As we lay our heads on the pillow every night and drift off to sleep, we enter a realm filled with wonder and mystery: the world of dreams. Dreams are our unconscious minds making sense of the day’s events and emotions. However, not all of us are lucky enough to experience peaceful and serene dreams every night. For some, dreams can turn into nightmares, and these individuals wake up in a state of anxiety and fear. What causes these anxious dreams? Is there a connection between poor sleep and dream anxiety? In this article, we will explore this perplexing topic and attempt to unlock the connection between the two.
The Importance of Sleep and Dreams
Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for overall well-being and plays an important role in maintaining physical and mental health. Sleep is a natural process that allows our body and mind to rest and rejuvenate, so that we feel refreshed and energized when we wake up in the morning. Our sleeping patterns are regulated by a combination of biological, psychological and environmental factors, and disruptions to this delicate balance can have serious consequences.
One of the key functions of sleep is to consolidate memories and learning. During the deep stages of sleep, the brain processes information and consolidates memories, which are essential for learning and cognitive function. Dreams also play an important role in this process, as they are believed to help us process emotions and memories from the day, allowing us to integrate new experiences into our existing knowledge.
Dreaming is a normal and natural part of the sleep cycle, and most people experience several dreams each night. Dreams can be mundane, bizarre, or downright terrifying, but they all serve an important function in helping us process emotions and experiences. However, when our sleep is disrupted or insufficient, it can have a negative impact on our ability to dream and process emotions, leading to anxiety and other negative outcomes.
It’s essential to prioritize getting enough quality sleep to maintain physical and mental health, and to recognize the importance of dreaming in processing emotions and experiences. By taking steps to improve the quality of our sleep, we can ensure that our body and mind are functioning optimally, allowing us to lead happy and healthy lives.
The Link Between Poor Sleep and Dream Anxiety
It is no secret that getting a good night’s sleep is crucial for our overall health and wellbeing. During sleep, our brain is able to process and consolidate memories, regulate emotions, and perform essential restorative functions. However, when we are unable to get proper sleep, it can have negative effects on our mental health, including an increase in anxiety levels, particularly during dreams.
Poor sleep and dream anxiety are often closely linked. When we experience sleep disruptions, it can cause our brains to produce more intense dreams, and there is evidence to suggest that anxiety and stress can exacerbate this effect. Sleep disturbances can also cause a decrease in the amount of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep we get, which is a stage of sleep where dreaming is most common. As a result, we may experience more vivid and disturbing dreams, which can then cause us to wake up feeling anxious and uneasy.
Sleep and anxiety share a reciprocal relationship, meaning that each can exacerbate the other. Those who experience anxiety are more likely to suffer from sleep disturbances, and vice versa. When someone is anxious or stressed, it can make it much harder to fall asleep or to stay asleep throughout the night. In turn, this lack of quality sleep can cause exaggerated, more intense anxiety during dreams.
While occasional disruption in sleep patterns is normal, chronic poor sleep can lead to more serious mental health problems, including anxiety disorders. Thus, it is important to understand the link between poor sleep and dream anxiety and take steps to improve one’s sleep habits in order to reduce the impact on mental health.
What Causes Poor Sleep?
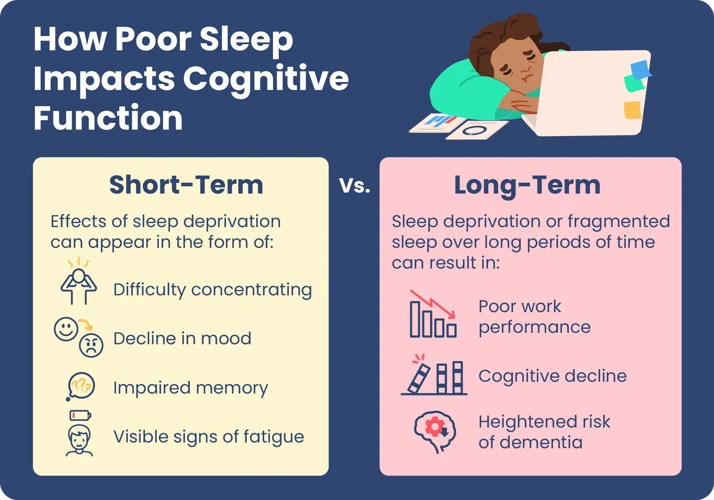
Getting a good night’s sleep is essential in maintaining an overall healthy lifestyle. However, certain sleep disorders can lead to poor sleep quality and affect one’s well-being. There are various factors that can cause poor sleep, including psychological and medical issues. Here are some of the most common issues that contribute to poor sleep:
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that affects a significant portion of the population. It is characterized by the inability to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to a lack of restorative sleep. Insomnia can be caused by stress, anxiety, depression, or medical conditions such as asthma or acid reflux.
Sleep Apnea is a severe sleep disorder in which an individual’s breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep. It occurs when the muscles at the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open. This can cause snoring, gasping, and choking noises that disrupt sleep, leading to daytime drowsiness, fatigue, and poor concentration.
Restless Leg Syndrome is a neurological disorder that causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs, leading to an irresistible urge to move them. These symptoms can worsen in the evening, leading to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Restless leg syndrome can be caused by underlying medical conditions, such as iron deficiency anemia, kidney failure, or multiple sclerosis.
Narcolepsy is a rare sleep disorder that causes excessive sleepiness during the daytime. Symptoms include sudden bouts of sleepiness, hallucinations, and loss of muscle control, known as cataplexy. Narcolepsy is caused by a deficiency in a brain chemical called hypocretin, which regulates sleep and wakefulness.
There are various sleep disorders that can lead to poor sleep quality, affecting overall health and well-being. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of these disorders and seek medical attention to improve sleep quality and reduce the impact of sleep-related anxiety.
Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, waking up too early, and having poor quality sleep. This can lead to exhaustion, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating during the day. Insomnia can be caused by various factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, and medical conditions. Some medications can also cause insomnia as a side effect.
The effects of insomnia on dream anxiety can be particularly significant. Studies have found that people with insomnia are more likely to experience vivid, disturbing dreams and nightmares. These dreams can be related to their daytime stress and anxiety, further exacerbating their sleep problems. People with insomnia tend to have a more negative emotional reaction to their dreams, which can increase their overall anxiety levels.
There are various treatments available for insomnia, including medications, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and relaxation techniques. However, it’s important to note that treating insomnia can also have a positive impact on dream anxiety. By improving the quality of sleep, people with insomnia may experience less vivid dreams and nightmares, and feel less distressed by the dreams they do have.
Insomnia is a complex sleep disorder that can have a significant impact on dream anxiety. Recognizing the link between poor sleep and dream anxiety is an important step in improving overall mental health and well-being.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can impact not only the quality of sleep but also a person’s overall health. It is characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep, which can result in frequent awakenings throughout the night. This interruption in sleep can lead to daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and irritability.
The symptoms of sleep apnea can vary from person to person, but may include: loud snoring, abrupt awakenings accompanied by gasping or choking, feeling tired throughout the day, morning headaches, difficulty staying asleep, and mood changes.
There are two types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the airway becomes blocked by soft tissue in the back of the throat or tongue, while central sleep apnea occurs when the brain fails to signal the muscles to breathe.
Factors that increase the risk of developing sleep apnea include: being overweight or obese, having a family history of sleep apnea, having a small airway in the mouth, nose, or throat, smoking, and being over the age of 40.
Left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to more serious health issues, such as: high blood pressure, stroke, heart disease, and depression.
Effective treatments for sleep apnea include: lifestyle changes such as losing weight or quitting smoking, positional therapy to encourage side sleeping, Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines, which deliver air pressure through a mask, and surgery in severe cases.
If you suspect that you have sleep apnea, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional who can help diagnose the condition and recommend an appropriate treatment plan. Taking steps to improve the quality of your sleep can also have a positive impact on reducing dream anxiety.
Restless Leg Syndrome
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. The condition is characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, especially while at rest. This sensation is often accompanied by a tingling or crawling feeling in the legs, leading to difficulty falling and staying asleep. Individuals suffering from RLS often experience disrupted sleep patterns and excessive daytime fatigue, contributing to the development of dream anxiety.
The exact cause of RLS is unknown, but several risk factors may increase an individual’s likelihood of developing the condition. Genetics, iron deficiency, chronic diseases, and pregnancy may all contribute to the development of RLS. Additionally, certain medications and substances, such as caffeine and nicotine, can exacerbate symptoms.
Since RLS directly impacts an individual’s ability to fall asleep and remain asleep, it can contribute to the development of dream anxiety. The constant urges and disturbances to restful sleep can cause heightened emotional reactivity, making people more susceptible to nightmares and anxiety-inducing dreams.
Treating RLS requires a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle changes, medications, and therapy. Lifestyle changes may include reducing caffeine and alcohol consumption, increasing exercise, and establishing a regular sleep routine. Medications such as dopamine agonists and iron supplements can help alleviate symptoms, while therapy can help individuals manage the emotional distress and anxiety associated with the condition.
It is critical for individuals suffering from RLS to seek treatment to address their sleep disturbances and manage any resulting anxiety. By implementing the proper management techniques, individuals can improve their overall sleep quality, reducing the likelihood of developing dream anxiety.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder that affects a small percentage of the population, but can have significant consequences on their daily lives. This disorder is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), which can cause individuals to fall asleep at inappropriate times and places, such as in the middle of a conversation or while driving. Narcolepsy can also cause sudden muscle weakness or paralysis, known as cataplexy, which can be triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or anger.
The exact cause of narcolepsy is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors. One theory is that it is caused by the loss of a type of brain cell called hypocretin, which helps regulate wakefulness and sleep. Other potential causes include autoimmune disorders or infections.
Living with narcolepsy can be challenging, not only because of the sudden onset of sleep, but also the social stigma that often accompanies it. Many people with this disorder are mistakenly labeled as lazy or unmotivated, when in reality they have a serious and debilitating medical condition.
In addition to impacting daily life, narcolepsy can also have a negative impact on dream anxiety. Because individuals with narcolepsy experience disrupted sleep patterns, they may be more likely to experience vivid and disturbing dreams, which can lead to an increase in dream-related anxiety.
Treatment options for narcolepsy typically involve a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. Stimulants such as modafinil or armodafinil can be used to help improve alertness during the day, while antidepressants or sodium oxybate may be used to manage cataplexy or improve nighttime sleep. Additionally, establishing a regular sleep schedule and sticking to a healthy diet and exercise regimen can help manage symptoms.
Narcolepsy is a complex and challenging sleep disorder that can have significant effects on an individual’s daily life and mental health. Seeking proper diagnosis and treatment is essential in order to manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
The Effects of Poor Sleep on Dream Anxiety
Poor sleep is known to have negative consequences on various aspects of mental and physical health, including the development of anxiety-related conditions. One area where the impact of poor sleep is becoming increasingly apparent is with regards to dream anxiety. Research indicates that poor sleep can have a significant effect on the nature of dreams and can lead to the development of anxiety-related issues.
Increased Emotional Reactivity
One of the most significant effects of poor sleep on dream anxiety is an increase in emotional reactivity. This means that individuals who experience poor sleep are more susceptible to experiencing emotional responses during their dreams. This heightened emotional reactivity can cause individuals to experience more intense emotional responses, which can contribute to the development of anxiety-related issues.
Worsening of Trauma-Related Nightmares
Individuals who have experienced trauma may be more susceptible to experiencing trauma-related nightmares. Poor sleep quality can make these nightmares more frequent and more severe, which can have a significant impact on mental health. Trauma-related nightmares can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues, making it essential to address poor sleep quality to improve overall mental health.
Heightened State of Anxiety
Poor sleep quality can also increase an individual’s overall level of anxiety. Individuals who suffer from poor sleep may be more prone to experiencing anxiety during the day, leading to an overall increase in anxiety levels. This heightened state of anxiety can exacerbate existing anxiety symptoms, leading to a vicious cycle that can be difficult to break.
Increased Prevalence of Nightmares
Research indicates that poor sleep quality can lead to an increase in nightmares. Nightmares can cause individuals to wake up feeling anxious and stressed, with these feelings often lingering throughout the day. Over time, this can lead to the development of anxiety-related issues, making it essential to address poor sleep quality to reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
Poor sleep quality can have significant effects on dream anxiety. The increased emotional reactivity, worsening of trauma-related nightmares, heightened state of anxiety, and increased prevalence of nightmares are all indicators of the connection between poor sleep and dream anxiety. It is imperative to establish healthy sleep habits, address sleep disorders, and manage stress to reduce the impact of poor sleep on mental health.
Increased Emotional Reactivity
Poor sleep has a significant impact on our emotional well-being, particularly in terms of our ability to regulate our emotions. When we are sleep-deprived, our brain becomes more reactive to negative stimuli and less responsive to positive ones. This means that even small setbacks or negative experiences can trigger strong emotional reactions. This is known as increased emotional reactivity.
Studies have shown that even one night of poor sleep can lead to increased emotional reactivity. This is because sleep deprivation affects the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for regulating our emotions. When this part of the brain is not functioning properly due to lack of sleep, we become more vulnerable to negative emotions like anxiety, fear, and anger.
This increased emotional reactivity can have a significant impact on our overall mental health. It can lead to more frequent mood swings, difficulty managing stress, and increased anxiety or depression. Over time, it can even lead to a reduced ability to cope with challenging situations or emotional stressors.
Additionally, if someone already suffers from a mental health disorder, such as anxiety or depression, poor sleep can exacerbate their symptoms. The increased emotional reactivity caused by poor sleep can make it even harder to manage these conditions and may lead to worsening symptoms over time.
It is crucial to understand the impact of poor sleep on emotional reactivity, and to take steps to prioritize healthy sleep habits to fully manage mental health.
Worsening of Trauma-Related Nightmares
Individuals who have experienced trauma may be particularly vulnerable to nightmares, and poor sleep can exacerbate this condition. Trauma-related nightmares are often vivid and realistic, and they can be extremely distressing for the individual experiencing them. These nightmares may be related to past traumatic experiences, and in some cases, they may be re-experiencing the trauma during sleep.
When an individual experiences poor sleep regularly, it can worsen the frequency and intensity of these trauma-related nightmares. This may occur due to the fact that the brain does not have time to properly process and consolidate traumatic memories during REM sleep. REM sleep is essential for healthy cognition, emotion regulation, and memory consolidation.
Additionally, trauma-related nightmares may increase general anxiety and promote fear avoidance, which can develop into a self-perpetuating cycle of anxiety and sleep disruption. The more disturbed sleep a person has, the more afraid of sleep they can become, which leads to more nightmares and ultimately, even less quality sleep. This vicious cycle can lead to a significant decline in overall quality of life.
Improving sleep quality is essential for individuals dealing with trauma-related nightmares. Sleep hygiene factors, such as reduction of caffeine, alcohol, and screen time before bed, can help improve sleep onset and overall sleep quality. In addition to these non-pharmacological methods, certain medications, such as prazosin, may be prescribed to help reduce the frequency and severity of nightmares in individuals with PTSD. It’s important for individuals to work with a healthcare professional to find the best treatment approach for them.
Understanding the connection between poor sleep and trauma-related nightmares underscores the importance of sleep in maintaining physical and mental health. Sleep hygiene promotion and management of sleep disorders are essential strategies for addressing trauma-related nightmares and improving overall quality of life.
Heightened State of Anxiety
Poor sleep is not only associated with an increase in nightmares, but it can also lead to a heightened state of anxiety. When we don’t get enough restful sleep, our bodies go into a state of hyperarousal, making us more sensitive to stress and anxiety triggers. This makes us more likely to experience anxious feelings during the day and to feel more anxious in our dreams at night.
During sleep, our bodies release hormones that help regulate our moods and emotions. One of these hormones is cortisol, also known as the “stress hormone”. When we don’t get enough sleep, our cortisol levels can increase, leading to a constant state of anxiety. This can cause us to feel worried or stressed even when there are no real threats to our safety.
Poor sleep can also affect our ability to deal with stress and anxiety. A lack of restful sleep can make it difficult for us to regulate our emotions and feelings, leaving us feeling overwhelmed and anxious in response to challenging situations. This can lead to a vicious cycle, where poor sleep leads to heightened anxiety, which in turn makes it even harder for us to sleep well.
It is crucial to address poor sleep to manage anxiety levels. Establishing a regular sleep routine and reducing stress before bed can help calm the mind and promote restful sleep. Additionally, managing any underlying sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, can also improve the quality of sleep and alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Poor sleep can lead to a heightened state of anxiety, making it difficult for individuals to manage stress and regulate their emotions. By addressing poor sleep through healthy sleep habits and managing any underlying sleep disorders, individuals can improve the quality of sleep and reduce their levels of anxiety.
Increased Prevalence of Nightmares
Poor sleep can also lead to an increased prevalence of nightmares. Nightmares are vivid, distressing dreams that often wake an individual up during the night. Nightmares can cause fear, anxiety, and a variety of other negative emotions that can linger throughout the day.
When an individual doesn’t get enough quality sleep, their brain may spend more time in REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is the stage of sleep in which most dreaming occurs. This increases the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Poor sleep quality can also exacerbate the emotional intensity of nightmares, making them even more distressing.
Individuals who suffer from mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, are more likely to experience nightmares, and poor sleep can exacerbate these conditions. Anxiety-provoking dreams can also cause an increase in overall anxiety levels, making it even harder for individuals to get the restful sleep their body needs.
An increased prevalence of nightmares due to poor sleep can have a negative impact on an individual’s mood, productivity, and overall well-being. It’s imperative to address any issues with sleep quality in order to minimize the impact of nightmares on mental and emotional health.
Improving Sleep to Reduce Dream Anxiety
Getting enough restful sleep is essential for maintaining good physical and mental health. Poor sleep, on the other hand, can negatively impact a person’s overall well-being in various ways. In this article, we have discussed how poor sleep can be linked to dream anxiety and explored some of the causes of poor sleep. Now, let’s take a closer look at some strategies to improve sleep quality and reduce dream anxiety.
Establishing a Healthy Sleep Routine: First and foremost, it’s crucial to establish a healthy sleep routine. This includes setting a consistent bedtime and wake-up time every day, even on weekends. It also means creating a relaxing atmosphere in the bedroom, keeping it cool, dark, and quiet. Avoid watching TV, reading, or working in bed as these activities can stimulate the mind, making it harder to fall asleep. A regular bedtime routine, such as taking a warm bath or drinking herbal tea, can also help signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
Reducing Stress Before Bed: Stress and anxiety can cause sleeping difficulties, resulting in more dreams and nightmares. Finding ways to reduce stress before bed can improve the quality of sleep and minimize the occurrence of dream anxiety. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or gentle yoga stretches to calm the mind and soothe the body. Dim the lights, listen to soft music or soothing sounds, or read a book to promote relaxation and help switch off your brain.
Managing Sleep Disorders: If you have been diagnosed with a sleep disorder like insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy, work with your doctor or a sleep specialist to manage your condition effectively. They may recommend medication, therapy, or lifestyle changes to help improve the quality of your sleep.
The quality of sleep can have a profound effect on our mental health and well-being. Poor sleep can contribute to increased dream anxiety and have negative consequences for our emotional stability. It’s important to take steps to establish healthy sleep habits, reduce stress before bed, and manage any diagnosed sleep disorders. These strategies can help you get better sleep and reduce the chances of experiencing disruptive dreams and nightmares.
Establishing a Healthy Sleep Routine
Creating a healthy sleep routine can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of experiencing dream anxiety. It is essential to maintain a consistent sleep schedule, which means waking up and going to bed at the same time every day, even on the weekends. This helps regulate the body’s internal clock, leading to more restful sleep.
In addition to having a consistent sleep schedule, it is crucial to create a relaxing environment in the bedroom. Keep the room cool, quiet, and dark to promote restful sleep. Avoid using electronics in bed, as the blue light emitted from screens can disrupt the body’s natural sleep cycle.
Another important aspect of establishing a healthy sleep routine is creating a relaxing bedtime routine. This can include activities such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or practicing meditation or deep breathing exercises. Avoid stimulating activities like watching television or working right before bed.
It is also important to limit caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. Both can interfere with sleep quality and lead to restlessness and anxiety.
By establishing a healthy sleep routine, individuals can improve the quality of their sleep, reduce the likelihood of experiencing dream anxiety, and wake up feeling refreshed and energized.
Reducing Stress Before Bed
One important way to improve sleep and reduce dream anxiety is to reduce stress before bed. High levels of stress can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep, leading to poor quality sleep overall.
There are several strategies you can use to reduce stress before bed:
Firstly, it can be helpful to establish a relaxing bedtime routine. This could involve taking a warm bath, practicing relaxation exercises such as deep breathing or meditation, or listening to calming music or a guided relaxation recording. By doing these activities consistently before bed, your body will begin to associate them with sleep and relaxation, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Another way to reduce stress before bed is to create a calming sleep environment. This could involve making sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet, and creating a comfortable sleeping space that promotes relaxation. It can also be helpful to limit technology use before bed and avoid stimulating activities such as exercise or work in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Additionally, practicing stress-reducing techniques throughout the day can also help improve sleep and reduce dream anxiety:
Regular exercise promotes physical and emotional well-being and can reduce stress levels overall. It is important to avoid exercising too close to bedtime, however, as this can stimulate the body and make it more difficult to fall asleep.
Mindfulness practices, such as yoga or meditation, can also be helpful in reducing stress and promoting relaxation throughout the day. By regularly engaging in these types of activities, you may find that you are better able to manage stress and anxiety, leading to improved sleep and reduced dream anxiety.
Reducing stress before bed is an important step in improving sleep and reducing dream anxiety. By establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, creating a calming sleep environment, and practicing stress-reducing techniques throughout the day, you can improve your overall well-being and sleep more soundly.
Managing Sleep Disorders
For many people, the root cause of poor sleep is a sleep disorder. These disorders can range from mild to severe and can have a significant impact on one’s overall sleep quality. However, managing sleep disorders can greatly improve one’s sleep quality and reduce the symptoms of dream anxiety.
Insomnia: Insomnia is the most common sleep disorder and is characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. There are several strategies that can be employed to manage insomnia, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, sleep hygiene practices, and medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy focuses on changing the negative thought processes and behaviors that contribute to insomnia, while sleep hygiene practices involve establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing sleep environment. Sometimes, medication may be prescribed in conjunction with these strategies to help individuals fall asleep and stay asleep.
Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder in which an individual’s breathing pauses and restarts throughout the night, often causing loud snoring or choking. Treatment for sleep apnea may involve the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine or oral appliances that keep the airway open during sleep. Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime, may also help alleviate symptoms of sleep apnea.
Restless Leg Syndrome: Restless leg syndrome (RLS) is a sleep disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move one’s legs, often accompanied by an uncomfortable sensation. Lifestyle changes, such as improving one’s diet and exercise routine, and medication may be helpful for managing RLS symptoms.
Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks. Treatment may involve medication to promote wakefulness during the day or medication to control rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which may reduce the prevalence of dream-related symptoms.
Managing sleep disorders may require the help of a healthcare professional or sleep specialist. However, taking steps to address these underlying conditions can greatly improve one’s overall sleep quality and reduce the symptoms of dream anxiety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, poor sleep can have a significant impact on dream anxiety. When we do not get enough restful sleep, our emotional reactivity increases, causing us to feel heightened anxiety throughout the day, and often leading to a higher prevalence of nightmares. This can be especially problematic for individuals who already struggle with anxiety or trauma-related disorders.
It is essential to identify the root cause of poor sleep, be it insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy. Once identified, there are various strategies that can be employed to improve sleep quality, such as establishing a healthy sleep routine, managing stress before bed, and effectively managing any sleep disorders. These interventions can help individuals get better quality sleep, reducing the risk of experiencing dream anxiety.
It is also worth noting that dreams, while sometimes connected to anxiety, can also be a source of creativity, insight, and personal growth. Dreams allow individuals to process emotions and experiences in a safe environment, helping us to better understand ourselves and the world around us. As such, it is important to maintain a healthy balance between healthy sleep patterns and embracing the potential benefits of our dream world.
In sum, by recognizing the link between poor sleep and dream anxiety and taking steps to improve sleep quality, individuals can experience a reduction in anxiety and better overall mental health. So, prioritize your sleep and take the necessary steps to ensure a peaceful night’s rest in order to achieve your best self.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dream anxiety?
Dream anxiety refers to feelings of fear, stress, and anxiety that occur during dreams, which can lead to sleep disturbances and waking up feeling unrefreshed.
How common is poor sleep?
Poor sleep is very common, affecting up to 30% of adults in the United States.
What is insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, or waking up too early in the morning.
What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep, leading to loud snoring and daytime fatigue.
What is restless leg syndrome?
Restless leg syndrome is a neurological disorder that causes an uncontrollable urge to move your legs, often leading to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
What is narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep during the day.
How does poor sleep affect emotional reactivity?
Poor sleep can increase emotional reactivity, leading to heightened feelings of anxiety, stress, and depression.
How does poor sleep impact trauma-related nightmares?
Poor sleep can worsen trauma-related nightmares, making them more vivid and frequent.
Can poor sleep lead to an increased prevalence of nightmares?
Yes, poor sleep can increase the prevalence of nightmares, leading to sleep disturbances and daytime fatigue.
What can I do to improve my sleep and reduce dream anxiety?
You can establish a healthy sleep routine, reduce stress before bed, and manage any sleep disorders you may have to improve your sleep and reduce dream anxiety.









