As we lay in bed at night, our brain goes through different phases of activity that are essential for a good night’s rest. Despite being in a state of rest, our brain keeps working and producing different types of brain waves that have their own unique characteristics and functions. Understanding these brain waves is crucial for developing healthy sleep habits and improving the quality of our sleep. In this article, we will explore the four different types of brain waves that activate during sleep and their importance in achieving a restorative and restful sleep.
Understanding Brain Waves During Sleep
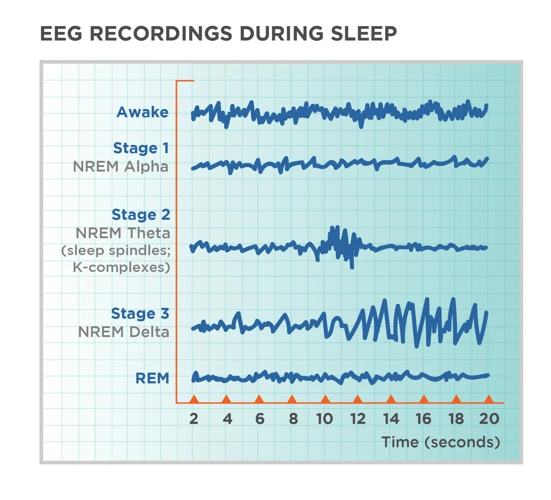
As we lay in bed each night, our brains continue to work, producing a series of brain waves that are associated with different stages of sleep. These brain waves are incredibly important for our overall health and well-being. Through the study of these brain waves, we can better understand the mechanisms behind sleep and develop strategies to improve the quality of our rest. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of brain waves during sleep and explore the different types of waves that occur.
Brain Waves and Sleep Stages
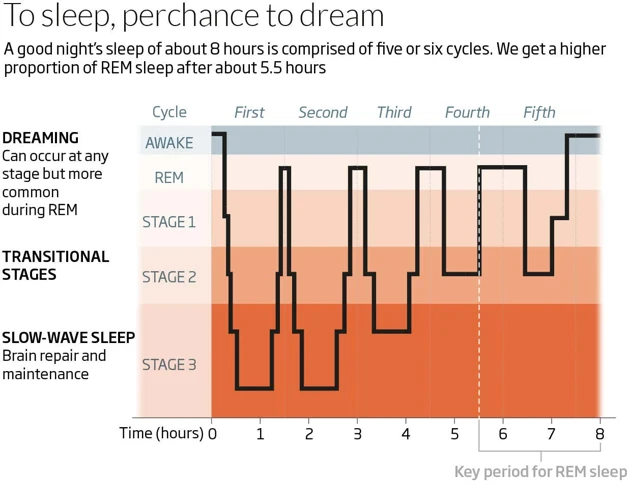
Sleep is a complex process that is characterized by distinct stages. These stages are defined by the patterns of brain waves that occur during sleep. There are four distinct types of brain waves that are present during sleep, each associated with a different stage of sleep.
The four types of sleep stages are as follows:
- Stage 1: This is the transitional stage between wakefulness and sleep. During this stage, theta waves are prominent as the body begins to relax and the brain activity begins to slow down.
- Stage 2: During this stage, the brain produces sudden bursts of rapid brainwave activity known as sleep spindles. Along with the sleep spindles, there are also K complexes which are sudden, high-amplitude waves that have been linked with memory consolidation.
- Stage 3: This is the stage when delta waves begin to occur. Delta waves are the slowest of all waves and occur in deep sleep.
- Stage 4: This stage is sometimes referred to as delta sleep or slow wave sleep. During this stage, delta waves are prominent, and the body is at its deepest level of relaxation.
It’s essential to understand the different types of brain waves present during sleep as they play a crucial role in the quality and restorative nature of sleep. As we move through the different stages of sleep, our brain waves change in frequency, and the different waves have different functions for our body and mind.
The Four Types of Brain Waves
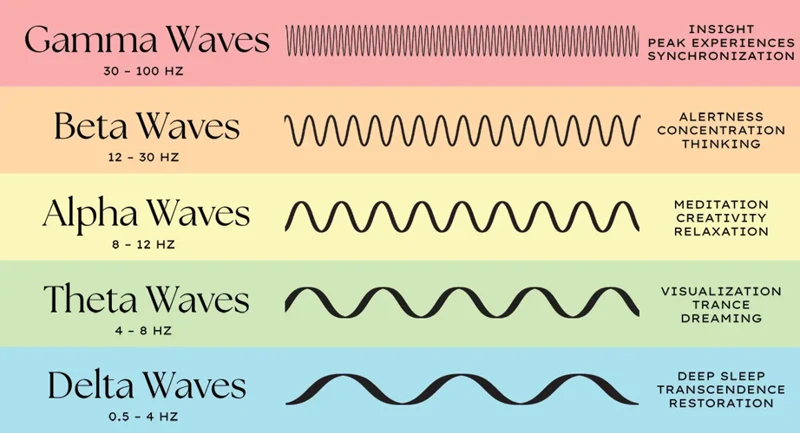
During sleep, our brain waves go through four main types. These brain waves are Delta, Theta, Alpha and Beta. The different types of brain waves are characterized by their frequency and amplitude. Here is a detailed description of each brain wave:
- Delta Waves: Delta waves have the lowest frequency and highest amplitude of all the brain waves. They typically occur during deep sleep and are associated with restorative sleep. Delta waves are important for physical and emotional renewal, as well as for the body’s natural healing processes.
- Theta Waves: Theta waves have the frequency range of 4-7 Hz and a moderate amplitude. They usually occur during light sleep and occur more frequently during deep meditation or hypnosis. Theta waves are associated with the dream state and have been linked to memory consolidation and learning.
- Alpha Waves: Alpha waves are in the frequency range of 8-12 Hz and are usually associated with a state of relaxation when the eyes are closed but not sleeping deeply. These waves can be used to induce a relaxed and peaceful state of mind, and they can also help to reduce anxiety and stress levels.
- Beta Waves: Beta waves have the highest frequency and lowest amplitude of all the brain waves. They occur during times of strong mental activity and are associated with a state of wakefulness and alertness. Beta waves are also present during periods of anxiety or stress and can make it difficult to fall asleep.
Understanding the four types of brain waves during sleep is crucial for optimizing our sleep patterns and improving our overall health and well-being. By recognizing the different types of brain waves, we can take steps to improve the quality of our sleep and achieve a greater sense of physical and mental rejuvenation.
Delta Waves
Delta waves are the slowest and the largest brain waves that occur during sleep. They have a frequency of less than 4Hz and a high amplitude. These waves are most commonly observed during the deep sleep stage, also known as slow-wave sleep. During this stage, the brain is in a state of deep relaxation and is much less responsive to external stimuli.
Synthesis: Delta waves – slowest and largest brain waves during sleep. Frequency is less than 4Hz, high amplitude. Occur during deep sleep stage, also known as slow-wave sleep. Brain is in state of deep relaxation and less responsive to external stimuli.
Delta waves are generated in the thalamus and neocortex in response to inhibitory signals from the reticular activating system (RAS). These waves play a critical role in promoting restorative sleep, which is essential for physical and mental recovery. They are associated with the release of growth hormone, which is critical for tissue repair and growth.
Synthesis: Delta waves generated in thalamus and neocortex in response to inhibitory signals from RAS. Play critical role in promoting restorative sleep, essential for physical and mental recovery. Associated with release of growth hormone, critical for tissue repair and growth.
Disruptions in delta waves have been associated with various sleep disorders, such as insomnia and sleep apnea. These disorders can result in decreased amounts of delta activity, leading to a reduction in restorative sleep.
Synthesis: Disruptions in delta waves associated with sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnea. Can result in decreased amounts of delta activity, leading to reduction in restorative sleep.
Improving delta wave activity can be beneficial for individuals who suffer from sleep disorders. This can be achieved through the use of relaxation techniques, sleep hygiene, exercise, and a healthy diet. These approaches can promote restorative sleep and allow the brain to recover and rejuvenate during the night.
Synthesis: Improving delta wave activity beneficial for individuals with sleep disorders. Achieved through relaxation techniques, sleep hygiene, exercise, and a healthy diet. Promotes restorative sleep and allows brain to recover and rejuvenate during the night.
Theta Waves
During a deeper stage of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, theta waves become more prominent. These brain waves have a frequency of around 4-7 Hz and are characterized by their slower frequency compared to alpha waves. Theta waves are generally associated with Stage 2 sleep and may also occur during brief periods of REM sleep.
Theta waves are important for memory consolidation and spatial navigation. Research has shown that the hippocampus, a brain region associated with memory and navigation, exhibits high levels of theta activity during sleep. This suggests that theta waves play a crucial role in transferring memories from short-term to long-term storage.
Additionally, theta waves are often associated with creativity and heightened intuition. Artists, musicians, and writers have been found to have increased theta activity in their brains during creative periods.
The following table provides a summary of the characteristics of theta waves during sleep:
| Frequency Range | 4-7 Hz |
|---|---|
| Associated Sleep Stage | Stage 2 NREM sleep, brief periods of REM sleep |
| Main Functions | Memory consolidation, spatial navigation, creativity, intuition |
| Brain Region | Hippocampus |
Theta waves are an important aspect of healthy sleep and play a crucial role in memory consolidation and creativity. Boosting theta activity through practices like meditation or mindfulness may have positive effects on cognitive function and overall wellbeing.
Alpha Waves
During sleep, alpha waves occur mostly during the transitional period between wakefulness and sleep, as well as during light sleep. These brain waves have an oscillation frequency of 8 to 12 Hz.
Alpha waves are associated with a relaxed state of mind and the inhibition of certain areas of the brain. They are often observed during meditation, daydreaming, and other states of relaxation.
The table below provides some key information about alpha waves:
| Wave Frequency | 8-12 Hz |
|---|---|
| Wave Amplitude | Small |
| When They Occur | Transitional period between wakefulness and sleep, during light sleep |
| Associated with | Relaxation, meditation, daydreaming |
| Benefits | Inhibits certain areas of the brain, promotes a relaxed state of mind |
Alpha waves play an important role in helping the brain transition from wakefulness to sleep. They promote a relaxed state of mind, which can help reduce anxiety and stress. Additionally, they may help improve cognitive function, including memory and attention.
If you want to improve your alpha waves during sleep, there are several things you can do. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, can help promote alpha waves. Additionally, good sleep hygiene, regular exercise, and a healthy diet can all contribute to healthy alpha wave activity during sleep.
Beta Waves
Beta waves are the fastest brain waves that occur during our waking hours. They are typically associated with heightened alertness and active thinking. When our mind is engaged in complex mental activities like solving problems, planning or decision-making, beta waves are dominant. These waves range from 12 Hz to 38 Hz and are produced by the neocortex, the outer layer of the brain which deals with conscious thinking and perception.
During sleep, the presence of beta waves is very minimal. However, in the REM stage of sleep, when we experience the most vivid dreams, beta waves do appear. This makes us believe that beta waves might play a role in our dreaming processes.
According to research, beta waves may also play a role in symptoms of anxiety and insomnia. People with anxiety and insomnia tend to have an overabundance of beta waves in specific regions of the brain. This overactivity might lead to increased rumination and inability to relax.
While beta waves are important for our daily activities, too much of them can lead to restlessness and anxiousness. It’s important to find ways to calm down the beta waves when necessary and allow other types of brain waves to take over.
To reduce the amount of beta waves in your mind, try incorporating mindfulness meditation to your daily routine. This will help you quiet your mind and get rid of the overactivity. Engaging in calming activities like spending time in nature, yoga or tai chi can also help reduce beta waves. Additionally, getting into a regular sleep pattern and practicing good sleep hygiene can help you avoid overthinking before bed and promote relaxation.
The Importance of Different Brain Waves During Sleep
When we fall asleep, our brain doesn’t simply shut off. In fact, it continues to be active, producing distinctive patterns of electrical activity that we know as brain waves. These brain waves are characterized by their frequency and amplitude, and each type of wave is associated with a different stage of sleep. Understanding the importance of different brain waves during sleep is crucial in order to comprehend why getting enough restorative sleep is so essential to our physical and mental health. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of these brain waves and how they impact our sleep quality.
Delta Waves and Restorative Sleep
During sleep, the brain goes through different stages, and each stage is characterized by specific brain wave patterns. One of the most prominent brain waves during deep, restorative sleep is Delta Waves. These slow and large brain waves have a frequency of fewer than four cycles per second and typically occur during the deepest stage of sleep, known as stage 3 or slow-wave sleep.
Delta waves are crucial for our physical and mental well-being. The body goes into a state of repair and rejuvenation during deep sleep, and Delta Waves play a significant role in this process. They facilitate the release of human growth hormone, which is essential for repairing tissues and promoting cell growth.
The Delta Waves promote the production of cytokines, which are essential for fighting inflammation and infection. These cytokines also enhance the immune response, which is necessary for preventing diseases.
Without adequate Delta Waves during sleep, the body’s restorative functions will be compromised, leading to a host of health issues, including chronic fatigue, weak immune system, and impaired cognitive function.
To ensure you get enough Delta Waves during sleep, you need to have a sufficient amount of deep, restorative sleep. This can be achieved by following good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a dark, quiet, and cool sleeping environment, sticking to regular bedtime and wake-up times, avoiding electronic devices before sleep, and reducing caffeine and alcohol intake.
Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or listening to relaxing music, can also help induce deep sleep and enhance Delta Wave production. Lastly, regular exercise and a healthy diet can optimize the quality of sleep, leading to a better, more restorative sleep, and ultimately, better overall health.
Theta Waves and Memory Consolidation
Theta waves are one of the four types of brain waves that occur during sleep. They typically have a frequency of 4-8 Hz and are associated with the early stages of sleep. Theta waves are also present during deep relaxation and meditation.
Research has found that theta waves are particularly important for memory consolidation. During sleep, the brain processes and consolidates memories from the day. Theta waves have been found to be especially active during this process, which helps to explain why a good night’s sleep is so important for memory retention.
Memory consolidation involves two main processes:
- Encoding: The process of converting information into a form that can be stored in the brain.
- Consolidation: The process of strengthening and stabilizing memories over time.
Theta waves are thought to play a key role in the consolidation process. Studies have shown that theta waves are especially active during REM sleep, which is the stage of sleep associated with vivid dreams. During this stage, the brain replays memories and consolidates them into long-term storage.
Researchers also believe that theta waves may help to integrate new memories with existing knowledge, which is known as schema consolidation. This process helps to make new information more meaningful and easier to remember in the future.
The importance of theta waves for memory consolidation highlights the importance of getting enough sleep each night. Without adequate sleep, it can be more difficult for the brain to process and consolidate memories, which can lead to forgetfulness and difficulty learning new information.
Alpha Waves and Relaxation
During sleep, the brain produces four different types of brain waves , and alpha waves are one of them. These are the slowest waves, with a frequency of 8-12 Hz and high amplitude. They usually occur when we are in a state of relaxation but still awake, such as during meditation, daydreaming, or just before sleep.
Alpha waves are commonly associated with a calm and relaxed mental state. When these waves are present, the mind is often free of distractions and stress, allowing for a peaceful and meditative state. These waves can be a powerful tool for stress reduction, as they promote relaxation and improve mental clarity.
Scientists have also found that alpha waves are linked to enhanced creativity and focus, making them an ideal state for artists, writers, and other creative professionals. Additionally, alpha waves are also believed to boost the immune system and improve overall well-being.
There are several ways to increase the presence of alpha waves during sleep. One effective method is through meditation or deep breathing exercises before bedtime. This can help calm the mind and promote an alpha state during the sleep cycle.
Another way to increase alpha waves is by practicing good sleep hygiene. This includes creating a relaxing environment in the bedroom, avoiding stimulating activities before bed, and maintaining a regular sleep schedule.
Exercise, particularly yoga and other calming forms of physical activity, can also help increase alpha waves in the brain. Finally, a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and protein can also support healthy alpha wave production during sleep.
Incorporating these practices into your daily routine can help promote the presence of alpha waves during the sleep cycle, increasing relaxation, creativity, and overall well-being.
Beta Waves and Dreaming
During the REM stage of sleep, the brain experiences **rapid and irregular** beta waves. These Beta waves are the same waves that are produced when we’re awake and alert, and they are typically linked with **high levels of mental activity**. The presence of beta waves during the REM stage has been linked to dreaming, which is one of the key characteristics of this stage of sleep.
**Dreaming** is a complex and fascinating mental process, and scientists have been studying it for centuries. While the exact purpose of dreaming remains a mystery, research suggests that it may play an important role in **memory consolidation**, **emotional processing**, and **problem-solving**.
During the REM stage, the brain’s activity is similar to that of someone who is awake, which can help explain the vivid and sometimes **bizarre** nature of our dreams. Beta waves during this stage are a sign that the brain is in a highly active and creative state, which can lead to both positive and negative dream experiences.
It’s important to note that beta waves during sleep are not limited to the REM stage. In fact, they can be present during any stage of sleep and are often the result of external stimuli, such as noise or light. This is why it’s important to create a comfortable and peaceful sleep environment, free from distractions, in order to promote good sleep health.
The presence of beta waves during REM sleep is a sign of high mental activity, which can be both beneficial and disruptive to our sleep experience. While we may not fully understand the purpose of dreaming, it is clear that our brain waves play a crucial role in this fascinating and mysterious process.
|Characteristics| Beta Waves|
|—————|———–|
|Activity level |High|
|Linked with |High levels of mental activity|
|Present during |REM stage and any stage of sleep|
|Result of |External stimuli such as noise and light|
|Impacts |Dreaming and can lead to vivid and sometimes bizarre dream experiences|
How to Improve Your Brain Waves During Sleep
As we have learned throughout this article, the various types of brain waves play an essential role in ensuring we get the most restorative and beneficial sleep possible. Improving our brain waves during sleep, therefore, can have a significant impact on our overall health and well-being. In this section, we’ll explore some practical strategies and techniques you can use to optimize your brain waves during sleep and wake up feeling more refreshed and rejuvenated every morning. So, let’s dive in and discover how you can take your sleep quality to the next level.
Relaxation Techniques
One way to improve your brain waves during sleep is to practice relaxation techniques. Here are a few techniques that you can try:
- Meditation: Meditation is a practice that involves focusing your attention on a particular object or activity, such as your breath or a mantra. Studies have shown that meditation can help reduce stress and improve sleep quality.
- Yoga: Yoga incorporates physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. It has been found to be effective in reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Deep breathing: Deep breathing involves taking slow, deep breaths in and out. This technique can help you relax and calm your mind before bed.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: This technique involves tensing and then relaxing each muscle group in your body, starting from your toes and working your way up to your head. It can help reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation.
These relaxation techniques can help you calm your mind and reduce stress, which can improve the quality of your sleep. Incorporating them into your bedtime routine can help you fall asleep faster and sleep more soundly throughout the night.
Sleep Hygiene
A crucial factor that can affect your brain waves during sleep is your sleep hygiene, which refers to the habits and practices that can impact the quality of your sleep. Having poor sleep hygiene can lead to disrupted sleep, resulting in an imbalance in your brain waves. Here are some tips to improve your sleep hygiene and promote healthy brain waves:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Stick to a consistent sleep schedule | Establishing a regular bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends, can help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. |
| Create a relaxing sleep environment | Ensure that your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet, and remove any distractions like electronic devices. |
| Avoid caffeine and nicotine | Both caffeine and nicotine are stimulants and can keep you awake, so it’s best to avoid consuming them in the hours leading up to bedtime. |
| Avoid large meals and drinks before bed | Eating a heavy meal or drinking a lot of fluids close to bedtime can interrupt your sleep by causing indigestion or frequent trips to the bathroom. |
| Limit daytime naps | While napping can be helpful, especially for those who don’t get enough sleep at night, it’s best to limit napping to no more than 30 minutes and avoid napping late in the day. |
| Establish a relaxing wind-down routine | Engage in calming activities, such as reading or taking a bath, before bed to help your body and mind wind down. |
| Limit exposure to electronics before bed | The blue light emitted by electronic devices can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep, so it’s best to avoid using them for at least an hour before going to bed. |
By implementing these tips, you can improve your sleep hygiene and promote healthy brain waves during sleep.
Exercise
Regular exercise has been shown to have numerous benefits for our physical and mental health. When it comes to improving brain waves during sleep, exercise can be particularly helpful. It has been found that physical activity and fitness can positively influence the amount and quality of delta and theta waves during sleep.
Physical activity helps to reduce stress levels in the body, which can lead to a more relaxed state of mind and better quality sleep. It also stimulates the production of endorphins, which are known to improve mood and reduce anxiety. This can lead to a more relaxed state of mind before bed, which can help promote the production of delta and theta waves.
To see the benefits of exercise on brain waves during sleep, it is important to exercise regularly and consistently. This can be as simple as taking a walk or engaging in light activities such as yoga and stretching. However, for more significant improvements, more intense activities such as running, cycling, and resistance training may be necessary.
It is important to note that exercise should be done in the morning or early afternoon, as exercising too close to bedtime can actually interfere with sleep. It is also important to avoid intense exercise before bed, as this can cause the body to produce beta waves, which can have the opposite effect of what we want during sleep.
Here is an example table of recommended exercises:
| Activity | Intensity Level | Time of Day |
|---|---|---|
| Walking | Low | Morning or Midday |
| Yoga | Low | Morning or Midday |
| Cycling | Medium | Morning or Midday |
| Running | High | Morning or Midday |
| Resistance Training | High | Morning or Midday |
Remember, regular exercise is just one way to improve brain waves during sleep, and it should be done in combination with other techniques such as relaxation and good sleep hygiene. With a little effort and dedication, you can improve the quality and quantity of delta and theta waves during sleep, leading to better overall health and well-being.
Healthy Diet
One of the key components of improving your brain waves during sleep is maintaining a healthy diet. This means consuming a range of nutrient-dense foods that support brain health and function. Here are some specific dietary recommendations for optimizing your brain waves during sleep:
| Food Group | Examples |
|---|---|
| Complex Carbohydrates | Whole grains, sweet potatoes, legumes |
| Healthy Fats | Avocados, nuts, seeds, fatty fish |
| Lean Proteins | Chicken, turkey, fish, tofu |
| Fruits and Vegetables | Leafy greens, berries, citrus fruits, colorful veggies |
| Herbs and Spices | Turmeric, ginger, garlic, cinnamon, rosemary |
Complex carbohydrates, like whole grains and legumes, provide a steady source of glucose, which is the brain’s main energy source. Healthy fats, like those found in avocados and fatty fish, improve cognitive function and support brain health. Lean proteins, like chicken and tofu, contain amino acids that are the building blocks of neurotransmitters, which are essential for communication between brain cells. Fruits and vegetables contain important vitamins and phytonutrients that support overall brain function. Herbs and spices, such as turmeric and cinnamon, have anti-inflammatory properties that can protect against neurodegenerative diseases.
It’s also important to reduce your intake of processed foods, refined sugars, and saturated fats, as these can be detrimental to brain health. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help optimize brain function during sleep.
By incorporating these dietary recommendations into your lifestyle, you can support and optimize your brain waves during sleep.
Conclusion
After delving into the intricate world of brain waves during sleep, it’s clear that each type of wave serves a specific purpose in the restorative process. Delta waves help us reach the deepest stage of sleep and allow our body to repair and renew itself. Theta waves play a key role in consolidating memories and facts that we’ve learned throughout the day. Alpha waves promote relaxation and tranquility, while beta waves are associated with dreaming.
Improving the quality of our sleep is essential in maintaining our overall wellbeing. By employing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, we can train our brain to naturally shift into deeper sleep states. It’s also important to establish a consistent sleep schedule and optimize our sleep environment with proper lighting and comfortable bedding.
Regular exercise and a healthy diet can also significantly impact the quality of our sleep and help promote the development of healthy brain wave patterns. And while technology can certainly be beneficial, it’s essential to limit exposure to blue light emitting electronic devices before bedtime.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of brain waves during sleep is crucial in optimizing our restorative process. By implementing healthy sleep hygiene practices and prioritizing a good night’s sleep, we can improve the quality of our brain waves, enhance our overall cognitive function, and enhance our overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are brain waves?
Brain waves are patterns of electrical activity that occur in the brain and can be measured using EEG.
What are the four types of brain waves?
The four types of brain waves are delta, theta, alpha, and beta waves.
What is delta sleep?
Delta sleep is the deepest stage of sleep where the brain shows delta wave activity.
What is theta sleep?
Theta sleep is the stage of sleep where the brain shows theta wave activity and is associated with light sleep and dreaming.
What is alpha sleep?
Alpha sleep is the stage of sleep where the brain shows alpha wave activity and is associated with relaxation and meditation.
What is beta sleep?
Beta sleep is a stage of sleep where the brain shows beta wave activity and is associated with active thinking, problem solving, and dreaming.
What is the importance of delta waves during sleep?
Delta waves during sleep are important for restorative sleep and physical recovery.
What is the importance of theta waves during sleep?
Theta waves during sleep are important for memory consolidation and learning.
What is the importance of alpha waves during sleep?
Alpha waves during sleep are important for relaxation and stress reduction.
What is the importance of beta waves during sleep?
Beta waves during sleep are important for active thinking and problem solving.
How can I improve my brain waves during sleep?
You can improve your brain waves during sleep by practicing relaxation techniques, maintaining good sleep hygiene, exercising regularly, and following a healthy diet.