We’ve all experienced the disturbing feeling of waking up from a nightmare, heart racing and palms sweating. But what happens when those nightmares become recurring, haunting us night after night? The psychological impact of recurring nightmares can be profound, leading to increased anxiety, stress, and even depression. In this article, we’ll explore the causes of recurring nightmares, their potential impacts on our mental health, and effective strategies for dealing with them. Through this exploration, we hope to provide insight and support for those who are struggling with the distressing effects of recurring nightmares.
What are Recurring Nightmares?
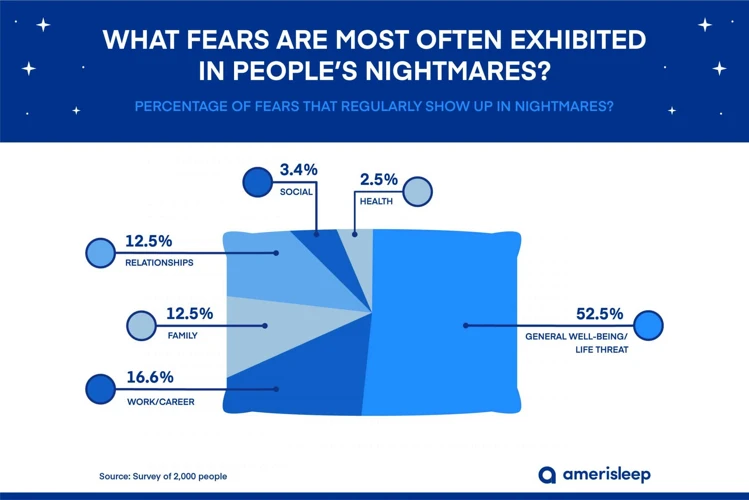
Recurring nightmares are vivid and frightening dreams that keep repeating themselves. These nightmares can occur in both adults and children, and can be disturbing enough to disrupt sleep or prevent a person from going back to sleep. Recurring nightmares often involve similar themes, characters, or situations, and the dreamer’s emotional response to them is usually quite intense.
Definition: Recurring nightmares are nightmares that persist over time and happen frequently. These nightmares are different from typical nightmares, which are occasional and don’t follow a pattern.
Causes: The causes of recurring nightmares can vary from person to person. Some of the most common causes include stress, anxiety, trauma, medications, and sleep disorders. Stress and anxiety can trigger nightmares because they create a state of hyperarousal, which makes it difficult for the mind to relax and let go. Trauma can also trigger recurring nightmares, as individuals who have experienced traumatic events may continue to relive those experiences in their dreams.
Types of Recurring Nightmares: There are several types of recurring nightmares, including ones related to personal safety, death and dying, being chased, falling, and natural disasters. Personal safety nightmares often involve being attacked, either physically or sexually. Death and dying nightmares can involve the dreamer or someone close to them dying or being already dead. Being chased nightmares involve being pursued by someone or something that wants to harm the dreamer. Falling nightmares involve falling from a great height, often without any support to hold onto. Natural disaster nightmares involve being caught in a hurricane, tornado, or other catastrophic event.
Recurring nightmares can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health, causing anxiety, depression, and PTSD. They can also negatively affect a person’s sleep and daily life. Fortunately, there are several techniques that can help an individual deal with recurring nightmares, including journaling, visualization, therapy, relaxation techniques, and medication. It’s also possible to prevent recurring nightmares by making lifestyle changes and avoiding triggers. In severe cases, professional help should be sought.
Definition
Recurring nightmares can be a distressing experience that can have a significant impact on mental health and overall wellbeing. Before delving into the effects of recurring nightmares, it is important to define what they are. In simple terms, recurring nightmares are powerful and vivid dreams that occur repeatedly over a period of time, causing negative emotions and physical responses. These vivid dreams can often leave individuals feeling confused, scared, and in some cases, traumatized. Understanding the definition of recurring nightmares is essential in recognizing the gravity of the situation and taking action to prevent long-term negative consequences.
Causes
Recurring nightmares can have various underlying causes, ranging from psychological to physical factors. The following table outlines some of the common causes of recurring nightmares:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Stress and Anxiety | When a person is under a lot of stress or experiencing anxiety, their brain may continue to process these emotions during sleep, leading to recurring nightmares. |
| Past Trauma | People who have experienced past traumatic events may be more susceptible to recurring nightmares. This is because the brain may continue to process the emotions and memories associated with the trauma during sleep. |
| Medication or Substance Use | Certain medications or substances, such as antidepressants or alcohol, can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to nightmares. |
| Physical Illness | Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to nightmares. Additionally, certain illnesses or conditions, such as fever or PTSD, can cause nightmares. |
| Emotional Triggers | Some people may experience recurring nightmares due to exposure to certain emotional triggers, such as watching a scary movie or experiencing a recent breakup. |
It is important to identify the underlying cause of recurring nightmares in order to effectively address and manage them. In some cases, seeking professional help may be necessary to address the underlying cause and alleviate the recurrence of nightmares.
Types of Recurring Nightmares
Recurring nightmares can be fodder for terrifying stories that keep us up all night or make us afraid to sleep altogether. According to research, there are several common types of recurring nightmares that people experience.
1. Chase Dreams: These dreams are characterized by being pursued by someone or something that wants to harm you. The person or thing chasing you can differ from dream to dream, but the sense of fear and panic is always present.
2. Falling Dreams: In these dreams, the dreamer experiences a sudden, frightening sensation of falling from a great height. This type of dream is often accompanied by a physical reaction, such as a jolt awake.
3. Being Trapped Dreams: In these nightmares, the dreamer feels trapped or confined in some way. This can manifest in various scenarios, such as being locked in a small space or being unable to move.
4. Losing Control Dreams: These nightmares often involve the dreamer being powerless or unable to control the situation they’re in. This can include losing control of a vehicle or finding themselves in a dangerous, uncontrollable scenario.
5. Test Dreams: These dreams are characterized by feelings of anxiety or stress related to an upcoming test or performance. It’s common for people who are preparing for high-stakes exams to experience test dreams.
6. Failing Dreams: Failing dreams can be related to test dreams, but the sense of failure is not always limited to academic performance. These dreams can manifest as losing a job, failing to complete a task or project, or any other situation that elicits feelings of disappointment or shame.
It’s important to note that while these are common types of recurring nightmares, they are not the only ones. Some people may experience nightmares that are unique to their own anxieties and fears. Regardless of the type of nightmare, they can take a toll on our mental health and well-being if they continue to recur.
The Psychological Impact of Recurring Nightmares
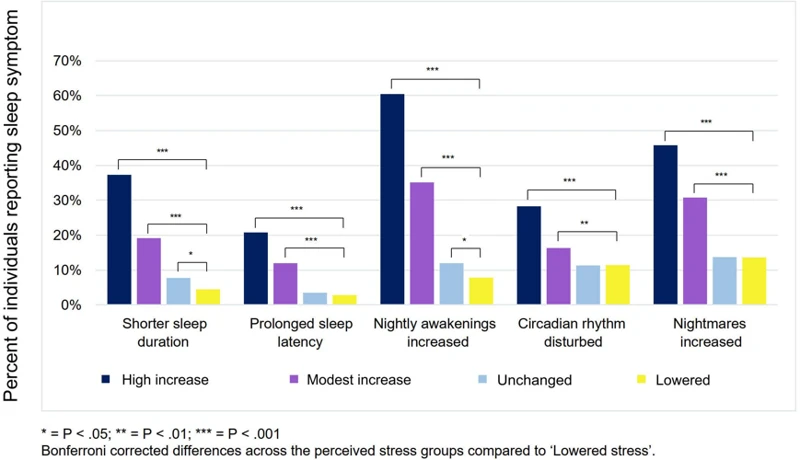
Recurring nightmares can have a significant psychological impact on individuals who experience them. The vivid and terrifying nature of these dreams can lead to feelings of anxiety, stress, and even depression. Additionally, they can disrupt sleep and interfere with daily activities, leading to a decrease in overall quality of life.
Anxiety and Stress
Recurring nightmares often revolve around themes of danger, death, or other traumatic events. These dreams can leave individuals feeling anxious and stressed, leading to persistent worrying and feelings of unease. The fear of having another nightmare can also lead to a general sense of apprehension and hyper-vigilance, making it difficult to relax and enjoy life.
Depression
In some cases, recurring nightmares can contribute to the development of depression. The constant barrage of distressing imagery and emotions can leave individuals feeling hopeless, helpless, and overwhelmed. Additionally, the interruption of sleep can disrupt important brain functions that regulate mood, leading to feelings of sadness and despair.
PTSD
For individuals who have experienced trauma, recurring nightmares can be a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These dreams can be a reenactment of the traumatic event, leading to intense feelings of fear and distress. The nightmares can also trigger other symptoms of PTSD, such as flashbacks, avoidance, and hyperarousal, which can have a significant impact on daily functioning.
Effects on Sleep and Daily Life
Recurring nightmares can interfere with quality sleep, leading to daytime drowsiness and difficulty concentrating. Additionally, the emotional impact of the nightmares can spill over into daily life, leading to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty with routine activities. These symptoms can have a negative impact on relationships, work, and overall quality of life.
The psychological impact of recurring nightmares should not be underestimated. These dreams can lead to significant distress and interfere with daily functioning. However, there are strategies available to deal with and prevent recurring nightmares, such as journaling, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Seeking professional help may also be necessary for individuals who are struggling to cope.
Anxiety and Stress
The psychological impact of recurring nightmares can lead to a range of emotional issues that can significantly affect one’s overall wellbeing. Among the most prevalent of these issues are anxiety and stress, which can be exacerbated by the disturbing and recurrent nature of nightmares. These negative emotions can be incredibly crippling and take a toll on one’s mental health. From constant feelings of unease to heightened nervousness and paranoia, the impact of anxiety and stress can be overwhelming and can often lead to a downward spiral leading towards further health issues. Let’s delve deeper into how recurring nightmares can lead to anxiety and stress and the implications for mental health.
Depression
Recurring nightmares don’t just affect a person’s sleep, but they can have serious impacts on one’s mental health. Depression is one of the most common psychological effects of recurring nightmares. Here are some ways in which recurring nightmares can lead to depression:
- Reduced quality of sleep: Recurring nightmares often lead to reduced sleep quality, which can trigger depression. Lack of sleep can lead to a chemical imbalance in the brain and may even cause changes in brain structure, leading to depression.
- Increased anxiety: Recurring nightmares may increase anxiety levels in the affected person, leading to feelings of hopelessness, sadness, and even suicidal thoughts.
- Disrupted daily life: Constant fear of experiencing recurring nightmares can make it difficult for people to carry out their daily routine, leading to social isolation, low self-esteem and eventually depression.
- Emotional turmoil: Recurring nightmares typically involve the person experiencing intense fear, trauma or sadness. This can lead to feelings of discomfort, agitation, and distress, which in turn can lead to depression.
It’s crucial to recognize and seek help for depression caused by recurring nightmares. Some coping mechanisms include journaling, cognitive-behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques or medication. It is important to speak to a mental health professional who can help navigate this difficult experience and provide appropriate treatment options.
PTSD
One of the most severe psychological impacts of recurring nightmares is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). This condition can develop after exposure to a traumatic event, such as a serious accident, natural disaster or violence. People with PTSD often experience a range of symptoms, including intrusive memories, flashbacks, and nightmares.
Recurring nightmares in people with PTSD can be particularly distressing, as they often relive the traumatic event in vivid detail. The nightmares can also interfere with their ability to get restful sleep. This can lead to feelings of exhaustion, difficulty concentrating during the day and other physical health issues.
PTSD can also cause a range of emotional and psychological symptoms, including irritability, anxiety, depression and hypervigilance. People with PTSD may also experience a sense of detachment from others and find it difficult to connect with friends and family.
It is not uncommon for people with PTSD to develop other conditions such as substance abuse or suicidal thoughts. Early diagnosis and treatment of PTSD is vital to improving a person’s overall quality of life.
Table:
| Symptoms of PTSD | Effects of Recurring Nightmares |
|---|---|
| Intrusive memories | Reliving traumatic event in detail through nightmares |
| Flashbacks | Hindered ability to get restful sleep |
| Anxiety | Exhaustion and physical health issues |
| Depression | Difficulty concentrating during day |
| Hypervigilance | Interference with normal daily activities |
Recurring nightmares can have a profound impact on a person’s mental and physical health. Seeking professional help and utilizing various coping mechanisms can aid in reducing the frequency and severity of these nightmares.
Effects on Sleep and Daily Life
Recurring nightmares can have a significant impact on an individual’s sleep and daily life. Here are some of the most common effects:
- Difficulty sleeping: People who experience recurring nightmares often struggle to fall asleep or stay asleep. They may also experience frequent awakenings throughout the night.
- Daytime fatigue: As a result of disrupted sleep, individuals with recurring nightmares may feel tired and fatigued during the day.
- Anxiety: Recurring nightmares can lead to increased anxiety and fear, both during waking hours and at night. This can cause a person to avoid certain activities or situations in an attempt to prevent triggering their nightmares.
- Difficulty concentrating: Fatigue and anxiety can also make it difficult for individuals with recurring nightmares to concentrate on tasks or remember important details.
- Mood changes: Chronic nightmares can lead to changes in mood, including irritability, mood swings, and feelings of hopelessness or despair.
- Physical symptoms: In some cases, recurring nightmares can also cause physical symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, or stomach problems.
While it’s common for people to experience nightmares from time to time, the consistent disruption to one’s sleep patterns and daily life caused by recurring nightmares can be detrimental. It’s important to seek professional help if the impact of recurring nightmares is significant and is affecting one’s quality of life.
How to Deal with Recurring Nightmares

Experiencing recurring nightmares can be a distressing and frustrating experience that can greatly impact one’s quality of life. But there are ways to deal with them.
Journaling and Visualization: Keeping a dream journal can be a helpful way to identify patterns or triggers behind recurring nightmares. Writing down the details of the dream and any emotions felt can help bring awareness to the subconscious and the underlying issues causing the dreams. Visualization techniques, such as imagining a different, more positive outcome to the nightmare, can also be helpful in reducing the anxiety surrounding the dream.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: CBT is a type of therapy that aims to change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to psychological problems. A therapist can work with individuals experiencing recurring nightmares to identify and address the underlying issues behind the dreams. CBT can help to change the way individuals think and feel about their nightmares, reducing the impact they have on daily life.
Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation, can be helpful in reducing the levels of anxiety and stress that contribute to recurring nightmares. These techniques can promote relaxation and calmness, helping individuals to better manage the emotions associated with their nightmares.
Medication: In certain cases, medication may be prescribed by a healthcare professional to help manage the symptoms of recurring nightmares. This option may be considered for individuals experiencing severe sleep disturbances or for those whose nightmares are associated with conditions such as PTSD.
Preventing Recurring Nightmares: There are certain lifestyle changes that can help prevent recurring nightmares, such as maintaining a regular sleep routine, avoiding certain foods or medications, and reducing exposure to stressful situations. It can also be helpful to identify and avoid triggers that contribute to nightmares, such as watching scary movies or experiencing traumatic events.
If recurring nightmares persist despite self-help techniques and lifestyle changes, it may be time to seek professional help. A therapist or healthcare provider can provide additional support and guidance in managing nightmares and addressing the underlying psychological issues. Remember that it is possible to overcome recurring nightmares and improve your quality of life.
Journaling and Visualization
Exploring different ways to cope with recurring nightmares can be a daunting task, but it is essential to find effective solutions. One such way is journaling and visualization. It is a simple yet powerful technique that helps individuals to uncover underlying emotions and fears, leading to a better understanding of the cause of their recurring nightmares. Through creating a written record of their dreams, they can begin to identify patterns and themes, and create a sense of control over their experiences. Additionally, the use of visualization techniques can help them replace negative emotions and recurring dreams with positive experiences, assisting with reducing the frequency and intensity of their nightmares. Let’s learn more about these effective techniques.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that focuses on identifying negative thought patterns and behaviors and replacing them with positive ones. It is a widely used treatment for recurring nightmares, as it aims to help individuals confront and overcome their fears.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative patterns of thinking and behavior. It is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected, and that changing one can help improve the others.
In the context of recurring nightmares, CBT can help individuals identify and challenge the negative thoughts and beliefs that may be contributing to their nightmares. This process involves several steps, including:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Identifying negative thoughts | The first step in CBT is to identify the negative thoughts or beliefs that may be contributing to the nightmares. This can involve keeping a journal to track the content of the nightmares and the thoughts and emotions associated with them. |
| Challenging negative thoughts | Once negative thoughts have been identified, the next step is to challenge them. A therapist may ask the individual to examine the evidence for and against their negative beliefs, helping them to develop a more balanced and realistic perspective. |
| Developing coping strategies | CBT also involves developing coping strategies to deal with the fear and anxiety associated with nightmares. This can involve relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, and other strategies for managing stress. |
| Testing new beliefs | Finally, CBT involves testing new beliefs by confronting the situations that previously triggered nightmares. This can involve exposure therapy, in which the individual is gradually exposed to the feared situation or stimulus in a safe and controlled environment. |
CBT can be an effective treatment for recurring nightmares, helping individuals to overcome their fears and develop more positive thought patterns and coping strategies. If you are struggling with recurring nightmares, consider speaking with a therapist to learn more about CBT and other treatment options.
Relaxation Techniques
One effective way to deal with recurring nightmares is through the use of relaxation techniques. These techniques aim to reduce stress and anxiety levels, allowing the individual to fall into a more peaceful state of mind. Here are some examples of relaxation techniques that can be helpful:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | This technique involves taking slow and deep breaths, focusing on the sensation of the air filling your lungs and then slowly releasing it. It helps to calm the nervous system and reduce anxious thoughts. |
| Muscle Relaxation | This technique involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups throughout the body, helping to release physical tension and reduce anxiety. |
| Meditation | This technique involves focusing on a particular object, thought, or sensation and allowing thoughts to drift away. It helps to cultivate a sense of calmness and mental clarity, reducing the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares. |
| Aromatherapy | This technique involves using fragrances or essential oils to promote relaxation and calmness. Certain smells like lavender, chamomile and sandalwood have been found to have a relaxing effect. |
All of these relaxation techniques can be done at home or with the assistance of a professional. It’s important to figure out which technique works best for you and to implement it regularly in order to see the most benefits. By incorporating these techniques into your daily routine, you can help reduce the impact of recurring nightmares on your mental health and overall wellbeing.
Medication
Medication can be helpful in treating recurring nightmares, especially if the root cause is a mental health condition such as anxiety or PTSD. However, it is important to note that medication should always be prescribed by a qualified healthcare professional and should only be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
There are several types of medications that may be used to treat recurring nightmares. These include:
| Medication | How it Works | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Help regulate serotonin in the brain, which can improve mood and reduce anxiety. | Nausea, drowsiness, insomnia, sexual dysfunction. |
| Beta Blockers | Reduce the effects of adrenaline and can help to reduce anxiety symptoms. | Fatigue, dizziness, lowered blood pressure. |
| Anti-Anxiety Medications | Help to reduce anxiety symptoms and induce a state of relaxation. | Drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination. |
| Antipsychotics | Can help to reduce symptoms of psychosis, which can be a contributing factor to recurring nightmares. | Drowsiness, weight gain, dry mouth. |
It is important to note that while medication can be effective in treating recurring nightmares, it is not a cure-all solution. Medication should always be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as therapy or lifestyle changes.
Additionally, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider when taking medication for recurring nightmares, as some medications can have potential side effects and may not be suitable for everyone. It is also important to follow the prescribed dosages and not to exceed them, as this can lead to further health problems.
Medication can be a helpful tool in treating recurring nightmares, but it should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan and under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
Preventing Recurring Nightmares

Recurring nightmares can be quite distressing and can significantly affect one’s quality of life. While there are various ways to deal with these nightmares, preventing them in the first place is always the best course of action. Here are some effective ways to prevent recurring nightmares:
Lifestyle Changes: Making some lifestyle changes can help reduce the likelihood of recurring nightmares. These changes may include things like getting enough exercise, eating a healthy diet, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and establishing a consistent sleep routine. All of these measures can promote better sleep, which in turn can help prevent nightmares.
Avoid Triggers: Recurring nightmares are often triggered by particular situations, events, or emotions. Identifying these triggers and avoiding them is an effective way to prevent the nightmares. Triggers may include stress, anxiety, trauma, or even certain medications. By avoiding these triggers, you can reduce the likelihood of recurring nightmares.
Another method for preventing recurring nightmares is to practice good sleep hygiene. This means establishing good habits around bedtime, such as keeping the bedroom cool and dark, avoiding screens for at least an hour before bedtime, and winding down before getting into bed. By establishing a consistent sleep routine and sticking to it, you can train your body to expect restful sleep rather than restless nights filled with nightmares.
It’s also important to address any underlying mental health issues that may be contributing to your recurring nightmares. These issues may include anxiety, depression, or PTSD. Seeking the advice of a mental health professional can help you develop coping strategies and work through any unresolved emotions that may be affecting your sleep.
Preventing recurring nightmares involves making some lifestyle changes, avoiding triggers, practicing good sleep hygiene, and addressing any underlying mental health issues. By taking proactive steps to prevent these nightmares, you can improve your quality of life and enjoy more restful, peaceful sleep.
Lifestyle Changes
As we’ve explored the causes and types of recurrent nightmares, it’s important to acknowledge that lifestyle choices can also play a significant role in their occurrence. Making changes to your daily routine and habits can help prevent recurring nightmares and improve your overall well-being. These changes can be small yet impactful, and may take some time to implement, but with consistency can lead to a better night’s sleep. Let’s take a closer look at some of the lifestyle changes you can make to tackle recurring nightmares.
Avoid Triggers
People may experience recurring nightmares due to certain triggers. These triggers can be related to daily life stressors, traumatic events, or exposure to certain media. To prevent or reduce the frequency of recurring nightmares, it is important to avoid these triggers as much as possible.
| Type of Trigger | Prevention Tips |
| — | — |
| Daily life stressors | Reduce stress through exercise, meditation, or therapy. Avoid consuming caffeine and alcohol before bed. Establish a consistent sleep schedule. |
| Traumatic events | Seek therapy or counseling to process and heal from the trauma. Avoid activities, people, or places that may remind you of the event. |
| Media exposure | Avoid watching or reading content that may be triggering or disturbing. Before bed, engage in calming activities such as reading or listening to relaxing music instead. |
It is essential to acknowledge and address the triggers that lead to recurring nightmares to reduce their impact on daily life. By making changes in one’s lifestyle and seeking professional help if needed, individuals can take control of their sleep and well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help
It’s important to know when to seek professional help if you’re experiencing recurring nightmares. If your nightmares are causing significant distress, interfering with your daily life, or have lasted for more than a month, it’s recommended to seek help from a mental health professional.
A therapist can help you identify the underlying cause of your nightmares and develop a treatment plan. They can also provide tools and techniques to help manage symptoms of anxiety, stress, and depression that may be contributing to your nightmares. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used approach to treating recurring nightmares, as it focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that may be contributing to the nightmares.
Additionally, a psychiatrist may be able to prescribe medication to help manage symptoms and improve sleep quality. However, it’s important to note that medication should not be the sole treatment method and should be used in conjunction with therapy.
If you or a loved one are experiencing suicidal thoughts, seek immediate professional help. You can call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255 or go to your nearest emergency room.
Remember that seeking professional help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Don’t suffer in silence – there is help available for those who need it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recurring nightmares can have a significant psychological impact on an individual’s mental health and overall well-being. The distress and anxiety caused by these nightmares can lead to depression, PTSD, and other serious mental health issues. Therefore, it is essential to address the root causes of recurring nightmares and seek appropriate treatment as needed.
Several techniques can help individuals deal with and prevent recurring nightmares. These include journaling and visualization, cognitive behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques, and medication. Making certain lifestyle changes and avoiding trigger points can also help prevent recurring nightmares from occurring in the first place.
However, it is essential to note that seeking professional help is necessary when recurring nightmares start to affect an individual’s ability to function in their daily life. Therapists and other mental health professionals can provide specialized treatments such as exposure therapy and EMDR to help manage and overcome the effects of recurring nightmares.
Overall, understanding and addressing the psychological impact of recurring nightmares is crucial for maintaining good mental health and improving overall quality of life. By taking proactive steps to manage and prevent recurring nightmares, individuals can find relief, improve their sleep quality, and restore their sense of well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What percentage of the population experiences recurring nightmares?
Studies suggest that up to 50% of adults experience nightmares, and about 5% of those experience recurring nightmares.
Can children experience recurring nightmares?
Yes, children can experience recurring nightmares, typically beginning around the age of three or four.
Can recurring nightmares be a symptom of a larger mental health issue?
Yes, recurring nightmares can be a symptom of various mental health issues such as PTSD, anxiety disorders, or depression.
Is it possible to completely eliminate recurring nightmares?
While it may not be possible to completely eliminate recurring nightmares, there are various coping mechanisms and therapies that can greatly reduce their frequency and intensity.
Can medication be an effective treatment for recurring nightmares?
Yes, certain medications such as antidepressants and beta blockers have been shown to reduce the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares.
How long do recurring nightmares usually last?
Recurring nightmares can vary in duration, but can last anywhere from a few weeks to several years.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent recurring nightmares?
Yes, implementing healthy habits such as exercise, meditation, and stress management techniques can potentially prevent the onset of recurring nightmares.
Can recurring nightmares have physical effects on the body?
Yes, recurring nightmares can lead to physical symptoms such as insomnia, headaches, and fatigue.
What is the difference between a nightmare and a night terror?
A nightmare is a bad dream that can be remembered upon waking, while a night terror is a sudden episode of fear or screaming during sleep, typically not remembered upon waking.
Can journaling really help reduce the frequency of recurring nightmares?
Yes, keeping a dream journal and reflecting on recurring nightmares has been shown to reduce their frequency and intensity.








