leading to improved sleep and overall well-being.
Effects of Nightmares on Mental Health

Nightmares can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health, affecting both their emotional and physical well-being. The distressing and vivid nature of these dreams can result in a range of negative psychological consequences, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
One of the main effects of nightmares is the impact they have on emotional well-being. Individuals who experience frequent and intense nightmares may find themselves feeling more anxious or fearful throughout the day. This can lead to disruptions in daily life, such as difficulty concentrating, decreased motivation, and decreased productivity.
Nightmares can also have physical effects on the body. For example, individuals who experience frequent nightmares may experience disrupted sleep, which can lead to fatigue, irritability, and decreased immune function. This can then lead to a vicious cycle, where the individual is more prone to experiencing further anxiety and nightmares due to their decreased physical and emotional well-being.
It’s important to note that nightmares are often comorbid with other mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders and PTSD. In fact, PTSD is a common cause of nightmares, and individuals with this condition may experience recurring vivid dreams of traumatic experiences. These nightmares can be so intense that they disrupt the individual’s sleep and lead to further psychological distress, making it challenging to manage other symptoms of PTSD.
Nightmares have also been linked to various sleep disorders, such as insomnia and sleep apnea. The fear of experiencing a nightmare can make it harder to fall asleep, and disrupted sleep can increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. This can then lead to a cycle of poor sleep and increased anxiety, which can further exacerbate the mental health effects of nightmares.
Thankfully, there are various techniques and treatments that can help prevent and manage anxiety-related nightmares. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and mindfulness meditation, can help calm the mind and decrease anxiety levels. Addressing the root cause of anxiety through therapy or counseling is also critical in reducing the frequency of nightmares. Additionally, medical treatment, such as medication or cognitive-behavioral therapy, can be helpful for reducing anxiety symptoms and improving sleep quality. By incorporating lifestyle changes such as healthy sleep habits, exercise, and nutrition, individuals can take positive steps towards reducing anxiety and preventing nightmares from negatively impacting their mental health.
Impact on Emotional and Physical Well-being
Experiencing anxiety-related nightmares can have a significant impact on both emotional and physical well-being. These nightmares can cause individuals to feel fear, terror, and anxiety that linger long after waking up. These emotions can negatively affect an individual’s mood and behavior, leading to depression, irritability, and difficulty concentrating on daily tasks. Additionally, nightmares can disrupt an individual’s sleep, causing them to wake up frequently throughout the night and experience difficulty falling back asleep. This lack of quality sleep can lead to daytime fatigue, decreased immune function, and an overall decline in physical health.
Anxiety-related nightmares can be a sign of an underlying mental health condition such as generalized anxiety disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). When left unresolved, these conditions can worsen over time and further impact an individual’s overall well-being. It is essential to address and treat the root cause of anxiety-related nightmares to prevent any long-term negative effects on an individual’s mental and physical health.
The impact of anxiety-related nightmares on emotional and physical well-being is significant and can have long-lasting effects if left unaddressed. Seeking help from a mental health professional or implementing lifestyle changes can aid in treating the underlying anxiety and reducing the occurrence of these distressing nightmares.
Relation to Sleep Disorders
Nightmares related to anxiety not only disturb our sleep but also disrupt our overall sleep patterns, leading to sleep disorders. Prolonged exposure to nightmares can induce insomnia and other sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, which can cause irregular breathing and impact sleep quality. When we experience repeated nightmares, our body’s natural response is to become hyper-vigilant, making it difficult for us to relax and fall back asleep.
Lack of sleep affects our mental and physical health causing fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. In turn, these factors amplify pre-existing anxiety and make it even more challenging to manage our symptoms. For those with chronic nightmares related to anxiety, obtaining enough restful sleep is critical to prevent the exacerbation of these symptoms.
The relationship between anxiety-related nightmares and sleep disorders can become cyclical, with one leading to the other, and vice versa. The sleep disorders caused by nightmares can, in turn, create situations that provoke anxiety-inducing events in daily life. It is crucial to address both anxiety and sleep disturbances together to provide the most effective treatment for the individual.
Treating sleep disorders related to anxiety often involves addressing the underlying anxiety itself. Techniques such as therapy and medication can help reduce anxiety symptoms and, in turn, lead to a reduction in the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Additionally, the implementation of healthy sleep habits such as avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime, as well as engaging in relaxation techniques before sleep, can also help calm the mind and promote restful sleep.
Understanding the relationship between anxiety-related nightmares and sleep disorders is essential in developing effective treatments. Addressing both areas together can bring relief to individuals suffering from anxiety and improve their overall quality of life.
Effects on Anxiety and Stress Levels
Experiencing nightmares can have a significant impact on an individual’s anxiety and stress levels. After a night of bad dreams, people often wake up feeling anxious, stressed, and exhausted. This stress can cause an increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and lead to a release of stress hormones like cortisol.
Persistent nightmares can create a vicious cycle. Anxiety can cause nightmares, and in turn, nightmares can lead to increased anxiety. This cycle can be difficult to break, but there are several strategies individuals can use to manage anxiety and prevent nightmares.
One technique is to practice relaxation techniques regularly. Breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can all help to calm the mind and reduce anxiety levels. Additionally, incorporating mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, into a daily routine can help individuals learn to focus on the present moment and reduce feelings of worry or fear.
Addressing the root cause of anxiety through therapy or counseling can also be a helpful approach. Talking to a mental health professional can provide insight into the underlying causes of anxiety and help individuals develop coping strategies.
It is also important to maintain healthy sleep habits. Create a relaxing bedtime routine, avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed, and stick to a consistent sleep schedule. A comfortable and supportive sleeping environment can also be beneficial to improving the quality of sleep.
Finally, engaging in regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet can also help to reduce anxiety levels. Exercise releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce stress. A healthy diet rich in whole foods and low in processed and sugary foods can provide the body with the nutrients it needs to manage stress and anxiety.
The effects of anxiety-related nightmares can be challenging, but there are effective strategies and lifestyle changes that can reduce their impact on an individual’s mental health.
Preventing Anxiety-Related Nightmares
Preventing anxiety-related nightmares involves several different techniques that can help in reducing the frequency and intensity of these episodes. One of the most effective strategies is practicing relaxation techniques and mindfulness.
Relaxation techniques and mindfulness: Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help to reduce stress and anxiety levels, which in turn can lead to fewer nightmares. Mindfulness, on the other hand, involves paying attention to the present moment and acknowledging any thoughts or feelings that arise without judgment. This approach can help to reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being, which can also lessen the likelihood of nightmares.
Another key strategy for preventing anxiety-related nightmares is addressing the root cause of anxiety. This involves identifying and addressing the underlying factors that contribute to anxiety, such as past trauma or chronic stress.
Addressing the root cause of anxiety: By seeking therapy or counseling, individuals can work through underlying emotional issues that contribute to anxiety, which in turn can help to reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and proper nutrition can also support overall mental health and reduce anxiety, leading to a lower incidence of anxiety-related nightmares.
Finally, some individuals may require medical treatment or therapy to effectively address anxiety and related nightmares.
Medical treatment and therapy: This can include medication to manage symptoms of anxiety disorders or trauma-focused therapy to address post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and related nightmares. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for managing anxiety and related symptoms.
Preventing anxiety-related nightmares involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological factors that contribute to anxiety. With the right combination of strategies, individuals can effectively manage anxiety-related nightmares and improve overall quality of life.
Relaxation Techniques and Mindfulness
One way to prevent anxiety-related nightmares is by practicing relaxation techniques and mindfulness. These techniques aim to reduce stress and anxiety levels, which can ultimately lead to a reduction in nightmares.
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualization can help calm the body and mind. Deep breathing involves taking slow, deep breaths and exhaling slowly, which can help slow down the heart rate and decrease tension in the body. Progressive muscle relaxation involves flexing and relaxing different muscle groups to release tension in the body. Visualization involves imagining calming and peaceful scenes, which can help ease anxiety and promote relaxation.
Mindfulness involves being present in the moment and paying attention to thoughts and feelings without judgment. Mindfulness techniques can include meditation, yoga, and other practices that promote relaxation and self-awareness. These techniques have been shown to reduce anxiety and improve overall mental health.
By incorporating these techniques into a daily routine, individuals may be able to reduce their anxiety levels and prevent anxiety-related nightmares. It is important to note that these techniques may take time and practice to be effective, and individuals may benefit from seeking guidance from a therapist or healthcare provider.
Addressing the Root Cause of Anxiety
One effective way to prevent anxiety-related nightmares is by addressing the root cause of the anxiety itself. This may involve identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, developing coping strategies for stress, and seeking support from loved ones.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy that can help individuals identify and change negative patterns of thinking and behavior. For example, individuals with anxiety disorders may have a tendency to catastrophize, or imagine the worst possible outcomes in any situation. CBT can help these individuals challenge those thoughts and learn to reframe them in more positive ways.
Mindfulness practices can also be helpful in addressing the root causes of anxiety. By learning to focus on the present moment without judgment, individuals can reduce their tendency to ruminate on the past or worry about the future. Mindfulness can be practiced through meditation, yoga, and other types of relaxation techniques.
Medication can also be an effective tool for addressing the root cause of anxiety. Anti-anxiety medications and antidepressants can help to regulate the brain chemicals that contribute to anxiety and depression. However, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage.
Lifestyle changes can also be helpful in addressing the root causes of anxiety. For example, engaging in regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep can all help to reduce stress and promote overall emotional well-being. Additionally, avoiding drugs and alcohol and engaging in positive social activities can help to promote feelings of calm and well-being.
Medical Treatment and Therapy
There are multiple medical treatment and therapy options available for those struggling with anxiety related nightmares. One option is medication, particularly benzodiazepines, which can help reduce anxiety levels and improve sleep quality. However, these medications can also come with potential side effects and may not be a long-term solution.
Another option is therapy, specifically cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). In CBT, individuals learn to recognize and change negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety and nightmares. This type of therapy is often conducted over a series of weeks or months, and can be very effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Another therapy option is Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), which has been specifically designed to treat trauma-related disorders. EMDR involves using rapid eye movements to process distressing memories in a therapeutic setting. This therapy can be particularly beneficial for those suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and subsequent nightmares.
It is important to note that therapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution and it may take time to find the right approach. In some cases, a combination of medication and therapy could be the best option. It is essential to work with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for individual needs.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Anxiety and Nightmares
Making lifestyle changes can also be an effective way to reduce anxiety and related nightmares. The following sections discuss some of the most beneficial lifestyle changes you can incorporate into your daily routine.
Healthy Sleep Habits: Maintaining healthy sleep habits is crucial in reducing anxiety-related nightmares. This means setting a consistent bedtime and wake-up time, avoiding stimulating activities before bed, and creating a relaxing sleep environment. Limiting exposure to screens, especially before bed, can also improve the quality of your sleep.
Exercise and Nutrition: Exercise and nutrition play a major role in reducing anxiety and promoting better sleep quality. Regular exercise can help reduce stress levels and anxiety, while a balanced diet can provide the nutrients required for restorative sleep. Avoiding stimulants such as caffeine and sugar can also help improve the quality of your sleep and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
Incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine can also be beneficial in reducing anxiety and related nightmares. Practicing mindfulness can help you become more aware of your thoughts and emotions, enabling you to better manage stress and anxiety levels.
Addressing the Root Cause of Anxiety: Making lifestyle changes can certainly help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and related nightmares, but it’s important to address the root cause of your anxiety as well. Consider speaking with a therapist or mental health professional to identify the underlying factors contributing to your anxiety.
Medical Treatment and Therapy: In some cases, medical treatment or therapy may be necessary to effectively manage anxiety and related nightmares. Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed, along with therapy to help you overcome your anxiety and develop coping strategies to manage symptoms.
Incorporating healthy sleep habits, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and relaxation techniques into your daily routine can be very effective in reducing anxiety and related nightmares. However, it’s important to address the underlying causes of anxiety, and seek medical treatment or therapy when necessary, to achieve the best possible results.
Healthy Sleep Habits
Getting a good night’s sleep is of utmost importance when it comes to managing anxiety-related nightmares. A key factor in achieving quality sleep is establishing healthy sleep habits. Sticking to a regular sleep schedule helps your body maintain its circadian rhythm, which can make falling asleep and staying asleep easier.
It’s important to create a comfortable sleep environment. Invest in high-quality bedding and a comfortable mattress that aligns with your sleeping preferences. Additionally, keeping your bedroom cool, quiet, and dark can help eliminate distractions and create an optimal sleeping environment.
Avoid consuming caffeine and alcohol before bedtime as these can interfere with sleep. Instead, consider drinking chamomile tea or warm milk, which can promote relaxation and restful sleep.
Ensure that your bedtime routine is relaxing and conducive to sleep. Engage in calming activities such as reading a book or taking a warm bath. Try to avoid using electronics before bed, as the blue light emitted by screens has been shown to suppress melatonin production and interfere with sleep.
If you struggle with falling asleep or staying asleep, consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation into your bedtime routine. These techniques can help reduce physical tension and relieve anxiety before bed, making it easier to drift off.
By prioritizing healthy sleep habits, you can not only reduce the frequency and intensity of anxiety-related nightmares, but also feel more rested and better equipped to manage daily stress and anxiety.
Exercise and Nutrition
Engaging in regular physical activity and adopting a healthy diet can be effective lifestyle changes to reduce anxiety and nightmares. Exercise is a natural stress-reducer that promotes the production of endorphins, the body’s natural mood-boosting chemicals. It can also improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
A study published in the Journal of Sleep Research found that individuals who incorporated moderate exercise into their daily routine experienced significant reductions in anxiety and improvements in overall sleep quality. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychology showed that a combination of exercise and cognitive behavioral therapy was more effective in reducing anxiety and sleep disturbances than either intervention on its own.
In addition to regular exercise, making dietary changes can also have a positive impact on anxiety and nightmares. Consuming a diet rich in nutrient-dense foods can help to regulate mood and improve overall health. Foods high in tryptophan, such as turkey, nuts, and bananas, can increase the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and sleep.
On the other hand, processed and high-sugar foods can have the opposite effect, causing blood sugar imbalances and mood swings. Additionally, consuming caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime can disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
Making small changes to diet and exercise habits can have a significant impact on reducing anxiety and nightmares. Starting with simple activities such as taking daily walks, practicing yoga, and incorporating fruits and vegetables into meals can improve overall well-being and promote restful sleep. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can also provide personalized recommendations for incorporating healthy habits into a daily routine.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that there is a significant link between anxiety and nightmares. Not only are anxiety disorders and nightmares prevalent in the population, but research has established a connection between them. The cause of nightmares related to anxiety is complex and involves emotions, the fight or flight response, and traumatic experiences such as PTSD. The effects of nightmares on mental health are significant, impacting emotional and physical well-being, sleep disorders, and anxiety and stress levels.
Fortunately, there are ways to prevent anxiety-related nightmares through relaxation techniques, addressing the root cause of anxiety, and seeking medical treatment and therapy. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as healthy sleep habits, exercise, and nutrition can further reduce anxiety and nightmares.
It is important for individuals who experience anxiety and nightmares to seek help and support from healthcare professionals and loved ones. By understanding the link between anxiety and nightmares and taking steps to address their causes, individuals can improve their mental health and overall well-being. It is vital to prioritize self-care and prioritize healthy habits in order to manage and reduce anxiety-related nightmares.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can anxiety cause nightmares?
Yes, anxiety can lead to nightmares, especially in individuals with anxiety disorders.
Are nightmares a symptom of PTSD?
Yes, nightmares are a common symptom of PTSD and can be triggered by traumatic events.
Can medication for anxiety help prevent nightmares?
Yes, medication for anxiety can sometimes help prevent nightmares, but it is important to talk to a medical professional about the best treatment plan.
Is it normal to have nightmares every night?
No, it is not normal to have nightmares every night. If the frequency and intensity of nightmares interfere with daily life, it is recommended to talk to a mental health professional.
Can anxiety-related nightmares be cured?
Anxiety-related nightmares can be managed and reduced with the help of medical treatment, therapy, and lifestyle changes. However, a complete cure may not always be possible.
Can practicing mindfulness help with anxiety-related nightmares?
Yes, practicing mindfulness can help reduce anxiety-related nightmares by promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels.
Is there a link between sleep disorders and anxiety-related nightmares?
Yes, individuals with sleep disorders such as insomnia or sleep apnea may be more likely to experience anxiety-related nightmares.
Can nightmares lead to anxiety disorders?
Repeated nightmares may contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, especially if they cause significant distress and interfere with daily life.
Are anxiety-related nightmares more common in children or adults?
Anxiety-related nightmares are common in both children and adults, but the causes and triggers may vary between age groups.
Can exercise and a healthy diet help reduce anxiety-related nightmares?
Yes, exercise and a healthy diet can help reduce stress levels and improve overall mental and physical health, which may in turn reduce the frequency and intensity of anxiety-related nightmares.








