Sleep is a state of mind and body that is essential to our overall health and well-being. While we spend a significant portion of our lives sleeping, the science behind this seemingly mundane act continues to baffle researchers and scientists alike. One of the most intriguing phenomena within the realm of sleep is sleep paralysis, a condition that can be terrifying and mystifying at the same time. On the other hand, lucid dreaming is a fascinating concept that has piqued the interest of many. What is the connection between these two distinct and seemingly unrelated experiences? In this article, we will delve into the science behind sleep paralysis and its connection to lucid dreaming, exploring the latest research and discoveries that have shed light on these intriguing topics.
What is Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon where a person is temporarily unable to move or speak while falling asleep or awakening. During an episode of sleep paralysis, the individual may experience vivid hallucinations and feel an intense sense of pressure or constriction in their chest. This can be a frightening and disorienting experience, especially for those who are unaware of what is happening to them. Many people who experience sleep paralysis may wonder if they are experiencing a medical emergency or if there is something seriously wrong with their minds or bodies. To better understand sleep paralysis, it is important to examine what causes it and how it affects the brain and overall sleep patterns.
Why Does Sleep Paralysis Occur?
The occurrence of sleep paralysis can be attributed to a number of factors, including:
- Sleep Disruptions: Interrupted or disrupted sleep patterns can trigger sleep paralysis. Certain conditions including insomnia or sleep apnea can increase the frequency and severity of sleep paralysis episodes.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic component to sleep paralysis, as it tends to run in families. Research has identified specific genes that may be involved in regulating sleep and wake cycles, which may contribute to the development of sleep paralysis.
- Stress and Anxiety: Extreme stress and anxiety can increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis. Stress hormones like cortisol can interfere with normal sleep processes, increasing the chances of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Narcolepsy: Sleep paralysis is a common symptom of narcolepsy, a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden attacks of sleep.
- Altered Sleep Patterns: Certain sleep patterns, such as sleeping on your back, can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Additionally, changes in sleep patterns such as irregular sleep schedules, jet lag, or shift work can all contribute to the onset of sleep paralysis.
These and other factors can all contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis, but the exact mechanisms behind this phenomenon are still not well understood.
Sleep Paralysis and the Brain
During sleep, our brain goes through several stages, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Sleep paralysis occurs when our brain experiences a disruption in the REM sleep stage, leading to the temporary inability to move or speak upon waking up.
The Role of the Brain in Sleep Paralysis
During REM sleep, our brain usually experiences muscle atonia, which is a temporary paralysis of the muscles. This paralysis helps prevent us from physically acting out our dreams and potentially harming ourselves or others. However, in individuals experiencing sleep paralysis, this muscle atonia persists even as they begin to wake up, leading to the sensation of being paralyzed.
Brain Chemistry and Sleep Paralysis
Researchers have found that sleep paralysis may be linked to a disruption in the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which plays a role in regulating muscle movements during sleep. Studies have shown that individuals with sleep paralysis have lower levels of GABA in their brains compared to those who do not experience sleep paralysis.
Additionally, there may be a genetic component to sleep paralysis. Some studies have suggested that certain genes may play a role in individuals’ susceptibility to the condition.
Other Factors Influencing Sleep Paralysis
While disruptions in brain chemistry and genetics may contribute to sleep paralysis, other factors may also influence an individual’s likelihood of experiencing it. These can include:
- Irregular sleep patterns
- Stress and anxiety
- Sleeping on your back
- Interruption of sleep
By understanding the role of the brain and various factors that can influence sleep paralysis, researchers can develop effective interventions and treatments for those experiencing this condition.
Lucid Dreaming
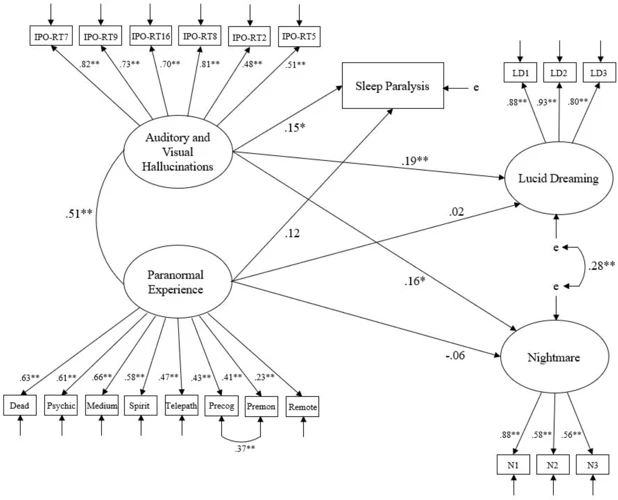
Lucid dreaming is a phenomenon where a person experiences a dream where they are aware that they are dreaming. This allows the dreamer to take control of the dream and explore their subconscious mind. The concept of lucid dreaming has fascinated mankind for centuries and has been a subject of discussion and research in the field of psychology and neuroscience.
What is Lucid Dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is a state where an individual is conscious during a dream. In other words, they are aware that they are dreaming. This allows the dreamer to take control of the dream and maneuver the dream environment as per their wishes. The dreamer can explore their subconscious mind and experience emotions, sensations, and experiences that they may not have in waking life. Lucid dreams can vary in length, level of control, and vividness.
Is Lucid Dreaming Real?
Lucid dreaming has been scientifically proven to be a real phenomenon. In fact, studies have shown that lucid dreaming is a learnable skill and can be practiced and developed over time. However, some people may have a natural talent for lucid dreaming and may experience it more frequently than others.
Lucid Dreaming and Sleep Paralysis
Interestingly, sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming are closely related. Sleep paralysis is a state where the body is immobilized during sleep, while the mind is still awake. This can be a scary experience for some people, but it can also be a gateway to lucid dreaming. When a person experiences sleep paralysis, they are in a unique position to enter a lucid dream state. By remaining calm and focused, a person can use the sensations of sleep paralysis to enter into a lucid dream.
The Benefits of Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis can have numerous benefits. They can help an individual explore their subconscious mind, face and overcome fears and anxieties, and improve their creativity and problem-solving skills. Lucid dreaming can also be a source of entertainment and a way to relieve stress.
Are Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming Safe?
While sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming are generally considered safe, they can be a scary and overwhelming experience for some individuals. It is important to approach these states with caution and seek professional help if they become too frequent or cause anxiety or distress.
Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that has been the subject of much research and discussion in the field of psychology and neuroscience. While it can be a learnable skill and provide numerous benefits, it should be approached with caution and care. Sleep paralysis can be a gateway to lucid dreaming, but it can also be a scary experience for some individuals. Seeking professional help is important if these states become too frequent or cause distress.
What is Lucid Dreaming?
Have you ever experienced a dream where you were fully aware that you were dreaming? Where you could control your actions and surroundings within the dream? If so, you may have experienced lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming is a state in which the dreamer is conscious and aware that they are dreaming, allowing for the possibility of more control and agency within the dream. This phenomenon has intrigued scientists and average dreamers alike for centuries, and there is still much to be learned about the science behind it. Let’s explore the concept of lucid dreaming and its potential implications.
Is Lucid Dreaming Real?
Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that has been scientifically studied and validated. Here are some interesting facts that prove the reality of lucid dreaming:
- Objective measurements: Using functional MRIs, studies have shown that the brain activity during lucid dreaming is similar to that of waking consciousness.
- Subjective experiences: Many people have reported experiencing lucid dreams and being able to control the dream narrative.
- Historical and cultural evidence: Lucid dreaming has been recorded in various cultures and even ancient texts like the Hindu Upanishads and Tibetan Buddhists texts.
- Therapeutic applications: Lucid dreaming has been used for a variety of therapeutic purposes, including treating nightmares and PTSD.
Despite the overwhelming evidence, there are still skeptics who doubt the reality of lucid dreaming. However, with advances in neuroscience and an increasing focus on the study of consciousness, it is likely that more research will confirm the existence and potential benefits of lucid dreaming.
Lucid Dreaming and Sleep Paralysis
Lucid dreaming is characterized as the ability to be aware that you are dreaming while the dream is still ongoing. In a lucid dream, the dreamer can control the events and their actions within the dream. The occurrence of this type of dreaming is closely related to sleep paralysis.
Sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming share many similarities, including:
- Brain activity: Both sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming occur during the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is characterized by intense brain activity and high levels of neural stimulation.
- Sensory awareness: During both sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, individuals experience a heightened sense of sensory awareness and can often hear, see, and feel things that are not present in their physical surroundings.
- Waking consciousness: Both sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming involve a state of consciousness that is somewhere between being fully awake and completely asleep, allowing for a level of control over the dream or paralysis.
The main difference between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is the level of control and awareness that the individual has:
- Sleep paralysis: In sleep paralysis, the individual is aware that they are awake, but cannot move or speak. They may also experience hallucinations and be unable to distinguish reality from the dream state.
- Lucid dreaming: In lucid dreaming, the individual is aware they are dreaming and can actively control and shape the dream’s events and outcomes.
The relationship between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is still being studied by scientists. However, it is believed that it may be possible to induce lucid dreaming from a state of sleep paralysis. By remaining calm and focusing on their thoughts, individuals may be able to transition from a state of paralysis to a lucid dreaming state.
Although both sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming can be frightening experiences, they can also be powerful tools for personal growth and exploration. With practice and guidance, individuals can learn to use these experiences to enhance their creativity, overcome fears, and gain a deeper understanding of their subconscious selves.
The Connection Between Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming

The connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is a fascinating subject that has garnered much interest in recent years. Both phenomena are related to the process of sleep and dreaming, and they share similar characteristics. Understanding the connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is key to unlocking the potential benefits of both experiences.
How Does Sleep Paralysis Relate to Lucid Dreaming?
Sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming are related in that they both occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep. During this stage, the body is paralyzed to prevent movements that could potentially harm the sleeper, while the mind is highly active, creating vivid and often surreal dream experiences.
Lucid dreaming is a state in which the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming, allowing them to control and manipulate their dream environment. Sleep paralysis, on the other hand, is a state in which the body remains paralyzed despite waking up from the sleep cycle, and the mind is often still in a dream-like state, leading to vivid hallucinations and sensations.
Studies have shown that those who regularly experience sleep paralysis may be more likely to have lucid dreams as well. This could be due to the fact that those who are regularly in a state of sleep paralysis are more aware of their sleep and dream states, leading to a greater ability to recognize when they are dreaming and subsequently control their dreams.
The Benefits of Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming
While sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming can be frightening experiences for some, they also hold great potential for personal growth and healing. Lucid dreaming has been shown to improve problem-solving skills, aid in creative thinking, and even alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Sleep paralysis, while often accompanied by terrifying hallucinations, can also serve as a launching pad for lucid dreaming and out-of-body experiences. Those who successfully enter a lucid dream state from a state of sleep paralysis report feeling empowered and in control of their dream environment.
Are Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming Safe?
While sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming are generally considered safe experiences, it is important to note that they can be scary and overwhelming for some individuals. Those with a history of anxiety or panic attacks may want to approach these experiences with caution and seek guidance from a healthcare professional if needed.
Additionally, it is important to practice good sleep hygiene and establish healthy sleep habits in order to reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis or disrupted sleep cycles.
Conclusion
The connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is a complex and fascinating topic that has captivated researchers and individuals alike. While there are potential benefits to be gained from these experiences, it is important to practice caution and establish healthy sleep habits. With further research and exploration, we may be able to unlock even more of the potential benefits these experiences have to offer.
How Does Sleep Paralysis Relate to Lucid Dreaming?
Many people who experience sleep paralysis may wonder if there is any connection between this terrifying sensation and the strange, fascinating phenomenon of lucid dreaming. Sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming are two separate experiences, but they do have some commonalities that have sparked the curiosity of scientists and dream enthusiasts alike. Let’s explore the potential relationship between these two unique states of consciousness.
The Benefits of Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis may seem like frightening experiences initially, but they can offer several benefits to those who experience them. Here are some of the benefits:
- Increased Self-Awareness: Lucid dreaming provides you an opportunity to practice introspection and self-awareness, something that can be carried over into your waking life.
- Improved Creativity: People who experience lucid dreams say that they are more creative and imaginative in their waking life, making them better problem-solvers and more innovative thinkers.
- Reduced Anxiety: Although sleep paralysis can be anxiety-inducing, it can also help people better manage their anxiety levels in their waking life. Learning to remain calm during a potentially scary experience can translate into improved coping mechanisms when dealing with the stressors of everyday life.
- Enhanced Memory: Dreams have been linked to memory consolidation, which means that experiencing lucid dreams could potentially improve your memory skills.
- Increased Confidence: Successfully navigating a lucid dream or overcoming a scary sleep paralysis episode can increase your confidence levels and give you a sense of empowerment.
While these benefits have not been scientifically proven, anecdotal evidence from those who experience lucid dreams and sleep paralysis suggest that they are real.
It is important to note, however, that these benefits come with risks, and anyone considering attempting to induce lucid dreaming or experience sleep paralysis should speak with a healthcare professional first.
Are Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming Safe?
It’s natural to wonder about the safety of sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming. While both have their risks, they can be safe for most people with proper guidance and precautions.
Sleep Paralysis:
Sleep paralysis, though terrifying, is not typically dangerous in and of itself. However, it can be a symptom of underlying health conditions such as narcolepsy, sleep apnea, and anxiety disorders. Seeking medical attention if sleep paralysis is affecting your daily life is recommended. Additionally, practicing good sleep hygiene habits like maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, and sleeping in a comfortable environment can help reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis episodes.
Lucid Dreaming:
Lucid dreaming itself is generally considered safe, with no inherent risks. However, there are some precautions to keep in mind for those who wish to experiment with lucid dreaming. As with sleep paralysis, maintaining good sleep hygiene and seeking medical attention for underlying health conditions is recommended. Additionally, it’s important to remember that dreams can be unpredictable, and some people may experience intense, frightening, or even traumatic content during lucid dreams. It’s essential to approach lucid dreaming with a level head and the ability to recognize when it’s time to end the experience.
Safety Comparison:
To simplify the comparison of safety between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, the table below outlines some of the risks associated with each phenomenon:
| Risks | Sleep Paralysis | Lucid Dreaming |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Health Conditions | Can be a symptom | No inherent risks |
| Frightening Content | Episodes can be terrifying | Dreams can be unpredictable |
| Safety Precautions | Practicing good sleep hygiene; seeking medical attention | Approaching with a level head; knowing when to end the experience |
With proper precautions and guidance, both sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming can be safe for most people. It’s essential to maintain good sleep hygiene, seek medical attention for underlying health conditions, and approach lucid dreaming with a level head to ensure a positive experience.
Latest Research and Discoveries
As the study of sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming continues to evolve, researchers are uncovering new and exciting findings that shed light on the mysterious world of sleep. Through advances in technology and innovative research methods, scientists are discovering more about the science behind these phenomena than ever before. In this section, we’ll explore some of the latest research and discoveries in the field of sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, and discover what these findings mean for our understanding of the human mind and its relationship with sleep.
What Scientists Know About Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming
Scientists have conducted extensive research on sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, leading to several remarkable findings. Here are some of the key points that have been discovered:
- Sleep paralysis and REM sleep: Researchers have found that sleep paralysis is most likely to occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep. During REM sleep, the brain is active and vivid dreams occur. This is also the time when sleep paralysis can happen.
- Lucid dreaming and the prefrontal cortex: Studies have shown that lucid dreaming is linked to increased activity in the prefrontal cortex of the brain. This is the region responsible for decision-making, self-awareness, and consciousness.
- Overlap between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming: Due to the fact that sleep paralysis occurs during REM sleep, which is also the time when lucid dreaming is most likely to occur, there is often an overlap between the two experiences.
- Emotional experiences during sleep paralysis: Some research suggests that individuals who experience sleep paralysis may be more likely to have negative emotional experiences during the episode, such as feeling like a threatening presence is in the room. However, this is not always the case and some people’s experience is neutral or even positive.
- Prevalence of sleep paralysis: While it is difficult to determine the exact prevalence due to underreporting, it is estimated that between 5% and 30% of the general population will experience sleep paralysis at some point in their lives.
- Possible risk factors for sleep paralysis: Studies have identified several possible risk factors that may increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis, including irregular sleep patterns, sleep deprivation, stress, and mental health conditions like anxiety and depression.
Researchers have made significant progress in understanding the mechanisms behind sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, paving the way for further discoveries in the field.
Studies on the Therapeutic Potential of Lucid Dreaming and Sleep Paralysis
There have been several studies conducted on the potential therapeutic benefits of lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis. These studies have explored how these experiences can be utilized in treating various mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
One study published in the “Journal of Clinical Psychology” found that individuals who practiced lucid dreaming techniques experienced a reduction in symptoms of anxiety and depression. These individuals reported feeling more in control of their emotions and thought processes, which led to an overall improvement in their mental health.
Another study conducted at the University of British Columbia found that individuals who experienced frequent sleep paralysis were more creative than those who did not. The study concluded that the paralysis experience allowed individuals to tap into their subconscious mind, which in turn fueled their creativity.
An ongoing study at Stanford University is exploring the use of lucid dreaming techniques as a treatment for individuals with PTSD. The study is examining how individuals can use lucid dreaming to confront and overcome traumatic memories in a controlled and safe environment, perhaps leading to a reduction in PTSD symptoms.
These studies suggest that lucid dreaming and sleep paralysis have potential therapeutic value that should be further explored by the scientific community.
| Study | Findings |
|---|---|
| Journal of Clinical Psychology | Lucid dreaming techniques can lead to a reduction in symptoms of anxiety and depression. |
| University of British Columbia | Sleep paralysis experiences can enhance creativity in individuals. |
| Stanford University | Lucid dreaming techniques may have potential as a treatment for individuals with PTSD. |
Possible Future Directions of Research
As the scientific community continues to explore the fascinating world of sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, new research is uncovering exciting possibilities for the future. Here are some possible future directions of research:
- Investigating the Mechanisms Behind Lucid Dreaming: Scientists are interested in learning more about how lucid dreaming happens and exploring the underlying neural mechanisms at play. Identifying the areas of the brain responsible for lucid dreaming could lead to exciting new therapies or techniques for achieving lucidity.
- Developing New Treatments for Sleep Paralysis: Although sleep paralysis is a fairly common occurrence, there are currently no treatments available for it. However, as more is learned about the condition, researchers may be able to develop novel interventions that could alleviate symptoms or prevent it from occurring altogether.
- Exploring the Therapeutic Applications of Lucid Dreaming: Studies have already shown that lucid dreaming may have therapeutic potential for mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. Further research could explore how lucidity might be leveraged to promote better sleep, enhance creativity, or boost cognitive function.
- Investigating the Relationship Between Sleep Disorders and Dreaming: Researchers are interested in exploring the connections between sleep disorders and dreaming, including sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming. Investigating these relationships could help improve treatments for sleep disorders or expand our understanding of the human mind and brain.
- Developing Tools to Facilitate Lucid Dreaming: Some scientists are investigating the feasibility of tools or technologies that could help individuals achieve lucidity more easily, such as certain types of audio or light stimulation.
As researchers continue to delve into the fascinating world of sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, the possibilities for what we might uncover are vast and exciting.
Conclusion
As the mysteries of the human mind continue to unfold, the relationship between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming remains a topic of intrigue and interest for scientists and dream enthusiasts alike. While we may not fully understand the intricacies of these phenomena, their potential benefits and therapeutic applications are becoming increasingly evident. In this article, we have explored the science behind sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, their connection, and the latest research and discoveries in this field. Let us now reflect on the implications of these findings with perplexity and wonderment, as we ponder the limitless possibilities of the human mind.
Wrapping It Up
Sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming are two fascinating phenomena that are still not fully understood by scientists. However, the available research has shed some light on the possible explanations and benefits of these experiences.
Key takeaways:
- Sleep paralysis is a sensation of being unable to move or speak during the transition between wakefulness and sleep.
- Lucid dreaming is a state where the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and can sometimes control the dream environment.
- There is a clear connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, as many lucid dream experiences start with sleep paralysis.
- While these experiences may sometimes be unsettling or frightening, they can also offer therapeutic benefits for some individuals.
- Research on the topic is ongoing, and may lead to a better understanding of how the brain works during sleep and dreaming.
It is important to note that while these experiences can be exciting and intriguing, they can also be unsettling for some individuals. If you experience frequent sleep paralysis or have concerns about your dreams, it may be helpful to speak with a healthcare provider or sleep specialist. In any case, it is clear that the connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is a fascinating area of study that will continue to generate interest and inspiration for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can sleep paralysis be dangerous?
Sleep paralysis itself is not dangerous, but it can cause anxiety or stress for some people.
Can lucid dreaming cause sleep issues?
Some people may find that practicing lucid dreaming techniques interferes with their ability to fall asleep or get restful sleep.
Can sleep paralysis be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent sleep paralysis, maintaining good sleep habits, managing stress, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can lower the likelihood of experiencing it.
Can lucid dreaming be used for therapy?
Some therapists use lucid dreaming techniques as a tool in therapy for individuals with anxiety or PTSD.
Why do some people experience sleep paralysis more often than others?
Research suggests that genetics, sleep habits, and mental health conditions may play a role in the frequency of sleep paralysis experienced by an individual.
Is it possible to lucid dream every night?
While some individuals do report being able to lucid dream every night, it is not typical for most people.
Can medication or supplements cause sleep paralysis?
Some medications and supplements, such as those for ADHD or depression, may increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
What is the difference between lucid dreaming and astral projection?
Lucid dreaming is a state of being aware that one is dreaming, while astral projection involves the belief that one’s consciousness can leave the physical body and travel elsewhere.
Is sleep paralysis a symptom of narcolepsy?
While sleep paralysis is often associated with narcolepsy, it is not necessarily a symptom of the disorder and can occur on its own.
Can sleep paralysis be treated with medication?
There is no specific medication for treating sleep paralysis, but treating underlying sleep disorders or mental health conditions may decrease episodes.








