As we drift off to sleep each night, our minds embark on a journey beyond the physical world. Dreams have fascinated humans since the earliest civilizations, and understanding the science and function of dreams has been a profound challenge. One aspect of this mystery is the complex relationship between nightmares and REM sleep. The experience of waking up from a nightmare can leave us feeling disoriented, anxious, and even terrified. But what is the cause of these frightening dreams, and what impact do they have on our physical and emotional wellbeing? In this article, we’ll explore the effects of nightmares on REM sleep and dream cycles, the science behind what causes nightmares, and the emotional, physical, and cognitive consequences of experiencing these unsettling dreams.
Nightmares and REM Sleep: A Complex Relationship
As humans, we spend roughly one-third of our lives sleeping. But what happens during that time remains a mystery to many of us. Sleep is not just a time of rest for our bodies, but it’s also an opportunity for our brains to recharge and process the events of our waking lives. One of the most interesting phenomena that happens during sleep is the concept of REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and its connection to nightmares.
What Is REM Sleep?
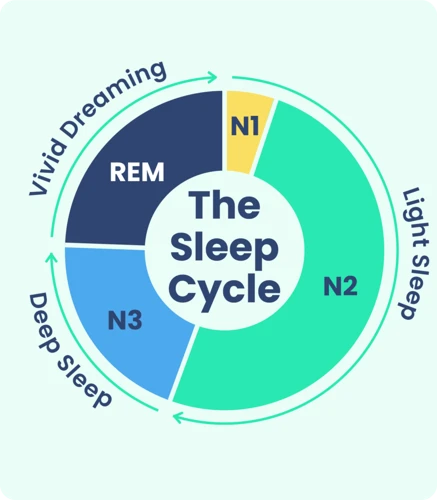
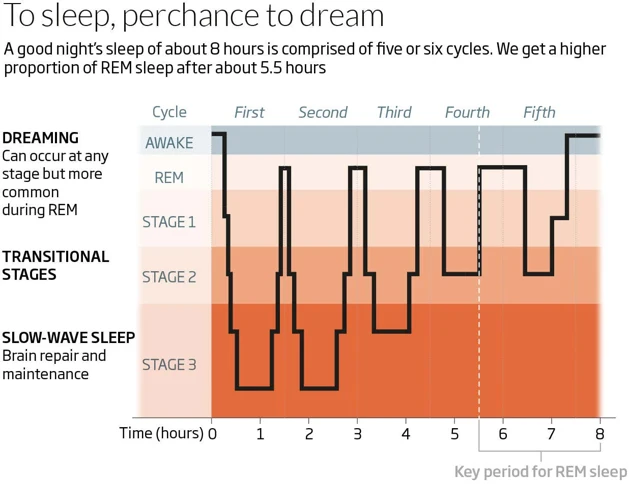
REM sleep is characterized by the rapid and random movement of the eyes, and it accounts for about 25% of the time we spend sleeping. During this phase, the brain is highly active, and our breathing and heart rate may quicken. It’s also during this time that we are most likely to dream, as our brains are actively processing and consolidating memories. Dreams during REM sleep tend to be more vivid and intense than those that occur during non-REM sleep.
The Stages of Sleep
There are four stages of sleep, and they cycle throughout the night. The first three stages are non-REM sleep, which is a period of deep sleep where brain activity slows down, and the body experiences periods of complete relaxation. The fourth stage is REM sleep, and it’s during this stage that the brain is highly active, and our breathing and heart rate can become irregular.
Nightmares and REM Sleep
Nightmares are vivid, highly distressing dreams that occur during REM sleep. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including anxiety, stress, and trauma. It’s not entirely clear why nightmares occur during REM sleep, but it’s thought to be related to the brain’s heightened activity during this stage.
The Role of Anxiety and Fear in Nightmares
Anxiety and fear appear to play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. Research has found that people who report higher levels of anxiety and stress are more likely to experience nightmares. Additionally, individuals who have experienced trauma, such as those with PTSD, are more likely to have nightmares.
The Physical Response to Nightmares
Nightmares can lead to physical responses, such as elevated heart rate and sweating. These physical reactions can cause the individual to wake up and disrupt their sleep cycle. This can lead to a feeling of exhaustion and fatigue during the day.
How Nightmares Affect Dream Cycles
Nightmares can affect our dream cycles by disrupting the natural progression from non-REM sleep to REM sleep. If a nightmare causes an individual to wake up during REM sleep, it can disrupt the dreaming process and result in a feeling of unrest during the day.
Why We Need REM Sleep and Dreams
REM sleep and dreams are essential for our physical and mental well-being. REM sleep is thought to be important for memory consolidation and learning, while dreams allow us to process and make sense of our experiences. Without REM sleep and dreams, individuals may experience cognitive and emotional difficulties.
What Is REM Sleep?
During sleep, the brain goes through different stages that play a crucial role in our physical and mental wellbeing. One of these stages is characterized by rapid eye movement (REM) and is known as the REM stage. This stage is associated with heightened brain activity, changes in heart rate and breathing, and, most notably, vivid dreaming. REM sleep is a critical component of a healthy sleep cycle, and disruptions to this stage can lead to a range of health problems. But what exactly is REM sleep, and why is it so important? In this section, we will dive deeper into the science of REM sleep and explore its many functions.
The Stages of Sleep
During a typical night’s sleep, our bodies cycle through several stages of sleep, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. These stages are generally divided into two categories: non-REM sleep and REM sleep.
Non-REM sleep includes the first three stages of sleep and is characterized by gradually deepening levels of relaxation and decreasing levels of brain activity.
- Stage 1: This is the lightest stage of sleep, lasting for only a few minutes. During this stage, our breathing and heart rate slow down, and we may experience twitching or jerking muscles.
- Stage 2: This stage lasts for the majority of our sleep cycle and is characterized by a further drop in heart and breathing rates, as well as a decrease in body temperature. Brain waves become slower with occasional bursts of rapid waves (known as sleep spindles).
- Stage 3: Also known as deep sleep, this stage is characterized by slow brain waves and is the most restorative stage of sleep. Our muscles are relaxed, and our breathing and heart rate are at their lowest. It is also during this stage that our bodies release growth hormones and repair muscle tissue.
REM sleep is the fourth and final stage of sleep and is characterized by a rapid movement of the eyes (hence the name, Rapid Eye Movement). This stage is where we experience the most vivid and memorable dreams. During REM sleep, our brain activity is similar to that of when we are awake, and our heart rate and breathing are irregular. REM sleep is believed to be important for learning, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation.
The stages of sleep are crucial for our physical and mental wellbeing. Each stage serves a distinct purpose in repairing and refreshing our bodies and minds, and an interruption in any of these stages can have negative consequences on our health.
Nightmares and REM Sleep
During the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, our bodies become paralyzed while our brain activity increases, resulting in dreaming. Nightmares are a type of dream that can occur during REM sleep and can often leave a lasting impression on the dreamer.
Nightmares and REM Sleep
Studies have found that nightmares are more likely to occur during the latter half of the sleep cycle, during which the period of REM sleep is longer. This suggests that there is a correlation between REM sleep and the occurrence of nightmares. Researchers have also discovered that people who experience more nightmares tend to have shorter periods of REM sleep, as if their bodies are trying to avoid the occurrence of distressing dreams.
Nightmares tend to occur more frequently among people who experience sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome, which can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to more frequent awakenings during the night. This can result in a greater proportion of REM sleep, making the occurrence of nightmares more likely.
The Role of Anxiety and Fear in Nightmares
Nightmares often involve fearful or anxious themes, such as being chased or attacked, falling, or experiencing the loss of a loved one. It is believed that these themes reflect the individual’s emotional state and may be a result of unresolved psychological issues, stress, or trauma.
The Physical Response to Nightmares
During a nightmare, the body may respond with physical symptoms such as sweating, increased heart rate, and rapid breathing. The body may also release stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can lead to feelings of anxiety and fear even after waking up from the dream.
How Nightmares Affect Dream Cycles
Nightmares can interrupt the normal cycle of REM sleep and affect the overall quality of sleep. This can lead to feelings of fatigue and difficulty concentrating during the day. Additionally, frequent nightmares can lead to sleep anxiety and further disrupt the sleep cycle, creating a cycle of poor sleep quality and more frequent nightmares.
Why We Need REM Sleep and Dreams
REM sleep and dreams are important for cognitive and emotional processing. During REM sleep, the brain consolidates memories and processes emotional experiences, helping us to make sense of our thoughts and feelings. Without enough REM sleep and dreaming, individuals may experience difficulties with memory and emotional regulation.
The Role of Anxiety and Fear in Nightmares
Nightmares are often caused by a number of factors, with anxiety and fear being two of the most significant triggers. The intense emotions of fear and anxiety can work together to create strong negative feelings that can be carried into our dreams. These feelings can be intensified by stressful events that occur in our day-to-day lives, making it more likely that we experience nightmares when we finally fall asleep. In this section, we will explore the complex relationship between anxiety and fear and how they play a role in the occurrence of nightmares during REM sleep.
The Physical Response to Nightmares
Nightmares can evoke a range of physical responses from the body, which can be quite distressing for the individual experiencing them. Some of the physical responses to nightmares include:
- Rapid Heart Rate: During a nightmare, the body may suddenly increase its heart rate, which can be felt as palpitations or a pounding sensation in the chest.
- Increased Breathing: When the body becomes anxious or fearful during a nightmare, it may also increase its respiratory rate, making it difficult to breathe calmly.
- Sweating: Sweating can be a common physical response to nightmares, especially those that cause extreme anxiety or fear.
- Muscle Tension: Nightmares can cause the body to tense up, which can lead to muscle pain or stiffness in the neck, shoulders, or other parts of the body.
- Trembling: Trembling or shaking can also occur as a physiological response to nightmares, particularly if they involve situations that evoke intense feelings of fear or anxiety.
- Disrupted Sleep: Additionally, nightmares can disrupt sleep quality, causing the individual to wake up feeling tired, groggy, and irritable.
These physical responses to nightmares can vary in intensity and duration, depending on the severity of the nightmare and the emotional state of the individual experiencing it. As a result, it’s important to recognize the impact that nightmares can have on both mental and physical wellbeing and seek appropriate support to address them.
How Nightmares Affect Dream Cycles
As we sleep, our brains go through a series of cycles that allow us to rest and rejuvenate. One of the most important of these cycles is the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) cycle. During REM, our brains are active and engaged, and we experience vivid dreams. Although nightmares are a common occurrence during sleep, many people don’t realize that they can have a significant impact on our REM cycles and the quality of our dreams. In this section, we will explore the ways in which nightmares affect our dream cycles and what this means for our overall well-being.
Why We Need REM Sleep and Dreams
REM sleep, also known as rapid eye movement sleep, is a vital part of our sleep cycle. During REM sleep, our brain is highly active and we experience vivid dreams. It is important for our overall well-being that we get enough REM sleep each night, as it plays a crucial role in various functions of our body and mind.
Here are some reasons why we need REM sleep and dreams:
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| Memory consolidation | During REM sleep, our brain processes and consolidates memories from the day before, helping us to retain new information and skills. |
| Mood regulation | REM sleep is linked to the regulation of emotions, and lack of REM sleep can contribute to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. |
| Creativity and problem-solving | Dreams that occur during REM sleep can help to stimulate creativity and provide solutions to problems we may be facing. |
| Physical restoration | During REM sleep, our body goes into a state of paralysis, allowing for the restoration and repair of our physical systems. |
| Brain development | REM sleep is particularly important for brain development in infants and children, as it aids in the formation of neural connections and is crucial for learning and cognitive development. |
| Overall health | Getting enough REM sleep and dreaming is essential for our overall health and well-being, as it helps to boost our immune system, regulate our metabolism, and protect against various health problems. |
As you can see, REM sleep and dreams are crucial for our mental, emotional, and physical health. It is important to prioritize getting enough sleep each night in order to ensure that we are able to reap the many benefits of REM sleep and dreaming.
The Science of Nightmares
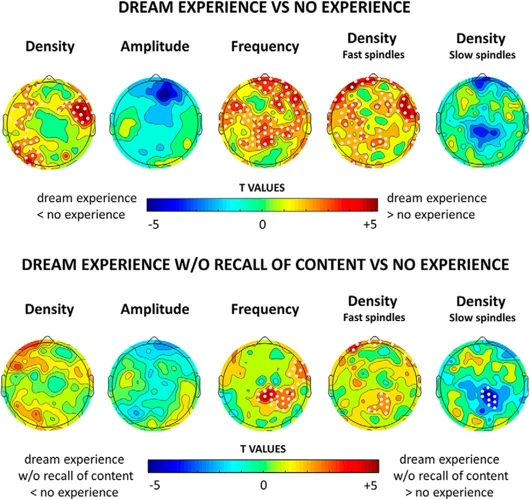
Nightmares are intense and disturbing dreams that can leave a person feeling anxious, frightened, and disoriented. Researchers have been studying the causes and effects of nightmares for many years, but the science behind this phenomenon is still not fully understood.
Causes of Nightmares
Nightmares can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, trauma, and certain medications. They may also be linked to certain sleep disorders or medical conditions, such as sleep apnea, depression, or anxiety. Studies have shown that nightmares are more common in individuals who have experienced some form of trauma or abuse.
PTSD and Nightmares
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop in people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. Individuals with PTSD often experience intense and recurring nightmares related to their trauma. These nightmares can be so severe that they interfere with the individual’s ability to function in their daily life.
Nightmares and Other Mental Health Disorders
Nightmares have been linked to other mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression. Individuals with these conditions may experience more frequent and intense nightmares, which can exacerbate their symptoms and contribute to a vicious cycle of poor mental health.
Can Nightmares Be Prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent nightmares, there are certain steps individuals can take to reduce their risk. These may include developing a consistent bedtime routine, reducing stress and anxiety before bed, and avoiding certain medications or substances that can disrupt sleep.
Treatment Options for Nightmares
For individuals who experience frequent or severe nightmares, there are several treatment options available. These may include cognitive-behavioral therapy, talk therapy, medication, or some combination of these approaches. The goal of treatment is to help the individual processing their trauma or anxiety in order to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
The science of nightmares is complex and multifaceted. While researchers have identified certain risk factors and treatment options, more research is needed to fully understand the causes and effects of this phenomenon. For individuals who experience frequent nightmares, it is important to seek treatment to address any underlying issues and improve overall sleep and mental health.
Causes of Nightmares
Nightmares can be a perplexing and unsettling experience for many people. They can leave us feeling disturbed and frightened, and often cause us to wake up with a sense of unease. While nightmares can have various causes, both psychological and physiological, they have been studied extensively by scientists in order to better understand how and why they occur. In this section of the article, we will explore some of the different factors that can contribute to nightmares, as well as some of the research that has been done on this topic. So, let’s take a closer look at the complex and mysterious world of nightmares.
PTSD and Nightmares
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after someone experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. People with PTSD often experience intrusive symptoms that can include nightmares. Nightmares related to PTSD can be incredibly vivid and disturbing, and they often feature themes related to the original traumatic event.
PTSD nightmares can:
- cause intense fear and anxiety
- lead to poor sleep
- cause a person to avoid sleep
- trigger flashbacks or other symptoms of PTSD during waking hours
Research has shown that people with PTSD nightmares tend to experience longer REM sleep periods compared to those without PTSD. This prolonged REM sleep may be a manifestation of the brain’s attempts to process and consolidate traumatic memories.
Unfortunately, the presence of nightmares can also make the symptoms of PTSD worse. The fear and anxiety experienced during nightmares can trigger other symptoms of PTSD even when a person is awake, making it difficult to relax or feel safe.
Treatment for PTSD nightmares often involves:
- addressing the underlying trauma through therapy
- using medications such as prazosin or trazodone to reduce nightmares and improve sleep quality
- learning coping skills for managing the anxiety and fear triggered by nightmares
It’s important for people with PTSD to seek appropriate care for their nightmares and other symptoms. With treatment, it is possible to reduce the impact of PTSD and improve quality of life.
Nightmares and Other Mental Health Disorders
Nightmares are often associated with other mental health disorders, such as anxiety, depression, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). According to researchers, individuals with these disorders are more likely to experience nightmares as they often have a higher level of emotional distress.
Table:
| Mental Health Disorder | Likelihood of Nightmares |
|---|---|
| Anxiety | High |
| Depression | High |
| PTSD | Very High |
Individuals with PTSD are especially vulnerable to nightmares, with up to 80% of those diagnosed with PTSD experiencing vivid, recurrent nightmares. These nightmares often involve the traumatic event that led to the disorder and can be distressing to the point of disrupting normal sleep patterns.
Research also indicates that individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Schizophrenia may experience more nightmares than the general population. One study found that 60% of individuals with BPD reported nightmares, and another study found that people with Schizophrenia experienced more bizarre and terrifying dreams than those without the disorder.
It’s important to note that nightmares do not necessarily indicate the presence of a mental health disorder. However, frequent and distressing nightmares may be a warning sign of an underlying issue and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Can Nightmares Be Prevented?
One of the biggest questions for those who experience frequent nightmares is whether or not they can be prevented. While the idea of never having a nightmare again may seem too good to be true, there are some strategies that have been shown to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Here, we explore some potential methods for preventing nightmares and easing the emotional toll they can take.
Treatment Options for Nightmares
When it comes to treating nightmares, there are a variety of options available. Here are some of the most common treatment options:
- Counseling or therapy: Talking to a mental health professional can help address the underlying causes of your nightmares. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or exposure therapy may be recommended to help reduce anxiety and fear associated with the content of your nightmares.
- Medication: Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed to reduce the occurrence and severity of nightmares, particularly for those with PTSD or other mental health disorders.
- Relaxation techniques: Engaging in relaxation exercises such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help reduce stress and anxiety, which in turn may lead to fewer nightmares.
- Improving sleep habits: Practicing good sleep hygiene, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can help improve the quality of your sleep and reduce the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
- Hypnosis: Some people find that hypnosis can be effective in reducing the occurrence of nightmares. During hypnotherapy sessions, a trained professional guides you into a state of deep relaxation and can help you reframe negative thoughts and emotions that may be contributing to your nightmares.
It is important to note that treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause of your nightmares and the severity of your symptoms. It is always recommended to talk to a medical or mental health professional to determine the best course of action for your individual needs.
The Impact of Nightmares on Our Lives
Nightmares can have a significant impact on various aspects of our lives. The emotional toll of frequent nightmares can be overwhelming, leading to feelings of fear, anxiety, and depression. These negative emotions can spill over into our waking lives, making it difficult to concentrate on daily tasks and interfering with our ability to form and maintain relationships.
Frequent nightmares can also contribute to the development of sleep disorders, such as insomnia. People who experience nightmares on a regular basis may become fearful of falling asleep, causing them to avoid sleep altogether. This can lead to severe sleep deprivation and other physical health problems such as headaches, high blood pressure, and even heart disease.
There is often a strong link between nightmares and daytime anxiety. After experiencing a nightmare, people may feel anxious and on edge throughout the day, making it difficult for them to function. This can negatively impact their work and personal relationships, as well as their ability to enjoy leisure activities.
In addition to their emotional and mental impacts, nightmares can also have physical consequences. Studies have shown that people who experience frequent nightmares are more likely to experience chronic pain, fatigue, and other physical health problems. This is likely due to the fact that nightmares can disrupt the body’s natural sleep cycles, preventing the body from getting the restorative sleep it needs to repair and recharge.
Dealing with frequent nightmares can be challenging, but there are steps that people can take to reduce their frequency and impact. These include practicing good sleep hygiene, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine. Additionally, therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy have been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
By taking proactive steps to address their nightmares, people can reduce their negative impact on their lives and improve their overall sense of well-being.
The Emotional Toll of Frequent Nightmares
For those who suffer from frequent nightmares, the emotional toll can be overwhelming. The constant fear and anxiety can lead to a sense of helplessness and desperation, affecting not only their sleep, but their waking hours as well. The impact of nightmares can be felt both mentally and physically, leaving individuals feeling drained and on edge. Coping with the aftermath of a nightmare can be a challenge, and knowing how to manage these emotions is vital to maintaining a healthy and happy life. Let’s explore the various ways that frequent nightmares can impact our emotions and how we can learn to deal with them.
Nightmares and Sleep Disorders
Nightmares can have a significant impact on our sleep patterns and overall well-being. In some cases, they can even be a symptom of an underlying sleep disorder. Let’s take a closer look at the relationship between nightmares and sleep disorders:
| Sleep Disorder | Characteristics | Connection to Nightmares |
| — | — | — |
| Sleep Apnea | Breathing interruption during sleep | May cause sleep disturbances and increase the likelihood of nightmares |
| Insomnia | Difficulty falling and/or staying asleep | Lack of sleep can increase the occurrence of nightmares |
| Restless Leg Syndrome | Uncontrollable urge to move legs while sleeping | Disrupts sleep and may increase incidence of nightmares |
| Narcolepsy | Excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden bouts of sleep | Can cause disruptions in REM sleep, leading to vivid dreams and nightmares |
| REM Sleep Behavior Disorder | Physical movement during REM sleep | Can cause vivid nightmares and increase the likelihood of acting out dreams |
As you can see, there are several sleep disorders that can either directly or indirectly contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. It’s important to address and manage any underlying sleep disorders in order to reduce the frequency of nightmares and improve overall sleep quality.
Disclaimer: This table is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. If you suspect you may have a sleep disorder, please consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Relationship between Nightmares and Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that can be caused by various factors, one of them being nightmares. When people experience frequent nightmares, they often develop insomnia as a result. This is because when they wake up from a nightmare, they may find it difficult to fall back asleep. They may also experience anxiety or fear that prevents them from fully relaxing and falling into a deep sleep.
Insomnia caused by nightmares can have a serious impact on a person’s daily life. It can lead to daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and mood swings. Over time, this can lead to other mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
There are several ways to treat insomnia caused by nightmares. One of the most effective ways is to address the underlying cause of the nightmares. This may involve working with a therapist to identify and address any underlying psychological issues that may be contributing to the nightmares.
Another approach is to use relaxation techniques to help reduce anxiety and promote restful sleep. This can include deep breathing exercises, meditation, or muscle relaxation techniques.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to help manage insomnia caused by nightmares. This may involve taking prescription medication such as benzodiazepines or antidepressants. However, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider when using medication to manage insomnia, as there can be side effects and potential interactions with other medications.
Managing insomnia caused by nightmares can be challenging, but there are effective treatment options available. By addressing the underlying cause of the nightmares and using relaxation techniques or medication as needed, individuals can reduce the impact that nightmares have on their sleep and daily life.
The Connection between Nightmares and Daytime Anxiety
Have you ever woken up from a nightmare only to still feel anxious and uneasy hours later in your waking life? Many people experience this unsettling phenomenon, known as daytime anxiety. This feeling can make it difficult to concentrate on work, school, and other daily activities. But what is the connection between nightmares and daytime anxiety? How do frequent nightmares contribute to these persistent feelings of apprehension and stress? Let’s delve into the research to better understand this puzzling relationship.
Nightmares and Physical Health
Nightmares not only affect our mental health but also have an impact on our physical health. Research has found that experiencing frequent nightmares can lead to a range of physical health issues such as an increased risk of heart disease, obesity, and even diabetes. Here are some ways how nightmares can affect our physical health:
- Disruption of sleep: Nightmares can cause disruptions in our sleep patterns and prevent us from getting the recommended amount of sleep that our bodies need. This can lead to fatigue, tiredness, and a lack of energy throughout the day.
- Increase in stress: Nightmares can also lead to an increase in stress levels, releasing stress hormones like cortisol into our bodies. This can lead to increased blood pressure, which in turn can lead to a range of health problems including heart disease.
- Increased risk of obesity: Lack of sleep has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, and nightmares can prevent us from getting the quality sleep that our bodies need to function properly.
- Compromised immune system: The stress caused by nightmares can weaken our immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
- Development of diabetes: Chronic stress caused by nightmares can lead to an increased risk of developing diabetes, particularly in those who have a family history of the condition.
It’s important to take nightmares seriously and seek help if they’re impacting your physical health. There are various treatments available, including therapy, medications, and healthy sleep hygiene practices that can help manage and reduce the frequency of nightmares.
Dealing with Nightmares
Nightmares can be an incredibly distressing experience for anyone who suffers from them. However, there are ways to manage them and minimize their impact on our lives.
What to Do When You Have a Nightmare: If you wake up in the middle of a nightmare, take a few deep breaths and try to calm down. Remind yourself that it was only a dream and that you are safe. Avoid getting out of bed or turning on bright lights, as this can disrupt your sleep and make it harder to fall back asleep. Instead, try to relax and calm yourself until you feel ready to go back to sleep.
Tips for Reducing Nightmares: There are several strategies that can help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. One of the most effective is a technique called “image rehearsal therapy.” This involves rewriting the nightmare script in your mind and visualizing a more positive outcome. Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can also help reduce stress and anxiety, which can contribute to nightmares. Additionally, avoiding alcohol, drugs, and caffeine can help improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
How to Take Control of Your Dreams: Lucid dreaming is a technique that involves becoming aware that you are dreaming and taking control of the narrative. This can be a powerful tool for those who suffer from nightmares, as it allows them to change the course of the dream and create a more positive outcome. There are several techniques to induce lucid dreaming, such as reality testing, keeping a dream journal, and practicing visualization before bed.
While nightmares can be a challenging experience to deal with, there are several options available for managing and reducing their impact. Whether through relaxation techniques, image rehearsal therapy, or lucid dreaming, taking proactive steps to deal with nightmares is key to improving our overall mental and physical health.
What to Do When You Have a Nightmare
Experiencing a nightmare can be a terrifying and unsettling experience. Whether it’s a one-time occurrence or a frequent problem, knowing how to respond can make all the difference in minimizing the impact on your mental and physical health. It’s important to remember that nightmares are a normal part of the sleep cycle and can be caused by a variety of factors. However, there are various strategies and actions you can take to reduce the likelihood of having nightmares and manage them when they do occur. In this section, we’ll explore some effective techniques for dealing with nightmares and promoting restful, peaceful sleep.
Tips for Reducing Nightmares
If you are someone who suffers from nightmares, you know how distressing and disruptive they can be to your sleep and daily life. Here are some tips for reducing nightmares:
- Develop a relaxing bedtime routine: Incorporate activities such as reading, meditation, or taking a warm bath into your bedtime routine to help your mind and body relax before sleep.
- Avoid consuming certain foods and drinks: Some foods and drinks, such as caffeine, alcohol, and heavy or spicy meals, can increase the likelihood of nightmares. Avoid these before bed.
- Reduce stress during the day: Find healthy ways to manage stress during the day, such as through exercise, therapy, or mindfulness techniques. This can help improve the quality of your sleep and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
- Practice lucid dreaming: Lucid dreaming is the ability to become aware that you are dreaming while you are in the dream. This can help you take control and turn a scary dream into a more positive experience.
- Consider therapy: If you are experiencing nightmares as a symptom of a mental health disorder such as PTSD, seeking therapy can help address the underlying issue and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
- Avoid watching or reading scary material before bed: Exposing yourself to scary movies, books, or TV shows before bed can increase the likelihood of nightmares. Choose more calming or positive material instead.
- Create a comforting sleeping environment: Make sure your sleeping environment is comfortable, cool, and dark. Use relaxing scents such as lavender, and consider using a noise machine to drown out any disturbing sounds.
By incorporating these tips into your routine, you may be able to reduce the frequency and intensity of your nightmares, and improve the quality of your sleep.
How to Take Control of Your Dreams
One technique for taking control of your dreams is called lucid dreaming. This involves becoming aware that you are dreaming and taking control of the dream. Here are a few tips on how to achieve lucid dreaming:
- Keep a dream journal: Keeping a journal can help you identify common themes or patterns in your dreams. This can help you recognize when you are dreaming.
- Reality checks: Throughout the day, ask yourself if you are dreaming. Look around and ask if what you are seeing is real. This habit will eventually carry over into your dreams.
- Set intentions before sleep: Tell yourself before bed that you will become aware during your dreams and take control.
- Visualize: Picture yourself becoming aware in your dreams and taking control. This can help set the intention in your subconscious mind.
Once you become aware that you are dreaming, there are different techniques to take control. Here are a few:
- Interact with your environment: If you are in a dream and recognize that you are dreaming, try interacting with the environment. This can include touching objects, talking to dream characters, and even flying.
- Create a dream plan: Before going to bed, choose a scenario that you would like to experience in your dream. This can help guide the dream and give you more control.
- Repeat affirmations: In your dream, repeat a phrase that affirms your control. This can help solidify the fact that you are in control of the dream.
Remember, lucid dreaming takes practice and patience. But once you master it, it can be a rewarding and empowering experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between nightmares and REM sleep is complex and multifaceted. While nightmares can disrupt the normal pattern of sleep cycles, they also serve an important function in allowing us to process and integrate emotionally charged information. However, frequent and intense nightmares can have a detrimental impact on our emotional and physical health.
It is important to understand the science of nightmares and explore potential causes and treatment options, particularly for those who suffer from PTSD or other mental health disorders. Seeking professional help may be necessary in some cases.
For those looking to reduce their risk of experiencing nightmares, practicing good sleep hygiene and managing stress and anxiety levels can be helpful. It is also important to take steps to address any underlying mental health issues and seek support from friends, family, or therapists.
Overall, while nightmares can be unsettling and disruptive, they are a normal and necessary part of the sleep and dreaming process. By understanding the science behind them and taking steps to mitigate their impact, we can work towards achieving a more restful and peaceful night’s sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a nightmare and a bad dream?
A nightmare is a type of bad dream that is often more vivid, intense, and disturbing than a typical bad dream. Nightmares are also more likely to wake you up and leave you feeling anxious or fearful.
Can nightmares affect the quality of my sleep?
Yes, nightmares can disrupt your sleep cycle and lead to poor quality sleep, which can have a negative impact on your mental and physical health over time.
Can medication be used to treat nightmares?
Yes, some medications such as antidepressants and beta-blockers have been shown to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. However, medication should only be considered after other treatment options have been explored.
Can lucid dreaming help prevent nightmares?
Yes, practicing lucid dreaming techniques can help you take control of your dreams and overcome the fear and anxiety that often contribute to nightmares.
Is it possible to have a nightmare during non-REM sleep?
No, nightmares typically occur during REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is a stage of sleep where the brain is more active and dreaming is more likely to occur.
What should I do if I have frequent nightmares?
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider if you are experiencing frequent nightmares, particularly if they are interfering with your daily life. Your healthcare provider can help you identify potential underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments.
Can trauma be a cause of recurring nightmares?
Yes, trauma is a known trigger for recurring nightmares, particularly in individuals with PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder).
Can certain foods or drinks trigger nightmares?
Yes, certain foods and drinks such as high-fat meals, alcohol, and caffeine have been linked to an increase in nightmares in some individuals.
Can changes in sleep patterns cause nightmares?
Yes, disruptions to your regular sleep schedule, such as jet lag or shift work, can increase the likelihood of nightmares.
Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are common in both children and adults, but are more common in children. Up to 50% of children between the ages of 3 and 6 experience nightmares, whereas only around 5% of adults report having frequent nightmares.








