Many of us have experienced the perplexing feeling of waking up from a dream and struggling to remember the details. And yet, these elusive and often nonsensical moments during Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep may hold the key to unlocking the mysteries of memory consolidation. REM sleep is a vital part of our sleep cycle, playing a significant role in memory formation and learning. In this article, we will explore the importance of REM sleep and delve into what happens during this stage of sleep. We will also uncover the link between REM sleep and memory consolidation, as well as the consequences of REM sleep deprivation. Finally, we will offer practical tips on how to improve REM sleep and optimize the memory consolidation process.
What is REM Sleep?
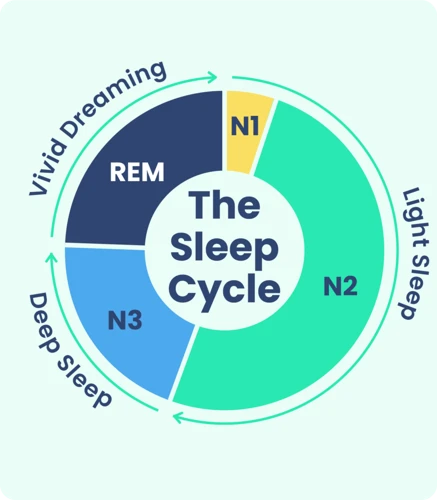
Have you ever woken up in the morning feeling either refreshed or groggy? Well, that all depends on what type of sleep you got throughout the night. Sleep is made up of different cycles, but one particular cycle that is crucial for our health is known as REM sleep. REM stands for Rapid Eye Movement and refers to the stage in our sleep where our eyes move quickly, and our brain activity increases. But what exactly happens during REM sleep, and why is it so important for our well-being? Let’s delve deeper into the mysteries of REM sleep.
Why is it Called REM?
During sleep, the human brain goes through different stages characterized by distinct brain wave patterns and physiological changes. One of these stages is called REM sleep or Rapid Eye Movement sleep. But why is it called REM?
The name “Rapid Eye Movement” refers to the rapid and uncontrolled movements of the eyes that occur during this stage. These movements are believed to be a reflection of the intense brain activity occurring during REM sleep.
To be more specific, REM sleep is associated with high levels of brain activity, similar to those experienced while the body is awake. Yet, despite this heightened activity, the body is in a state of paralysis, which is thought to be a protective mechanism to prevent injury that may result from acting out dreams.
Interestingly, not all animals experience REM sleep in the same way humans do. For example, some animals like dolphins and birds can sleep with only one hemisphere of their brain at a time, allowing them to still be partially awake while sleeping.
In conclusion, REM sleep gets its name from the rapid eye movements that occur during this stage, which are believed to be a reflection of heightened brain activity despite the body being in a state of paralysis. The way REM sleep is experienced differs across species, highlighting the intricate nature of sleep and its function in the brain.
What Happens During REM Sleep?
During REM sleep, the brain experiences several physiological changes. Here are some things that happen during this stage of sleep:
- The eyes move quickly in different directions, hence the name rapid eye movement.
- Brain activity increases, similar to when we are awake.
- Heart rate and blood pressure also increase.
- Muscles become relaxed to the point of nearly being paralyzed, which helps prevent us from acting out our dreams.
- Dreams occur, although we may not always remember them.
These changes are thought to be important for various neurological processes, such as memory consolidation and emotional regulation. The exact mechanisms are still under investigation, but recent research suggests that REM sleep plays a vital role in consolidating memories and facilitating learning.
REM Sleep and Memory Consolidation
As we sleep, our brain goes through different stages of activity, each playing a critical role in processing and consolidating memories. One of the most crucial stages is REM sleep, also known as rapid eye movement sleep. During this stage, our brain becomes highly active, and our eyes move rapidly back and forth behind our closed eyelids. While scientists have long recognized the importance of REM sleep in memory consolidation, the underlying mechanisms are still shrouded in mystery. In this section, we’ll explore the fascinating interplay between REM sleep and memory consolidation and delve deeper into why getting enough REM sleep is crucial for optimal brain function.
How REM Sleep Affects Memory
During REM sleep, the brain actively consolidates memories, particularly those related to emotional events and procedural tasks. The following table highlights the specific ways in which REM sleep affects memory:
| Memory Type | How REM Sleep Affects Memory |
|---|---|
| Emotional Memories | REM sleep helps to regulate emotions and strengthen memories associated with strong emotions. |
| Procedural Memories | REM sleep is particularly important for consolidating procedural memories, which involve learning a new skill or task, such as playing an instrument or driving a car. |
| Declarative Memories | REM sleep strengthens declarative memories, which involve learning factual information, such as a phone number or historical event. |
Without adequate REM sleep, these memory types may not be effectively consolidated, leading to memory impairments and difficulty retaining new information. It’s important to prioritize getting enough quality REM sleep in order to optimize memory consolidation and overall cognitive function.
The Role of Dreams in Memory Consolidation
Studies have suggested that dreaming during REM sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation. During REM sleep, our brains essentially replay the events of the day, consolidating memories and forming stronger connections between different pieces of information. This process is known as memory reactivation.
Researchers believe that dreams themselves may play a role in this reactivation and consolidation process. One theory is that dreams represent a visual and emotional replay of the day’s events, allowing us to review and process information in a coherent way.
To support this theory, a study conducted at Harvard Medical School found that participants who were awakened during REM sleep and immediately asked to recall their dreams had a higher rate of memory retention than those who were awakened during non-REM sleep.
Additionally, another study conducted at the University of California, Berkeley found that participants who were more successful at completing a complex maze had more REM sleep than those who struggled, suggesting a link between REM sleep and the consolidation of spatial memories.
Dreams play a crucial role in consolidating and strengthening memories during REM sleep, and may serve as a tool for reviewing and processing information in a coherent way.
The Link Between REM Sleep and Learning
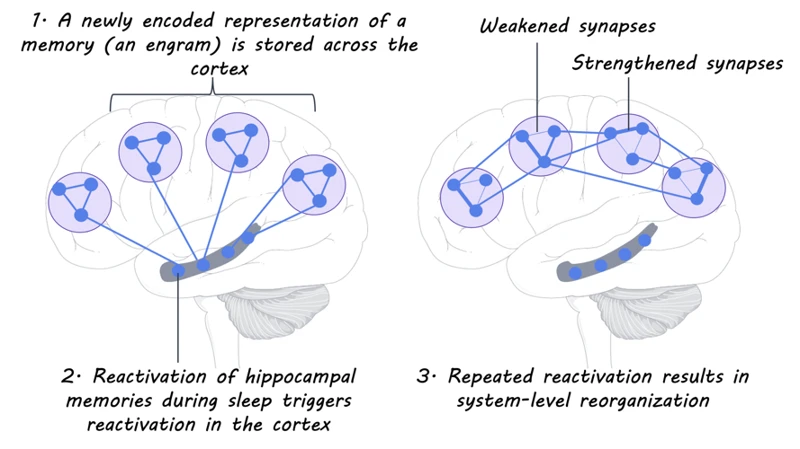
During REM sleep, the brain is thought to consolidate memories, which includes the process of learning. This is because when we learn something new, it is initially stored in the hippocampus, which is the region of the brain responsible for forming new memories. However, during REM sleep, these memories are replayed and transferred to the neocortex, which is the region of the brain responsible for long-term memory storage. This transfer of memories from the hippocampus to the neocortex is necessary for the memories to be retained over a long period of time.
Research has found that REM sleep plays a key role in the consolidation of procedural memories, which are memories involving the learning of skills and tasks. This type of memory is important for tasks such as playing a musical instrument, driving a car, or playing a sport. During REM sleep, the brain replays these procedural memories, which reinforces the neural connections necessary for learning and performing these skills.
Additionally, REM sleep has been linked to the consolidation of emotional memories. Studies have shown that emotional memories are more likely to be consolidated during REM sleep compared to non-REM sleep. This is thought to be due to the fact that during REM sleep, the amygdala, which is the region of the brain responsible for processing emotions, is highly active. This heightened activity during REM sleep may help to strengthen emotional memories.
The link between REM sleep and learning is critical for the formation and consolidation of memories. Without adequate REM sleep, the brain may struggle to transfer new memories from the hippocampus to the neocortex, leading to difficulties with retaining information over time. The consolidation of procedural and emotional memories may also be impaired, which can have negative consequences for daily life.
The Consequences of REM Sleep Deprivation
Sleep is essential for our overall health and wellbeing. And during sleep, our brain goes through different stages, including REM sleep. REM sleep has been found to play a crucial role in memory consolidation and learning. However, the consequences of REM sleep deprivation can be severe and may affect both our physical and mental health. The lack of REM sleep has been linked to impaired memory formation, emotional instability, and impaired cognitive performance. In this section, we will explore the consequences of REM sleep deprivation and how it can impact our daily lives.
Impaired Memory Formation
When we fail to get enough REM sleep, one of the major consequences is that it can lead to impaired memory formation. Our brain uses this stage of sleep to consolidate memories and transfer them from short-term to long-term storage. REM sleep is crucial for the retention and recall of new information, therefore any disruption to this process can severely impact our ability to form new memories.
Studies have shown that students who deprive themselves of sleep before a test are much more likely to struggle with recalling facts and remembering material they had previously learned. Similarly, individuals who suffer from various sleep disorders, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, may also experience problems with forming and retaining memories due to the disruption of REM sleep.
Aside from the immediate effects of poor memory formation, chronic REM sleep deprivation over a long period of time can lead to permanent memory impairment and even neurological disorders. This is because during REM sleep, our brains also carry out processes such as neural pruning, which clears out unnecessary or unused connections in the brain to make room for new ones. Without proper REM sleep, our brain may accumulate more connections than it can adequately maintain, leading to cognitive decline and other long-term memory issues.
The essential role of REM sleep in consolidating and retaining memories cannot be overstated. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply someone looking to maintain healthy cognitive function, it is crucial to prioritize getting enough high-quality REM sleep each night to ensure optimal brain function and memory retention.
Emotional Instability
One of the consequences of REM sleep deprivation is the increased likelihood of experiencing emotional instability. Without adequate REM sleep, the brain is unable to properly regulate emotions, leading individuals to experience strong and often unexplained emotional reactions. These emotional reactions can range from excessive irritability and frustration to feelings of sadness and depression.
Some potential causes of emotional instability due to REM sleep deprivation include:
- Increased amygdala activity: The amygdala is a part of the brain that plays a key role in processing emotions. Research has found that when individuals are deprived of REM sleep, the amygdala becomes hyperactive, making it more difficult for individuals to regulate emotions.
- Disrupted prefrontal cortex activity: The prefrontal cortex is another region of the brain that is important for emotional regulation. When individuals are deprived of REM sleep, prefrontal cortex activity can become disrupted, leading to impaired emotional regulation.
The consequences of emotional instability due to REM sleep deprivation can be significant, impacting not only an individual’s emotional state but also their social and professional relationships. It’s important to recognize the link between REM sleep and emotional regulation and take steps to prioritize healthy sleep habits.
Impaired Cognitive Performance
The consequences of REM sleep deprivation are not limited to impaired memory formation and emotional instability; it also affects cognitive performance. Research has shown that sleep deprivation, particularly the loss of REM sleep, can have a negative impact on cognitive functions such as attention, decision making, and problem solving.
Attention: Sleep deprivation can lead to a decrease in sustained attention and vigilance. This can result in an inability to focus on tasks for extended periods of time, and an increased likelihood of making errors.
Decision Making: REM sleep deprivation can also impair decision making abilities. Individuals who are sleep deprived may struggle with complex decision making tasks, and may be more likely to make impulsive decisions.
Problem Solving: REM sleep deprivation can also interfere with problem solving abilities. Studies have shown that individuals who are deprived of REM sleep may struggle with tasks that require creative problem solving or the ability to think outside of the box.
It is important to note that these cognitive impairments are not limited to individuals who are completely deprived of REM sleep. Even partial REM sleep deprivation, such as that experienced by individuals with sleep disorders like sleep apnea, can have negative effects on cognitive performance. It is crucial to prioritize getting adequate amounts of REM sleep in order to maintain optimal cognitive function.
How to Improve REM Sleep
After learning about the importance of REM sleep in memory consolidation and cognitive function, you might be wondering how to ensure you’re getting enough of this crucial stage of sleep. Improving REM sleep can be challenging, especially if you’re dealing with sleep disorders or a hectic schedule. However, there are several strategies you can try to boost your chances of experiencing deep, restorative REM sleep. In this section, we’ll explore various techniques and habits that can support healthy REM sleep and overall sleep quality. By implementing these suggestions, you may find yourself waking up feeling refreshed, energized, and ready to tackle the day ahead.
Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Creating a consistent sleep schedule is essential for improving your REM sleep. Our bodies thrive on routines and establishing a regular bedtime and wake-up time can help regulate our internal clocks, making it easier to fall asleep and promoting better sleep quality.
To establish a consistent sleep schedule, it’s important to first identify your optimal sleep duration. While everyone’s needs vary, the National Sleep Foundation recommends 7-9 hours of sleep per night for adults. Once you’ve determined your ideal sleep duration, try to stick to a set bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends.
It’s also important to avoid napping during the day as it can disrupt your established sleep schedule. If you do feel tired during the day, taking a short power nap of 20-30 minutes can be beneficial, but try to avoid longer naps that can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night.
In addition to setting a regular sleep schedule, it’s important to create a relaxing bedtime routine to help prepare your body for sleep. Consider taking a warm bath, reading a book, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation. By developing a consistent sleep schedule and bedtime routine, you can help promote better REM sleep and improve other aspects of your health and well-being.
To summarize, here are some tips for establishing a consistent sleep schedule:
- Determine your optimal sleep duration
- Set a regular bedtime and wake-up time
- Avoid napping, or limit naps to 20-30 minutes
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine
Creating a Relaxing Sleep Environment
The environment in which you sleep plays a crucial role in the quality and quantity of your REM sleep. Creating a relaxing sleep environment can help promote deep, uninterrupted sleep and increase your chances of experiencing several cycles of REM sleep throughout the night. Here are a few tips on how to create a soothing and comfortable sleep environment:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Temperature Control | Keep the temperature of your bedroom cool and comfortable, around 65°F (18°C), to promote deeper sleep. If you get too hot or too cold while sleeping, it can disrupt your REM sleep. |
| 2. Lighting | A dark, quiet bedroom can help promote uninterrupted sleep. Invest in heavy curtains, a sleep mask, or earplugs to help block out any unwanted light or noise that may disrupt your REM sleep. |
| 3. Bedding | Comfortable and cozy bedding can also contribute to a relaxing sleep environment. Invest in high-quality pillows, sheets, and blankets that promote comfort and support throughout the night. |
| 4. Technology Control | Avoid using electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones, or tablets while in bed. The blue light emitted from these devices can disrupt your natural circadian rhythm and make it harder to fall asleep. |
| 5. Aromatherapy | Essential oils such as lavender or chamomile can promote relaxation and help calm the mind before sleep. Use a diffuser or spray to disperse the oils throughout your bedroom for a peaceful sleep environment. |
By incorporating these tips into your sleep routine, you can create a sleep environment that promotes deep, uninterrupted sleep and increases your chances of experiencing several cycles of REM sleep throughout the night. This can help improve memory consolidation, cognitive performance, and emotional stability, ultimately leading to better overall health and well-being.
Avoiding Foods and Drinks that Disrupt Sleep
When it comes to getting a good night’s sleep, it’s not just about what you do before bedtime or what your sleep environment is like. What you eat and drink can also have a major impact on your quality of sleep. Certain foods and drinks can disrupt sleep and make it difficult to get the restorative REM sleep that your body needs. Here are some of the foods and drinks you should avoid or limit if you want to improve your sleep quality.
| Caffeine | Caffeine is a stimulant that can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. It’s found in coffee, tea, soda, and chocolate. To get better sleep, avoid consuming caffeine in the afternoon and evening. |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | While alcohol may help you relax and fall asleep faster, it actually disrupts sleep later in the night. It can make you wake up frequently and prevent you from entering REM sleep, which is essential for memory consolidation. |
| Sugar | Sugar can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes that can disrupt sleep. It may also cause nighttime awakenings and increase the likelihood of developing sleep disorders. |
| Spicy Foods | Spicy foods can cause indigestion and heartburn, which can make it difficult to fall and stay asleep. If you want to eat spicy foods, do so earlier in the day to give your body time to digest them before bedtime. |
| Processed or Heavy Foods | Processed or heavy foods can also cause indigestion and heartburn, which can lead to disrupted sleep. Eating a light meal a few hours before bedtime can help you sleep better. |
By avoiding or limiting these foods and drinks, you can improve your sleep quality and increase your chances of getting the restorative REM sleep that your body needs for memory consolidation and learning.
Practicing Sleep Hygiene
Practicing sleep hygiene is essential for achieving and maintaining a proper sleep cycle. Sleep hygiene refers to a set of habits and practices that promote healthy and restful sleep. These practices include:
| Avoiding Stimulants before Bedtime |
| Stimulants such as caffeine and nicotine can interfere with sleep and should be avoided before bedtime. It is recommended to avoid them for at least 4-6 hours before going to bed. |
| Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine |
| Establishing a relaxing pre-sleep routine can help signal your body that it’s time to sleep. Some examples of relaxing activities include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or practicing meditation. |
| Avoiding Excessive Exposure to Screens |
| The blue light emitted by screens such as smartphones, laptops, and TVs can disrupt the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. To improve the quality of your sleep, it is recommended to avoid screens for at least one hour before bedtime. |
| Maintaining a Comfortable Sleep Environment |
| Creating a comfortable and soothing sleep environment can help improve the quality of your sleep. Some tips include keeping your bedroom cool and dark, using comfortable bedding, and minimizing noise and distractions. |
| Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule |
| Consistency is key when it comes to establishing healthy sleep habits. It is recommended to maintain a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, in order to regulate your body’s internal clock. |
By practicing good sleep hygiene, you can improve the quality of your sleep, increase the amount of REM sleep you get, and ultimately enhance memory consolidation and cognitive function.
Conclusion
After delving into the mysteries of REM sleep, it is clear that this stage of sleep is crucial for memory consolidation and learning. During REM sleep, the brain is active, processing and storing memories, and dreaming which helps to solidify these memories in our minds.
It is important to understand that the link between REM sleep and memory is bidirectional. In other words, an improvement in memory consolidation can lead to better quality REM sleep, and vice versa. Sleep hygiene plays a vital role in establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing sleep environment, both of which are necessary for achieving high-quality REM sleep.
REM sleep deprivation can cause significant impairment of cognitive performance, emotional instability, and impaired memory consolidation, leading to a range of negative outcomes. Therefore, it is critical to take steps to improve REM sleep, such as avoiding foods and drinks that interfere with sleep, practicing good sleep hygiene, and creating a relaxing sleep environment.
While the mechanisms underlying the relationship between REM sleep and memory consolidation are still being explored, what is certain is that our understanding of the importance of REM sleep for memory and learning has come a long way in recent years. It is clear that by prioritizing quality REM sleep, we can significantly improve our cognitive abilities and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much REM sleep do we need?
Adults need around 1.5 – 2 hours of REM sleep every night.
What happens if we don’t get enough REM sleep?
If we don’t get enough REM sleep, our memory formation, emotional stability, and cognitive performance can all be impaired.
Can we dream in non-REM sleep?
While it’s possible to dream during non-REM sleep, dreams during REM sleep tend to be more vivid and memorable.
Do all animals experience REM sleep?
No, not all animals experience REM sleep. Some birds and reptiles, for example, do not have this stage of sleep.
Can we control our dreams during REM sleep?
While it is difficult to intentionally control our dreams during REM sleep, some people practice lucid dreaming to gain some level of control.
Is it harmful to wake up during REM sleep?
No, it is not harmful to wake up during REM sleep. In fact, we naturally cycle through various stages of sleep throughout the night.
Does medication affect REM sleep?
Some medication can affect REM sleep. For example, antidepressants can suppress REM sleep while some sleep aids can increase it.
Do children need more REM sleep than adults?
Yes, children need more REM sleep than adults. Babies may spend up to 50% of their sleep time in REM sleep.
Can REM sleep help us learn new skills?
Yes, studies have shown that REM sleep can help consolidate memories related to the acquisition of new motor and cognitive skills.
Can we measure REM sleep?
Yes, we can measure REM sleep using an electroencephalogram (EEG) to record brain activity and measure eye movements during sleep.