Introduction
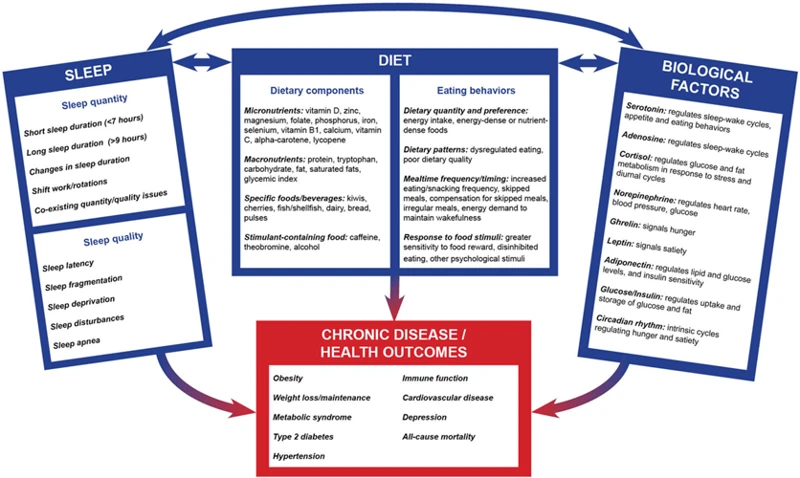
Many of us have experienced the frustration of tossing and turning in bed, unable to fall asleep. Lack of sleep not only leaves us feeling groggy and unmotivated the next day, but it can also take a toll on our physical and mental health in the long term. While there are many factors that can affect the quality of our sleep, one that is often overlooked is our eating habits. Yes, what we eat and when we eat it can actually impact how well we sleep at night. In this article, we’ll explore the connection between eating habits and sleep, and provide tips on how to improve both for a better, more restful night’s sleep.
The Importance of Good Sleep
One of the most essential components of a healthy lifestyle is good sleep. Sleep is a period when your body regenerates and recovers from the stresses of the day, both physically and mentally.
According to the National Sleep Foundation, adults should aim for seven to nine hours of sleep each night. However, modern lifestyles often prioritize work, socializing, and other activities over sleep. Chronic sleep deprivation can have a detrimental impact on your health and well-being, leading to issues like weight gain, weakened immune system, and even an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Sleep quality is equally important as sleep quantity. Even if you’re getting the recommended amount of sleep each night, you won’t feel rested and restored if you experience frequent interruptions, wake up feeling groggy, or have trouble falling asleep. Poor sleep quality can disrupt your focus, mood, and even lead to depression.
It’s crucial to prioritize your sleep habits and take steps to ensure you’re getting the best quality sleep possible. Directly or indirectly, good sleep affects every aspect of your health and well-being, from productivity and mood to appetite and energy levels.
| Benefits of Good Sleep | Consequences of Poor Sleep |
|---|---|
|
|
The Connection Between Eating Habits and Sleep

Have you ever wondered why some nights you struggle to fall asleep, while other nights you doze off as soon as your head hits the pillow? The answer may actually lie in your eating habits. Studies have shown a strong connection between what we eat and the quality of our sleep. It’s not just about what we consume, but also when we consume it. The timing and quality of our meals can impact our sleep patterns and even affect the intensity of our dreams. In this section, we’ll explore the intricate relationship between eating habits and sleep, so you can start making changes to improve your restful nights.
How Eating Before Bedtime Affects Your Sleep
It’s common knowledge that consuming a large meal too close to bedtime can have negative effects on sleep quality. But, just how does eating before bedtime impact your sleep? Let’s take a closer look.
The Effects of Eating Before Bedtime on Sleep Quality
Studies have suggested that eating a large meal before bed can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep disturbances. This occurs because the digestive system is still hard at work breaking down the food, which can lead to discomfort, bloating, and heartburn. These physical sensations can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night.
Impact on REM Sleep
Additionally, eating before bedtime can have a negative impact on REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is commonly known as “deep sleep”. This stage of sleep is essential for the body’s restoration and healing, as well as for dreaming. Consuming a large meal too close to bedtime can disrupt the natural sleep cycle, reducing the amount of time spent in REM sleep and leaving individuals feeling groggy and tired upon waking.
The Role of Food Selection
It’s not just the timing of when you eat, but what you eat that can impact your sleep quality. Consuming foods high in fat, sugar, or caffeine prior to bedtime can lead to increased energy levels, making it more difficult to fall asleep. Similarly, alcohol consumption can impact the quality of sleep, reducing the amount of time spent in restorative REM sleep.
To summarize, eating before bedtime can have negative impacts on sleep quality, disrupting the natural sleep cycle and reducing REM sleep. It’s best to avoid consuming large meals or foods high in fat, sugar, or caffeine before bedtime. Instead, opt for lighter meals and snacks and allow sufficient time for digestion before heading to bed.
The Effects of Diet Quality on Sleep
The quality of our diet plays a crucial role in determining the quality of our sleep. A poor diet can cause various sleep disturbances including insomnia and sleep apnea. In contrast, a healthy and well-balanced diet can help promote better sleep. The following table highlights the effects of different nutrients on sleep quality:
| Nutrient | Effects on Sleep Quality |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | May improve sleep quality by increasing the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate sleep. However, consuming too many refined carbohydrates like sugar can disrupt sleep by spiking blood sugar levels. |
| Protein | Can promote sleep by increasing the production of tryptophan, an amino acid that is needed for the synthesis of serotonin. However, consuming large amounts of protein before bed may cause digestive discomfort, which can interfere with sleep. |
| Fat | High-fat diets have been shown to disrupt sleep by increasing the chances of sleep apnea and other breathing problems. However, consuming healthy fats like omega-3 fatty acids may help promote better sleep by reducing inflammation in the body. |
| Minerals | Minerals like magnesium and potassium are essential for proper sleep and muscle relaxation. Deficiencies in these minerals can lead to sleep disturbances and insomnia. |
| Vitamins | Vitamins like B6 and B12 are necessary for the synthesis of neurotransmitters like serotonin and melatonin, which are important for regulating sleep. Deficiencies in these vitamins can lead to poor sleep quality and insomnia. |
To summarize, a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of healthy carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals can help promote better sleep quality. However, it’s important to avoid consuming large amounts of any one type of nutrient before bed, as this can cause digestive discomfort and disrupt sleep.
What to Eat for Better Sleep Quality

Are you struggling with getting a good night’s sleep? One factor that may be impacting your quality of sleep is your diet. Eating the right foods can actually help promote better sleep quality, while eating the wrong foods can make it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep. So what should you be eating for better sleep? Let’s take a closer look at some foods that can promote a better night’s rest and some foods to avoid.
Foods That Promote Sleep
There are several foods that can promote better sleep quality when consumed regularly. These foods work by stimulating the production of sleep hormones, reducing stress, and promoting relaxation. Below is a table outlining some of the best foods for promoting better sleep:
| Food | Why it Promotes Sleep |
|---|---|
| Turkey | Contains tryptophan, an amino acid that helps increase the production of serotonin and melatonin, hormones that promote relaxation and sleep. |
| Cherries | Contains melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles and promotes better sleep quality. |
| Almonds | Contain magnesium, a mineral that can help reduce stress and promote better sleep quality. They also contain tryptophan, which can help increase the production of sleep hormones. |
| Jasmine Rice | Has a high glycemic index, which means it can help promote the production of sleep hormones like serotonin and melatonin. It can also help reduce the amount of time it takes to fall asleep. |
| Warm Milk | Contains tryptophan, which can help increase the production of sleep hormones. It can also promote relaxation and reduce stress levels. |
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help improve your sleep quality and promote better overall health. However, it’s important to note that simply eating these foods is not a guarantee of better sleep. It’s also important to establish good sleep habits and maintain a regular sleep schedule to maximize the benefits of these sleep-promoting foods.
Foods to Avoid Before Bedtime
The foods you choose to eat before bedtime can significantly impact your quality of sleep. Consuming certain types of foods close to bedtime can lead to more restlessness and even disrupt your sleep altogether. Here are some examples of foods to avoid before bedtime:
| Food | Reasons to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Caffeine | Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you alert and awake. Avoid consuming coffee, tea, chocolate, and other caffeinated beverages and foods in the evening. |
| Alcohol | While alcohol may initially make you feel sleepy, it can disrupt your sleep during the night. Avoid drinking alcohol before bedtime, especially in large quantities. |
| Spicy Foods | Spicy foods can cause heartburn and indigestion, which can make it difficult to fall and stay asleep. |
| High-Fat Foods | High-fat foods require more digestion and can lead to discomfort and indigestion. Avoid consuming fatty foods before bedtime, as it can cause heartburn and disrupt your sleep. |
| Sugary Foods | Avoid consuming sugary foods before bedtime, as they can spike your blood sugar levels and disrupt your sleep. Opt for foods that are high in protein or complex carbohydrates instead. |
By avoiding these foods before bedtime, you can promote better sleep quality and improve your overall health and well-being.
The Role of Meal Timing and Frequency
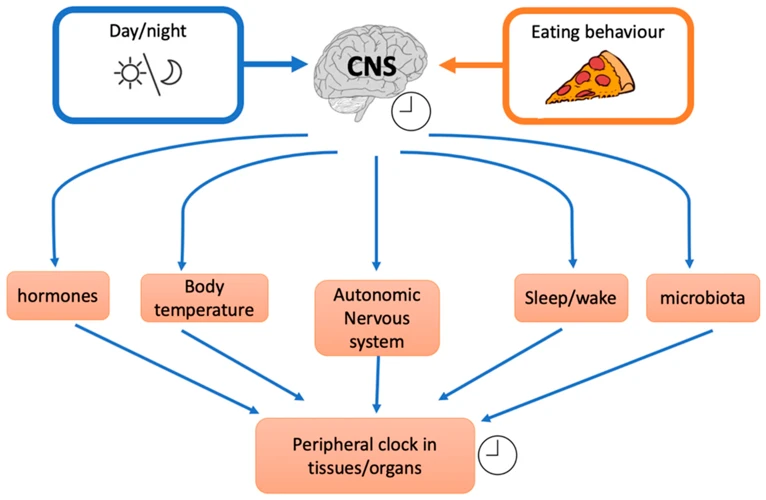
One of the most overlooked factors that affect our sleep quality is the timing and frequency of our meals. Are you baffled by the idea that your meal schedule could play a significant role in your sleep patterns? Well, the truth is that meal timing and frequency can affect not only the quantity but also the quality of our sleep. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at how meal timing can influence our sleep and the benefits of establishing a regular meal frequency.
How Meal Timing Affects Sleep Quality
The timing of our meals can have a significant impact on our sleep quality. Eating large and heavy meals close to bedtime can cause discomfort and indigestion, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Our body’s internal clock also plays a role in how our meals are metabolized. This clock, also known as the circadian rhythm, regulates many physiological processes, including sleep and digestion. Eating meals at irregular times can disrupt this clock and negatively affect our sleep quality.
According to research, Eating meals too close to bedtime can lead to an increase in body temperature, which can interfere with our natural sleep cycle. Additionally, consuming caffeine or alcohol late in the evening can also disrupt sleep by stimulating the brain and causing nighttime awakenings.
On the other hand, eating a lighter meal and finishing dinner earlier in the evening can improve our sleep quality. This allows time for our body to properly digest the food before going to bed, which can reduce discomfort and indigestion.
One study found that eating a meal high in carbohydrates a few hours before bed can actually improve sleep quality by increasing the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleep.
Our meal timing can have a significant impact on our sleep quality. To improve sleep, it’s important to eat a lighter dinner earlier in the evening, avoid meals too close to bedtime, and limit consumption of caffeine and alcohol before sleep.
The Benefits of Establishing a Regular Meal Frequency
Eating meals at a consistent time each day has numerous benefits for obtaining better sleep quality. Establishing a regular meal frequency helps regulate your body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, which in turn impacts your sleep-wake cycle.
Here are some specific benefits of establishing a regular meal frequency:
- Improved digestion: Eating meals at consistent times each day helps your body develop a routine for digesting food more efficiently. This can lead to less indigestion and discomfort, allowing you to fall asleep more easily.
- Regulated blood sugar: Regular meal times can help keep your blood sugar levels stable throughout the day, which can prevent energy crashes and fluctuations in insulin levels that can disrupt sleep.
- Increased satiety: Eating regular meals can help regulate hunger hormones, which can prevent overeating and nighttime snacking. Consuming larger meals at consistent times can also help you feel more satisfied and full, reducing the likelihood of waking up hungry in the middle of the night.
- Better sleep quality: Establishing a regular meal frequency can lead to more consistent and deeper sleep, as your body and brain become accustomed to a routine. This can also allow you to wake up feeling more rested and alert.
So, if you’re looking to improve your sleep quality, consider establishing a consistent meal schedule. By doing so, you’ll not only regulate your circadian rhythm, but you’ll also reap the benefits of improved digestion, regulated blood sugar, increased satiety, and better sleep quality.
Tips to Improve Your Eating Habits and Sleep Quality
So, you’ve learned about the impact of eating habits on your sleep and how your diet can affect the quality of your rest. Now, it’s time to put that knowledge into action and improve your eating habits to promote better sleep. In this part, we’ll provide you with some practical tips that can help you achieve this goal. By implementing these strategies, you can optimize your diet for healthier sleep and wake up feeling more refreshed and energized. So, let’s dive in and explore these tips together.
Keep a Food and Sleep Diary
One effective way to improve your eating habits and sleep quality is to keep a food and sleep diary. This may seem like an arduous task at first, but it can provide valuable insights into how your diet and sleep patterns are affecting each other.
How to Keep a Food and Sleep Diary
Keeping a food and sleep diary is relatively simple. All you need is a notepad or an app on your phone where you can record what you eat and when you sleep. Here is a table to help you get started:
| Date | Food and Drink Intake | Bedtime | Wake-Up Time | Quality of Sleep |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Breakfast: Oatmeal, banana, almond milk Lunch: Chicken salad, whole grain bread Dinner: Grilled salmon, brown rice, steamed vegetables Snack: Apple, peanut butter |
11:00 PM | 7:00 AM | Restless, woke up several times |
| Day 2 | Breakfast: Greek yogurt, blueberries, granola Lunch: Turkey sandwich, carrot sticks Dinner: Veggie stir-fry with tofu, quinoa Snack: Popcorn |
10:30 PM | 6:30 AM | Sound, uninterrupted sleep |
Make sure to record everything you consume, including snacks, drinks, and supplements. You should also note the time you go to bed, the time you wake up, and the quality of your sleep.
What to Look for in Your Food and Sleep Diary
After a week or two of keeping a food and sleep diary, review your entries and look for patterns. Do you notice any correlations between certain foods or beverages and your sleep quality? Do you tend to sleep better on days when you eat a balanced and varied diet?
Perhaps you will also notice that certain foods or drinks are causing you discomfort or interfering with your sleep. For instance, if you have a cup of coffee after dinner, you may find it harder to fall asleep at night. By identifying these correlations, you can make informed decisions about what to eat and drink and when to consume them.
Keeping a food and sleep diary can be a powerful tool in improving your eating habits and sleep quality. It helps you identify patterns and make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle. Take some time to track your habits, and you may be surprised at the insights you gain.
Eat a Balanced and Varied Diet
It’s important to maintain a balanced and varied diet in order to improve your sleep quality. A balanced diet means including foods from all major food groups, such as proteins, carbohydrates, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Eating a varied diet means including a wide range of different foods within each food group.
Proteins are essential for muscle repair and cellular growth, but consuming too much protein can be disruptive to sleep. Aim for a moderate intake of lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and legumes.
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy and can also promote the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that can help regulate sleep. Choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Fruits and vegetables are packed with vitamins and minerals that help promote overall health and wellbeing. Choose a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to ensure a wide range of nutrients.
Healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish are essential for brain function and hormone production. However, consumption of large amounts of fatty foods right before bedtime can cause discomfort and disrupt sleep.
It’s also important to pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating. Consuming too much food right before bedtime can lead to discomfort and indigestion, which can disrupt sleep.
Consider using the following table as a guide for balancing your diet:
| Food group | Examples |
|—————-|——————————————————|
| Proteins | Chicken, fish, beans, legumes, tofu, nuts |
| Carbohydrates | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables |
| Fruits & veggies| Berries, leafy greens, citrus fruits, carrots, peas |
| Healthy fats | Avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish |
Aim to incorporate a variety of foods from each food group in your diet to ensure a balanced and varied approach.
Avoid Stimulants Before Bedtime
If you want to improve your sleep quality, it’s important to avoid consuming stimulants before bedtime. Stimulants are substances that increase alertness, making it difficult to relax and fall asleep. Here are some common stimulants that you should avoid:
- Caffeine: Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant found in coffee, tea, chocolate, and many soft drinks. It can take hours before caffeine is completely metabolized, so it’s best to avoid it at least 4-6 hours before bedtime.
- Nicotine: Nicotine is a stimulant found in tobacco products. Smoking or using other tobacco products before bedtime can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
- Alcohol: While alcohol is a sedative, it can also disrupt your sleep. It can cause you to wake up frequently during the night and can lead to a decrease in sleep quality.
- Sugar: Sugary foods and drinks can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, which can interfere with your sleep. It’s best to avoid sugary snacks and desserts before bedtime.
If you want to avoid these stimulants, try to reduce your consumption of coffee, tea, and soft drinks throughout the day. You can also try to avoid smoking or using tobacco products altogether. If you do drink alcohol, try to limit your intake and avoid drinking before bedtime. Instead of sugary snacks, try to choose healthy snacks like fruits or nuts. By avoiding these stimulants before bedtime, you can improve your sleep quality and wake up feeling refreshed and energized.
Establish a Regular Meal and Sleep Schedule
One of the most basic yet effective ways to improve your eating habits and sleep quality simultaneously is by establishing a regular meal and sleep schedule. According to sleep experts, the human body functions best when it adheres to a consistent routine, particularly when it comes to waking up and going to bed at the same time each day. In fact, irregular or insufficient sleep has been linked to an increased risk of various physical and mental health problems, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, anxiety, and depression.
Similarly, irregular meal times can cause disruptions to the body’s natural circadian rhythm and affect sleep quality. For example, eating a large, heavy meal too close to bedtime can interrupt your digestion and cause discomfort, making it harder to sleep soundly. Conversely, skipping meals or going too long without food can lead to hunger pangs and lower blood sugar levels, which can also interfere with sleep.
To establish a regular meal and sleep schedule, consider using a table to track your daily routine. This can help you identify patterns and inconsistencies in your eating and sleeping habits, as well as highlight opportunities for improvement. Here’s an example of what your table might look like:
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wake up time | 6:30 am | 6:30 am | 6:30 am | 6:30 am | 6:30 am | 8:00 am | 9:30 am |
| Breakfast | 7:00 am | 7:00 am | 7:00 am | 7:00 am | 7:00 am | 8:30 am | 10:00 am |
| Lunch | 12:00 pm | 12:00 pm | 12:00 pm | 12:00 pm | 12:00 pm | 1:30 pm | 3:00 pm |
| Dinner | 6:00 pm | 6:00 pm | 6:00 pm | 6:00 pm | 6:00 pm | 7:30 pm | 9:00 pm |
| Bedtime | 10:00 pm | 10:00 pm | 10:00 pm | 10:00 pm | 10:00 pm | 11:30 pm | 1:00 am |
As you can see from the table, the person in question wakes up at the same time every day, which helps to regulate their body’s internal clock. They also eat breakfast, lunch, and dinner at roughly the same times each day, and go to bed at a consistent time each night. This routine can help to promote better sleep quality and overall health.
In addition to establishing a regular meal and sleep schedule, there are other tips you can follow to improve your eating habits and sleep quality. These include keeping a food and sleep diary, eating a balanced and varied diet, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and alcohol before bedtime. By taking a holistic approach to your health and wellbeing, you can unlock the mysteries of dreaming and enjoy a more restful, fulfilling sleep.
Conclusion
After analyzing the impact of eating habits on sleep, it is clear that what we eat and when we eat can greatly affect the quality and quantity of our sleep. Poor eating habits such as consuming heavy meals before bedtime or consuming stimulants like caffeine and alcohol can have negative impacts on sleep quality. On the other hand, incorporating foods that promote sleep and establishing a regular meal and sleep schedule can improve sleep quality.
It is important to note that good sleep patterns are crucial for overall health and well-being. Poor sleep patterns can lead to various health problems such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Thus, making necessary changes to eating habits can not only improve sleep but also promote overall health.
It is recommended to keep a food and sleep diary to track the impact of eating habits on sleep patterns. By monitoring what we eat and the quality and quantity of our sleep, we can make necessary adjustments to our eating habits and sleep patterns to improve sleep quality.
Overall, it is essential to prioritize good sleep habits and make necessary changes to our eating habits to ensure better sleep quality. By incorporating foods that promote sleep and establishing a regular meal and sleep schedule, we can not only enhance our sleep quality but also improve overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common foods that can cause sleep disturbances?
Caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and foods high in fat can all interfere with sleep quality.
Is it better to eat a large dinner or a small dinner before bed?
It’s better to eat a smaller dinner at least 2-3 hours before bed to give your body enough time to digest and avoid potential sleep disturbances.
What types of foods can promote better sleep quality?
Foods rich in protein, complex carbohydrates, and magnesium, such as nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes, can promote better sleep quality.
Can eating too late at night cause sleep disturbances?
Yes, eating too close to bedtime can disrupt your sleep cycle and make it harder to fall and stay asleep.
Can drinking water before bed affect sleep quality?
Drinking water before bed can hydrate your body, but drinking too much can cause you to wake up to use the bathroom during the night.
How can keeping a food and sleep diary help improve sleep quality?
A food and sleep diary can help you identify patterns and associations between your eating habits and sleep quality, allowing you to make necessary adjustments to improve sleep quality.
What are some healthy snack options to eat before bed?
Healthy snack options include a banana, a piece of whole-grain toast with almond butter, or a small serving of low-fat yogurt with berries.
Can a lack of regular meal times affect sleep quality?
Yes, irregular meal times can disrupt your body’s natural circadian rhythm and affect sleep quality.
Is it true that turkey can help you sleep better?
Turkey contains an amino acid called tryptophan, which can promote better sleep quality if consumed in moderate amounts.
How important is creating a relaxing bedtime routine for improving sleep quality?
A relaxing bedtime routine can help signal to your body that it’s time for sleep, leading to improved sleep quality and more restful nights.








