Our dreams have intrigued and fascinated us for centuries, with their mysterious landscapes, vivid characters, and uncanny symbolism. As we sleep, our brains enter a complex and intricate state of consciousness that remains both enigmatic and captivating to scientists and dreamers alike. Despite the endless research and theories surrounding the content and purpose of our dreams, much remains unknown about this enigmatic area of the human mind. However, recent research has begun to uncover the fascinating connection between our dreams and emotional processing, shedding light on the potential benefits that paying attention to our dreams can have on our mental and emotional health. In this article, we will explore the latest findings on the link between dreams and emotional regulation, as well as the theories surrounding the purpose and meaning of our dreams.
What Happens In Our Brain During Dreaming?
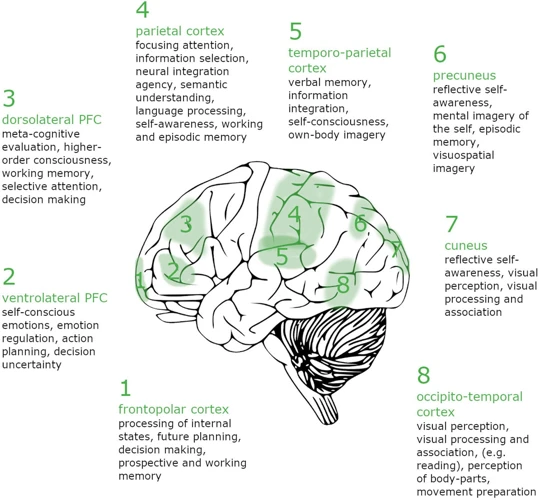
During dreaming, our brain goes through several processes that help us experience dreams. These processes are characterized by two distinct stages of sleep: NREM sleep and REM sleep.
NREM Sleep:
During NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep, the brain slows down, and the body relaxes. The activity in the frontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making, problem-solving, and planning, decreases. The brain brings up memories from our day and consolidates them into long-term storage. This process is essential for learning and memory consolidation.
REM Sleep:
During REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, the brain becomes very active. This stage is characterised by intense brain activity, vivid dreams and rapid eye movements. The limbic system, which is responsible for our emotions, becomes more active. The amygdala, a part of the limbic system that is associated with fear and anxiety, becomes more active in REM sleep.
The activity in the frontal cortex is low during REM sleep, which makes it difficult for us to distinguish between reality and our dreams. The brainstem, which controls basic functions such as breathing and heart rate, prevents us from acting out our dreams by paralyzing our muscles.
During the different stages of sleep, our brain goes through various activities that help us experience dreams. These activities are crucial for consolidating memories and may also have a role in processing emotions.
NREM Sleep
As we drift off into slumber, our brains go through several stages of sleep characterized by distinct patterns of brain activity. The first of these stages is characterized by what is known as non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. During this phase, the brain undergoes a period of deep relaxation, where our muscles relax and our breathing slows down. While it may seem like a passive state, ongoing research is revealing the active role that NREM sleep plays in our overall emotional and cognitive health. Let’s delve deeper into the mysteries of this first stage of sleep.
REM Sleep
REM sleep, also known as Rapid Eye Movement sleep, is a stage of sleep that occurs after NREM sleep. During REM sleep, the brain is highly active, with brainwaves resembling those of an awake person. REM sleep is crucial for the processing of emotions and memories.
In REM sleep, the body is paralyzed to prevent acting out dreams. This is known as atonia. Atonia is regulated by a group of neurons in the brainstem called the pontine tegmentum. In some cases, this paralysis does not occur, resulting in a condition called REM sleep behavior disorder. This disorder can cause a person to physically act out their dreams.
REM sleep also plays a role in the consolidation of memories. Studies have shown that REM sleep helps strengthen procedural memories, such as learning to play a musical instrument or a new language. REM sleep also aids in emotional processing, allowing the brain to integrate emotional experiences and react appropriately in future situations.
During REM sleep, the brain is more active in regions associated with emotions, such as the amygdala and hippocampus. This increased activity allows for the processing and integration of emotional experiences. The language center of the brain, the prefrontal cortex, is less active during REM sleep, which may explain why dreams can sometimes be difficult to remember or seem nonsensical.
In addition to emotional processing and memory consolidation, REM sleep may also play a role in creativity. Studies have shown that brain activity during REM sleep is similar to that of the waking brain during the creative process. This may explain why people often report having vivid and imaginative dreams during REM sleep.
REM sleep is a crucial stage of sleep that plays a vital role in emotional processing, memory consolidation, and creativity. Understanding the importance of REM sleep can help us prioritize and improve our sleep habits for better emotional and cognitive functioning.
| REM Sleep |
|---|
| Increased brain activity in regions associated with emotions |
| Regulated by a group of neurons in the brainstem |
| Plays a role in the consolidation of memories |
| May contribute to creativity |
| Language center of the brain is less active |
Why Do We Have Bad Dreams?

Throughout our lives, we all experience bad dreams that leave us feeling frightened, anxious, or uneasy. The reasons for why we have bad dreams are varied and complex, but they often stem from unresolved issues or psychological disorders.
Unresolved Issues
One of the most common reasons for bad dreams is unresolved issues that we may have pushed deep down into our subconscious minds. These can be anything from everyday stressors to significant traumas that we may not have fully processed. Our dreams often act as a reflection of our unconscious selves, bringing these unresolved issues to the surface in powerful and emotional ways. This can be both helpful and distressing, as it can force us to confront issues that we may have been avoiding, but it can also be overwhelming and leave us feeling anxious or fearful.
Psychological Disorders
Another reason why we may have bad dreams is due to psychological disorders. Certain disorders such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD can trigger nightmares and other disturbing dreams. These disorders affect our emotional regulation, making us more susceptible to negative emotional experiences in our dreams. Our brains may also be processing experiences from these disorders during our sleep, leading to intense emotions and vivid dreams.
The reasons for why we have bad dreams are complicated and often interconnected. They can stem from unresolved issues that we may not have fully processed or psychological disorders that affect our emotional regulation. It is important to address any issues causing negative dreams to improve our emotional health and overall well-being.
Unresolved Issues
Dreams have always been a topic of great fascination for many of us. The ongoing debate on the significance and purpose of dreams throughout history has intrigued scholars and researchers alike. One of the most intriguing aspects of dreams is the occurrence of seemingly senseless and frightening nightmares. These unpleasant dreams can cause distress and confusion, leaving us with a lingering sense of unease. However, psychologists have uncovered a hidden connection between negative dreaming and emotional processing. It is now believed that dreams, including bad ones, can offer us valuable insight into our unresolved issues, fears, and anxieties. Let’s delve deeper into this topic and explore the link between bad dreams and unresolved issues.
Psychological Disorders
Research has shown that psychological disorders can also contribute to the occurrence of negative dreams. Individuals with conditions such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and depression have been found to have more frequent nightmares and negative dreams.
Anxiety disorders can cause individuals to experience general feelings of unease and worry that can carry over into their sleep. These feelings can manifest in negative dreams, further exacerbating the individual’s anxiety. Similarly, individuals with PTSD may experience frequent nightmares related to their past traumas.
Depression, on the other hand, has been linked to decreased dream activity. Research suggests that individuals with depression tend to have fewer dreams overall and experience less emotional content in their dreams. This may be because depression can lead to a decreased ability to process emotions effectively, both during waking life and during sleep.
It’s important to note that while some psychological disorders may contribute to negative dreaming patterns, bad dreams do not necessarily signify the presence of a psychological disorder. If you are experiencing frequent nightmares or negative dreams, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional who can help diagnose any underlying conditions and provide appropriate treatment.
How Dreams Help Emotional Processing?

As we have seen, dreams are experiences during sleep that involve a wide range of mental images, emotions, and sensations. While the content and purpose of dreams have been debated for centuries, one of the most intriguing aspects of dreaming is the role it plays in emotional processing.
Dream Interpretation: One approach to understanding the emotional significance of dreams is to interpret their content. By analyzing the symbols and themes that appear in our dreams, we may gain insight into our hidden desires, fears, and conflicts that we may not be aware of in waking life. In this way, dream interpretation can help us identify and process unresolved emotions.
Lucid Dreaming: Another way to harness the emotional benefits of dreaming is through lucid dreaming, which is the act of recognizing you are in a dream and being able to control its content. Lucid dreaming has been used as a means to confront and work through difficult emotions and overcome nightmares. It can also be a tool for practicing new behaviors and enhancing self-confidence.
Journaling Dreams: Keeping a dream journal is a simple yet powerful way to process emotions during sleep. By recording the details of your dreams as soon as you wake up, you can analyze your thoughts and feelings and gain a better understanding of your inner self.
Therapeutic Approaches: Many therapists use dreamwork as a tool to help clients process emotions and gain insight into their unconscious mind. This may involve exploring recurring dreams, interpreting symbols, or using guided imagery to reframe negative patterns.
Dreams can help us process emotions by allowing us to confront unresolved issues, provide a space for creative problem-solving, and access our unconscious mind. By paying attention to our dreams and exploring their content, we can gain valuable insights into our emotional health and wellbeing.
Dream Interpretation
Dreams have been a subject of fascination and confusion for centuries. While we spend a significant amount of time sleeping, dreaming is still not entirely understood. One of the most intriguing aspects of dreaming is the possibility that it can reveal our deepest desires, fears, and emotions. Dream interpretation involves the analysis of these hidden messages in our dreams. The process can be perplexing, but it offers a unique opportunity to gain insights into our subconscious minds. In this section, we will explore the importance of dream interpretation and how it can aid in emotional processing.
Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming is a state of consciousness in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and can exert some control over the dream. It is believed that this type of dreaming can aid in emotional processing because it allows individuals to confront and work through challenging emotions and experiences in a safe, controlled environment. Here are some techniques for inducing lucid dreaming:
- Dream Journalling – Keep a dream journal and write down as much detail as you can about your dreams each morning. This can help you become more aware of patterns in your dreams, making it easier to recognize when you are dreaming.
- Reality Testing – Throughout the day, ask yourself if you are dreaming. This habit can carry over into your dreams, making it more likely that you will realize you are dreaming.
- Wake-Back-To-Bed Technique – Wake up after 5-6 hours of sleep, stay awake for 30-60 minutes, and then go back to bed. This can increase the chances of having a lucid dream during the second half of the night when REM sleep is more prominent.
Lucid dreaming can be a powerful tool for emotional processing, as it allows individuals to work through issues within the safety of their own minds. While it takes time and practice to develop the skill of inducing lucid dreams, the benefits of lucid dreaming can be profound.
Journaling Dreams
One way to facilitate the emotional processing that occurs during dreaming is by journaling our dreams. Keeping a dream journal can be a helpful tool for increasing self-awareness, understanding our emotions, and gaining insight into our thoughts and behaviors.
Here are some tips for journaling our dreams:
- Write down the dream as soon as possible: It’s important to write down the dream as soon as we wake up to avoid forgetting important details.
- Include sensory details: Describing the sights, sounds, smells, and feelings we experienced in the dream can help us recall it more vividly.
- Reflect on the emotions: Take note of the emotions we experienced during the dream and try to identify any underlying concerns or issues that may have triggered them.
- Look for recurring themes or symbols: Recurring themes or symbols in our dreams can indicate patterns in our thoughts and emotions that are worth exploring further.
- Consider possible meanings: Reflecting on the dream’s content and context can help us derive possible meanings and interpretations.
By journaling our dreams regularly, we can identify patterns or recurring themes. This may help us uncover hidden emotions or issues that we may not have been consciously aware of, which can aid our emotional processing and promote self-awareness. Additionally, dream journaling can also be used as a tool for discussing dreams with a therapist or mental health professional as part of a broader mental health treatment plan.
Therapeutic Approaches
Therapeutic approaches aimed at using dreams to enhance emotional processing and healing vary in methodology, but most involve some form of active engagement with dream content. Here are some examples of such approaches:
- Imagery Rehearsal Therapy: This therapeutic approach involves the patient visualizing the content of their nightmares and changing the outcome to something positive. The idea behind this is that by rewriting the story, the patient can confront and conquer their fears, leading to a reduction in the frequency and intensity of the nightmares.
- Dream Incubation: This involves actively trying to direct the content of one’s dreams through focused thought or meditation before going to sleep. The idea is that by consciously setting an intention for the dream, the dreamer can access valuable insights or work through specific emotional issues.
- Interpretive Approaches: These approaches involve working with a therapist to analyze the underlying meaning of dreams. The therapist may ask the patient to describe the dream in detail and then work with them to identify symbolisms, patterns or conflicts revealed in the dream that may relate to the patient’s emotional struggles or stressors.
- Transference-Focused Psychotherapy: This approach focuses on exploring the patient’s unconscious emotional reactions to the therapist or other people in their lives based on unresolved issues from the past. Dreams are used as a means of accessing and discussing these emotions in a safe and therapeutic setting.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: This approach involves exploring the patient’s thoughts and beliefs surrounding their fears or anxieties, and then working to shift those thoughts to more positive ones through techniques such as challenging negative self-talk, exposure therapy, and relaxation techniques. Dreams may be used as a way to identify and explore negative thought patterns present in the patient’s subconscious mind.
It is important to note that not all approaches work for everyone, and some people may need to try several different approaches before finding what works best for them. Additionally, it is recommended that anyone pursuing therapeutic approaches to dream work consult with a qualified therapist or mental health professional.
The Role of Sleep in Emotional Regulation
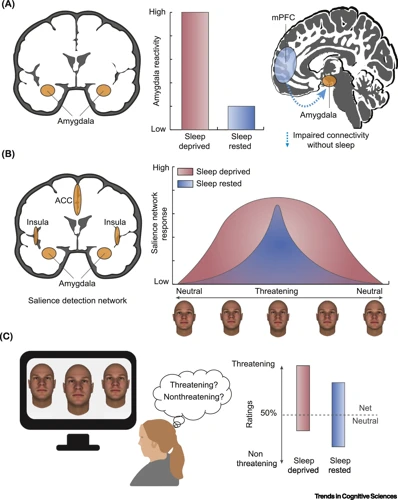
Sleep plays a crucial role in emotional regulation, affecting our ability to process and regulate emotions. The body’s natural circadian rhythm dictates our sleep and wake cycles by regulating the release of neurotransmitters, hormones, and chemical signals that are essential for emotional balance.
Sleep Deprivation and Emotional Dysregulation: Sleep deprivation, whether acute or chronic, can significantly impact our emotional wellbeing. Sleep-deprived individuals often exhibit irritability, moodiness, and increased emotional reactivity. They may also struggle with recognizing and accurately responding to emotional cues from oneself or others, which can negatively impact social interactions.
Sleep Hygiene and Emotional Health: Maintaining healthy sleep habits, also known as sleep hygiene, plays a significant role in emotional regulation. Regular sleep patterns, a comfortable sleep environment, and bedtime rituals can improve the quality of sleep and promote emotional balance.
Adopting relaxation techniques before bedtime such as meditation, deep breathing, or guided imagery can reduce stress and anxiety, which may interfere with sleep quality. Engaging in regular physical activity during the day can also promote better sleep quality by reducing stress levels and increasing the body’s production of hormones that support healthy sleep.
Poor sleep hygiene, on the other hand, can lead to sleep disturbances, which can negatively impact emotional regulation, increasing the risk for developing mood disorders and other psychological conditions.
To maintain healthy sleep patterns, individuals should aim to establish consistent sleep and wake times, avoid stimulants such as caffeine or nicotine near bedtime, and establish a relaxing bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and winding down before sleep.
Sleep Deprivation and Emotional Dysregulation
It’s no secret that sleep plays a vital role in our emotional and mental well-being. However, what happens when we don’t get enough sleep? The consequences of sleep deprivation are countless and dire, but one of the most significant ones is emotional dysregulation. When our bodies and brains don’t get the rest they need, it affects the way we process and handle our emotions. This article will explore the connection between sleep deprivation and emotional dysregulation, and how we can combat it for the sake of our mental and emotional health.
Sleep Hygiene and Emotional Health
Maintaining good sleep hygiene is essential for optimal emotional health. Poor sleep quality and inadequate sleep duration can lead to various emotional dysregulations such as increased negative emotions, reduced positive emotions, and decreased emotional intelligence. Here are some tips for improving sleep hygiene:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, including weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine that helps unwind before bed such as taking a warm bath or reading a book.
- Make sure the sleep environment is comfortable, quiet, dark, and cool.
- Avoid stimulating activities such as using electronic devices or watching TV before bed.
- Limit caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol intake, especially in the evening.
- Exercise regularly, but avoid strenuous exercise close to bedtime.
- Avoid large meals close to bedtime and opt for light, healthy snacks if needed.
- Address any underlying sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, insomnia, or restless leg syndrome with medical help.
Practising good sleep hygiene not only promotes high-quality sleep but also enhances emotional well-being by reducing stress, anxiety, and depression symptoms. It helps facilitate emotional processing during dream states that can contribute to personal growth and development.
Theories on The Purpose of Dreaming
Throughout history, the mystery surrounding the purpose of dreams has fascinated scientists, philosophers, and ordinary people alike. There are many theories that attempt to explain why we dream and what role dreams play in our physical, emotional, and spiritual lives. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most compelling theories on the purpose of dreaming.
The Psychoanalytic Theory: This theory, developed by Sigmund Freud, suggests that dreams are a way for our unconscious minds to express our repressed desires and impulses. According to Freud, dreams contain symbolically disguised information about our deepest desires and fears. By interpreting these symbols, we can gain a better understanding of our unconscious thoughts and emotions.
The Information Processing Theory: This theory proposes that dreams help us consolidate and process the information we’ve absorbed throughout the day. While we sleep, our brains sort through memories and experiences, discarding unimportant information and reinforcing important ones. Dreams provide a way for our brains to make sense of the vast amount of information they process every day.
The Threat Simulation Theory: This theory posits that dreams evolved as a way for our brains to practice responding to threats and dangers. During sleep, our brains simulate threatening scenarios, allowing us to practice our responses without putting ourselves in harm’s way. This theory seems to be supported by the fact that many people report having nightmares during times of stress or trauma.
There are many other theories on the purpose of dreaming, and it’s important to note that no single theory can fully explain why we dream. However, by exploring these theories, we can gain a better understanding of the many roles dreams may play in our lives.
The Psychoanalytic Theory
One of the most well-known and controversial theories on the purpose of dreaming is often attributed to Sigmund Freud and his followers. This view suggests that dreams are a reflection of our unconscious desires and anxieties that are kept hidden from our conscious mind. By analyzing dreams, individuals can gain a better understanding of their inner thoughts and motivations. However, this perspective has faced criticism and scrutiny from other researchers and fields of psychology. Regardless, the psychoanalytic theory continues to stimulate debate and curiosity surrounding the meaning behind our dreams.
The Information Processing Theory
One of the popular theories explaining the purpose of dreaming is the Information Processing Theory. This theory views dreaming as a mechanism for our brain to process and consolidate the information gathered during our waking hours. Here are some key aspects of this theory:
- The theory suggests that during our waking hours, we constantly receive sensory inputs from our environment, which we need to process and make sense of. This involves categorizing, storing, and retrieving the information required to navigate through our daily life.
- According to the Information Processing Theory, the brain processes this information in two stages – acquisition and consolidation. During acquisition, the brain collects the new information, which is then consolidated into our memory during sleep. Sleep, particularly the REM stage, plays a vital role in consolidating our memories and integrating them with our existing knowledge.
- Studies have shown that the brain is active during sleep, and the patterns of brain activity observed during sleep are similar to those seen during information processing and learning tasks during the day. This suggests that sleep, particularly the REM stage, may serve as a critical time for consolidating and integrating our newly acquired information.
- The Information Processing Theory suggests that the content of our dreams reflects the information processing that occurs during sleep. Our dreams may be a reflection of our brain’s attempt to consolidate and integrate new information with our existing knowledge, leading to creative problem-solving and the formation of new insights.
- The Information Processing Theory suggests that when we dream, our brain selectively processes and consolidates the most salient and relevant information. This serves as a filter mechanism, allowing our brain to prioritize and retain the most important information while discarding the irrelevant details.
The Information Processing Theory suggests that dreaming is a mechanism for processing and consolidating the vast amount of information that we acquire during our waking hours. Sleep, particularly the REM stage, plays a critical role in consolidating our memories and integrating them with our existing knowledge, leading to creative problem-solving and the formation of new insights.
The Threat Simulation Theory
According to the threat simulation theory, dreaming serves as a mechanism for simulating threatening events and preparing us to face these situations in waking life. This theory suggests that dreams are a sort of dress rehearsal for our minds, allowing us to practice what we would do and how we would feel in potentially dangerous scenarios.
Dreams can be an avenue to explore potential physical and emotional risks without actually experiencing them. This is why nightmares, although unpleasant, can be beneficial in terms of our emotional processing. They offer a platform for our brains to develop coping mechanisms for potential stressors we may encounter in real life.
The concept of threat simulation is further supported by the fact that during dreaming, the amygdala, which is responsible for our emotional responses, is highly active. By experiencing emotions in a controlled dream environment, we may learn to regulate them more effectively in daily life.
The threat simulation theory suggests that the scenarios depicted in our dreams do not need to be realistic or directly related to our real life experiences. Instead, our dreams could tap into our unconscious fears and anxieties, which are influenced by cultural, personal and evolutionary factors.
The potential benefits of dreaming as a way of coping with potential threats exemplify the important role that dreams play in terms of emotional processing and overall psychological functioning.
The Benefits of Paying Attention to Our Dreams
Dreams can be an incredibly powerful tool for self-discovery and emotional healing. By paying attention to our dreams and taking the time to analyze them, we can gain insight into our subconscious mind and better understand our deepest thoughts and feelings.
Better Emotional Health: Research has shown that paying attention to our dreams can lead to improved emotional health. Dream analysis can help us identify unresolved emotional conflicts and work through them in a safe and non-judgmental environment. By processing our emotions in this way, we can reduce stress and anxiety, and achieve greater emotional balance and wellbeing.
Increased Self-Awareness: Dreams also have the power to reveal aspects of ourselves that may be hidden or suppressed in our waking life. By analyzing our dreams, we can gain a deeper understanding of our inner workings, including our fears, desires, and motivations. This increased self-awareness can lead to personal growth, greater self-acceptance, and a more authentic sense of self.
Enhanced Creativity: Dreams are often a source of inspiration and creativity. By paying attention to our dreams, we can tap into our innate creativity and harness it to achieve our goals and pursue our passions. Whether it’s writing, painting, or engaging in any other creative pursuit, our dreams can provide us with a wealth of ideas and insights that we may not have access to in our waking life.
Paying attention to our dreams can be an incredibly powerful tool for personal growth and emotional healing. By taking the time to analyze our dreams, we can gain insight into our inner world and better understand ourselves on a deeper level. So next time you have a vivid dream, take a moment to reflect on it and see what it may be trying to tell you.
Better Emotional Health
It’s natural to prioritize physical health, but we should pay just as much attention to our emotional well-being. After all, our emotions affect every aspect of our lives. One way to improve our emotional health is by paying attention to our dreams. Yes, dreams! Research has shown that by analyzing our dreams, we can gain insight into our subconscious thoughts and emotions, leading to a better understanding and management of our feelings. Let’s delve deeper into the connection between our dreams and better emotional health.
Increased Self-Awareness
One of the most significant benefits of paying attention to our dreams is the increased self-awareness that comes with it. Dreams can provide us with insights into our innermost thoughts, feelings, and desires that we may not be aware of while we are awake. By exploring and understanding our dreams, we can gain a deeper understanding of ourselves and our lives.
There are many ways in which dreams can increase self-awareness, including through dream journaling, dream interpretation, and working with a therapist who specializes in dream analysis. It’s important to approach these practices with an open mind and a willingness to explore the symbols and meanings that emerge from our dreams.
Dream journaling is perhaps the most accessible and straightforward way to increase self-awareness through our dreams. It involves simply writing down our dreams as soon as we wake up, before the details fade from our memory. By reviewing our dreams over time, we may start to notice patterns, recurring themes, or unresolved conflicts that can provide valuable insight into our emotional state or current life situation.
Dream interpretation takes dream journaling a step further by attempting to decode the symbols and meanings within our dreams. This can involve consulting books on dream symbology or working with a professional dream analyst who can help us understand what our dreams may be telling us about ourselves. Interpretation is a highly personal process and may require experimentation and learning to trust our intuition.
Finally, working with a therapist who specializes in dream analysis can be a powerful way to gain insight into our inner world. Therapists trained in dream analysis can help us explore the symbols and feelings in our dreams and connect them to our waking lives. In therapy, we can learn to integrate what we learn from our dreams into our daily lives, helping us grow in self-awareness and build a stronger connection to ourselves.
Increased self-awareness through dreams can be a powerful force for personal growth and deeper understanding of ourselves. By paying attention to our dreams and exploring their meanings, we can gain valuable insight into our thoughts, feelings, and desires, leading to a more fulfilling and aligned life.
Enhanced Creativity
One of the most exciting benefits of paying attention to our dreams is the potential for enhanced creativity. Dreams have long been a source of inspiration for artists, writers, and musicians alike. However, it is not just artists who can benefit from this creativity boost. Everyone has some level of creativity in them, and tapping into the unconscious mind through dreams can fuel inspiration and generate new ideas.
1. Unique Imagery: Dreams are known for their surreal and often bizarre imagery. When we pay attention to our dreams, we can utilize this imagery as a source of inspiration. The visual scenes in dreams can be used to create beautiful artwork or unique stories.
2. Fresh Perspectives: Dreams can also provide us with fresh perspectives on problems we might be struggling with in our waking lives. By analyzing the symbolism in our dreams, we can often find creative solutions to challenges we face.
3. Emotional Expression: Dreams can provide a space for emotional expression that might be difficult to express in waking life. This emotional outlet can lead to artistic expression, whether it be through poetry, music or visual arts.
4. Lucid Dreaming: Lucid dreaming, or the ability to control and manipulate our dreams, can also lead to enhanced creativity. By actively participating in the dream, we can direct its outcome and create new scenarios or explore new ideas.
Paying attention to our dreams can greatly enhance our creativity and provide us with a unique perspective on the world. By tapping into the unconscious mind, we can unlock new ideas and generate inspiration for artistic endeavors or problem-solving in our waking life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between dreams and emotional processing is a complex and fascinating topic that has intrigued scientists and psychologists for decades. Through the different stages of sleep, our brains process and consolidate emotional information that we have encountered during the day. Dreams help us to make sense of this emotional information and integrate it into our conscious awareness.
By paying attention to our dreams and utilizing techniques such as dream interpretation, lucid dreaming, and journaling, we can gain insights into our emotional states and work through unresolved issues. This can lead to better emotional health and increased self-awareness.
Furthermore, the theories on the purpose of dreaming continue to evolve and shed light on the various ways in which dreams serve important functions in our daily lives. Whether it is through the psychoanalytic theory, the information processing theory, or the threat simulation theory, dreams are seen as vital mechanisms that help us to regulate our emotions and cope with stressful situations.
It is important to remember that sleep plays a crucial role in our emotional regulation. Lack of sleep or poor sleep hygiene can lead to emotional dysregulation, so it is essential to prioritize good sleep habits in order to maintain optimal emotional health.
In summary, by paying attention to our dreams and understanding the role they play in our emotional processing, we can lead happier, healthier, and more fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between dreams and emotional processing?
Dreams play a significant role in emotional processing as they help us process and regulate our emotions while we sleep.
How does the brain function during dreaming?
During dreaming, the brain undergoes various stages of neural activity; in NREM sleep, the brain is in a state of low activity, while it is highly active in REM sleep.
Why do we have bad dreams?
Bad dreams can occur due to unresolved issues or psychological disorders that we may have thus affecting our emotional processing while we sleep.
How can interpreting dreams help with emotional regulation?
Interpreting dreams can help individuals identify and process deep-seated emotions that may be difficult to explore while awake.
What is lucid dreaming and how can it aid emotional processing?
Lucid dreaming is the state in which an individual is aware that they are dreaming. It can aid emotional processing by allowing individuals to address and resolve emotions that may be causing distress.
What is sleep deprivation, and how does it affect emotional regulation?
Sleep deprivation is the state of not getting enough sleep. It can lead to emotional dysregulation and can amplify negative emotions.
How does maintaining proper sleep hygiene contribute to emotional health?
Practicing good sleep hygiene habits can lead to better-quality sleep, which can aid in emotional regulation and overall emotional health.
What is the psychoanalytic theory of dreaming?
The psychoanalytic theory of dreaming states that dreams are a reflection of repressed desires and wishes and are therefore crucial to understanding an individual’s subconscious.
What is the information processing theory of dreaming?
The information processing theory hypothesizes that dreams are a way for the brain to process and organize information gathered while awake.
What are some benefits of paying attention to our dreams?
Paying attention to our dreams can lead to better emotional health, increased self-awareness, and enhanced creativity.








