For those who suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), the effects can be devastating. Recurring nightmares are a common symptom that often lead to sleep disruptions and further exacerbate the effects of PTSD. Despite their prevalence, the specific link between PTSD and recurring nightmares can be difficult to understand. However, with effective treatment strategies and lifestyle changes, it is possible to alleviate the distressing symptoms and restore a sense of normalcy in daily life. In this article, we will explore the unbreakable link between PTSD and recurring nightmares, as well as delve into effective treatment strategies and lifestyle changes that can lead to better sleep and overall well-being.
What is PTSD?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, or PTSD, is a mental health condition that can affect individuals who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. PTSD can cause a range of distressing symptoms, including flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, and nightmares. These symptoms can be extremely debilitating, making it difficult for individuals with PTSD to carry out everyday activities and maintain healthy relationships. Despite its prevalence, PTSD is not yet fully understood, and there is still much to be learned about the causes and most effective treatments.
Symptoms of PTSD
PTSD is a serious psychiatric disorder that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It can cause a range of symptoms that significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Here are some common symptoms of PTSD:
| Re-experiencing symptoms | Avoidance symptoms | Arousal and reactivity symptoms | Cognition and mood symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flashbacks – feeling as if the traumatic event is happening again | Avoiding reminders – avoiding people, places or situations that may trigger memories of the event | Hypervigilance – feeling constantly on guard or easily startled | Negative thoughts – feeling stuck or negative about the world, including oneself or others. |
| Nightmares – dreams that are so vivid and disturbing that they wake the person up or cause sleep disruptions | Emotional numbness – feeling detached or disconnected from others | Irritability and aggression – feeling angry or irritated often and without cause | Difficulty remembering – struggling to recall specific details about the traumatic event |
| Panic attacks – sudden and overwhelming feelings of fear and distress | Avoiding thoughts and feelings – trying to push away memories, thoughts, or feelings associated with the event | Sleep disturbances – trouble sleeping, staying asleep, or falling asleep | Loss of interest – feeling a loss of interest in activities or hobbies once enjoyed |
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop PTSD, and the symptoms can vary in severity and type between individuals. However, experiencing any of these symptoms may warrant seeking professional help to properly diagnose and manage PTSD.
Causes of PTSD
PTSD is a mental health condition that is triggered by a traumatic event. The experience may be directly experienced, witnessed or experienced repeatedly in any way (such as police officers, soldiers or firefighters), or learned about a close family member or friend who experienced it. The causes of PTSD can vary and may include:
| Cause | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Combat exposure | Combat veterans are at high risk of developing PTSD due to exposure to combat and its challenges, such as risk of injury, witnessing death and destruction. |
| Physical or Sexual Assault | Victims of sexual assault, physical abuse or violence of any type also experience PTSD. The trauma of the event can significantly disrupt a person’s sense of safety, control, and self-worth. |
| Unexpected Trauma | PTSD can occur from any unexpected and traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, car accident, or sudden death, leading to a lasting physical and emotional response to the trauma. |
| Childhood Trauma | Childhood trauma, whether physical, sexual, or emotional abuse, can lead to PTSD in adults, especially when it is ongoing, prolonged or repetitive. |
| Military Sexual Trauma (MST) | Military sexual trauma is a term used to describe sexual assault or repeated threatening encounters experienced by military service members. MST can lead to PTSD as it is a traumatic event that disrupts a person’s sense of well-being and safety. |
| Medical Trauma | Medical procedures that are prolonged, invasive, or uncomfortable due to serious illnesses or accidents contributes to physical traumas and post-traumatic stress disorder. People who were subjected to this kind of trauma experience compulsive pain and distressing memories. |
| Life Stressors | Traumatic events that are not as severe, such as relationship problems, financial issues, or work overload, may cause PTSD. Although these are everyday life stressors, some people may be more vulnerable to them, and the events can impact them deeply. |
PTSD can result from various causes that can significantly affect a person’s mental, emotional and physical well-being. Seeking professional help and support is essential to understand the underlying causes of PTSD, determine the best treatment method and move towards healing and recovery.
Treatment of PTSD
Treatment of PTSD typically involves a combination of therapy and medication. Here are some commonly used options for treating PTSD:
| Therapy Options | Medication Options |
|---|---|
|
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This type of therapy helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that are contributing to their PTSD symptoms. CBT can be done in individual or group settings, and can be particularly effective when combined with other treatments.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR involves guided eye movements while recalling traumatic experiences in a safe, controlled environment. This therapy has shown promising results in reducing PTSD symptoms and improving overall well-being. Exposure Therapy: This involves gradually exposing individuals to the situations or triggers that cause their PTSD symptoms in a safe, controlled manner. This exposure can help individuals learn how to cope with and overcome their symptoms. Couples or Family Therapy: Sometimes, PTSD can have a significant impact on a person’s relationships. Couples or family therapy can help individuals and their loved ones learn how to communicate better and support each other through the healing process. |
Antidepressants: Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are often prescribed to help manage symptoms of PTSD, such as depression and anxiety. These medications can take several weeks to start working.
Prazosin: This medication is used to help manage nightmares in individuals with PTSD. It works by blocking the effects of adrenaline, which can contribute to nighttime symptoms. Benzodiazepines: While these medications can help manage symptoms of anxiety in the short term, they are generally not recommended for long-term use in individuals with PTSD due to the risk of dependence and other potential side effects. |
It’s important for individuals with PTSD to work with a medical or mental health professional to determine the best course of treatment for their specific needs. It’s also worth noting that there are alternative approaches such as yoga, meditation, and acupuncture that some individuals find helpful in managing their symptoms.
Recurring Nightmares and PTSD
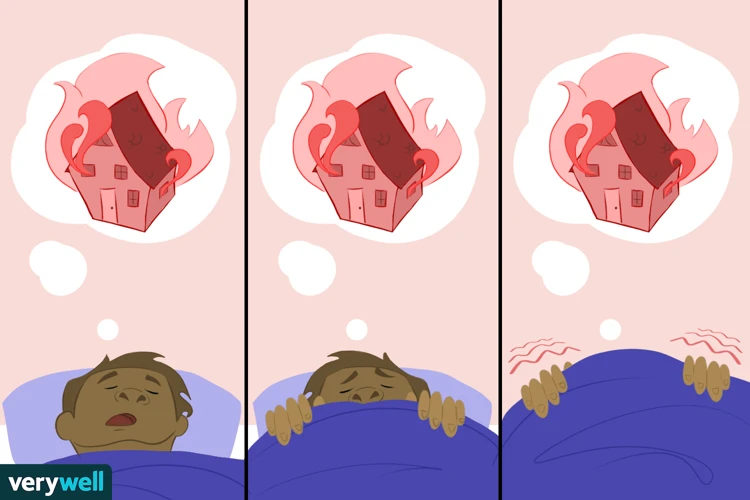

For many people living with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), recurring nightmares can be a vicious cycle that feels impossible to escape. These dreams can be incredibly vivid, causing the person to feel as though they are experiencing the trauma all over again. This can further exacerbate their PTSD symptoms and significantly disrupt their quality of life. In this section, we will explore the unbreakable link between PTSD and recurring nightmares, why they occur, and how to effectively manage them.
Why PTSD Causes Recurring Nightmares
PTSD or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a mental health condition that can develop following exposure to a traumatic event or experience. PTSD can have a profound impact on an individual’s life, with one of the most common symptoms being recurring nightmares.
There are several reasons why PTSD can cause recurring nightmares, including:
- Intrusive thoughts: Individuals with PTSD may experience intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and vivid memories of their traumatic experience. These intrusive thoughts can disrupt sleep and lead to recurring nightmares.
- Hypervigilance: People with PTSD often feel on edge and hyperaware of their surroundings. This hypervigilance can make it difficult to relax and fall asleep, resulting in more frequent nightmares.
- Emotional arousal: PTSD can cause intense emotional reactions, such as fear, anxiety, and anger. These emotional responses can carry over into dreams and contribute to the development of recurring nightmares.
- Fragmented sleep: People with PTSD often experience poor sleep quality and may have trouble staying asleep due to nightmares and other sleep disturbances. This fragmented sleep can exacerbate the symptoms of PTSD and contribute to the development of recurring nightmares.
Recurring nightmares are a common symptom of PTSD that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the factors that contribute to these nightmares is an important step in developing effective treatment strategies.
How Recurring Nightmares Affect PTSD
Recurring nightmares can have a profound impact on individuals with PTSD, further exacerbating their symptoms and overall mental health. Here are some of the ways in which recurring nightmares can affect PTSD:
- Disturbed sleep: Recurring nightmares can cause individuals to experience disrupted and inadequate sleep, which can further worsen their PTSD symptoms. Sleep deprivation can lead to heightened anxiety, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, among other negative effects.
- Increased fear and anxiety: The content of recurring nightmares is often closely related to the traumatic event(s) that caused the individual’s PTSD in the first place. As a result, these nightmares can cause individuals to feel a heightened sense of fear and anxiety, even during waking hours. The fear and anxiety that result can become crippling and impair day-to-day functioning.
- Trauma re-experiencing: Recurring nightmares involving traumatic events can feel as vivid and real as the original event(s), causing individuals to essentially “re-live” their trauma in their sleep. This can exacerbate feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and despair, and can cause individuals to feel a sense of powerlessness and helplessness.
- Somatic symptoms: Recurring nightmares can also cause individuals to experience physical symptoms, such as sweating, rapid heartbeat, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can further increase feelings of anxiety and dread, and can cause individuals to avoid situations that trigger these symptoms.
Recurring nightmares can be a major obstacle to recovery for individuals with PTSD. Addressing the nightmares and working to reduce their frequency and intensity is a key component of a comprehensive treatment plan for PTSD.
Effective Treatment Strategies
When it comes to treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), there are several effective treatment strategies that can help those suffering from this debilitating condition. From therapy to medication and alternative approaches, there are options for everyone. However, it’s essential to understand that no single treatment approach works for everyone, and it may take time to find the right combination of strategies that work best for each individual. In this section, we will explore some of the most successful treatment approaches available to help individuals with PTSD move towards recovery and better mental health.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
One effective treatment option for individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). This type of therapy focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to the symptoms of PTSD.
During CBT, patients work closely with a trained therapist to develop coping strategies to manage their PTSD symptoms. This may include techniques such as exposure therapy, which involves gradually exposing the patient to their traumatic experience in a safe and controlled environment. By facing their trauma in a supportive and safe setting, patients can start to process and eventually reduce their PTSD symptoms.
CBT may also involve other techniques such as cognitive restructuring, where patients learn to identify and challenge negative thoughts related to their trauma, and relaxation training, which teaches patients how to manage their physical and emotional reactions to stress.
CBT has been shown to be an effective treatment for PTSD and recurring nightmares. Through this therapy, patients can learn to identify and manage their triggers, reduce the intensity of their nightmares, and develop effective coping strategies for managing their symptoms.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) is a form of therapy that has been proven to be effective in treating PTSD and recurring nightmares. It involves a structured process that incorporates elements of talk therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and exposure therapy, along with the use of eye movements or other forms of rhythmic stimulation.
The EMDR process typically involves eight phases:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | During the first phase, the therapist establishes a rapport with the patient and works to determine what specific traumatic event or events may be contributing to their PTSD and recurring nightmares. |
| 2 | In the second phase, the patient is taught various coping skills and relaxation techniques to help them handle any distress that may arise during the EMDR treatment. |
| 3 | During the third phase, the patient is guided to focus on a specific traumatic event and to identify any negative thoughts, emotions, or bodily sensations associated with it. |
| 4 | In the fourth phase, the therapist leads the patient through a series of guided eye movements or other rhythmic stimulation while the patient focuses on the traumatic event. |
| 5 | During the fifth phase, the patient is instructed to notice any new thoughts, emotions, or bodily sensations that arise as a result of the eye movements or rhythmic stimulation. |
| 6 | In the sixth phase, the patient is encouraged to replace any negative thoughts or beliefs about themselves that may have originated from the traumatic event with more positive thoughts and beliefs. |
| 7 | During the seventh phase, the therapist leads the patient through another set of eye movements or rhythmic stimulation, focusing on the positive thoughts and beliefs that were established in the previous phase. |
| 8 | In the final phase, the therapist and patient evaluate the progress made during the treatment and identify any additional areas of focus for future sessions. |
Research has shown that EMDR can be highly effective in treating PTSD and the recurring nightmares that often accompany it. Studies have found that EMDR can reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, lower levels of anxiety and depression, and improve overall quality of life for individuals with PTSD. EMDR has even been shown to be effective in treating veterans with complex and treatment-resistant PTSD.
If you are struggling with PTSD and recurring nightmares, EMDR may be a worthwhile treatment option to explore with a qualified therapist.
Medication
One of the options for treating PTSD and recurring nightmares is through medication.
Medication can be effective in helping to reduce the severity of symptoms and improve sleep. However, it is important to note that medication should not be considered the sole treatment for PTSD and recurring nightmares. It should be used in conjunction with therapy and lifestyle changes for the best results.
Here is a table of some common medications used to treat PTSD and recurring nightmares:
| Medication | Function | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Help regulate mood and reduce anxiety | Nausea, weight gain, sexual dysfunction |
| Benzodiazepines | Reduce anxiety and promote relaxation | Dizziness, drowsiness, dependence |
| Prazosin | Reduces nightmares and improves sleep | Dizziness, headache, low blood pressure |
| Anticonvulsants | Help stabilize mood and reduce anxiety | Drowsiness, dizziness, nausea |
It is important to keep in mind that medication may not work for everyone and may also have potential side effects. It is recommended to speak with a medical professional to determine the best course of treatment for individual needs.
Alternative Approaches
Alternative approaches to treating PTSD and recurring nightmares include a range of techniques that focus on healing the mind, body, and spirit. These approaches may not work for everyone, but they offer valuable tools that individuals can use alongside traditional therapy.
One alternative approach is mindfulness meditation, which involves paying attention to the present moment and observing thoughts and emotions without judgment. This technique can help individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares become more aware of their triggers and reactions, which can lead to greater self-regulation.
Another approach is yoga, which has been found to be beneficial for PTSD and related symptoms. Yoga combines physical movement with breathing techniques and meditation, providing a holistic approach to healing.
Note: There is substantial evidence regarding the effectiveness of mindfulness meditation and yoga for treating PTSD and recurring nightmares. However, it is important to work with a trained practitioner to ensure you are doing exercises correctly and safely.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting needles into specific points on the body to regulate the flow of energy. Some individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares have found that acupuncture helps to reduce anxiety and improve sleep.
- Hypnotherapy: This approach involves guided relaxation and visualization techniques to access the subconscious mind and help individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares process traumatic experiences. It can be a powerful tool when used in conjunction with traditional therapy.
- Herbal supplements: Certain herbal supplements, such as valerian root and chamomile, have been found to have calming effects and promote better sleep. However, it is important to speak to a healthcare provider before taking any supplements, as they may interact with other medications or health conditions.
- Animal-assisted therapy: This approach involves working with trained therapy animals, such as dogs and horses, to help individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares feel more at ease and comfortable. Interacting with animals can provide a sense of safety and emotional support.
While these alternative approaches may not work for everyone, they offer individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares additional tools to help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. It is important to work with a healthcare provider or mental health professional to determine the best course of treatment.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Sleep
Good sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being. For individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a good night’s rest can be elusive due to recurring nightmares, hypervigilance, or other symptoms. However, certain lifestyle changes can improve sleep quality, reduce triggers, and promote relaxation. In this section, we will discuss some effective approaches to achieving better sleep that may be particularly helpful for those with PTSD.
Establishing a Sleep Routine
Establishing a consistent sleep routine is essential for improving the quality of sleep of individuals suffering from PTSD and recurring nightmares. A good sleep routine can decrease the frequency and intensity of nightmares while also reducing overall stress and anxiety levels.
Here are some effective ways to establish a sleep routine:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Set a consistent bedtime and waking time | Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This can help regulate your body’s internal clock and improve sleep quality. |
| Avoid stimulating activities before bed | Avoid things that can be overstimulating before bed, such as watching TV, using the computer, or exercising. Instead, try to engage in calming activities such as reading or taking a warm bath. |
| Create a relaxing bedtime routine | Engaging in relaxing activities before bed can help calm the mind and prepare it for sleep. Options include drinking herbal tea or practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises. |
| Optimize sleep environment | Ensure that the sleeping environment is comfortable by investing in a high-quality mattress and pillows, keeping the room dark and quiet, and keeping the temperature at a comfortable level. |
| Avoid napping during the day | Avoiding daytime napping can help regulate the sleep-wake cycle and avoid disrupting nighttime sleep patterns. However, if you do feel tired during the day, a short nap (no more than 30 minutes) can be beneficial. |
By establishing a consistent sleep routine and sticking to it, individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares can significantly improve the quantity and quality of their sleep, leading to improvements in overall health and wellbeing.
Avoiding Triggers
To avoid triggering recurring nightmares, it is important to take steps to minimize exposure to potential triggers. Some common triggers for individuals with PTSD include certain smells, sounds, images, and situations that remind them of the traumatic event. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, individuals can reduce the likelihood of experiencing recurring nightmares that can exacerbate their symptoms of PTSD.
One effective way to avoid triggers is to create a list of potential triggers and then develop a plan for avoiding or coping with each trigger. For example, if a certain smell triggers a flashback, the individual may choose to avoid locations or situations where that smell is present. If a particular image is a trigger, the individual may choose to avoid movies or television shows that feature that image. By being proactive and developing a plan for avoiding or coping with triggers, individuals can improve their quality of sleep and reduce the frequency of recurring nightmares.
Another effective way to avoid triggers is to practice relaxation techniques when exposed to potential triggers. For example, taking deep breaths, focusing on a mental image, or repeating a calming phrase can help reduce the intensity of the triggering experience and prevent a nightmare from occurring. By practicing relaxation techniques regularly, individuals can develop a greater sense of control over their triggers and reduce the frequency and intensity of their nightmares.
Additionally, individuals may find it helpful to avoid consuming substances that can disrupt their sleep, such as alcohol or caffeine. These substances can interfere with sleep quality and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. By avoiding these substances, individuals can improve their sleep quality and reduce the frequency of nightmares.
To summarize, avoiding triggers is an important part of managing recurring nightmares for individuals with PTSD. Developing a plan for avoiding or coping with triggers, practicing relaxation techniques, and avoiding sleep-disrupting substances can all help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares and improve sleep quality.
| Ways to Avoid Triggers | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Create a list of potential triggers and develop a plan for avoiding or coping with each one | Improves sense of control over triggering situations, reduces frequency of nightmares |
| Practice relaxation techniques when exposed to potential triggers | Reduces intensity of triggering experiences, prevents nightmares from occurring |
| Avoid consuming substances that can disrupt sleep, such as alcohol or caffeine | Improves sleep quality, reduces frequency of nightmares |
Relaxation Techniques
One effective way to improve sleep quality for individuals with PTSD who experience recurring nightmares is through relaxation techniques. These techniques can help reduce stress levels and promote a sense of calm, making it easier to fall and stay asleep. Here are some popular relaxation techniques:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Focusing on slow, deep breaths can help slow down the heart rate and relax the body. Breathe in slowly through the nose, hold for a few seconds, and then exhale slowly through the mouth. |
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) | This technique involves tensing and then relaxing each muscle group of the body. It can help relieve tension and promote relaxation. Start by tensing the muscles in the toes and feet, holding for a few seconds, and then releasing the tension. Move up the body, tensing and relaxing each muscle group. |
| Mindfulness Meditation | Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on the present moment and being aware of one’s thoughts and feelings without judgment. It can help train the mind to let go of intrusive thoughts and worries that can interfere with sleep. |
| Yoga | Yoga combines physical postures, controlled breathing, and meditation to promote relaxation and reduce stress. Practicing yoga regularly can help improve sleep quality. |
It’s important to find a relaxation technique that resonates with the individual and makes them feel comfortable. Practicing these techniques regularly can help individuals with PTSD and recurring nightmares feel more in control of their sleep and reduce the frequency and intensity of their nightmares.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is important to understand the link between PTSD and recurring nightmares. While it can be a difficult and challenging experience for those who suffer from it, there are effective treatment strategies available to help manage both the symptoms of PTSD and the nightmares that often come with it.
Both cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) have shown great promise in reducing the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares. Medication and alternative approaches may also be helpful, depending on individual circumstances.
In addition to seeking professional treatment, making lifestyle changes such as establishing a consistent sleep routine, avoiding triggers, and utilizing relaxation techniques can also greatly improve sleep quality for those with PTSD and recurring nightmares.
It is important to remember that healing from PTSD and managing recurring nightmares is a journey, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. With the right support and resources, however, it is possible to break the unbreakable link between PTSD and recurring nightmares and work towards a better, more restful night’s sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risk factors for developing PTSD?
Experiencing a traumatic event, having a history of mental health issues, and having poor social support are all risk factors for developing PTSD.
How common are recurring nightmares in people with PTSD?
Recurring nightmares are very common in people with PTSD, with up to 80% experiencing them.
What is the difference between a regular nightmare and a nightmare caused by PTSD?
Nightmares caused by PTSD often involve the re-experiencing of a traumatic event, and can lead to severe anxiety and fear upon waking.
Can recurring nightmares make PTSD symptoms worse?
Yes, recurring nightmares can exacerbate other symptoms of PTSD, such as hypervigilance and avoidance behaviors.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)?
CBT is a type of therapy that focuses on changing negative patterns of thought and behavior, often used to treat PTSD.
How does eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) work?
EMDR involves recalling traumatic events while following a therapist’s finger movements, with the goal of desensitizing the person to the trauma.
Can medication be effective in treating PTSD?
Yes, certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and benzodiazepines, can be effective in treating PTSD symptoms.
What are some alternative approaches to treating PTSD?
Alternative approaches can include art therapy, equine therapy, and mindfulness techniques.
How can lifestyle changes improve sleep for people with PTSD?
Lifestyle changes, such as establishing a sleep routine, avoiding triggers, and practicing relaxation techniques, can improve sleep quality for people with PTSD.
Is it possible to fully recover from PTSD?
While not everyone completely recovers from PTSD, treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. With the right care, many people with PTSD are able to lead fulfilling lives.








