Do you ever find yourself feeling sluggish and unfocused during the day? Perhaps you’ve heard that taking a nap can help, but you’re not sure if it’s a good idea. The idea of napping has been around for centuries, but it’s only in recent years that scientists have started to uncover the true benefits and potential risks of this daily activity. In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of napping, exploring the different types of napping, how napping affects sleep quality, and the multitude of benefits that come with incorporating short periods of rest into your daily routine. We’ll also provide tips on how long to nap for and the best times of day to nap. By the end, you may just be convinced to add a quick snooze to your daily schedule!
What is Napping?
Have you ever found yourself feeling groggy after a long day’s work or struggling to keep your eyes open during an afternoon meeting? Perhaps you’ve considered taking a nap. Napping is a short period of rest that is taken during the day to help improve energy levels and mental alertness. While many people view napping as a sign of laziness or lack of productivity, research has shown that napping can actually provide numerous benefits to overall health and well-being. Let’s explore the different types of napping and some important dos and don’ts to keep in mind.
The Different Types of Napping
When it comes to napping, not all naps are created equal. In fact, there are actually several different types of naps that you can take, each with its own unique benefits and drawbacks. Here are the most common types of napping:
- Planned Nap: This is a nap that is scheduled in advance and taken at a specific time each day. It is also known as a “power nap” and typically lasts between 10 and 30 minutes.
- Emergency Nap: This is a nap that is taken when you unexpectedly become too tired to continue with your daily activities. This type of nap can occur at any time, and typically lasts between 20 and 30 minutes.
- Habitual Nap: This is a nap that is taken at the same time every day, typically after lunch. It is a regular part of your daily routine and typically lasts between 30 minutes and an hour.
- Nap for Creative Problem Solving: This is a nap that is taken specifically to help improve creativity and problem-solving abilities. It typically lasts between 90 minutes and 2 hours, which is the amount of time needed to complete an entire sleep cycle.
Each type of nap has its own benefits and drawbacks, and which one you choose to take will likely depend on your specific needs and preferences. It’s important to keep in mind that napping is not a substitute for a good night’s sleep, but rather a supplement that can help improve your alertness and productivity throughout the day.
The Dos and Don’ts of Napping
When it comes to napping, there are certain dos and don’ts to keep in mind. Here are some key tips to follow:
Do:
- Find a quiet, dark, and cool place to nap. This will help create a conducive environment for sleep.
- Use a comfortable pillow or eye mask to block out any light or noise that might interfere with your nap.
- Give yourself enough time to nap. Even a short nap can be effective, but it’s important to give your body enough time to enter a deep sleep cycle so that you can reap the full benefits of napping.
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule. This will help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and make it easier to fall asleep and wake up.
- Listen to your body. If you feel sleepy, go ahead and take a nap. But if you’re wide awake, don’t force yourself to nap just for the sake of it.
Don’t:
- Nap too late in the day. This can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night.
- Nap for too long. If you nap for too long, you might end up feeling groggy and disoriented when you wake up.
- Drink caffeine before napping. Caffeine is a stimulant that can make it harder to fall asleep.
- Use your phone or computer right before napping. The bright light from electronic devices can interfere with your body’s natural sleep cycle.
- Feel guilty about napping. Napping is a natural and healthy habit that can improve your overall health and wellbeing.
By following these dos and don’ts of napping, you can maximize the benefits of napping and improve your sleep quality. Remember to create a comfortable and serene environment for napping, listen to your body, and stick to a consistent sleep schedule.
The Science Behind Napping and Sleep
As we drift off to sleep, our brains and bodies undergo a complex series of processes that help us feel rested and rejuvenated upon waking. However, the intricacies of these processes are not always clear, and many people may not understand how napping can impact their overall sleep quality. Delving into the science behind napping and sleep, we can gain a better understanding of the different stages of sleep and the ways in which napping can affect our physical and mental health. Let’s explore the fascinating world of sleep and its interactions with napping in more detail.
Understanding the Stages of Sleep
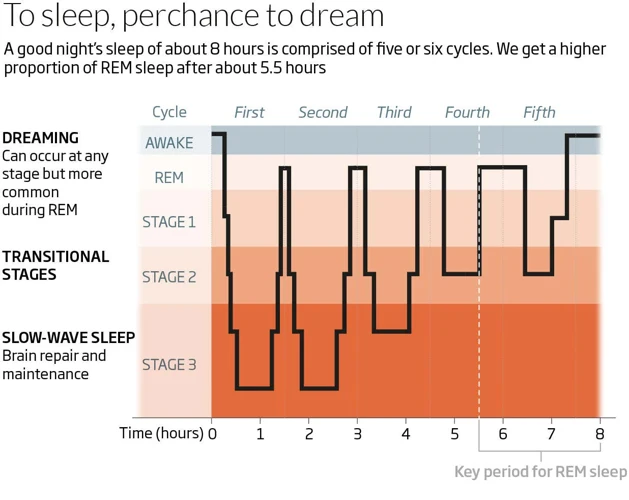
To understand the effects of napping on our sleep quality, it’s important to first comprehend the different stages of sleep that the human body goes through. There are four distinct stages of sleep, which can be classified as either non-rapid eye movement (NREM) or rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
NREM Sleep
During the first stage of NREM sleep, we experience a drowsy state between being awake and asleep. Our brain activity slowly begins to decrease, and our eyes move more slowly. In the second stage, our body temperature drops, and our heart rate slows down. The third and fourth stages (also known as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep) are when our brain activity is at its lowest. Our muscles relax, and it becomes more difficult to be awakened from this state.
REM Sleep
REM sleep is also known as the dreaming stage of sleep. During this stage, our eyes move rapidly, and our breathing becomes faster and more irregular. Our brain activity increases, and our body is essentially paralysed except for small muscle twitches.
Each stage of sleep is important for different reasons, and getting enough of each stage is critical for achieving a restful night’s sleep. Napping can be beneficial in providing additional rest and access to these different stages of sleep, but the timing and duration of the nap can impact the quality of sleep achieved.
How Napping Affects Sleep Quality
When it comes to napping, many people wonder how it might impact their sleep quality. Surprisingly, research has shown that napping can actually improve sleep quality, as long as it’s done correctly. Here are a few ways in which a well-timed nap can enhance your overall quality of sleep:
- Relieves sleep debt: Sleep debt is the difference between the amount of sleep needed by an individual and the amount of sleep they actually get. When you’re not able to get a full night’s rest, napping can help make up for this deficit and reduce the overall sleep debt.
- Reduces sleepiness: A quick nap can help to reduce feelings of sleepiness throughout the day. This can help you feel more alert and refreshed during waking hours without the need for caffeine or other stimulants.
- Boosts cognitive function: A short nap can help to boost cognitive function, including memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities. This can be particularly helpful for those who need to perform intellectually demanding tasks throughout the day.
- Improves mood: A brief nap can have a positive impact on mood and overall well-being. Research has shown that a short nap can reduce stress levels and improve overall mood, making you feel better equipped to handle the challenges of daily life.
- Reinforces circadian rhythms: A well-timed nap can help to reinforce your body’s natural circadian rhythms, promoting healthier and more regular sleep patterns overall.
Napping can have numerous benefits for your overall health and well-being, including improving sleep quality. However, it’s important to keep in mind that napping isn’t right for everyone, and that the optimal nap length and timing can vary based on individual needs and preferences. By understanding how napping impacts sleep quality and tailoring your approach accordingly, you can reap the full benefits of this restorative practice.
The Benefits of Napping

It’s amazing how a quick nap can make all the difference in our day. Beyond the obvious perk of feeling rested, napping has numerous benefits for our productivity, health, and overall wellbeing. Whether you’re a devoted napper or just starting to explore the world of snoozing mid-day, read on to learn about the myriad advantages of incorporating napping into your routine. From boosting memory to reducing stress, let’s dive into the science-backed ways that napping can improve your life.
Increased Productivity and Alertness
Taking a nap can do wonders for your productivity and alertness levels, especially if you didn’t get enough sleep the night before. Studies have shown that napping can help you feel more awake and attentive, which can lead to better performance at school or work.
When you are sleep-deprived, your body releases hormones that cause you to feel sleepy, and your cognitive function may be impaired. However, a 20-30 minute nap can help reduce the sleep debt and improve your cognitive function, enabling you to be more productive and alert.
Napping has been found to be especially beneficial for people who work irregular schedules, such as shift workers, and those who need to be alert and focused for prolonged periods, such as medical professionals or pilots. A short nap during a break can help reset their sleep-wake cycle and improve their overall performance and safety.
Incorporating naps into your daily routine can also help prevent the mid-day slump that many people experience. By taking a brief nap during the day, you can recharge your batteries and power through your tasks with renewed energy and focus.
Napping is a great way to increase productivity and alertness. It can help you feel more awake, attentive, and focused, which can lead to better performance and safety at school or work. So, the next time you’re feeling sluggish, take a power nap and see the difference for yourself!
Improved Mood and Reduced Stress
One of the most significant benefits of napping is its ability to improve mood and reduce stress. Taking a nap can help alleviate feelings of anxiety and tension, leaving individuals feeling more relaxed and refreshed. Here are some more specific ways that napping can lead to a better mood and lower stress levels:
- Reduced Cortisol Levels: Cortisol is a hormone that is involved in the stress response in the body. When cortisol levels are too high for too long, they can lead to a host of negative health outcomes, including depression, anxiety, and weight gain. Napping has been shown to reduce cortisol levels in the body, helping to counteract the effects of chronic stress.
- Increased Serotonin: Another hormone that plays a role in mood regulation is serotonin. When serotonin levels are low, individuals may experience feelings of sadness or depression. Napping has been shown to increase serotonin levels in the brain, which can help improve mood and decrease feelings of stress.
- Enhanced Emotional Control: When individuals are sleep-deprived, they may have a harder time controlling their emotions. Taking a nap can help restore emotional control, leading to fewer mood swings and less stress overall.
- Improved Cognitive Functioning: When individuals are well-rested, they tend to perform better cognitively. This can lead to increased confidence and a better overall mood. Napping can help individuals feel more alert and focused, leading to improved cognitive functioning and a better mood.
While the benefits of napping on mood and stress levels are clear, it’s important to note that napping is not a substitute for proper sleep. Rather, napping should be viewed as a supplement to regular sleep habits. By incorporating naps into one’s routine, however, individuals can experience a wide range of positive benefits, including improved mood and reduced stress levels.
Boosted Memory and Learning
One of the most significant benefits of napping is the boost it provides to memory and learning. Scientific research has shown that taking naps regularly improves cognitive function, including memory retention and learning ability.
The Science Behind Memory and Learning
When we learn something new, our brain stores the information in our long-term memory through a process called consolidation. This process involves transferring the information from the hippocampus, which handles short-term memory, to the neocortex, which deals with long-term memory.
Research has shown that during sleep, the brain consolidates memories by replaying and strengthening the neural connections formed during the learning process.
The Benefits of Napping for Memory and Learning
Although several studies have shown that napping can improve memory and learning, the exact mechanism behind these benefits remains unclear.
Napping has been shown to improve memory retention and learning, and researchers believe that it’s due to the same consolidation process that occurs during sleep. By taking a nap, you’re providing your brain with an opportunity to replay and strengthen the neural connections formed during the learning process, leading to better memory retention and more effective learning.
The Ideal Nap Lengths for Memory and Learning
While napping can provide significant benefits for memory and learning, the ideal nap length for these benefits varies. Short naps of around 10-20 minutes have been found to improve alertness and mental functioning without causing grogginess. Longer naps of around 60-90 minutes have been associated with improved memory consolidation and learning abilities.
The Best Time to Nap for Memory and Learning
The best time of day to take a nap for memory and learning benefits may vary depending on factors such as age, sleep deprivation, and circadian rhythm. Research has shown that the mid-afternoon, around 2-3 pm, is the best time for most people to take a nap. At this time, our bodies experience a natural dip in energy and alertness, making it the perfect time to improve memory and learning.
Napping has been shown to have significant benefits for memory and learning. By providing your brain with the downtime it needs to consolidate memories and strengthen neural connections, you can improve your ability to learn and retain information. To reap the benefits of napping for memory and learning, aim to nap for 10-20 minutes or 60-90 minutes in the mid-afternoon.
Reduced Risk of Heart Disease and Better Physical Health
One of the surprising benefits of napping is reducing the risk of heart disease and promoting better overall physical health. Studies have shown that people who take regular naps have noticeably lower blood pressure than those who don’t, and high blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease. Napping has also been linked to lower levels of stress hormones like cortisol, which can contribute to inflammation and high blood pressure over time.
Additionally, napping has been shown to help boost the immune system. When we sleep, our bodies produce higher levels of certain cytokines, which are proteins involved in our body’s immune response. This means that regular napping may help to decrease our susceptibility to common illnesses and infections.
But the benefits of napping don’t stop there. Lowered stress levels and better physical health can lead to a cascade of other benefits, including better mental health and improved overall well-being. By taking care of our bodies through regular napping, we can help to promote a healthier lifestyle and a happier outlook on life. So the next time you feel the urge to doze off, don’t feel guilty – you may actually be doing your body a favor!
How Long to Nap For
Many people are unsure of how long they should nap for to reap the numerous benefits of napping without negative side effects. Some fear that a longer nap might disrupt their nighttime sleep, while others worry that a shorter nap won’t provide them with the necessary rest they need. So, what is the ideal nap length and how can you determine it for yourself? Let’s take a closer look at the science and tips behind finding the perfect nap duration.
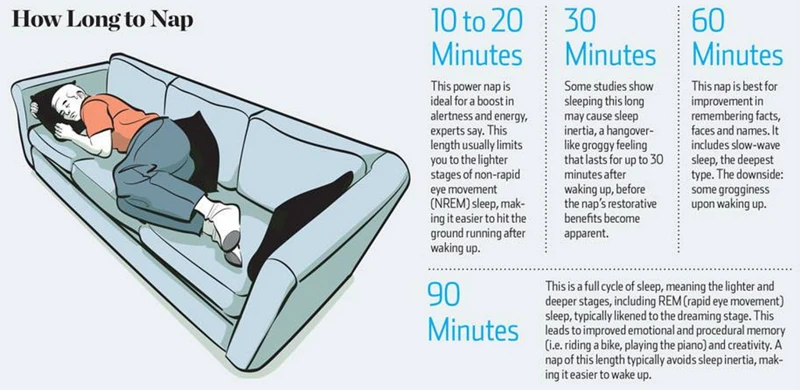
The Ideal Nap Lengths for Different Purposes
When it comes to napping, it’s important to consider the length of your nap in order to reap its benefits. Different nap lengths have different effects on the body and mind. Here’s a breakdown of the ideal nap lengths for different purposes:
| Purpose of Nap | Ideal Nap Length |
|---|---|
| Restorative Nap – to feel more alert and refreshed | 20-30 minutes |
| Creative Nap – to boost creativity and problem-solving skills | 60 minutes |
| Mental Fatigue Nap – to combat mental fatigue and increase alertness | 90 minutes (full sleep cycle) |
| Physical Fatigue Nap – to combat physical fatigue and improve physical performance | 90 minutes (full sleep cycle) |
For a restorative nap, a short 20-30 minute nap is ideal. This length of nap is enough to reduce feelings of sleepiness and improve alertness without disrupting nighttime sleep. If you’re looking to boost your creativity and problem-solving skills, a longer 60-minute nap may be more beneficial. This length of nap allows for increased activity in the brain’s right hemisphere, leading to an influx of creative ideas and solutions.
If you’re feeling mentally fatigued, a 90-minute nap (a full sleep cycle) may be necessary to combat this fatigue and increase alertness. Similarly, if you’re experiencing physical fatigue and looking to improve physical performance, a 90-minute nap (again, a full sleep cycle) may be the best option.
It’s important to note that longer naps (60-90 minutes) can potentially disrupt nighttime sleep or cause sleep inertia upon waking, so it’s best to limit these longer naps to occasional use rather than a daily habit. Additionally, the time of day you take your nap can also impact its effectiveness.
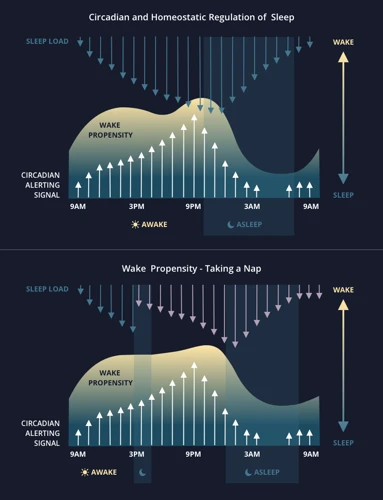
The Best Time to Nap
Napping at the wrong time can actually harm your sleep quality and lead to grogginess, so it is important to consider the best time to nap.
Here are some factors to consider when deciding on the best time to nap:
- Circadian rhythm: The body’s natural sleep-wake cycle can impact the ideal time to nap. Most people experience a natural dip in alertness in the mid-afternoon, around 2-3pm, which can make this an ideal time for a nap.
- Sleep schedule: If you have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep at night, it may be best to avoid napping too late in the day, as this can interfere with your nighttime sleep.
- Nap duration: The length of your nap can also impact the best time to nap. For example, a shorter nap of 20-30 minutes may be beneficial in the mid-afternoon, while a longer nap of 90-120 minutes may be best earlier in the day to avoid disrupting nighttime sleep.
Ultimately, the ideal time to nap will vary based on individual factors such as sleep schedule, circadian rhythm, and nap duration. It is worth experimenting with different nap times to see what works best for you and your body. Remember to also create a peaceful nap environment that is conducive to sleep, such as a cool, dark room with minimal noise.
Conclusion
After exploring the different types of napping, the science behind sleep, and the many benefits associated with napping, it’s clear that this practice is not just for the lazy or unproductive. In fact, napping has been shown to boost productivity, mood, and even physical health. However, as with any aspect of sleep, there are dos and don’ts to keep in mind for the most effective and restorative nap. With this in mind, let’s take a final look at what we’ve learned about napping and how incorporating it into your routine can lead to a happier, healthier, and more well-rested life.
Final Thoughts on Napping and its Benefits
After diving deep into the science behind napping and the effects it has on sleep quality, productivity, mood, and physical health, it is clear that taking a nap can be a powerful tool for overall well-being.
The benefits of napping are numerous and varied. Napping can lead to increased productivity and alertness, improved mood and reduced stress, boosted memory and learning, and reduced risk of heart disease and better physical health. Depending on the individual’s needs and the purpose of the nap, different nap lengths and time of day may be ideal.
It is important to note, however, that napping is not a substitute for a good night’s sleep. While a nap can help make up for lost sleep or provide a mid-day energy boost, it should not be relied upon as the sole source of sleep. A consistent, healthy sleep routine is key to overall health and well-being.
Additionally, not everyone may have the luxury of being able to take a nap during the day. Those who work long hours or have demanding schedules may not have the ability to incorporate naps into their routine. It is important for individuals to listen to their bodies and prioritize getting enough sleep at night if napping is not a feasible option.
Overall, napping can be a highly effective tool for enhancing overall health and well-being when used appropriately and in conjunction with a healthy sleep routine. Experiment with different nap lengths and times of day to find what works best for you, and prioritize getting a good night’s sleep as the foundation for a healthy and productive lifestyle.
| Pros of Napping | Cons of Napping |
|---|---|
| Increased productivity and alertness | Not a substitute for a good night’s sleep |
| Improved mood and reduced stress | May not be feasible for everyone’s schedule |
| Boosted memory and learning | |
| Reduced risk of heart disease and better physical health |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can napping replace regular nighttime sleep?
No, napping cannot fully replace regular nighttime sleep, but it can supplement it.
What is the best time of day to take a nap?
The best time to take a nap is generally early afternoon, around 1-3pm.
How long should a power nap be?
A power nap should be around 20 minutes in length to avoid entering deep sleep stages.
Can napping negatively impact nighttime sleep?
If napping is done for too long or too late in the day, it may negatively impact nighttime sleep quality.
Can napping improve memory and learning?
Yes, napping has been shown to improve memory and learning retention.
Does napping reduce stress levels?
Yes, napping can reduce stress levels and improve mood.
What is the difference between a nap and sleep?
Naps are shorter periods of sleep during the day, whereas sleep refers to the longer period of rest during the night.
What is the ideal length for a nap?
The ideal length for a nap varies depending on the purpose, but generally ranges from 20-90 minutes.
Can napping reduce the risk of heart disease?
Yes, napping has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and better physical health in general.
Is it normal to feel groggy or disoriented after waking up from a nap?
It is normal to experience sleep inertia or feeling groggy after waking up from a nap, but it should subside within a few minutes.