It’s no secret that getting a good night’s sleep is crucial for our overall well-being, but what happens when we just can’t seem to drift off? Insomnia affects millions of people worldwide and can have a debilitating impact on our day-to-day lives. While medication can be a quick-fix solution, it’s not always the best long-term option. That’s where Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) comes in. This cutting-edge approach to treating insomnia has shown great promise, with studies suggesting that it may be even more effective than medication. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of CBT for insomnia and how it can help you unlock the solution to a better night’s sleep.
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?

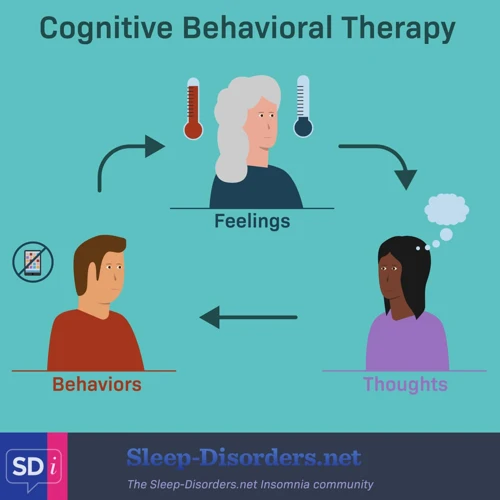
If you’re familiar with the world of psychotherapy, you’ve likely heard of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). But what exactly is it? CBT is a type of therapy that aims to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs in order to promote positive behavior change. This approach operates under the assumption that how we think and react to situations impacts our emotions and behaviors. Through CBT, individuals can develop tools to overcome unhelpful thought patterns and improve their overall mental health. In this section, we’ll explore the ins and outs of CBT, including its components and how it can be used to address insomnia.
Understanding CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT, is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative patterns of thinking and behavior. It is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected and that changing one can have an impact on the others. CBT is a structured, short-term therapy that typically lasts between 6-20 sessions.
CBT is based on several key principles, including:
- Collaboration: The therapist and the person seeking therapy work together to set goals and develop a treatment plan.
- Evidence-Based: CBT is grounded in research and has been shown to be effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including insomnia.
- Goal-Oriented: CBT has specific objectives and aims to help the person seeking therapy achieve their goals.
- Problem-Focused: CBT focuses on the specific problems or issues that the person seeking therapy is experiencing, rather than on general personality traits.
- Present-Focused: The focus of CBT is on the here-and-now rather than on past experiences or future worries.
- Empirical: CBT relies on empirical evidence to support the effectiveness of its techniques.
In CBT, the therapist helps the person seeking therapy to identify negative thoughts and behaviors that are contributing to their insomnia. Once these patterns are identified, the therapist works with the person seeking therapy to develop new, more positive patterns of thinking and behavior.
CBT for insomnia may involve a variety of techniques, including sleep hygiene education, cognitive restructuring, sleep restriction therapy, mindful relaxation, and stimulus control therapy. By incorporating these techniques into their daily routine, individuals can improve their quality of sleep and overall well-being.
Components of CBT protocol
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for insomnia is a structured, short-term, and goal-oriented treatment. The goal of CBT for insomnia is to recognize and modify negative thoughts and behaviors that interfere with good sleep.
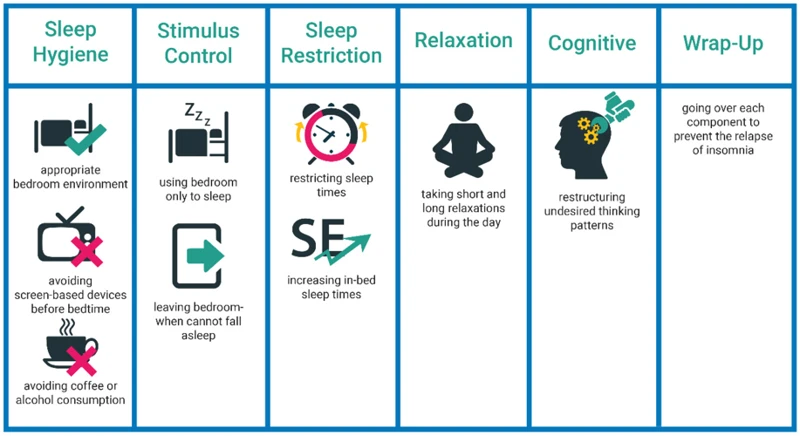
The components of the CBT protocol include sleep hygiene education, cognitive restructuring, sleep restriction therapy, relaxation techniques, and stimulus control therapy.
Sleep hygiene education is the initial step in the CBT protocol. It involves educating patients on good sleep hygiene practices such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine, and creating a sleep-conducive environment.
Cognitive restructuring helps patients identify and modify negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to insomnia. The therapist helps patients challenge these thoughts and replace them with more positive, realistic thoughts.
Sleep restriction therapy involves limiting the time spent in bed to the actual time slept. This means that if a patient spends 8 hours in bed but only sleeps 6 hours, they will be instructed to limit their time in bed to 6 hours. The goal of sleep restriction therapy is to increase sleep efficiency and decrease the time spent awake in bed.
Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, help patients relax and prepare for sleep. These techniques can be particularly useful for patients who experience anxiety or tension that interferes with sleep.
Stimulus control therapy involves re-associating the bed with sleep rather than with wakefulness. This involves instruction on only using the bed for sleep, avoiding activities such as reading or watching TV in bed, and getting out of bed if unable to sleep within 20-30 minutes.
By incorporating these components, CBT for insomnia provides a comprehensive approach to treating the disorder. The combination of education, cognitive restructuring, and behavioral techniques helps patients break the cycle of negative thoughts and behaviors that perpetuate insomnia.
CBT for Insomnia
Millions of people worldwide struggle with insomnia and its detrimental effects on their mental and physical health. While medication is a commonly prescribed solution, it often carries the risk of dependency and adverse side effects. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as a promising alternative with its non-invasive, natural approach. But what exactly is CBT and how can it help individuals struggling with insomnia? Let’s explore the components and benefits of CBT in detail.
Assessing insomnia using CBT
Assessing insomnia using Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) involves a comprehensive evaluation of a patient’s sleep patterns, daily routine, and overall lifestyle habits. CBT for insomnia aims to identify and address the underlying causes of insomnia, such as anxiety, stress, or poor sleep hygiene.
The following are some key components of assessing insomnia using CBT:
- Sleep Diary: A sleep diary is a record of a patient’s sleep patterns, including the time they went to bed and woke up, any awakenings during the night, and how they felt upon waking up. This information can be used to identify any patterns or triggers that may be contributing to insomnia.
- Medical History: A thorough medical history is necessary to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to insomnia, such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or chronic pain.
- Psychological Assessment: A psychological assessment is used to evaluate a patient’s mood, anxiety levels, and overall mental health. This can help identify any underlying psychological factors that may be contributing to insomnia, such as depression or anxiety.
- Sleep Study: A sleep study may be ordered to rule out any underlying sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome. This involves spending a night in a sleep laboratory where your sleep patterns will be monitored and evaluated.
By conducting a thorough assessment of a patient’s sleep habits and lifestyle, a CBT therapist can develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific factors contributing to insomnia. This may include a combination of relaxation techniques, sleep hygiene education, and other behavioral strategies to help promote better sleep.
Is CBT better than medication for insomnia?
Some people with insomnia may turn to medication to help them with sleep. However, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has been shown to have long lasting benefits without the risk of side effects associated with medication. In fact, CBT has been found to be more effective than medication for insomnia in the long run.
Comparison of CBT and medication for insomnia:
| CBT | Medication | |
|---|---|---|
| Duration of effectiveness | Long-term: the benefits last after treatment has ended | Short-term: the benefits end when medication is stopped |
| Side effects | None | Side effects such as dizziness, headaches, and nausea |
| Cost | May be more expensive up front, but results in long term cost savings as treatment is not ongoing | May be cheaper up front, but ongoing costs accumulate over time with continued use |
| Dependency | Non-habit forming | Potential for dependence, which may lead to addiction |
It’s important to note that while medication can be helpful in the short term, it doesn’t address the underlying causes of insomnia. CBT, on the other hand, can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that are contributing to their insomnia. This leads to long lasting improvements in sleep and overall well-being.
The Benefits of CBT for Insomnia
For those who struggle with insomnia, finding a solution can often feel like a challenge. While medication may provide temporary relief, it may not address the root cause of the problem. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as a promising solution for those looking to improve their sleep quality. Through a combination of self-monitoring, cognitive restructuring, and other techniques, CBT can help individuals overcome their insomnia and experience better quality sleep. In this section, we will explore the numerous benefits that CBT can provide for individuals suffering from insomnia. From improved sleep quality to a reduction in anxiety and depression, CBT offers a comprehensive approach to treating insomnia that is both effective and long-lasting.
Improvement in sleep quality
One of the primary benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for insomnia is the improvement in sleep quality. CBT addresses the root cause of sleep problems, which is often linked to an individual’s thoughts and behaviors surrounding sleep. Here are some of the ways in which CBT can improve sleep quality:
| Benefits of CBT for Insomnia | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduction in time to fall asleep | CBT helps individuals learn relaxation techniques and manage racing thoughts that can keep them up at night, resulting in a faster time to fall asleep. |
| Increased sleep efficiency | CBT helps individuals make positive changes to sleep habits and routines, resulting in increased sleep efficiency or the amount of time spent asleep versus the amount of time spent in bed. |
| Decrease in nighttime awakenings | Stimulus control therapy, a technique used in CBT, helps re-associate the bed with sleep and reduce the number of times individuals wake up during the night. |
| Improved sleep quality | CBT promotes healthy sleep habits and helps reduce negative sleep-related thoughts, leading to an overall improvement in sleep quality. |
In addition to the benefits listed above, CBT for insomnia has also been found to have a lasting effect. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, individuals who received CBT for insomnia showed significant improvements in sleep quality six months after treatment compared to those who received medication alone. CBT not only improves sleep quality in the short-term but also has long-term efficacy.
Reduction in anxiety and depression
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for insomnia not only improves sleep quality but also helps in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. Research has shown that people who suffer from insomnia are more likely to experience symptoms of anxiety and depression compared to those who do not. Treating insomnia not only helps in improving sleep quality but also contributes to overall mental well-being.
According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, participants who underwent CBT for insomnia reported significant reduction in symptoms of both anxiety and depression. In fact, the study showed that the reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms was directly related to the improvement in sleep quality.
Anxiety is often the result of worrying about future events, and CBT for insomnia helps in teaching individuals how to change their negative thought patterns and focus on the present moment. By analyzing and challenging negative thoughts, individuals can learn to manage anxiety and reduce stress levels, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Depression can also be a common issue for individuals dealing with insomnia. Lack of sleep can lead to feelings of exhaustion, hopelessness, and loss of interest in daily activities. CBT for insomnia not only helps in changing behaviors that lead to poor sleep, but also in promoting positive thinking patterns that can aid in combating depression.
Below is a table summarizing the reduction of symptoms of anxiety and depression through CBT for insomnia:
| Anxiety | Depression | |
|---|---|---|
| Study Results | Participants reported significant reduction in anxiety symptoms | Participants reported significant reduction in depression symptoms |
| Root Cause | Anxiety often results from worrying about future events | Lack of sleep can cause exhaustion, hopelessness, and loss of interest in daily activities |
| CBT Solution | CBT helps individuals change negative thought patterns and focus on the present moment | CBT promotes positive thinking patterns and helps combat depression by changing behaviors that lead to poor sleep. |
By addressing the root cause of their insomnia, individuals can experience significant improvements not only in their sleep quality but also in their overall mental health. CBT for insomnia can be an effective tool for those seeking relief from symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Long-term effectiveness of CBT
Research suggests that the long-term effectiveness of CBT for insomnia is high. Studies have found that individuals who undergo CBT experience a significant improvement in sleep quality, and that these results persist even after treatment has ended. In fact, one study found that individuals who underwent CBT for insomnia showed lasting improvements in sleep quality for up to two years after the end of treatment.
Additionally, research has shown that the benefits of CBT for insomnia go beyond just improving sleep. Individuals who undergo CBT for insomnia have also shown improvements in symptoms of anxiety and depression, which are commonly associated with insomnia. This is likely due to the fact that CBT helps individuals to address negative thoughts and emotions that may contribute to their insomnia.
The long-term effectiveness of CBT for insomnia is a major reason why it is often considered the treatment of choice for chronic insomnia. Not only does it offer lasting improvements in sleep quality, but it also helps to address other underlying factors that may contribute to insomnia, such as anxiety and depression.
Who can benefit from CBT?

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a highly effective treatment method for managing insomnia. CBT is a form of psychotherapy that aims to change a patient’s patterns of thinking or behavior that are negative or unhealthy. As a result, it can be an incredibly beneficial treatment option for those who are struggling with insomnia.
Individuals with Chronic Insomnia: People who suffer from chronic insomnia can benefit from CBT. Chronic insomnia is defined as difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early that persists for at least three months. CBT can help individuals overcome the negative thinking patterns and behaviors that contribute to insomnia.
Individuals with Difficulty Sleeping: Even people who have difficulty sleeping occasionally can benefit from CBT. CBT can teach individuals healthy sleep habits and relaxation techniques that can help them fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer.
Individuals Who Want to Avoid Medications: Those who prefer to treat their insomnia without medication may find CBT to be a great solution. Unlike medication, CBT does not carry the risk of addiction, dependency, or side effects.
Individuals Who have Tried Medications without Success: People who have tried medications as a treatment for insomnia and did not achieve desired results may want to give CBT a try. CBT can provide a long-term solution that addresses the root cause of insomnia, rather than masking the problem with medication.
Older Adults: Older adults who experience trouble sleeping may find CBT to be a preferred method of treatment because it does not involve medication, which may be contraindicated for some elderly individuals.
CBT is an excellent treatment option for individuals of all ages who suffer from insomnia. It offers a natural and effective way to manage insomnia, providing a long-term solution that emphasizes behavioral changes rather than medication.
How to find a CBT therapist?
If you’re struggling with insomnia and want to try CBT, the first step is finding a qualified therapist. There are a few things you can do to find a CBT therapist in your area. One option is to ask your primary care doctor for a referral. They may have a list of therapists in your area who specialize in CBT for insomnia.
You can also search for a therapist online. There are plenty of directories that allow you to search for therapists in your area based on their specialization. Websites like Psychology Today and GoodTherapy can be good resources to find a CBT therapist.
Another option is to check with your health insurance provider. They may have a list of therapists who are covered under your plan. This can be a good way to find a therapist who is affordable for you.
Once you’ve found a potential therapist, it’s important to make sure that they have experience in treating insomnia with CBT. You can ask them about their experience and credentials during an initial consultation. It’s important to feel comfortable with your therapist and confident in their abilities to help you overcome your insomnia.
Finally, it’s important to keep in mind that finding a therapist can take time and effort. You may need to meet with a few therapists before finding the right fit. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t find the right therapist right away. Keep searching and remember that help is available.
Steps Involved in CBT for Insomnia
As insomnia can significantly affect an individual’s overall health and quality of life, it is important to seek out effective treatments. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has been found to be a highly effective approach for treating insomnia. This therapy consists of several steps or techniques that focus on changing negative thought patterns, regulating sleep patterns, and promoting relaxation. In this section, we will delve into the specific steps involved in CBT for insomnia and explore how they can help individuals overcome their sleep difficulties.
Step 1: Self-Monitoring
Self-monitoring is the first step in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for insomnia. This step helps individuals understand their sleep patterns and identify the factors that contribute to difficulty in falling or staying asleep.
The self-monitoring process involves keeping a journal or sleep diary that tracks various aspects of sleep, such as bedtime, wake time, sleep onset latency (how long it takes to fall asleep), and the number of awakenings throughout the night. Additionally, individuals are asked to record specific details related to their sleep, such as the quality of their sleep, how rested they feel in the morning, and any factors that may have affected their sleep, such as stress or caffeine intake.
The information gathered through self-monitoring can be used to identify patterns and triggers that contribute to sleep difficulties. For example, self-monitoring may reveal that an individual has difficulty falling asleep on nights when they consumed caffeine later in the day. Recognizing these patterns allows individuals and their therapists to develop targeted interventions to address behaviors or habits that may be interfering with sleep.
The benefits of self-monitoring include increased awareness of sleep patterns and better understanding of the factors that contribute to sleep difficulties. It can also help individuals identify specific behaviors or habits that are affecting their sleep, allowing them to make changes and develop better sleep hygiene practices.
Below is an example of a sleep diary used for self-monitoring:
| Date | Bedtime | Wake time | Time to fall asleep | Number of awakenings | Quality of sleep | Factors affecting sleep |
| Monday, May 3 | 11:00 PM | 6:30 AM | 20 minutes | 2 | Fair | Stressful day at work |
| Tuesday, May 4 | 10:45 PM | 6:15 AM | 30 minutes | 3 | Poor | Drank coffee at 7 PM |
| Wednesday, May 5 | 11:30 PM | 7:00 AM | 15 minutes | 1 | Good | Read before bed |
Self-monitoring is an important first step in CBT for insomnia. By tracking sleep patterns and identifying contributing factors, individuals and their therapists can develop targeted interventions to improve sleep quality and quantity.
Step 2: Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring is a crucial step in the Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) protocol for insomnia. This step is focused on identifying and modifying negative thoughts and beliefs about sleep that might interfere with the sleep process. During this process, patients work with their therapist to identify and challenge negative thoughts related to sleep using specific strategies. Let’s take a look at the strategies involved in cognitive restructuring in detail.
| Strategy | Description |
| Identification of Negative Thoughts | In this step, the therapist helps the patient identify negative thoughts related to sleep. These thoughts might include worries about not being able to sleep, being tired the next day, or the belief that one is “not a good sleeper.” |
| Evaluation of the Validity of Negative Thoughts | Once the negative thoughts have been identified, the therapist helps the patient evaluate how valid these thoughts are. Patients are asked to consider the evidence that supports and contradicts the negative thoughts. |
| Challenging Negative Thoughts | After evaluating the validity of negative thoughts, the patient is encouraged to challenge them. Patients are asked to generate alternative more balanced thoughts that take into account evidence that contradicts their negative thoughts. |
| Positive Self-Talk | Positive self-talk involves helping the patient come up with positive and realistic statements to replace the negative beliefs about sleep. These statements might include phrases like, “I am capable of sleeping well,” or “I can manage my worries about sleep.” |
| Mindfulness Techniques | Patients are taught mindfulness techniques to help them focus on the present moment and reduce anxiety and worry about the future. This might include techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or visualization. |
Cognitive restructuring is aimed at helping the patient develop a more positive and balanced attitude towards sleep. By identifying and challenging negative thoughts about sleep, patients are better able to change unhelpful beliefs and behaviors that contribute to insomnia. This step is key in the overall CBT protocol for insomnia, and by incorporating these strategies, patients are able to develop more effective coping mechanisms and sleep habits.
Step 3: Sleep Restriction
Sleep restriction is a key component of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia. This step involves restrictive sleep scheduling to help individuals increase their sleep drive and improve sleep efficiency. Here are the steps involved in the sleep restriction protocol:
- Assess baseline sleep: The first step involves assessing the baseline sleep pattern of the individual. This includes tracking their bedtime, wake-up time, and overall sleep duration for a week or two.
- Determine the time in bed: Once you have assessed the baseline sleep pattern, the next step is to determine the amount of time that the individual spends in bed each night. This includes the time that they spend trying to fall asleep, wake-ups during the night, and any other non-sleep activities that take place in bed.
- Establish a consistent wake-up time: The next step is to establish a consistent wake-up time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate the circadian rhythm and ensures that the individual gets up at the same time every day.
- Calculate sleep window: The sleep window is calculated by subtracting 30 minutes from the total sleep time (time spent actually sleeping) and rounding it to the nearest 15-minute interval. This ensures that the individual spends more time asleep in bed instead of trying to fall asleep.
- Set a bedtime: A bedtime is then established based on the calculated sleep window. This bedtime is adjusted every week based on the total time spent sleeping during the previous week.
- Stick to the sleep schedule: The individual must stick to the sleep schedule even if they are unable to sleep. This helps increase the sleep drive and trains the brain to associate the bed with sleep rather than non-sleep activities.
- Gradual adjustment: The sleep schedule is gradually adjusted over time to help the individual attain their desired sleep duration.
Note: It is important for individuals to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any sleep restriction protocol. Sleep restriction may not be recommended in certain medical conditions or if the individual has a history of sleep disorders.
Step 4: Relaxation Techniques
In the fourth step of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Insomnia, relaxation techniques are taught to individuals. These techniques can help decrease stress and anxiety, which are often associated with insomnia. The following are some of the relaxation techniques that may be included in CBT for insomnia:
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in the body. It can help reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation.
- Deep Breathing: Deep breathing techniques can help slow down racing thoughts and calm the body. Individuals are taught to take deep breaths in through the nose and out through the mouth.
- Meditation: Meditation can help focus the mind and promote relaxation. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation and mantra meditation may be included in CBT for insomnia.
- Visualization: Individuals may be asked to imagine a peaceful scene or situation to promote relaxation. This can help to calm the mind and reduce stress and anxiety.
It is important for individuals to practice these relaxation techniques consistently to see results. These techniques can be used as a tool for falling asleep more easily and for reducing stress throughout the day. By incorporating relaxation techniques into their daily routine, individuals may experience improved sleep quality and a reduction in insomnia symptoms.
Step 5: Stimulus Control Therapy
Stimulus Control Therapy is a technique used in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Insomnia. The goal of this technique is to re-associate the bed with sleep, instead of wakefulness, and create a positive sleep environment.
Step 5: Stimulus Control Therapy
Stimulus Control Therapy involves the following essential steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Create a sleep-friendly environment: The patient should use the bed only for sleeping and should remove all electronic devices, such as television, laptop, or phone, from the bedroom. The room should be dark, quiet, and at an appropriate temperature to promote sleep. |
| 2 | Associate the bed with sleep: If the patient is unable to fall asleep within 20 minutes, they should get out of bed and engage in a relaxing activity, such as reading or meditating, until they feel sleepy. This step ensures that the bed is associated with sleep and only sleep. |
| 3 | Gradually increase wakefulness: The patient should wake up at the same time every day, regardless of the amount of sleep they received the night before. This step helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle and gradually increases wakefulness. |
| 4 | Avoid naps: Napping should be avoided during the day to promote regular sleep-wake patterns. |
Stimulus Control Therapy is an effective technique for re-associating the bed with sleep and creating a positive sleep environment. By following these steps, patients can improve their sleep quality and reduce insomnia symptoms. However, it may take time to see the results, and consistency is key.
CBT and Other Sleep Disorders

Conditions such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and periodic limb movement disorder are not directly treated with Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). However, these conditions may contribute to poor sleep quality, difficulty staying asleep, and waking up frequently during the night. In such cases, treatment for the underlying sleep disorder may also improve the effectiveness of CBT for insomnia.
Additionally, CBT may not be the most appropriate treatment for certain sleep disorders such as narcolepsy or circadian rhythm disorders. Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime drowsiness and sudden sleep attacks. Circadian rhythm disorders involve disruptions to the natural sleep-wake cycle and may require treatment such as bright light therapy or melatonin supplementation.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment options for specific sleep disorders. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary to achieve optimal sleep quality and duration. CBT can be a highly effective treatment for insomnia and may provide benefits beyond just improving sleep quality, such as reducing anxiety and depression.
CBT vs. Other Psychotherapies

When it comes to treating insomnia, there are a variety of psychotherapies that have been used with varying levels of success. However, research has consistently shown that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is the most effective form of psychotherapy for treating insomnia.
One reason for the effectiveness of CBT over other psychotherapies is because it is specifically tailored to address the specific thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia. CBT focuses on helping individuals change their negative beliefs and attitudes towards sleep, and teaches them how to develop healthier sleep habits through a variety of techniques.
Other psychotherapies, such as relaxation therapy, guided imagery and mindfulness-based therapy can be helpful for promoting relaxation and reducing stress, but they do not necessarily target the underlying thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to insomnia in the same way that CBT does.
For example, relaxation therapy might help an individual feel calmer and less anxious before bed, but it does not address the underlying negative thought patterns that may be playing a role in their insomnia. In contrast, CBT helps individuals identify and challenge these negative thought patterns directly, which in turn leads to lasting changes in behavior and improvements in sleep.
Additionally, while medication may be effective in the short term, it does not address the root causes of insomnia and can be associated with a number of negative side effects. CBT, on the other hand, is a safe, non-invasive treatment that can provide lasting relief from insomnia without any of the negative side effects associated with medication.
CBT has been shown to be the most effective form of psychotherapy for treating insomnia due to its specific focus on addressing the underlying thoughts and behaviors that contribute to the condition. While other psychotherapies and medications may be helpful in certain cases, CBT provides a comprehensive approach that can lead to lasting improvements in sleep quality and overall quality of life.
How Long Does CBT take to Work?
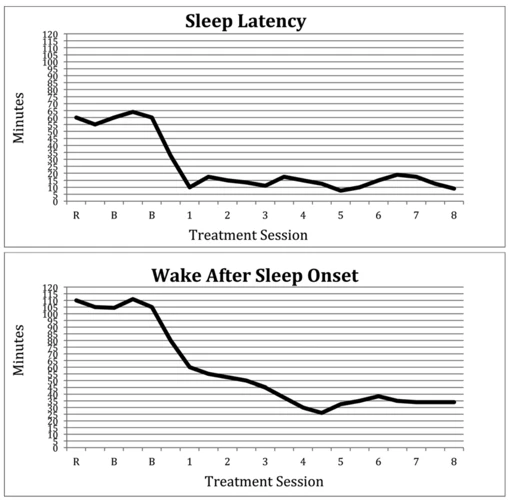
The effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia varies from person to person, and therefore, the time it takes to see improvements can differ as well. It is important to remember that CBT is not a quick fix for insomnia, but rather a long-term, effective solution that requires persistence and dedication.
Some studies have shown that improvements in sleep quality can be seen within four to eight weeks of beginning CBT therapy. However, these improvements can vary depending on the severity of the insomnia and other individual factors. It is also important to note that the benefits of CBT for insomnia are often long-lasting, with many individuals maintaining better sleep quality years after completing therapy.
The duration and intensity of the therapy sessions can also impact how long it takes for CBT to work. Some individuals may benefit from only a few sessions, while others may need more frequent and longer therapy sessions to see results. The therapy sessions are often tailored to the individual’s needs, and the therapist will work closely with the patient to adjust the course of therapy as necessary.
While CBT may take longer to see results compared to medication treatments, the benefits of CBT are often longer-lasting. CBT helps individuals develop skills to manage their insomnia on their own, whereas medication is often a temporary solution that does not address the underlying causes of insomnia.
It is crucial for individuals seeking treatment for insomnia to approach CBT with realistic expectations and a willingness to put in the effort needed to see results. With persistence and dedication, CBT can be an effective long-term solution for improving sleep quality and managing insomnia.
The Drawbacks of CBT for Insomnia
While Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has proven to be incredibly effective in treating insomnia, there are still some drawbacks to this treatment that should be considered. One of the major drawbacks is that it may not work for everyone. Like any type of therapy, CBT requires a certain level of dedication and effort from the patient in order to be successful. Some people may not be ready or willing to put in the work required to make CBT effective.
Another potential drawback of CBT is the cost. While CBT is often covered by insurance, the cost of therapy sessions can still be a barrier for some individuals. Additionally, finding a therapist who specializes in CBT for insomnia may be challenging in certain areas. This can lead to long wait times for appointments and difficulties in accessing treatment.
Another concern is that some individuals may experience an initial increase in sleep disturbance during the first few weeks of CBT. This can be especially frustrating for patients, as they may initially feel like the treatment is making their insomnia worse rather than better. However, this is a normal and expected part of the treatment process as the body adjusts to the new sleep schedule and habits. It is important for patients to stick with the program and trust that the benefits will come with time.
Lastly, CBT for insomnia may not be appropriate for individuals with severe psychiatric or medical conditions. It is important for patients to consult with their healthcare provider to determine if CBT is a safe and appropriate treatment option for their specific situation.
While there are some potential drawbacks to CBT for insomnia, it is still one of the most effective and long-lasting treatments available. With proper dedication and guidance from a trained therapist, many individuals can experience a significant improvement in their sleep quality and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as an effective treatment for insomnia, providing a holistic and long-lasting solution for individuals who suffer from sleep disturbances. This therapy targets the root cause of insomnia rather than just treating the symptoms, making it a different approach from medication.
Through CBT, individuals can learn to identify and modify negative thoughts and beliefs that lead to sleep disturbances. They can also learn techniques to manage their worries and anxiety and improve their relaxation skills. By addressing these underlying factors, CBT can improve sleep quality and quantity, reduce sleep onset time and wake time during the night, and decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression.
While medication may provide short-term relief, it does not address the underlying problems that cause insomnia. Additionally, medication may have side effects and can be habit-forming, leading to dependence and further sleep disturbances. CBT, on the other hand, provides a natural and sustainable solution by equipping individuals with the tools to manage their insomnia in the long term.
It is important to note that CBT is not a one-size-fits-all approach, and success may vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. However, with the help of a qualified CBT therapist, individuals can work through the necessary steps to effectively manage their sleep disorder.
In summary, if you suffer from insomnia, CBT is a safe and effective option to consider. By changing negative patterns of thinking and behavior, and learning strategies for relaxation, you can effectively manage your insomnia and achieve better sleep for a healthier and happier life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common causes of insomnia?
Insomnia can be caused by various factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, medical conditions, medications, and poor sleep habits and environment.
Is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) effective for treating insomnia?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is considered an effective first-line treatment for insomnia, as research has shown its efficacy in improving sleep quality and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
How does CBT differ from medication as a treatment for insomnia?
CBT is a non-pharmacological approach that involves teaching patients skills and techniques to help them overcome negative thoughts and behaviors that may be contributing to their insomnia. Medications, on the other hand, are often used as a short-term solution for insomnia but their long-term effectiveness is still debated.
What are the benefits of CBT for insomnia?
Some benefits of CBT for insomnia include improving sleep quality, reducing anxiety and depression, and long-term effectiveness without medication dependence.
Who can benefit from CBT for insomnia?
Anyone who is experiencing chronic insomnia or poor sleep quality may benefit from CBT. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
How long does CBT take to work?
CBT for insomnia typically involves several weekly sessions over a period of 4-12 weeks, although a patient may see improvements in sleep quality within the first few weeks of treatment.
Can CBT be used to treat other sleep disorders besides insomnia?
While CBT is most commonly used to treat insomnia, it has also been utilized in the treatment of other sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and restless legs syndrome.
What can I expect during a CBT session for insomnia?
During a CBT session for insomnia, a therapist will work with the patient to identify negative thoughts, behaviors, and environmental factors that may be contributing to their insomnia. The therapist will then teach the patient skills and techniques to overcome these challenges and improve sleep quality.
Is CBT covered by insurance?
Most health insurance plans do cover CBT for mental health conditions, including insomnia. It is important to check with your insurance provider for specific coverage details.
What are the potential drawbacks of CBT for insomnia?
Some potential drawbacks of CBT for insomnia may include the cost of sessions or difficulty finding a qualified therapist. Additionally, some individuals may not respond positively to CBT and may require alternative forms of treatment for their insomnia.








