Sleep is an essential aspect of our overall health and wellbeing, allowing the body to recharge and regenerate for the upcoming day. However, for many individuals, sleep can be disrupted by nightmares, causing both physical and psychological distress. Despite the common occurrence of nightmares, many people are still perplexed by their impact on sleep quality and quantity. In this article, we will explore the relationship between nightmares and sleep, as well as the potential consequences of experiencing frequent nightmares. We will also discuss various strategies that individuals can use to manage and prevent nightmares, ultimately leading to a more restful and peaceful night’s sleep.
Definition of Nightmares
When we close our eyes at night, our unconscious mind takes over and can create vivid and often disturbing images known as nightmares. These experiences can be frightening and are defined as vivid, realistic, and often terrifying dreams that occur during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Nightmares are different from regular dreams, as they cause the dreamer to experience feelings of fear, terror, and distress, which can often lead to a disrupted night’s sleep. Despite being a common experience for many individuals, the exact cause of nightmares remains perplexing to researchers.
Types of Nightmares
Nightmares are vivid and distressing dreams that can negatively impact our sleep quality and mental health. There are several types of nightmares that people may experience, each with their own unique characteristics and potential triggers.
1. Recurrent nightmares: These are dreams that occur repeatedly, usually involving the same themes or fears. Recurrent nightmares can be a symptom of a larger issue, such as anxiety or trauma.
2. Situational nightmares: As the name suggests, situational nightmares are triggered by a specific event or situation in someone’s life. For example, someone going through a divorce may have nightmares about arguments with their ex-spouse.
3. Progressive nightmares: These are nightmares that become progressively worse as they continue. They may start out mildly scary and evolve into more terrifying scenarios.
4. False awakenings: This type of nightmare involves dreaming that you have woken up, only to realize later that you are still dreaming. False awakenings can be disorienting and cause a lack of confidence in your own perception of reality.
5. Lucid nightmares: These are nightmares in which the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming, but is unable to alter the dream’s storyline. This can result in a feeling of being trapped in the nightmare.
Understanding the different types of nightmares can help individuals identify potential triggers and seek appropriate treatment if necessary.
The Link Between Nightmares and Sleep Quality

Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for overall health and well-being. However, some people suffer from nightmares that can significantly impact their sleep quality. Nightmares can cause sleep disruptions, leading to impaired sleep onset, shortened sleep duration, and an inability to fall back asleep. The relationship between nightmares and sleep quality is complex and requires further exploration. In this section, we will delve into the link between nightmares and sleep quality, examining how nightmares can affect different aspects of one’s sleep.
Impaired Sleep Onset
One of the main impacts of nightmares on sleep quality is impaired sleep onset. This means that individuals who experience nightmares may have difficulty falling asleep at the beginning of the night. This can be caused by the fear of experiencing another nightmare or by the hyperaroused state that nightmares can cause.
- Fear of nightmares: After experiencing a nightmare, individuals may be afraid to fall back asleep, as they do not want to experience another frightening dream. This fear can make it difficult for them to relax and fall asleep, leading to a delay in sleep onset.
- Hyperarousal: Nightmares can cause individuals to experience a state of hyperarousal, where their heart rate and breathing may increase, and they may feel more alert and awake. This hyperarousal can make it difficult for them to fall asleep, as their body is in a state of heightened activity.
Both of these factors can result in a delay in sleep onset, which can lead to sleep deprivation and other negative consequences. Sleep onset latency (SOL) refers to the amount of time it takes for an individual to fall asleep after going to bed. An SOL of more than 30 minutes is considered prolonged and can be an indicator of impaired sleep onset. Individuals who experience nightmares may have a longer SOL due to the difficulties they face when trying to fall asleep. This can result in a shorter total sleep time and a lower quality of sleep overall.
Shortened Sleep Duration
One of the negative impacts of nightmares on sleep quality is a shortened sleep duration. This means that individuals who experience nightmares tend to spend less time asleep than those who don’t. This can be due to a number of factors, including the content of the nightmares themselves, as well as the resulting anxiety or fear that can linger after waking up from a bad dream.
According to research, nightmares can result in a decrease in total sleep time of up to 25%. This reduction in sleep time can have serious consequences, as sleep is essential for the body and brain to function properly.
Below, is an html table which summarizes the potential effects of shortened sleep duration associated with nightmares:
| Effects of Shortened Sleep Duration due to Nightmares |
|---|
| Daytime fatigue and sleepiness |
| Decreased cognitive function and memory retention |
| Increased risk of accidents and injuries |
| Increased risk of chronic health conditions, such as obesity and diabetes |
| Decreased immune function and increased susceptibility to illness and infection |
Shortened sleep duration can also have long-term effects on physical and mental health. For example, chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke, as well as mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
It’s important to address the issue of shortened sleep duration associated with nightmares in order to improve overall sleep quality and prevent potential health consequences. This may involve seeking professional help, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, or making lifestyle changes that promote better sleep hygiene.
Inability to Fall Back Asleep
Nightmares not only disrupt the quality and duration of sleep but can also lead to inability to fall back asleep after waking up in the middle of the night. This can have serious repercussions for those who suffer from recurring nightmares. Those who wake up in the middle of the night after a nightmare are likely to experience heightened anxiety, which interferes with their ability to get back to sleep.
Research has shown that the inability to fall back asleep after a nightmare primarily occurs during the second half of the night, which is when we experience deeper stages of sleep. When we wake up from a nightmare, it is difficult for our minds and bodies to return to the deep, restorative sleep that we need, which can lead to further sleep deprivation and fatigue.
To better understand the impact of nightmares on the inability to fall back asleep, let’s take a closer look at the different stages of sleep.
|Stages of Sleep|Description|
|:—:|:—:|
|Stage 1|A light sleep where the brain produces alpha and theta waves.|
|Stage 2|The brain produces bursts of rapid brain waves known as sleep spindles.|
|Stage 3|Deep sleep begins in this stage, where the brain starts producing delta waves.|
|Stage 4|The deepest stage of sleep where the brain almost exclusively produces delta waves.|
|REM Sleep|The stage where most dreaming occurs, and the brain is highly active.|
After a nightmare, it is common to wake up during stages 3 and 4 of sleep. These stages are crucial for our physical and mental restoration, but they can also make it challenging to return to sleep after awakening because the body needs to go through several stages of lighter sleep before reaching the deeper stages again.
To combat the inability to fall back asleep after a nightmare, it is essential to find strategies to reduce anxiety and calm the mind. Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualization can be helpful for promoting relaxation and easing feelings of fear and anxiety. Additionally, practicing good sleep hygiene and creating a sleep-conducive environment can increase the chances of falling back asleep after a nightmare.
The Relationship Between Nightmares and Sleep Quantity
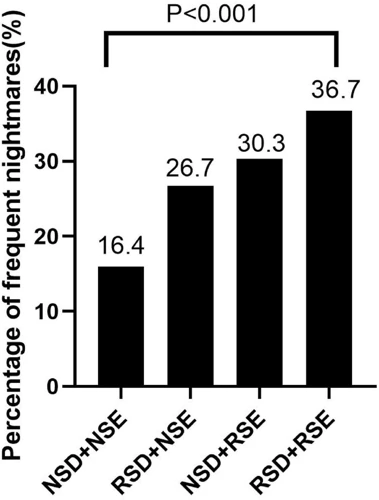
When it comes to the impact of nightmares on our overall sleep patterns, it’s not just the quality of sleep that is affected. In fact, the relationship between nightmares and sleep quantity is just as significant. Nightmares often disrupt the natural sleep cycle and can lead to a variety of interruptions throughout the night. This can result in a decreased amount of time spent in crucial sleep stages and an overall reduction in the amount of restorative sleep achieved. In this section, we’ll dive deeper into the effects of nightmares on sleep quantity, from their impact on specific sleep stages to the overall fragmentation of sleep.
Nightmares and REM Sleep
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is a stage of sleep where the brain is very active, but the body is mostly paralyzed. It is during this stage that most dreaming occurs, and nightmares are no exception. Nightmares tend to happen during the later part of the night, during the periods of REM sleep. Here are some things to keep in mind about the relationship between nightmares and REM sleep:
- Nightmares are most likely to occur during the latter part of the night, when REM sleep is more prevalent. During these periods of REM sleep, the brain is highly active, and this can lead to vivid, often unsettling dreams.
- During REM sleep, the body is usually in a state of paralysis, which prevents people from physically acting out their dreams. This is why nightmares are mostly a mental experience, rather than a physical one.
- While REM sleep is important for many reasons, including memory consolidation and emotional regulation, experiencing nightmares during this stage can lead to negative effects on mental health, specifically by causing anxiety and depression.
- People who experience repeated nightmares may develop a fear of going to sleep, which can disrupt their sleep patterns even further. This can lead to a vicious cycle of disrupted sleep, more nightmares, and more anxiety.
While REM sleep is an important stage of sleep that serves many important functions, it is also the stage where nightmares are most likely to occur. Understanding the relationship between nightmares and REM sleep is an important step in managing and preventing these troubling experiences.
Impact on Deep Sleep
Nightmares can have a significant impact on deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), which is a crucial stage of the sleep cycle responsible for physical and mental restoration. According to research studies, nightmares can lead to a reduction in the amount of time spent in SWS, as well as a decrease in the quality of this sleep phase.
One study conducted by Schredl and Reinhard (2008) found that individuals who reported experiencing nightmares had significantly less SWS than those who did not. Additionally, the nightmares were associated with more arousals during SWS, which could further disrupt the restorative effects of this sleep phase. These findings suggest that nightmares can interfere with the body’s ability to fully engage in the restorative process of deep sleep.
Another study by Robert and colleagues (2016) found that frequent nightmares were associated with more shallow or light sleep, and less time spent in both SWS and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. This means that, in addition to reducing the amount of deep sleep, nightmares can also disrupt the overall sleep architecture, contributing to further sleep fragmentation.
The consequences of decreased SWS due to nightmares can be far-reaching, affecting both physical and mental health. During deep sleep, the body repairs and regenerates tissues, strengthens the immune system, and consolidates memories. Thus, the reduction in SWS caused by nightmares can impact physical well-being, as well as cognitive functioning and emotional regulation.
It is essential to address any underlying factors contributing to nightmares and prioritize strategies for preventing or managing them to minimize their negative impact on deep sleep and overall sleep architecture. These can include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques, mindfulness practices, and lifestyle changes such as improving sleep hygiene and reducing stress.
Overall Sleep Fragmentation
Overall sleep fragmentation is another concerning aspect of nightmares. When a person experiences a nightmare, they are likely to wake up multiple times throughout the night, which can lead to a disruption in their sleep cycle. This can cause a domino effect, where overall sleep quality is severely impacted.
Here are some of the ways in which overall sleep fragmentation can impact the body:
- Exhaustion: When sleep is fragmented, individuals may experience a feeling of exhaustion when they wake up in the morning. This can lead to reduced productivity and low energy levels throughout the day.
- Irritability: Sleep fragmentation can also cause irritability and mood swings. This is due to the brain not receiving the amount of rest it needs to function efficiently.
- Memory problems: Sleep is essential for consolidating memories, and interrupted sleep can cause difficulties with memory retention and recall.
- Weakened immune system: Research has shown that sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining a person’s immune system. Interrupted sleep can weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of contracting illnesses.
- Weight gain: Disrupting the natural sleep cycle can lead to an increase in appetite and a decrease in the hormone that regulates hunger (leptin). This can cause individuals to gain weight over time.
It is evident that sleep fragmentation due to nightmares can have far-reaching consequences on the body and mental health. It is essential to take steps to manage and prevent nightmares to improve overall sleep quality and reduce the risk of developing related health issues.
Effects of Nightmares on Mental Health
Nightmares are not just terrifying dreams that make us feel scared and vulnerable; they can also have a significant impact on our mental health. Sleep is essential for our well-being, and when we experience nightmares, it can disrupt our mental and emotional balance. The effects of nightmares on mental health can range from mild anxiety to severe depression and trauma. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which nightmares can affect mental health, including anxiety and depression, PTSD and trauma, and nightmare disorder. It is crucial to understand the significance of these effects to start taking effective measures to manage and prevent nightmares.
Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health conditions associated with nightmares. Research has found that individuals who experience frequent nightmares are more likely to report symptoms of anxiety and depression. In fact, a study published in the Journal of Sleep Research found that individuals who reported frequent nightmares were more likely to report symptoms of depression and anxiety than those who reported infrequent nightmares.
The relationship between nightmares and anxiety and depression appears to be bidirectional. This means that not only can nightmares worsen symptoms of anxiety and depression, but individuals suffering from anxiety and depression may also be more likely to experience nightmares.
The exact mechanisms underlying the relationship between nightmares and anxiety and depression are not yet fully understood. However, it is believed that nightmares may trigger emotional reactions that can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and depression. Additionally, the lack of restful sleep caused by frequent nightmares can also contribute to the development and exacerbation of anxiety and depression.
Table:
| Effect of Nightmares on Mental Health | Impact |
|---|---|
| Anxiety symptoms | Increased prevalence and severity |
| Depression symptoms | Increased prevalence and severity |
| Bidirectional relationship | Nightmares can worsen symptoms of anxiety and depression, and individuals with these conditions may be more likely to experience nightmares |
| Underlying mechanisms | Nightmares trigger emotional reactions that exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and depression, and lack of restful sleep caused by nightmares can contribute to development and exacerbation of both conditions |
It is important for individuals experiencing frequent nightmares and symptoms of anxiety and depression to seek professional help. Treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication can be effective in managing these conditions and improving sleep quality. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques and implementing healthy sleep habits can also be helpful in managing symptoms and preventing the occurrence of nightmares.
PTSD and Trauma
PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder) and trauma are common causes of nightmares. According to research, about 80% of individuals with PTSD experience nightmares. Nightmares in this population are often replay of the traumatic event and can lead to further distress and anxiety. These post-traumatic nightmares can negatively impact sleep quality and quantity, leading to daytime symptoms such as fatigue, lack of concentration, and irritability.
Trauma and PTSD nightmares also differ from other types of nightmares in terms of dream content. They may contain intense emotions, vivid sensory details, and a sense of reliving the traumatic event. In some cases, the nightmares may become so distressing that individuals may avoid sleep altogether, leading to sleep deprivation and other associated problems.
There are various treatments available for PTSD and trauma-related nightmares, including medication, therapy, and other coping strategies. Strong evidence supports the use of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) as an effective treatment for PTSD-related nightmares. This therapy focuses on reducing the intensity and frequency of nightmares by changing negative thought patterns and associations with the traumatic event. Certain medications such as prazosin and clonidine also appear to be effective for treating nightmares associated with PTSD.
In addition to therapy and medication, there are other coping strategies that individuals can use to manage their PTSD nightmares. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the mind and promote relaxation before sleep. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and good sleep hygiene habits such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and avoiding caffeine and alcohol can also help improve sleep quality and quantity.
It is important for individuals experiencing PTSD and trauma-related nightmares to seek appropriate treatment and take steps to manage their symptoms. With the right support, it is possible to improve sleep quality and reduce the impact of nightmares on daily life.
| PTSD and Trauma Nightmares | Effects on Sleep | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Nightmares often relive the traumatic event | May result in avoidance of sleep and sleep deprivation | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, Medication (Prazosin, Clonidine) |
| Contain intense emotions and vivid sensory details | Can lead to daytime symptoms such as fatigue, lack of concentration, and irritability | Relaxation Techniques, Exercise, Healthy Diet, Sleep Hygiene Habits |
Nightmare Disorder
Nightmare disorder is a sleep disorder characterized by frequent and distressing nightmares that interfere with a person’s ability to function during the day. People with nightmare disorder often experience anxiety and fear of going to sleep in anticipation of the next nightmare. It affects approximately 2-8% of the general population and can occur at any age, although it appears to be more common in children and adolescents.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of nightmare disorder is the recurrent occurrence of frightening dreams that cause emotional distress, anxiety, and fear. People with nightmare disorder may experience:
- Difficulty falling or staying asleep
- Feeling tired or fatigued during the day
- Difficulty concentrating
- Reduced performance at school or work
- Decreased mood, motivation, or interest in activities
These symptoms can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, leading to mood disorders, such as depression or anxiety, and decreased social or occupational functioning.
Causes
Nightmare disorder can result from a variety of factors, or it may develop without a clear cause. Some of the common causes of nightmare disorder include:
- Stressful life events, such as trauma, abuse, or loss
- Medications or substances that affect sleep or the brain
- Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome
- Mental health conditions, such as anxiety or PTSD
Treatment
The treatment for nightmare disorder often involves a combination of approaches, depending on the underlying causes and severity of the symptoms. Some of the common treatments for nightmare disorder include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): a form of talk therapy that helps people learn to identify and change negative patterns of thinking and behavior that contribute to nightmares and other sleep problems.
- Medications: antidepressants or medications that affect chemical messengers in the brain, such as serotonin or norepinephrine, may be prescribed to help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
- Relaxation techniques: mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality.
It’s important to seek treatment for nightmare disorder, as chronic nightmares can have a negative impact on mental health and overall well-being. With the right treatment, it’s possible to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares and improve sleep quality and daytime functioning.
Managing and Preventing Nightmares
If you’re someone who has experienced frequent nightmares, you know how they can disrupt your sleep and negatively impact your mental health. Luckily, there are various methods to manage and prevent them. Let’s explore some of these strategies so that you can take action towards enjoying a more peaceful and restful night’s sleep.
CBT for Nightmares
One effective approach to managing and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). CBT is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
During CBT for nightmares, a trained therapist works with the individual to identify triggers and thought patterns that may contribute to recurring nightmares. The therapist then helps the individual develop coping strategies to manage these triggers and thoughts.
One common technique used in CBT for nightmares is called “imagery rehearsal therapy” (IRT). During IRT, individuals are encouraged to replace their negative or scary dream imagery with a more positive or neutral scenario. For example, if someone frequently has nightmares about being chased by a monster, the therapist might work with them to develop a new scenario where they successfully escape the monster.
Another technique used in CBT for nightmares is called “exposure and desensitization.” During this technique, the individual is gradually exposed to the content of their nightmares in a safe and controlled setting. Over time, they become less sensitive to the content and are less likely to experience nightmares.
CBT for nightmares typically involves several sessions with a trained therapist. It is important to note that CBT may not work for everyone and some individuals may require a combination of therapies to effectively manage their nightmares.
CBT for nightmares is a promising approach for managing and reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. By identifying triggers and negative thought patterns, individuals can develop coping strategies to help them sleep more soundly and reduce the negative impact of nightmares on their mental health.
| Approach | Technique | Description |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT) | Replace negative dream imagery with a more positive/neutral scenario |
| Exposure and Desensitization | Gradually expose individual to nightmare content in a safe and controlled setting |
Mindfulness Techniques
One possible way to approach the topic of mindfulness techniques for managing and preventing nightmares is to break it down into specific practices that have been shown to be effective. Several studies suggest that mindfulness-based interventions can improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Here are some examples of mindfulness techniques that have been applied in this context:
- Meditation: Regular meditation practice can help calm the mind and reduce stress, which in turn can promote better sleep and reduce the likelihood of having nightmares. Some types of meditation that have been found to be particularly helpful include mindfulness meditation, loving-kindness meditation, and body scan meditation.
- Breathing exercises: Focusing on your breath can be a powerful tool for reducing anxiety and promoting relaxation. Deep breathing exercises, where you inhale slowly through your nose and exhale slowly through your mouth, can help quiet the mind and body and prepare you for sleep.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: This technique involves tensing and then releasing groups of muscles throughout the body, starting with the feet and working your way up to the head. This can help ease physical tension and promote physical relaxation.
- Guided imagery: This involves using your imagination to create soothing mental images or scenarios, such as a peaceful beach or a relaxing forest. You can use guided imagery before bed or during the night if you wake up from a nightmare to help calm your mind and return to sleep.
It’s worth noting that while mindfulness techniques can be helpful for managing nightmares, they may not work for everyone. It’s important to experiment with different practices and find what works best for you. Additionally, it’s important to seek professional help if your nightmares are interfering with your daily life or causing significant distress. A mental health professional can provide a comprehensive assessment and offer treatment recommendations based on your individual needs.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on reducing the occurrences of nightmares. Some of these changes may include:
| Implementing a Relaxation Routine: | Creating a pre-bedtime routine that focuses on relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, gentle stretching or calming music, can reduce stress and anxiety levels that are often a trigger for nightmares. |
| Establishing a Regular Sleep Schedule: | Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can help regulate circadian rhythms and promote better sleep, which can reduce the likelihood of experiencing interrupted sleep patterns that could trigger nightmares. |
| Avoiding Triggering Stimuli: | Avoiding stimuli that have been linked to nightmares, such as watching horror movies before bed or eating heavy meals close to bedtime, may help to decrease the frequency of nightmares. |
| Keeping a Dream Journal: | Recording any recurring nightmares or particular themes within them can help identify the root cause of the nightmares, which can then be addressed through other management techniques. |
| Improving Sleep Environment: | Creating a comfortable sleep environment that is free from distractions, such as removing electronics from the bedroom, can promote better sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of nightmares. |
By making these lifestyle changes, individuals who experience frequent nightmares can take control of their sleep quality and reduce the impact of nightmares on their overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is evident that nightmares have a significant impact on one’s sleep quality and quantity. The vivid, disturbing, and often terrifying dreams can affect an individual’s ability to fall asleep, stay asleep, and achieve quality restorative sleep. This, in turn, can result in physical and psychological problems, affecting a person’s overall health and well-being.
Through various studies and research, it has been confirmed that nightmares are not only linked to decreased sleep quality but also reduced sleep quantity, including interrupted REM and deep sleep. As a result, individuals are left feeling fatigued and lacking energy, impacting their day-to-day activities and productivity levels.
Moreover, it is clear that nightmares can lead to mental health problems, including anxiety, depression, PTSD, and even nightmare disorder. These issues can severely affect an individual’s quality of life, leading to further sleep disturbances and a vicious cycle of poor health outcomes.
However, with the right management and prevention techniques, such as CBT, mindfulness, and lifestyle changes, individuals can improve their sleep quality, reduce nightmares, and enhance their overall well-being. These techniques can help reduce anxiety symptoms, overcome trauma, and provide relief from the distress of recurring nightmares.
In conclusion, it is crucial to prioritize good sleep hygiene, seek appropriate medical and psychological assistance, and take proactive measures to manage and prevent nightmares. By doing so, individuals can experience improved sleep quality and quantity, better physical and mental health, and a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes nightmares?
Nightmares can be caused by a variety of factors including stress, anxiety, traumatic events, medication side effects, and sleep disorders.
How common are nightmares?
Nightmares are fairly common, with up to 85% of people reporting having at least one nightmare in their lifetime.
Can nightmares affect your physical health?
Yes, nightmares have been linked to physical health problems including headaches, migraines, and even heart disease.
Is it normal to have nightmares every night?
No, it is not normal to have nightmares every night. This could be a sign of a more serious sleep disorder or underlying mental health condition.
Can nightmares be a symptom of PTSD?
Yes, nightmares are a common symptom of PTSD and can be related to the traumatic events that a person has experienced.
Can medication help with nightmares?
Yes, in some cases medications can be used to treat nightmares, particularly if they are related to an underlying mental health condition such as PTSD.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy for nightmares?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for nightmares is a form of therapy that helps individuals change their thought patterns and behaviors related to sleep, reducing the frequency and severity of nightmares.
Can lifestyle changes help reduce nightmares?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as reducing stress, avoiding alcohol and drugs, and establishing a consistent sleep routine can help reduce the frequency and severity of nightmares.
Can mindfulness techniques help with nightmares?
Yes, mindfulness techniques such as meditation and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can in turn decrease the likelihood of nightmares.
What is nightmare disorder?
Nightmare disorder is a sleep disorder characterized by frequent and recurring nightmares that significantly disrupt a person’s sleep and daily life. It is typically treated with therapy or medication.








