Have you ever woken up from a dream feeling rested and refreshed, but curious about what exactly happened in your brain while you slept? Sleep is a complex process that involves various stages, each playing a crucial role in restoring both mental and physical health. However, one stage – REM sleep – has been the subject of much scientific inquiry due to its unique characteristics and potential benefits. In this article, we’ll delve into what exactly REM sleep is, why it’s important, and how you can get more of it. So grab a pillow, find a cozy spot, and let’s explore the mysteries of sleep together.
What is REM sleep?

Have you ever woken up from a dream feeling confused or curious about what just occurred in your subconscious? It’s likely that you were in the stage of sleep known as REM sleep, which is characterized by rapid eye movement and intense brain activity. During this stage, your brain undergoes a series of physiological changes that can affect your overall health and well-being. Let’s explore what exactly REM sleep is, the stages of sleep, and the relationship between your brain and this important part of your sleep cycle.
Definition of REM sleep
During sleep, the body goes through different stages of sleep, with the most important and well-known stage being Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movement, as the name implies, along with heightened brain activity and muscle relaxation.
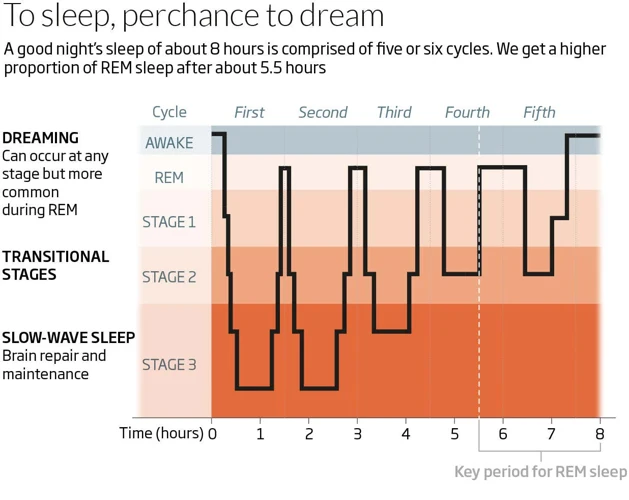
REM sleep is a stage of sleep where the body is very active mentally, but completely inactive physically. It is a period during which the brain is actively dreaming, creating dreams that are more vivid and memorable than those experienced during other sleep phases. REM sleep is usually experienced several times during the night, with each period of REM sleep lasting longer than preceding ones.
There are several physiological markers that define REM sleep. One of these is the presence of rapid eye movements, which can be seen through closed eyelids. The brain activity during this stage is also very similar to when we are awake, with patterns of high-frequency electrical impulses. Unlike other sleep stages, one’s muscles are entirely relaxed in REM sleep, to the point that even breathing and heartbeats slow down.
REM sleep is an essential natural process as it aids in the regulation and restoration of the body. It is considered to be the stage that consolidates memories and enhances cognitive processes such as learning and creativity. It also helps regulate emotions, maintaining overall brain health, and physical restoration.
Stages of sleep
During our sleep, our bodies go through different stages of sleep. These stages are categorized into two groups: Non-REM (NREM) Sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep. NREM sleep is further subdivided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3. Meanwhile, REM sleep is considered a separate stage on its own.
N1 Stage: This stage marks the transition from wakefulness to sleep. It can last for a few minutes and is characterized by theta waves in the brain. During this stage, people can still be easily awakened, and their muscles may twitch.
N2 Stage: This stage is also known as light sleep and is the longest stage. This stage makes up about half of our sleep. Our breathing and heart rate are regular, and our body temperature drops. It’s also during this stage that our body prepares for deep sleep, where the body can restore and repair tissue and strengthen the immune system. Brain waves become slower, and sleep spindles and K-complexes occur.
N3 Stage: This stage is also known as slow-wave or deep sleep, and it’s when the body is at its most restorative state. Brain waves are slow, and the body temperature drops even more. Blood pressure and breathing rate are at their lowest. It’s also when the body secretes growth hormone, which is crucial for tissue growth and repair.
REM Stage: This stage is characterized by rapid eye movements, hence the name. During this stage, the brain becomes very active, and heart rate and breathing become irregular. It’s also when most dreaming occurs. REM sleep is important for brain function because it helps consolidate memory and regulate emotions.
There are four stages of sleep, each with unique characteristics and roles in bodily restoration, repair, and brain function. Understanding these stages can help individuals improve their sleep habits and overall health.
REM Sleep and Brain Activity
During REM sleep, the brain activity is incredibly active, even more so than during waking hours. This is due to the fact that REM sleep is where most dreaming occurs. During REM sleep, the brain becomes hyperactive with strong bursts of electrical energy that resemble wakefulness. This activity can be seen in brain scans, where it would appear as if the person is awake.
The brain during REM sleep:
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid eye movements | The eyes move rapidly in all directions during REM sleep. This is where the term REM sleep comes from. |
| Muscle paralysis | The body is usually paralyzed during REM sleep to prevent acting out dreams. |
| Increase in heart rate and blood pressure | The autonomic nervous system is more active during REM sleep. |
| Activation of the limbic system | The limbic system is responsible for emotions and memory. |
| Suppression of the prefrontal cortex | The prefrontal cortex is responsible for logical thinking and decision-making. This suppression explains why dreams can often be illogical. |
During REM sleep, the brain consolidates memories and processes emotions. It is also believed that the brain uses this time to problem-solve and form new neural connections. Getting enough REM sleep is essential for both physical and mental wellbeing.
Why is REM sleep important?

As we continue to learn more about the science of sleep, one thing is becoming increasingly clear: REM sleep is absolutely essential for our health and well-being. This deep stage of sleep may seem mysterious and difficult to understand, but the more we delve into the research, the more we can see just how vital it is for our bodies and minds. From consolidating memories to regulating our emotions, REM sleep plays a critical role in helping us function at our best. So let’s take a closer look at the many reasons why this stage of sleep matters so much.
Memory consolidation
During REM sleep, the consolidation of memories occurs. This process is essential for retaining information learned during the day. The hippocampus, responsible for learning and memory, replays the information acquired while awake with the neocortex during this stage of sleep. The brain forms new neural connections to store the memories, which are then more easily retrieved.
The following are some ways that REM sleep can improve memory consolidation:
- Elimination of insignificant memories: During REM sleep, the brain discards unnecessary information, focuses on relevant data, and strengthens that information.
- Integration of new information: The information we learn during the day is processed and integrated into our cognitive schema during REM sleep. This process makes it more comfortable for the brain to retrieve a particular memory.
- Retention of procedural memory: REM sleep is critical in consolidating and retaining procedural memory. Studies have shown that people who underwent REM sleep after learning a new motor skill showed significant improvement in their performance the next day.
Adequate REM sleep is crucial for memory consolidation, and lack of it can hinder retention of new information. If you have a big exam or a presentation, it is crucial to ensure you get enough sleep the night before to consolidate those memories.
Emotional regulation
During REM sleep, our brain processes emotions and experiences from the day, which can greatly impact our emotional well-being. Studies show that individuals who lack REM sleep have difficulty regulating their emotions and may experience emotional disturbances.
REM sleep plays a critical role in processing and regulating emotions, allowing us to effectively manage and cope with stress and anxieties. During this stage, the brain consolidates emotional memories and helps us understand, categorize, and respond appropriately to different emotional stimuli.
Furthermore, REM sleep therapy has been used to treat individuals with mood disturbances, such as depression and anxiety. By enhancing REM sleep, individuals have shown improvement in mood and ability to regulate their emotions.
In summary, REM sleep is crucial for emotional regulation and managing stress and anxiety. Ensuring sufficient REM sleep can greatly improve emotional well-being and overall quality of life.
Learning and Creativity enhancement
During REM sleep, the brain is actively working towards enhancing not only our memory but also our creativity and learning abilities. Studies have revealed that REM sleep helps with consolidating memory and assists in learning complex tasks. Additionally, during REM sleep, the brain tends to form new connections between different areas, resulting in creative problem-solving abilities.
REM sleep is crucial for individuals who require a high level of creativity in their day-to-day work. Scientists suggest that REM sleep allows the brain to free-associate, making it possible to find unique solutions to problems.
To understand better how REM sleep can enhance creativity and learning, one must consider the brain’s activities during this stage. The brain is actively processing the day’s events and experiences, reorganizing the information to create a coherent story. During REM sleep, neural connections are formed, which can provide a new perspective on the day’s events. This process helps individuals become more creative and reflective.
The importance of REM sleep for enhancing learning and creativity cannot be overstated. Studies have shown that REM sleep helps consolidate memories, learn complex tasks, and provides a fertile environment for creative problem-solving. It is essential to ensure adequate REM sleep to keep our cognitive abilities sharp and efficient.
Physical restoration and growth
During REM sleep, our bodies also undergo physical restoration and growth. This is due to the release of growth hormones that stimulate tissue and muscle repair. Here are some key ways REM sleep helps with physical restoration and growth:
- Muscle Repair: During REM sleep, muscle tissue repairs itself from the wear and tear of daily activities. This is especially important for athletes or anyone involved in physically demanding jobs.
- Cell Regeneration: REM sleep also aids in the regeneration of skin and other tissues. This helps to maintain a healthy immune system and youthful appearance.
- Bone Growth: Growth hormone release during REM sleep also helps to stimulate bone growth and regeneration, which is especially important for growing children and teenagers.
- Energy Restoration: REM sleep is essential for restoring the body’s energy levels. Without enough REM sleep, you may feel lethargic and unmotivated throughout the day.
It’s important to note that the amount of REM sleep needed varies depending on age and other factors. Infants may spend up to 50% of their sleep time in REM sleep, while adults typically only spend about 20-25% in this stage. However, regardless of age, it’s crucial to get enough REM sleep in order to experience the physical restorative and growth benefits it offers.
Maintenance of brain function
REM sleep plays an important role in the maintenance of various brain functions. During REM sleep, the brain works to consolidate memories, repair and restore itself, and maintain neurological functioning.
One crucial aspect of REM sleep is its ability to facilitate the formation of new neural connections. The brain uses this time to process information and consolidate new memories, allowing for easier access and retrieval later on. Studies have shown that REM sleep enhances creativity and problem-solving abilities, making it an important factor in cognitive development.
Additionally, REM sleep is linked to emotional regulation, helping to reduce the impact of negative emotions on daily life. When we don’t get enough REM sleep, we may experience increased stress, anxiety, and even depression.
Apart from cognitive and emotional functions, REM sleep also aids in physical restoration and growth. During this sleep stage, the body produces human growth hormone (HGH), which is essential for repairing and rebuilding muscles, bone tissue, and other vital organs.
The maintenance of brain function through REM sleep is essential for optimal cognitive, emotional, and physical health. It is recommended that adults get 7-9 hours of sleep each night to ensure sufficient time in REM sleep. Those who consistently get less REM sleep may experience cognitive impairment, emotional instability, and poor physical health.
To summarize, the role of REM sleep in maintaining brain function is vital for our overall wellbeing. The table below highlights some of the key functions of REM sleep:
| Function of REM Sleep | Description |
|---|---|
| New Neural Connections | Facilitates the formation of new neural connections, which aids in cognitive development |
| Emotional Regulation | Reduces the impact of negative emotions on daily life, helping to regulate our emotional responses |
| Physical Restoration and Growth | Produces human growth hormone essential for repairing and rebuilding muscles, bone tissue, and other vital organs |
How to get more REM sleep
Are you struggling with feeling tired and groggy every morning? Do you want to improve the quality of your sleep and feel more rested throughout the day? One of the crucial stages of sleep is REM, which is essential for various physiological and cognitive functions. Improving the amount of REM sleep you receive each night can hold numerous benefits. In this section, we will explore different strategies on how to boost the duration and quality of your REM sleep. Let’s dive into some practical tips that can help you enhance the quality of your sleep!
Establish a sleep routine
Establishing a sleep routine is crucial to getting more uninterrupted REM sleep. A regular sleep schedule trains the body to expect rest at a certain time, encouraging the various stages of sleep to progress as intended. Here are a few tips to help you establish and stick to your sleep routine:
| Tips for establishing a sleep routine |
|---|
| Set a consistent sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps set your body’s internal clock and improves the quality of your sleep. |
| Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Develop a series of calming activities before bed to help prepare your body and mind for sleep. This may include reading, taking a bath, or listening to relaxing music. |
| Avoid bright screens: Exposure to screens emitting blue light, such as smartphones or laptops, can disrupt the production of the sleep hormone melatonin. Try to avoid using them in the hour before bedtime. |
| Make your sleeping environment comfortable: An optimal sleeping environment includes a cool temperature, comfortable mattress, and minimal noise and light disturbances. |
| Avoid consuming caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol: These substances can all interfere with sleep quality and disrupt your sleep cycle. Avoid consuming them in the hours leading up to bedtime. |
By following these tips, you may find that it becomes easier to fall asleep and stay asleep for longer periods. Keep in mind that it may take a few days or even a couple of weeks to fully establish a solid sleep routine, but the benefits of consistent, quality sleep are well worth the effort.
Avoid disturbances
One of the best ways to improve REM sleep is to avoid disturbances during the night. Here are some possible disruptions that may reduce REM sleep:
| Possible disturbances that reduce REM sleep |
|---|
| Noise: It is important to keep the sleeping environment as quiet as possible. Exposure to loud noises can lead to arousals that can disrupt REM sleep. Consider using earplugs or white noise machines to reduce the impact of external sounds. |
| Light: Light is another factor that can interfere with sleep. Exposure to light, even dim light, can decrease melatonin production and prevent deep REM sleep. It is advised to use dark, heavy curtains to block out any light that could get in through windows or doors. Additionally, avoid using electronic devices before bedtime. |
| Temperature: The ideal temperature for sleeping is around 60-67°F (15-19°C), as it allows your body to cool down just enough to fall asleep and stay asleep. Temperature fluctuations (such as a room that is too hot or too cold) can interrupt the sleep cycle. |
| Food and drink: It is recommended to avoid heavy meals or snacks right before bedtime. Additionally, certain substances such as caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can alter the quality of sleep and impact the amount of time spent in REM sleep. |
| Bathroom trips: Waking up in the middle of the night to go to the bathroom can cause interruptions in REM sleep, making it difficult to fall back asleep. Consumption of fluids before bedtime should be reduced to limit the frequency of trips to the bathroom. |
By limiting or eliminating these potential disruptions, individuals can increase their chances of achieving longer and more restful periods of REM sleep.
Reduce stress
One of the key factors that can affect the quality and duration of REM sleep is stress. Stress and anxiety have been shown to disrupt sleep patterns and prevent the brain from entering the deep stages of sleep, including REM sleep. To get more REM sleep, it’s essential to find effective ways to reduce stress.
Here are some tips for reducing stress and promoting better REM sleep:
| Tips for Reducing Stress |
|---|
| Practice relaxation techniques: |
| Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help calm the mind and reduce stress levels. |
| Exercise: |
| Regular exercise can help reduce stress and promote deeper, more restful sleep. Just be sure to exercise earlier in the day, as exercising too close to bedtime can actually make it harder to fall asleep. |
| Avoid caffeine and alcohol: |
| Caffeine and alcohol can interfere with sleep and increase stress levels, so it’s best to limit or avoid them, especially in the evening. |
| Establish a relaxing bedtime routine: |
| Developing a consistent bedtime routine can help signal to your brain that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. This could involve reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music. |
| Talk to a therapist: |
| If stress and anxiety are affecting your sleep on a regular basis, it may be helpful to talk to a therapist or counselor. They can help you identify the root causes of your stress and develop effective coping strategies. |
By reducing stress levels and promoting relaxation, it’s possible to improve the quality and duration of REM sleep. Incorporating these tips into your regular routine can help you get the restful sleep you need to function at your best.
Consider supplements and therapy
There are various supplements and therapy options available that can help improve REM sleep. Below are some of the most effective ones:
- Valerian root: This is a natural herb commonly used in supplements to promote relaxation and better sleep. Studies have shown that valerian root helps improve the quality of sleep, including the length and depth of REM sleep.
- Melatonin: This is a natural hormone that regulates sleep and wake cycles. Melatonin supplements can be taken to help improve sleep quality, including REM sleep. However, it is important to use this supplement with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it may not be suitable for everyone.
- Aromatherapy: The use of essential oils, such as lavender or chamomile, can help promote relaxation and improve the quality of sleep. These oils can be used in a diffuser or applied topically before bedtime.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): This is a form of therapy that helps change negative thought patterns and behaviors that can affect the quality of sleep. CBT has been shown to be effective in improving sleep quality and reducing the symptoms of insomnia.
- Acupuncture: This is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting needles into specific points on the body. Acupuncture can help improve the quality of sleep, including REM sleep.
It is important to note that supplements and therapy options should only be used after consulting with a healthcare professional. While some of these options can be helpful, they may not be suitable for everyone and may have potential side effects. Additionally, it is important to focus on establishing healthy sleep habits first, as these will have the greatest impact on improving REM sleep.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of REM sleep, it is impossible not to be amazed by the extent of its benefits. From memory consolidation and emotional regulation to physical restoration and growth, the role of REM sleep in our overall well-being cannot be overstated. It is a critical component of our sleep cycle, and understanding its purpose can help us fully appreciate the importance of dreaming. In this final section, we will recap the key takeaways from our discussion and look at the long-term benefits of making sure we get enough REM sleep.
Importance of Dreaming
Dreaming is a fundamental component of the REM sleep stage, and it serves a crucial role in sleep psychology. During REM sleep, the brain becomes incredibly active, and we experience vivid and often surreal dreams. These dreams can be puzzling and difficult to interpret but are believed to offer meaningful insights into our psyche and emotional state.
Dreams and Emotional Processing: One of the vital functions of dreaming is to facilitate emotional processing. During dreams, we often encounter situations that may evoke strong emotions such as anxiety, fear, or even joy. By experiencing and processing these emotions in a safe and non-threatening environment, we can learn to regulate our emotions better during waking life.
Neuroplasticity: Dreams may also aid in neuroplasticity, the process by which the brain forms new connections and adapts to changing environments. The brain’s activity during REM sleep can help consolidate learning and may play a role in creativity enhancement as well.
Mental Health: Dreams have also been linked to mental health. Studies have shown that people with depression and other mental health disorders may experience less REM sleep and may have fewer and less complex dreams. Dreams may serve as a barometer of mental health and could offer insights into the effectiveness of certain treatments.
Dreaming represents a critical aspect of REM sleep and plays a vital role in our mental and emotional wellbeing. By fostering emotional processing, aiding in neuroplasticity, and potentially serving as a mental health barometer, it is clear that REM sleep and dreaming matter deeply.
Long-term Benefits of REM Sleep
REM sleep not only provides immediate benefits for our cognitive and physical functions, but also long-term advantages that are crucial for our overall wellbeing. Here are some of the long-term benefits of REM sleep:
| Benefits | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease | Studies have found that insufficient REM sleep can increase the buildup of beta-amyloid proteins in the brain, which can lead to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. On the other hand, deep and longer periods of REM sleep have been associated with decreased risk of this disease. |
| Better mental health | REM sleep has been linked to better mental health, particularly in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. During REM sleep, the brain processes emotions and helps regulate mood, leading to improved mental health overall. |
| Increased life span | Research has found that individuals who consistently get enough REM sleep have a longer life expectancy compared to those who don’t. This is because REM sleep promotes physical restoration and regeneration, which in turn helps to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. |
| Improved brain function | REM sleep plays a crucial role in consolidating memories, processing emotions, and encouraging creative thinking. Lack of REM sleep can lead to decreased cognitive function and memory loss over time. |
| Weight management | REM sleep is important for regulating metabolism and hormone production, which can help with weight management. Insufficient REM sleep has been linked to weight gain and an increased risk of obesity. |
These long-term benefits emphasize the importance of getting enough REM sleep on a regular basis. By prioritizing sleep and taking steps to improve sleep hygiene, we can ensure that we reap the many benefits of REM sleep for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens during REM sleep?
During REM sleep, the brain is highly active and dreaming occurs. The eyes also move rapidly back and forth, hence the name REM or Rapid Eye Movement sleep.
How long does each REM cycle last?
Each REM cycle typically lasts between 90 and 120 minutes, with each cycle becoming longer as the night goes on.
What are the stages of sleep?
There are four stages of sleep, with the first three being non-REM sleep and the fourth being REM sleep. Non-REM sleep is characterized by slower brainwaves and little to no eye movement.
Why is it important to get enough REM sleep?
REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional regulation, learning and creativity enhancement, physical restoration and growth, and maintenance of brain function.
Can REM sleep improve my mood?
Yes, REM sleep has been shown to improve mood and emotional regulation. Lack of REM sleep can actually lead to increased rates of depression and mood disorders.
What are some common disturbances that can prevent REM sleep?
Some common disturbances that can prevent REM sleep include noise, light, discomfort, and stress.
Is it possible to increase the amount of REM sleep I get?
Yes, there are several strategies that can help increase the amount of REM sleep you get each night. These include establishing a sleep routine, avoiding disturbances, reducing stress, and considering supplements and therapy.
What supplements can help improve REM sleep?
Supplements such as melatonin, valerian root, and magnesium may help improve the quality and quantity of REM sleep. However, it is important to speak to a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Can therapy help improve REM sleep?
Yes, cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) has been shown to improve the quality of sleep, including REM sleep.
Is it harmful to have too little REM sleep?
Yes, having too little REM sleep can have negative effects on cognitive function, emotional regulation, and physical health. Chronic REM sleep deprivation has also been linked to an increased risk of certain mental health disorders.