As we drift off to sleep, our minds continue to wander, taking us on fantastical journeys to places beyond our imagination. Dreams have always held a mesmerizing power, but what causes them? The quest to unravel the mysteries of dreaming has puzzled scientists for years. One factor that may hold the key is a phenomenon known as circadian rhythm. This natural internal process influences our sleep and wake cycles, but its effects are not limited to just those functions. In this article, we will explore the role of circadian rhythm in sleep and dreams and how we can harness its power to improve our overall health and well-being.
Understanding Circadian Rhythm
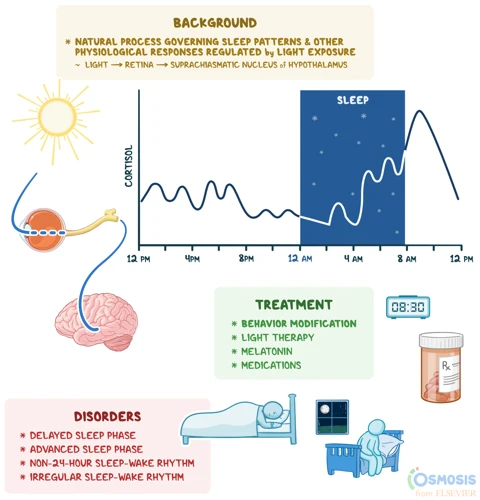
Have you ever wondered why you wake up naturally at the same time every day, without needing an alarm clock? Or why you feel more awake during the day and more tired at night? The answer lies in a natural process that is present in all living creatures, including humans. This process is called the circadian rhythm, and it plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep and wake cycles. Understanding what circadian rhythm is and how it works is key to unlocking the mysteries of our sleep patterns and ensuring that we get the rest we need to stay healthy and productive. Let’s delve deeper into this fascinating topic.
What is circadian rhythm?
Circadian rhythm refers to the natural internal process that regulates the cycle of sleep and wakefulness in the body. It is a biological cycle that lasts around 24 hours and is influenced by external factors such as light and temperature. Here are some key points to understand about circadian rhythm:
- It is controlled by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the brain: The SCN is a small group of cells located in the hypothalamus that acts as the “master clock” of the body. It receives signals from the eyes regarding light and darkness, and uses this information to regulate the production of hormones that affect sleep and other bodily functions.
- It follows a roughly 24-hour cycle: While the length of the circadian rhythm can vary slightly from person to person, it generally follows a cycle of approximately 24 hours. This means that the body naturally feels sleepy and alert at roughly the same times each day.
- It is influenced by external factors: The SCN uses cues from the environment, such as light exposure and mealtimes, to adjust the body’s internal clock. This means that factors such as night shift work, jet lag, and exposure to bright screens late at night can disrupt the natural circadian rhythm.
- It regulates many bodily functions: In addition to sleep and wakefulness, the circadian rhythm also affects things like body temperature, hormone production, digestion, and even mood. Disruptions to the circadian rhythm can lead to a range of health issues, including insomnia, depression, and metabolic disorders.
The circadian rhythm is a complex and important biological process that plays a key role in regulating many aspects of our health and well-being. By understanding how it works and what factors can disrupt it, we can take steps to optimize our sleep and overall health.
How does it affect sleep?
The circadian rhythm has a crucial impact on our sleep patterns. Our body is naturally wired to follow a consistent sleep-wake cycle based on the circadian rhythm. This biological clock regulates the timing and duration of our sleep, as well as our level of wakefulness and alertness during the day.
If our circadian rhythm is disrupted in any way, it can have negative effects on our sleep. For example, if we go to bed at the same time each night and wake up at the same time each morning, our body becomes accustomed to this pattern and expects it. However, if we suddenly change our sleep schedule, our body will experience a disruption in the circadian rhythm, leading to difficulty falling asleep and waking up.
Another way circadian rhythm affects sleep is through the release of certain hormones. The body naturally releases melatonin when it is time to sleep, but this release is regulated by the circadian rhythm. When the circadian rhythm is disrupted, it can lead to a decrease in the amount of melatonin that is released, making it difficult to fall asleep.
Additionally, the circadian rhythm affects our level of alertness during the day. When our body’s internal clock signals that it’s time to be awake, our level of alertness and cognitive function increases. In contrast, when it’s time to sleep, these functions decrease to help facilitate the transition into restful sleep.
The circadian rhythm plays a critical role in regulating our sleep patterns and maintaining good sleep hygiene. By understanding its impact on sleep and taking steps to maintain a consistent sleep schedule and promote proper hormone release, we can improve our overall quality of sleep and reduce the negative effects of disruptions to our circadian rhythm.
What factors affect circadian rhythm?
Various factors can affect the circadian rhythm, including external cues such as light and temperature as well as internal cues such as hormones and genetics. Here is a table summarizing the factors that can affect circadian rhythm:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Light exposure | Exposure to bright light or lack of light can have a significant effect on circadian rhythm. Bright light in the morning can help to reset the body’s internal clock and promote wakefulness, while exposure to light at night can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle and make it harder to fall asleep. |
| Temperature | The body’s temperature can also affect circadian rhythm. The internal body temperature naturally drops at night, which signals the body that it is time to sleep. Exposure to cooler temperatures can help facilitate this drop in temperature and promote sleepiness. |
| Hormones | The release of hormones such as melatonin and cortisol can also affect circadian rhythm. Melatonin is typically released in response to darkness and promotes sleep, while cortisol is released in response to stress and promotes wakefulness. |
| Genetics | The body’s internal clock is regulated by a group of genes that influence the production of specific proteins. Variations in these genes can affect the body’s circadian rhythm and make it harder to maintain a regular sleep-wake cycle. |
| Social cues | Factors such as work schedules, school schedules, and social activities can also affect circadian rhythm. Irregular schedules and late-night activities can disrupt the body’s internal clock and make it harder to maintain a consistent sleep-wake cycle. |
Understanding these various factors can help individuals take steps to promote a healthy circadian rhythm and improve sleep quality.
The Importance of Circadian Rhythm for Sleep
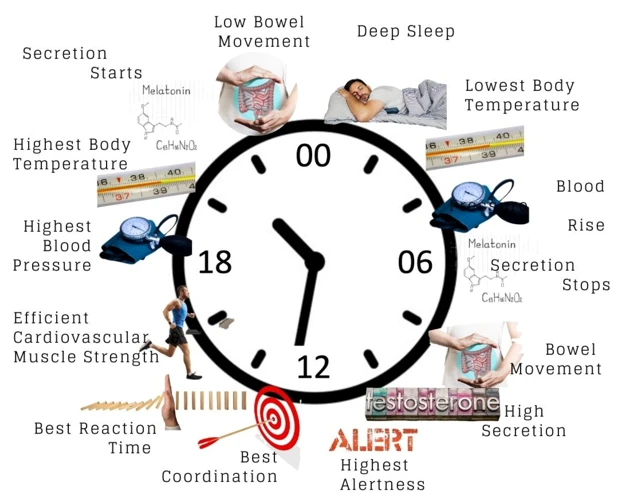
Ensuring a good night’s sleep is crucial to maintaining overall health and well-being. However, it’s not just the duration of sleep that matters, but also the quality. One of the main factors influencing the quality of sleep is the body’s internal clock or circadian rhythm. By understanding the importance of circadian rhythm for sleep, you can learn to make necessary changes and adjustments to optimize your sleep quality. In this section, we’ll explore how circadian rhythm affects sleep, the potential harm of irregular sleep schedules, and the vital role of circadian rhythm in dreaming.
How circadian rhythm affects sleep quality
Circadian rhythm, also known as the body’s internal clock, plays a crucial role in determining the quality of our sleep. This rhythm regulates our natural sleep-wake cycle and helps us to feel awake and alert during the day and sleepy at night.
Disrupted circadian rhythms can lead to poor sleep quality or even insomnia. Research has shown that people with disrupted circadian rhythms have an increased risk of developing sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome.
Irregular sleep schedules can also negatively impact circadian rhythms and sleep quality. For example, people who work night shifts or have jet lag from traveling across time zones often experience disruptions in their circadian rhythms, leading to poorer sleep quality.
Circadian rhythm affects the different stages of sleep, including deep sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. During deep sleep, the body repairs and regenerates tissues and strengthens the immune system, while REM sleep is important for consolidating memories and processing emotions.
Inconsistent sleep schedules can disrupt these important stages of sleep and affect our overall health and well-being. For example, a lack of deep sleep can lead to increased levels of stress hormones and impaired immune function, while a lack of REM sleep can lead to mood swings and difficulty regulating emotions.
In order to optimize sleep quality, it is important to maintain a consistent sleep schedule and to synchronize our internal clock with our daily routines. This can be achieved through regulating exposure to light, adjusting sleep schedules gradually, and taking melatonin supplements to help reset the body’s internal clock. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet can also help to support a healthy circadian rhythm and improve sleep quality.
| Ways in which disrupted circadian rhythms can affect sleep quality: |
|---|
| Increases risk of developing sleep disorders |
| Disrupts the different stages of sleep |
| Leads to impaired immune function |
| Causes mood swings and difficulty regulating emotions |
| Can lead to stress and anxiety |
Why irregular sleep schedules can be harmful
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is essential for optimal health and well-being. Irregular sleep schedules can disrupt the body’s natural circadian rhythm, which can have numerous negative effects. Here are some reasons why irregular sleep schedules can be harmful:
- Decreased alertness: When you don’t get enough sleep or have an irregular sleep schedule, you may experience daytime sleepiness and a decrease in your overall alertness. This can be dangerous, especially if you operate heavy machinery or drive a vehicle.
- Increased risk of chronic diseases: Studies have shown that people with irregular sleep schedules may have a higher risk of developing chronic health conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. This may be caused by disruptions in the body’s hormonal and metabolic processes.
- Mood disturbances: Irregular sleep patterns can also cause mood disturbances, such as irritability, depression, and anxiety. This can be especially problematic if you’re dealing with a pre-existing mental health condition.
- Impact on cognitive function: A lack of sleep or an inconsistent sleep schedule can also have negative effects on your cognitive function. This can manifest as difficulty with memory, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Disrupted social life: Irregular sleep patterns can also affect your social life. If you’re constantly tired and unable to keep up with social obligations, you may start to feel isolated and disconnected from others.
It’s clear that maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is crucial for both physical and mental health. If you’re struggling with getting enough sleep or keeping a regular sleep schedule, it may be worth speaking with a healthcare professional to discuss ways to improve your sleep hygiene.
The role of circadian rhythm in dreaming
The circadian rhythm plays an important role in our sleep, and it also affects our dreaming. During the day, our bodies build up a natural urge to sleep, and this urge is strongest at night, when we are supposed to be sleeping. This urge is driven by the circadian rhythm, which helps to regulate many bodily functions, including our sleep-wake cycle.
Research has shown that REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, the stage of sleep where most of our dreaming occurs, is strongly influenced by the circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm can affect the time of day that we have our dreams, as well as the content of our dreams.
One study found that people are more likely to have nightmares during the second half of the night, when REM sleep is most prevalent. This timing is thought to be related to the natural drop in body temperature that occurs during this time, which can make us more susceptible to bad dreams.
On the other hand, people are more likely to have positive, vivid dreams during the earlier part of the night, when slow-wave sleep dominates. This is thought to be because the circadian rhythm is at its strongest at this time and helps to support restful, restorative sleep.
The circadian rhythm is important for regulating many aspects of our sleep, including dreaming. Disruptions in the circadian rhythm, such as those caused by jet lag or shift work, can lead to changes in our dreams and may contribute to sleep disturbances.
Ways to Sync Your Circadian Rhythm
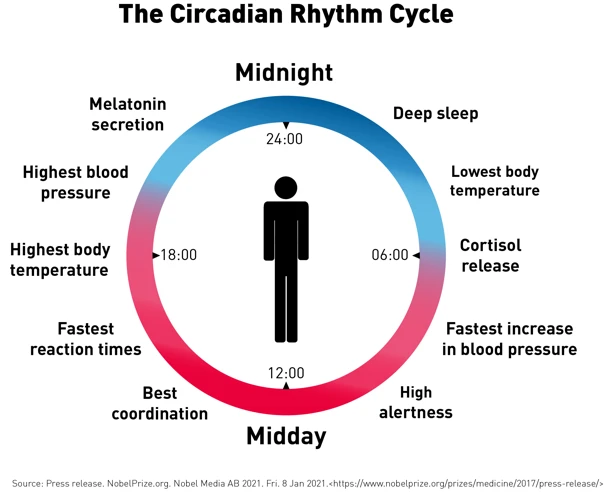
If you’re struggling with sleep and suspect that your circadian rhythm might be out of sync, don’t worry! There are several strategies that can help synchronize your body’s internal clock and improve your sleep quality. From adjusting your exposure to light to adopting healthy habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and exercise routine, there are various ways to reset your body’s clock and improve your sleep health. In this section, we’ll explore some effective ways to get your circadian rhythm back on track.
How light exposure affects circadian rhythm
Strong scientific evidence suggests that light exposure plays a crucial role in regulating the circadian rhythm. In particular, exposure to light in the morning can help to reset the biological clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up at the desired times. On the other hand, excessive exposure to light at night can have the opposite effect, making it harder to fall asleep and disrupting the natural sleep-wake cycle.
This is because light exposure controls the production of the hormone melatonin, which helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Melatonin is produced in the pineal gland, a small gland located in the brain, and is naturally released in response to darkness. This means that exposure to bright light during the day can help to regulate melatonin production at night, causing us to feel more awake during the day and sleepier at night.
On the other hand, exposure to artificial light at night, including the blue light emitted by electronic devices, can suppress melatonin production and disrupt the sleep-wake cycle. This is because the blue light has a similar wavelength to daylight, which can confuse the biological clock and reduce melatonin production, leading to difficulty falling asleep and poor sleep quality.
To mitigate the negative effects of artificial light on the circadian rhythm, experts recommend practicing good sleep hygiene, such as avoiding using electronic devices for at least an hour before bedtime, and using blue-light blocking filters or glasses if necessary. Additionally, it’s important to go outside and get regular exposure to natural light throughout the day, especially in the morning, in order to reset the biological clock and improve sleep quality.
Light exposure is a critical factor in regulating the circadian rhythm, and can have a significant impact on our sleep quality and overall health. By understanding the role of light in the circadian rhythm, and taking steps to regulate light exposure throughout the day, we can improve our sleep quality and promote overall well-being.
| Ways light exposure affects circadian rhythm: |
|---|
| Exposure to light in the morning can reset the biological clock |
| Excessive exposure to light at night can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle |
| Light exposure controls melatonin production |
| Exposure to artificial light at night can suppress melatonin production |
| Artificial blue light can have a negative impact on the circadian rhythm |
| Regular exposure to natural light can improve sleep quality |
Ways to reset your circadian rhythm
One effective way to reset your circadian rhythm is to optimize your exposure to light. Expose yourself to bright light during the day to signal to your body that it is daytime and time to be awake. Consider taking a walk outside during your lunch break or sitting near a window if you work indoors. On the other hand, limit your exposure to bright light before bedtime. This can mean minimizing screen time before bed, avoiding bright overhead lights, and using a dimmer lamp instead.
Another strategy is to establish a consistent sleep and wake schedule and stick to it as much as possible. This means waking up at the same time every day, including weekends, and going to bed at a similar time each night. Avoid napping or sleeping in on the weekends, as this can throw off your sleep schedule and make it more difficult to fall asleep at night.
If you need to shift your sleep schedule, say for a new job or a travel destination in a different time zone, gradually shift your sleep and wake times in small increments. For example, if you need to wake up three hours earlier than usual, start by waking up 15 minutes earlier each day until you reach your target wake time.
In addition to these strategies, implementing a relaxing bedtime routine can help signal to your body that it is time to wind down and get ready for sleep. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, practicing yoga or meditation, or listening to calming music.
Finally, consider supplementing with melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep-wake cycles. While it is available over the counter, it is important to check with a healthcare provider before taking melatonin to ensure proper dosage and minimize any potential side effects.
The role of melatonin in regulating sleep
The human body has a natural sleep-wake cycle, which is regulated by the internal body clock known as the circadian rhythm. The hormone melatonin plays an important role in regulating this cycle and promoting healthy sleep habits.
What is melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone that is produced by the pineal gland in the brain. It is released during periods of darkness and suppressed during periods of light. Melatonin is often referred to as the “sleep hormone” because it is involved in promoting sleep and controlling the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
How does melatonin affect sleep?
Melatonin plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s internal clock and sleep-wake cycle. When melatonin levels are low, it can be difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. This is why some people choose to take melatonin supplements, especially when traveling across time zones or working night shifts.
What are the factors that affect melatonin production?
There are several factors that can impact the body’s production of melatonin, including:
| Factor | How it affects melatonin production |
|---|---|
| Light exposure | Exposure to light, especially blue light, can suppress the body’s production of melatonin. |
| Diet and Nutrition | Eating a diet rich in tryptophan, a precursor to melatonin, can increase melatonin production. |
| Age | Melatonin production decreases with age. |
| Medications | Some medications, such as beta-blockers and antidepressants, can interfere with the body’s production of melatonin. |
How can melatonin be used to promote healthy sleep habits?
Melatonin supplements can be used in certain situations to promote healthy sleep habits. For example, it may be helpful for travelers who are experiencing jet lag or individuals who work night shifts. However, it is important to note that melatonin supplements are not a cure for insomnia or other sleep disorders.
What are the potential side effects of melatonin supplements?
While melatonin supplements are generally considered safe, they can have side effects such as headaches, dizziness, and daytime drowsiness. For this reason, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using melatonin supplements to address sleep issues.
Melatonin is an important hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s internal clock and promoting healthy sleep habits. While supplements may be helpful in certain situations, it is important to prioritize healthy sleep habits and address any underlying sleep disorders with the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Other strategies for improving sleep quality
There are numerous strategies that can be employed to improve sleep quality, especially for individuals whose circadian rhythms are out of sync. These strategies include:
- Creating a calming bedtime routine: This can include activities such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or practicing meditation or deep breathing exercises. By engaging in activities that are calming, the mind can relax and prepare for sleep.
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed: Both caffeine and alcohol can disrupt the sleep cycle, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep. It is best to avoid these substances in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help regulate the sleep-wake cycle by helping to tire the body out and release energy. It is best to exercise earlier in the day, however, as exercising too close to bedtime can have the opposite effect on sleep.
- Ensuring a comfortable sleep environment: This can include everything from having a comfortable mattress and pillows to making sure the room is at a cool, comfortable temperature.
- Avoiding screens before bedtime: The blue light emitted from electronic devices can suppress the production of melatonin, which is essential for regulating sleep. It is best to avoid screens for at least an hour before bed.
- Practicing relaxation techniques: Techniques such as yoga or progressive muscle relaxation can help the body and mind relax, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
By incorporating these strategies into one’s daily routine, it can be easier to improve sleep quality and maintain a healthy circadian rhythm.
The Impact of Modern Lifestyles on Circadian Rhythm
As our world becomes increasingly fast-paced and connected, it’s easy to fall out of sync with our natural sleep rhythms. The pressures of technology, shift work, and modern diets can all have a profound impact on our circadian rhythms. In this section, we’ll explore how the modern lifestyle affects our internal sleep clocks and what we can do to restore balance. From understanding the role of light exposure to exploring dietary strategies for improvement, we’ll dive deep into the complexities of modern sleep patterns.
How technology affects circadian rhythm
In today’s digital age, technology has become an integral part of our daily lives. However, excessive use of technology can negatively impact our circadian rhythm, causing sleep disturbances and other health issues. Here are some ways in which technology affects our circadian rhythm:
- Blue light exposure: Most electronic screens, such as those on our smartphones, computers, and TVs, emit blue light which suppresses the production of melatonin – a hormone that helps regulate sleep. This can disrupt our sleep-wake cycle and lead to difficulty falling asleep.
- Increased arousal: Using technology before bed can increase mental arousal, making it harder to relax and fall asleep. Social media and other forms of online content can also be stimulating, leading to heightened emotions and interrupting our natural sleep cycle.
- Disrupting sleep patterns: Late-night use of technology can impact the quality of sleep, leading to difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and a reduced amount of time spent in deep sleep, which is essential for feeling refreshed and energized.
- Irregular sleep schedules: Binge-watching TV shows, playing video games, and working late into the night can disrupt our regular sleep patterns, leading to a misaligned circadian rhythm. This can result in fatigue, irritability, and a reduced ability to concentrate during the day.
It is important to be mindful of our technology usage and make an effort to minimize our exposure to blue light before bed. One way to do this is to use blue light filters on electronic screens which reduces the amount of blue light emitted. It is also beneficial to avoid using technology before bed and establish a regular sleep schedule to maintain a healthy circadian rhythm.
The impact of shift work
Shift work is any schedule outside of the traditional nine-to-five workday which commonly includes evening, night, early morning, and rotating shifts. This type of work schedule can significantly impact an individual’s circadian rhythm and, as a result, their sleep quality and overall health.
The negative effects of shift work on circadian rhythm
Shift work can disrupt the natural alignment between the body’s internal clock and the external environment, leading to a mismatch between the timing of an individual’s sleep and their circadian rhythm. This can cause difficulties in falling asleep and staying asleep during the day or night, leading to chronic sleep deprivation in the long term. Studies have shown that shift workers experience more sleep disturbances, excessive daytime sleepiness, reduced alertness, and difficulty concentrating compared to people working standard working hours.
The impact of shift work on physical health
The effect of shift work on the body’s natural rhythms can also affect an individual’s physical health. The irregular schedule and lack of sleep have been linked to a range of health conditions, such as digestive problems, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even some cancers. Studies have indicated that shift workers have an increased risk of developing these conditions, mainly due to disturbances in the circadian rhythms affecting the production of hormones regulating hunger and metabolism during the inappropriate hours.
Strategies for managing shift work
Fortunately, there are some strategies that can help individuals who need to work irregular hours to improve their sleep quality and minimize the negative effects of shift work. One of the key strategies includes establishing a consistent sleep routine, which can help regulate the body’s internal clock. This means setting a consistent bedtime and wake-up time, even on days off. Additionally, avoiding exposure to electronic devices, caffeine, and alcohol before bedtime can also help improve sleep quality.
Other strategies for improving sleep quality include:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Creating a sleep-conducive environment | Minimizing noise and light in the bedroom to promote relaxation and restful sleep. |
| Practicing relaxation techniques | For example, deep breathing or meditation before bed can help relax the mind and create a positive atmosphere conducive to sleep. |
| Engaging in regular physical activity | Regular exercise can help promote better sleep, reduce stress levels and improve overall health outcomes. |
Conclusion
Shift work can negatively affect an individual’s health and sleep quality due to disruptions in their natural circadian rhythms. However, some strategies can help minimize these negative effects, including the development of healthy sleep habits, relaxation techniques and regular exercise. By prioritizing good sleep habits, individuals working nontraditional hours can help improve their overall health and well-being.
The role of diet and exercise in synchronizing circadian rhythm
The role of diet and exercise in synchronizing circadian rhythm is often overlooked but is actually essential in maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle. Here are some important factors that one should consider when it comes to diet and exercise:
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Diet | A healthy and balanced diet can help regulate circadian rhythm by providing the necessary nutrients and energy required for bodily functions. Some studies suggest that consuming high-fat or high-carbohydrate meals, especially at night, may disrupt circadian rhythm and decrease sleep quality. |
| Meal Timing | The timing of meals can also impact circadian rhythm. Eating at regular times throughout the day, particularly in line with daylight exposure, can enhance circadian alignment. As a general rule, breakfast should be consumed soon after waking up, lunch around midday and dinner in the early evening. |
| Exercise | Regular physical exercise can improve sleep quality by increasing the production of serotonin, which is involved in the sleep-wake cycle. However, exercising too close to bedtime can have the opposite effect, making it difficult to fall asleep. It is recommended to exercise at least a few hours before bedtime. |
| Outdoor Activity | Spending time outdoors, especially in the morning, can help regulate circadian rhythm as exposure to natural light synchronizes our internal clock. Even on gloomy days, natural light outdoors is still stronger than indoor lighting, so it is beneficial to go outside whenever possible. |
By paying attention to these factors, one can help synchronize their circadian rhythm and improve their overall sleep quality. It is important to remember that while diet and exercise play a role, they are not the only factors that affect our internal clock. Other important strategies include regulating exposure to light and darkness, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and practicing good sleep hygiene.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of circadian rhythm in sleep is crucial and has a major impact on our overall health and well-being. Understanding the nature of circadian rhythm, how it affects our sleep patterns, and the factors that influence it is essential in developing strategies to improve the quality of our sleep.
It is clear that irregular sleep schedules can be harmful and may contribute to a variety of health problems. However, there are ways to reset our circadian rhythm and improve our sleep quality. Exposure to light plays a major role in controlling our circadian rhythm, and it is important to manage our exposure to light to promote healthy sleep patterns. Additionally, melatonin is a hormone that can be used to aid in regulating sleep.
Modern lifestyles have had a major impact on our circadian rhythm, with the use of technology and shift work being two significant contributors. It is important to be aware of these factors and take steps to mitigate their impact on our sleep patterns. In addition, making dietary and exercise changes can also help to improve the synchronization of our circadian rhythm.
Overall, recognizing the importance of circadian rhythm in our sleep patterns and taking active steps to improve it can have a positive impact on our overall health and well-being. By prioritizing our sleep and developing healthy sleep habits, we can unlock the mysteries of dreaming and achieve a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the circadian rhythm affect mood?
The circadian rhythm plays a crucial role in regulating mood, as it affects the production of certain hormones such as cortisol and melatonin. Irregular sleep patterns and disruptions in the circadian rhythm can lead to mood changes, such as increased anxiety and depression.
Can the circadian rhythm be disrupted by certain medications?
Yes, certain medications such as antidepressants and sleep aids can disrupt the natural circadian rhythm, leading to sleep disturbances and other issues. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing any sleep-related issues while taking medication.
Can exercise help regulate the circadian rhythm?
Yes, regular exercise can help regulate the circadian rhythm by promoting more restful sleep and reducing stress levels. However, it is important to avoid intense exercise close to bedtime, as this can actually disrupt sleep patterns.
Can the use of electronic devices before bed affect the circadian rhythm?
Yes, exposure to the blue light emitted by electronic devices such as smartphones and tablets can inhibit the production of melatonin, which can disrupt the circadian rhythm and make it difficult to fall asleep.
What is the ideal sleep schedule for synchronizing the circadian rhythm?
The ideal sleep schedule for synchronizing the circadian rhythm varies depending on the individual’s specific circadian rhythm. Generally, it is recommended to stick to a consistent sleep schedule and to avoid drastic changes in sleep/wake times.
Can jet lag disrupt the circadian rhythm?
Yes, crossing multiple time zones can wreak havoc on the circadian rhythm and lead to sleep disturbances and other issues. It is recommended to gradually adjust sleep patterns before and after traveling to minimize the effects of jet lag.
Can caffeine consumption affect the circadian rhythm?
Yes, caffeine can inhibit the production of melatonin and disrupt the natural circadian rhythm. It is important to limit caffeine consumption, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Is it possible to permanently reset the circadian rhythm?
No, the circadian rhythm is a natural biological process that cannot be permanently reset. However, certain lifestyle changes and environmental factors can help regulate the circadian rhythm.
Can the circadian rhythm affect weight gain/loss?
Yes, disruptions in the circadian rhythm can lead to hormonal imbalances that can affect weight gain or loss. Studies have shown that individuals who experience irregular sleep patterns and circadian rhythm disruptions are more likely to develop obesity and other health issues.
What are some natural supplements that can help regulate the circadian rhythm?
Melatonin is a popular natural supplement that can help regulate the circadian rhythm and promote restful sleep. Certain herbal supplements such as valerian root and chamomile have been shown to have calming effects and can facilitate healthy sleep patterns.








