Sleep is the body’s way of rejuvenating and repairing itself. It is an essential aspect of our lives, and a lack of restful sleep can lead to a host of health problems. However, for some individuals, sleep can become a source of fear and anxiety due to a condition known as sleep paralysis. Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that occurs when a person is unable to move their body or speak during the transition between wakefulness and sleep. While sleep paralysis can occur naturally, it is also a side effect of certain medications. In this article, we will explore the causes and treatment of sleep paralysis as a side effect of medications.
What is sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a condition that occurs when a person is unable to move or speak while transitioning in or out of sleep. It is essentially the inability to move voluntary muscles, which affects a person’s ability to speak or even breathe. This phenomenon can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes, and can be a terrifying experience for those who suffer from it.
Sleep paralysis is often accompanied by vivid hallucinations, which can range from frightening to bizarre. These hallucinations can be so real that sufferers often have difficulty differentiating them from reality. However, it is important to note that while these hallucinations can be disturbing, they are not indicative of any underlying mental health problems.
Sleep paralysis can occur as a symptom of a number of different sleep disorders, including narcolepsy and sleep apnea. However, it can also occur as a side effect of certain medications, which we will discuss in more detail below.
Sleep paralysis is a relatively common experience, affecting approximately 25% of the general population at least once in their lifetime. While the condition can be distressing, there are treatments available that can help to alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of episodes. It is important to seek medical advice if you experience sleep paralysis on a regular basis, as this could be indicative of an underlying sleep disorder or other medical condition.
Medications that can cause sleep paralysis and how they work
There are several medications that can cause sleep paralysis as a side effect, including certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, prescription sleep aids, and sedatives. These medications work by affecting chemicals in the brain that regulate sleep, mood, and anxiety.
Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are two classes of antidepressants that have been linked to sleep paralysis. These medications increase the levels of certain neurotransmitters, including serotonin and norepinephrine, which can disrupt the sleep cycle and lead to episodes of paralysis during the night.
Antipsychotics: Antipsychotic medications are often used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other mental health conditions that involve psychosis. These medications work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which can help alleviate symptoms of hallucinations and delusions. However, they can also disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to episodes of sleep paralysis.
Prescription Sleep Aids and Sedatives: Prescription sleep aids and sedatives are commonly used to treat insomnia and other sleep disorders. These medications work by increasing the activity of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps calm the brain and induce sleep. However, they can also cause disruptions in the sleep cycle, leading to episodes of sleep paralysis.
Other Medications that Can Cause Sleep Paralysis: There are several other medications that have been linked to sleep paralysis as a possible side effect, including some medications used to treat ADHD, migraines, and high blood pressure. It is important to note that not everyone who takes these medications will experience sleep paralysis, and the risk of this side effect varies depending on the individual and the dosage of the medication.
The Relationship Between Sleep Paralysis and Certain Medications

Sleep paralysis is a condition where one is unable to move or speak during the transition between wakefulness and sleep. It can be a terrifying experience for those who suffer from it. While there can be multiple factors that contribute to the development of sleep paralysis, certain medications have been identified as a potential cause.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are one of the most commonly prescribed medication classes for depression and anxiety disorders. However, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which are commonly used antidepressants, have been known to cause sleep paralysis. SSRIs may affect the levels of serotonin in the brain, which is a neurotransmitter that regulates sleep. It is believed that the disruption of this cycle can lead to sleep paralysis in some people. In some cases, sleep paralysis may also occur as a withdrawal symptom when one stops taking SSRIs.
Antipsychotics
Antipsychotic medication is often used to treat conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. They work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which is a chemical messenger involved in sleep regulation. However, antipsychotics have also been associated with sleep paralysis. While the exact mechanism is not fully understood, it is believed that the dopamine-blocking effect of antipsychotics is the reason behind this side effect.
Prescription Sleep Aids and Sedatives
Prescription sleep aids and sedatives are commonly used to treat insomnia and other sleep disorders. However, they can also cause sleep paralysis. These medications are known to suppress the central nervous system, which can make it difficult for the body to transition smoothly into different stages of sleep. As a result, one may experience sleep paralysis.
Other Medications that Can Cause Sleep Paralysis
Other medications such as muscle relaxants, narcolepsy medication, and even some allergy medications have been implicated in causing sleep paralysis. Muscle relaxants work by reducing muscle tone, which can interfere with normal breathing and lead to sleep disturbances. Narcolepsy medication can also disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to sleep paralysis. Some allergy medications contain diphenhydramine, which is a sedating antihistamine that can cause drowsiness and increase the risk of sleep paralysis.
It is important to be aware of the potential side effects of any medication that you may be taking. If you suspect that your medication is causing sleep paralysis, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to discuss possible alternatives or adjustments to your treatment plan.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are a class of medications that are commonly prescribed to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and other related conditions. However, a common side effect of antidepressants is sleep paralysis. This occurs because certain antidepressants affect the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to sleep paralysis.
One of the most commonly prescribed antidepressants is selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SSRIs. These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood and sleep. While effective at treating depression and anxiety, SSRIs can also disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to sleep paralysis.
Another type of antidepressant that can cause sleep paralysis is tricyclic antidepressants. These medications work by blocking the reuptake of certain neurotransmitters, including serotonin and norepinephrine. However, this can also disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to sleep paralysis.
If you are experiencing sleep paralysis as a side effect of antidepressants, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider. They may be able to adjust your medication or prescribe a different one that does not cause sleep paralysis. Additionally, practicing good sleep hygiene and implementing relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, may also help alleviate symptoms of sleep paralysis.
Antipsychotics
Antipsychotics are medications primarily used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other mental illnesses that can cause delusions, hallucinations, and disordered thinking. While they are effective in managing these symptoms, some antipsychotics have been known to cause sleep paralysis as a side effect. These medications work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which can interfere with the normal functioning of the REM sleep cycle.
Common antipsychotics that can cause sleep paralysis include:
- Clozapine
- Risperidone
- Olanzapine
- Quetiapine
Sleep paralysis caused by antipsychotic medication typically occurs during the onset of sleep or upon waking in the morning. The individual may experience an inability to move or speak, as well as vivid dreams or hallucinations. These symptoms can be distressing and may further exacerbate mental health symptoms, leading to increased anxiety and sleep disturbances.
It is essential for patients taking antipsychotics to discuss any sleep paralysis symptoms with their healthcare provider. Adjusting the dosage, switching to a different medication, or adding a medication to treat the sleep paralysis symptoms may be options to consider.
In addition to medication management, practicing good sleep hygiene can help prevent sleep paralysis. This includes establishing a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants such as caffeine and nicotine before bedtime, and creating a relaxing sleep environment. It is also crucial to manage any underlying mental health conditions and reduce stress levels, as these factors can increase the risk of sleep paralysis.
While antipsychotics can be a helpful medication in managing mental health symptoms, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effect of sleep paralysis. Patients should communicate any symptoms or concerns with their healthcare provider to ensure the best course of treatment.
Prescription Sleep Aids and Sedatives
Prescription sleep aids and sedatives are medications that are commonly prescribed to those suffering from sleep disorders. These medications are designed to help individuals fall asleep faster and stay asleep for longer periods of time. However, they can come with potential side effects, including sleep paralysis.
Sleep aids and sedatives work by depressing the central nervous system, causing the individual to feel relaxed and drowsy. These medications can also decrease the amount of time it takes to fall asleep and increase the overall length of sleep. Unfortunately, these benefits can come with some risks.
Sleep paralysis is a potential side effect of prescription sleep aids and sedatives. This occurs when the individual is unable to move or speak during a period of wakefulness or while transitioning between wakefulness and sleep. The individual will often have vivid hallucinations and may feel as though they are suffocating.
The risk of experiencing sleep paralysis as a side effect of prescription sleep aids and sedatives increases with the dosage and duration of use. It is also more common in individuals who already suffer from sleep disorders and those who have a history of depression or anxiety.
If an individual experiences sleep paralysis as a side effect of prescription sleep aids or sedatives, it is important to speak with their healthcare provider. Their provider may adjust the dosage or switch to a different medication that is less likely to cause sleep paralysis.
In addition to working with a healthcare provider, there are lifestyle changes that individuals can make to help reduce the risk of sleep paralysis. These changes can include improving sleep hygiene and avoiding drugs or substances that can interfere with the central nervous system.
While prescription sleep aids and sedatives can be effective in helping individuals achieve better sleep, they can also come with potential side effects such as sleep paralysis. It is important for individuals to work closely with their healthcare provider and make necessary lifestyle changes to prevent and treat sleep paralysis.
Other Medications that Can Cause Sleep Paralysis
In addition to antidepressants, antipsychotics, and prescription sleep aids, there are other medications that can cause sleep paralysis as a side effect.
Blood Pressure Medications: Certain medications used to treat high blood pressure, such as beta-blockers and alpha-agonists, have been known to cause sleep paralysis in some individuals.
Acne Medications: Isotretinoin, a medication commonly used to treat severe acne, has been reported to cause sleep paralysis in some individuals. This medication is known to affect neurotransmitters in the brain, which can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to sleep paralysis.
Stimulants: Stimulants, such as amphetamines and methylphenidate, have been known to cause sleep paralysis in some individuals. These medications can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to episodes of sleep paralysis.
Antihistamines: Some over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), can cause sleep paralysis. These medications can cause drowsiness and lead to disrupted sleep, which can increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis.
It is important to note that not everyone who takes these medications will experience sleep paralysis as a side effect. However, if you are experiencing sleep paralysis and are taking any of these medications, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine if the medication could be contributing to your symptoms.
What are the Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis?
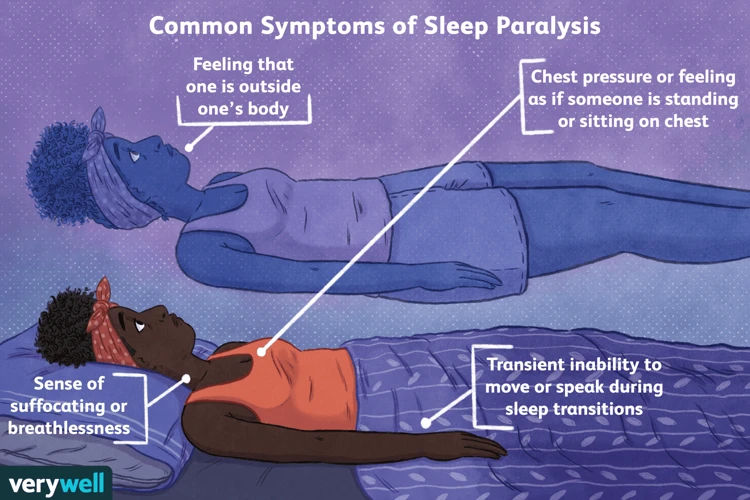
Sleep paralysis is a sleep disorder that can be caused by various factors, including medications. It is characterized by a temporary inability to move or speak during the transition between sleep and wakefulness. The symptoms of sleep paralysis can be scary and overwhelming, especially for those who experience it for the first time.
During Sleep Paralysis
During an episode of sleep paralysis, the individual may feel as though they are awake, but they are unable to move or speak. They may also experience a sensation of pressure on their chest or difficulty breathing. This can be accompanied by vivid hallucinations, which can often be terrifying in nature. These hallucinations can include feelings of being touched or grabbed, a presence in the room, or even the sensation of being levitated.
After Sleep Paralysis
After a sleep paralysis episode, the individual may feel disoriented, anxious, and fearful. They may also have difficulty falling back to sleep or may experience other disruptions to their sleep patterns.
It is important to note that the symptoms of sleep paralysis can vary from person to person, and not everyone will experience every symptom. Additionally, the severity and frequency of sleep paralysis episodes can also vary depending on the underlying cause.
If you are experiencing symptoms of sleep paralysis, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider to determine the cause and appropriate treatment options.
During Sleep Paralysis
During sleep paralysis, individuals may experience a range of frightening symptoms that can be incredibly distressing. During an episode of sleep paralysis, the individual is unable to move their limbs or body, despite being fully awake and conscious. This can be incredibly scary, causing feelings of panic, anxiety, and even terror.
One of the most commonly reported sensations during sleep paralysis is a feeling of pressure or weight on the chest, which can make it difficult to breathe or speak. Individuals may also experience vivid hallucinations, where they see, hear, or feel things that aren’t really there. These hallucinations can be incredibly vivid, making it difficult to distinguish them from reality.
Some individuals may also report an intense feeling of dread or impending doom, which can be accompanied by a sense that something dangerous or threatening is present in the room with them. Additionally, during sleep paralysis, individuals may feel like they are being dragged or pulled from their bed, or see shadowy figures lurking in the corner of the room.
All of these symptoms can be incredibly frightening and distressing. It is important to note, however, that sleep paralysis is not dangerous and does not cause any harm to the body. While the experience itself can be very unpleasant, it is not a sign of any underlying medical condition or mental health problem. With proper treatment and management, individuals can learn to cope with and overcome the symptoms of sleep paralysis.
After Sleep Paralysis
After sleep paralysis, individuals may experience a wide range of emotions and physical sensations. Some people report feeling anxious, scared, or on edge. Others may feel exhausted or drained, as though they have just run a marathon.
It is not uncommon for people to experience muscle soreness or stiffness after a bout of sleep paralysis. This is because during sleep paralysis, the muscles are often tense and contracted, as the body struggles to move despite being in a state of paralysis. The longer the episode of sleep paralysis lasts, the more likely it is that the individual will experience muscle soreness or stiffness afterward.
For some people, sleep paralysis can disrupt their sleep patterns, making it more difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. This can lead to feelings of exhaustion or fatigue during the day, making it difficult to concentrate or be productive.
Individuals who experience frequent or severe episodes of sleep paralysis may develop anxiety or other mood disorders as a result of the condition. This may be due to the fear and uncertainty that often accompany sleep paralysis, particularly if they are not aware of the condition or do not understand what is happening to them.
The experience of sleep paralysis can be uncomfortable and distressing, particularly if it occurs frequently or is accompanied by other symptoms. However, with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes, it is often possible to manage the condition effectively and reduce its impact on daily life.
What Causes Sleep Paralysis?
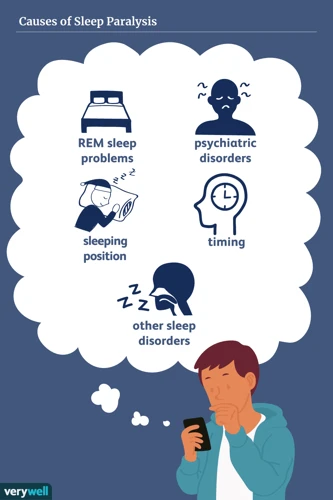
Medical Conditions that Increase the Risk of Sleep Paralysis
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. These conditions include narcolepsy, a disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden loss of muscle tone, and sleep apnea, a condition that causes interruptions in breathing during sleep.
Other medical conditions that can increase the risk of sleep paralysis include anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and migraines. Those with a family history of sleep paralysis may also be more susceptible to experiencing it themselves.
Stress and Sleep Deprivation
Stress and sleep deprivation can also increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. When the body is under stress, it can affect sleep patterns and cause disruptions in the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is when most episodes of sleep paralysis occur.
Sleep deprivation, whether chronic or acute, can also disrupt the sleep cycle and lead to sleep paralysis. This is because the body needs to go through several stages of sleep, including REM sleep, in order to fully rest and rejuvenate.
Other Factors that Contribute to Sleep Paralysis
Other factors that contribute to sleep paralysis include a disrupted sleep schedule or changes in sleep environment, such as traveling to a different time zone. Substance abuse, such as alcohol or drug use, can also increase the risk of sleep paralysis.
Individuals who have experienced trauma, such as sexual abuse, may be more likely to experience sleep paralysis. Finally, some research suggests that genetics may play a role in the development of sleep paralysis, although further studies are needed to fully understand this potential link.
Sleep paralysis can be caused by a combination of factors, including medical conditions, stress and sleep deprivation, and other external and internal factors. Understanding these causes can help individuals take steps to prevent or mitigate sleep paralysis episodes.
Medical Conditions that Increase the Risk of Sleep Paralysis
There are several medical conditions that can increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. One such condition is narcolepsy, a chronic sleep disorder that affects a person’s ability to regulate their sleep-wake cycles. Narcolepsy can cause sudden and uncontrollable bouts of sleepiness during the day, as well as vivid dream-like hallucinations and episodes of sleep paralysis during the night.
Another condition that may increase the risk of sleep paralysis is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA occurs when a person’s airway becomes blocked during sleep, causing them to briefly stop breathing before waking up to gasp for air. This disrupted sleep can lead to vivid dreams, hallucinations, and episodes of sleep paralysis.
In addition to these conditions, people with anxiety disorders or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may be more prone to experiencing sleep paralysis. In fact, some researchers believe that sleep paralysis may be a symptom of these conditions rather than a separate disorder.
It is also worth noting that certain neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, can increase the risk of sleep paralysis. Parkinson’s disease affects the part of the brain that controls movement, and can cause a range of symptoms including tremors, stiffness, and difficulty sleeping.
If you have any of these medical conditions and experience episodes of sleep paralysis, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan.
Stress and Sleep Deprivation
Stress and sleep deprivation can also play a role in causing sleep paralysis. Stress can lead to an increase in the hormones cortisol and adrenaline, which can disrupt normal sleeping patterns and lead to episodes of sleep paralysis. Additionally, stress can also lead to anxiety and depression, which are both linked to an increased risk of sleep paralysis.
Sleep deprivation can also disrupt the normal sleeping pattern and increase the risk of sleep paralysis. When the body doesn’t get enough sleep, it can’t function at its optimal level, leading to a range of problems that can include sleep paralysis. The body needs adequate rest to perform body system functions that ensure the proper engagement of organs, muscles, and nerves during the day.
Additionally, both stress and sleep deprivation can lead to other sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy, which is also linked to an increased risk of sleep paralysis. Narcolepsy is a disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and is often accompanied by other symptoms such as hallucinations and sleep paralysis.
To prevent sleep paralysis caused by stress and sleep deprivation, it’s important to manage stress levels and get enough sleep each night. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help manage stress levels, while establishing a regular sleep routine and practicing good sleep hygiene can ensure that the body gets enough rest each night.
Other Factors that Contribute to Sleep Paralysis
Apart from medical conditions and sleep-related issues, there are various other factors that can contribute to sleep paralysis. Stress and anxiety are some of the major factors that can increase your risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. When you are under stress, your body releases hormones like cortisol, which can disrupt your sleep pattern and make you more prone to sleep paralysis.
Certain lifestyle choices such as consuming caffeinated drinks or alcohol can also influence the likelihood of sleep paralysis. Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you awake, leading to sleep deprivation and triggering sleep paralysis. On the other hand, alcohol can disrupt your REM sleep, which is the stage when you are most likely to experience sleep paralysis.
Irregular sleep patterns, sleeping on your back, and physical exhaustion can also trigger sleep paralysis. Sleeping on your back can cause your airways to become blocked, leading to shortness of breath and a sense of suffocation, which can lead to sleep paralysis. Additionally, physical exhaustion can make it harder for your body to enter a deep sleep, which can result in sleep paralysis.
It is also essential to note that genetics can play a role in experiencing sleep paralysis. If you have a family history of sleep paralysis, you may be more prone to experiencing it yourself. Finally, certain cultural beliefs and experiences, such as sleep demons or spirit possession, can also contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis in some individuals.
Thus, it is essential to pay attention to these contributing factors and make necessary changes if needed, such as managing stress levels, improving sleep hygiene, and avoiding caffeine or alcohol before bedtime.
How to Treat and Prevent Sleep Paralysis
When it comes to treating and preventing sleep paralysis, there are a number of lifestyle changes and medical treatments that can be effective.
Lifestyle Changes: These may include reducing stress and ensuring that you get plenty of good quality sleep on a regular basis. Additionally, it can be helpful to avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol in the hours leading up to bedtime. Engaging in relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can also help reduce the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes.
Sleep Hygiene: Practicing good sleep hygiene can go a long way in preventing sleep paralysis. This means going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, and creating a comfortable sleeping environment that is conducive to restful sleep. This may include using a comfortable mattress and pillows, keeping your bedroom cool and dark, and avoiding electronic devices in bed.
Medical Treatment: In some cases, medication may be necessary to treat sleep paralysis. This may involve prescribing a medication to help manage an underlying medical condition or to help regulate sleep patterns. For example, if you are experiencing sleep paralysis as a side effect of an antidepressant, your doctor may lower the dosage or switch you to a different medication. In some cases, a medication like clonazepam may be prescribed to help alleviate the symptoms of sleep paralysis.
It is important to note that while there are treatments available for sleep paralysis, it may not be possible to completely eliminate the condition. However, with the right interventions and lifestyle changes, it is possible to reduce the frequency and intensity of episodes, allowing individuals to get the restful, restorative sleep they need to feel their best.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help prevent sleep paralysis from occurring. These changes involve alterations to daily habits that can impact sleep quality.
One crucial lifestyle change is to maintain a consistent sleep schedule. This means going to bed and waking up at the same time every day. A regular sleep pattern helps regulate the body’s natural clock and can reduce the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Reducing stress is also important for preventing sleep paralysis. Stress can disrupt sleep and increase the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation can be helpful.
Additionally, avoiding substances that can interfere with sleep, such as caffeine and alcohol, can be beneficial for preventing sleep paralysis. Both caffeine and alcohol can disrupt sleep and exacerbate sleep disorders like sleep paralysis.
Engaging in regular exercise can also be helpful in preventing sleep paralysis. Exercise helps regulate the body’s natural rhythm and promotes overall health, leading to better sleep quality.
Lastly, creating a comfortable sleep environment can help prevent sleep paralysis. This involves keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Using relaxing scents like lavender and maintaining a comfortable sleeping surface can also help improve sleep quality.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing sleep paralysis as a side effect of certain medications. Although these changes may take some time to become habit, the benefits of better sleep hygiene and a reduction in sleep paralysis episodes can be well worth the effort.
Sleep Hygiene
In order to prevent sleep paralysis, it is important to prioritize good sleep hygiene practices. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, both in terms of bedtime and wake-up time. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can help regulate your body’s natural sleep cycle, reducing the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Another important aspect of sleep hygiene is creating a relaxing sleep environment. This means keeping your bedroom cool, dark and quiet, and using comfortable bedding and pillows. Additionally, it is important to avoid stimulating activities such as phone use or watching TV in bed, as these can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
In addition to maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment, it is also important to prioritize relaxation techniques before bed. This can include activities such as taking a warm bath or practicing meditation or deep breathing exercises, all of which can help calm the mind and promote restful sleep.
Finally, it is important to avoid certain substances before bed that can interfere with sleep, including caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol. These substances can disrupt the body’s natural sleep cycle, making it more difficult to fall asleep and increasing the risk of sleep disturbances, including sleep paralysis. By prioritizing good sleep hygiene practices, you can reduce your risk of experiencing sleep paralysis as a side effect of certain medications.
Medical Treatment
When it comes to treating sleep paralysis as a side effect of certain medications, medical treatment may be necessary in some cases. One common approach to treating sleep paralysis is by adjusting the dosage or changing the medication that is causing the symptom. This is typically done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, who will carefully monitor the patient’s symptoms and adjust their medication as needed.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed specifically to help treat sleep paralysis. For example, certain antidepressants and antipsychotic medications that are known to cause sleep paralysis may be paired with other medications that can counteract this side effect. These medications may help to reduce episodes of sleep paralysis and improve overall sleep quality.
Another form of medical treatment that may be used for sleep paralysis is therapy. This may include cognitive behavioral therapy, which can help patients to better understand and cope with their symptoms. Therapy may also involve focus on addressing any underlying medical or psychological conditions that may be contributing to sleep paralysis.
It is worth noting that medical treatment for sleep paralysis is not always necessary. In many cases, making lifestyle changes and improving sleep hygiene can help to reduce episodes of sleep paralysis without the need for medication or therapy. However, for some patients, medical treatment may be an important part of addressing this condition and improving overall sleep quality. If you are experiencing sleep paralysis as a side effect of medication, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider about the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
Conclusion
After exploring the relationship between sleep paralysis and certain medications, as well as the symptoms, causes, and treatment options of this condition, it is clear that sleep paralysis can be a troublesome side effect of various medications. Those who experience sleep paralysis often report feeling anxious or frightened during episodes, and it can lead to poor sleep quality and negative impacts on daily life.
To prevent sleep paralysis, it is important to maintain good sleep hygiene and practice stress-reducing activities. Additionally, individuals taking medication should speak with their healthcare provider if they experience sleep paralysis to discuss potential alternatives or adjustments to their treatment plan.
Overall, while sleep paralysis can be a daunting and uncomfortable experience, there are various ways to manage and prevent it. It is important to stay vigilant of its potential causes and to seek medical treatment if necessary to ensure better sleep health and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can any medication cause sleep paralysis?
Not all medications can cause sleep paralysis, but there are certain medications with a higher likelihood of causing this side effect.
How common is sleep paralysis as a side effect of medication?
The frequency of sleep paralysis as a side effect of medication varies depending on the type of medication and individual factors.
What are some of the most common medications that can cause sleep paralysis?
Some of the most common medications include antidepressants, antipsychotics, and prescription sleep aids and sedatives.
How does antidepressant medication cause sleep paralysis?
Antidepressants can affect the balance of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, including serotonin, which can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to sleep paralysis.
Can sleep paralysis from medication occur during the day?
Sleep paralysis typically occurs during the transition between sleep and wakefulness, which means it can happen during the day or at night.
Can you still take medication that causes sleep paralysis if you experience this side effect?
If sleep paralysis is a side effect of a medication, it is important to discuss the situation with your doctor before stopping or changing the medication.
What are the symptoms of sleep paralysis?
Symptoms of sleep paralysis include the inability to move or speak, a sense of pressure or weight on the chest, and vivid hallucinations.
Can stress and sleep deprivation cause sleep paralysis?
Yes, both stress and sleep deprivation can increase the risk of sleep paralysis.
What are some lifestyle changes that can help prevent sleep paralysis?
Some lifestyle changes that can help prevent sleep paralysis include establishing a regular sleep schedule, reducing stress, avoiding stimulants, and improving sleep hygiene.
What should you do if you experience sleep paralysis?
If you experience sleep paralysis, try to remain calm and focus on moving your fingers or toes. Practicing good sleep hygiene and reducing stress may also help prevent future episodes.








