The Role of Sleep in Emotional Regulation
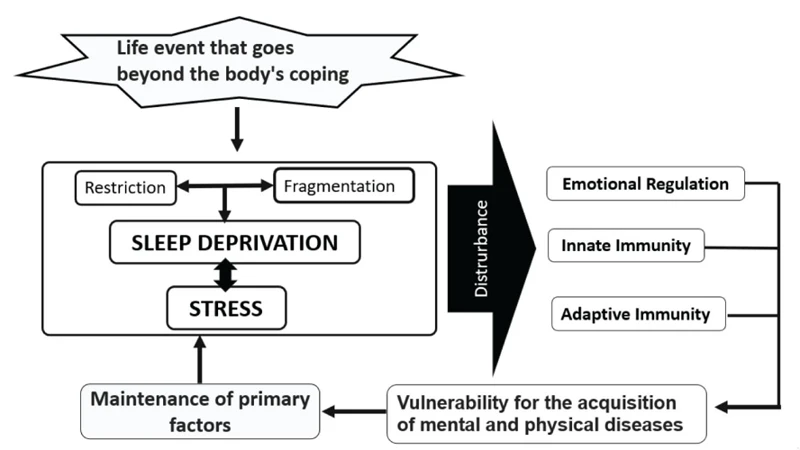
Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating emotions. It is during sleep that our brains process emotional experiences and consolidate memories, allowing us to better understand and manage our emotions when awake. Research has shown that lack of sleep can lead to increased emotional reactivity and difficulty regulating emotions. This is because sleep deprivation can negatively impact the functioning of the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for regulating emotions and making rational decisions.
During sleep, the brain also actively works to regulate the levels of neurotransmitters that affect emotions, such as dopamine, serotonin, and GABA. Adequate sleep helps maintain a healthy balance of these neurotransmitters, which are essential for regulating mood and emotional responses to stressors.
The link between sleep and emotional regulation is supported by studies showing that individuals with sleep disorders, such as insomnia, are more likely to experience anxiety and depression. This highlights the importance of ensuring that we get enough good quality sleep on a regular basis to maintain emotional well-being.
While the exact mechanisms of how sleep regulates emotions are still being studied, it is clear that getting enough sleep is essential for emotional health. Without sufficient sleep, we may find it harder to regulate our emotions and may experience increased stress and anxiety in our daily lives. It is therefore important to prioritize sleep hygiene habits and make sure we are taking steps to promote good quality sleep.
REM Sleep and Emotional Memory Processing
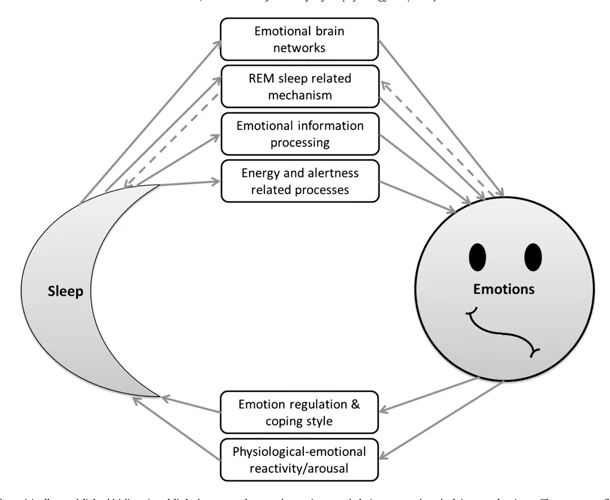
During the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, the brain undergoes a unique process of emotional memory processing. The amygdala, the part of the brain responsible for emotional response, becomes more active during REM sleep. This increased activity allows the brain to process and consolidate emotional memories, integrating them with existing memories.
Research has shown that emotional experiences are more likely to be remembered if they are experienced during REM sleep. This is because of the increased activity in the amygdala, which helps to strengthen the emotional memory.
During REM sleep, the brain shifts from the prefrontal cortex, responsible for logical and analytical thinking, to the hippocampus, the area responsible for long-term memory formation. This shift in activity allows the brain to integrate emotional experiences with existing memories, and to process and consolidate emotional memory.
This emotional processing during REM sleep is crucial for our emotional well-being, as it helps us to regulate our emotions and cope with stress. When we don’t get enough REM sleep, we may experience emotional instability and find it difficult to regulate our emotions.
It is important to note that not all dreams occur during the REM stage of sleep. However, emotional processing occurs during other stages of sleep as well, although to a lesser extent. During non-REM sleep, the brain still processes and consolidates memories, although the emotional component is not as prominent.
The REM stage of sleep plays a crucial role in emotional memory processing. This process helps us to regulate our emotions and cope with stress, improving our emotional well-being. It is essential to prioritize adequate sleep, including sufficient REM sleep, to ensure optimal emotional regulation.
The Connection Between Dreams and Emotional Processing
As we drift off to sleep each night, our brains continue to work tirelessly, playing a key role in processing our emotions. One of the most fascinating aspects of this process is the connection between our dreams and our emotional regulation. During sleep, the brain processes and consolidates emotional memories, which can manifest in our dreams. These mysterious and often perplexing dream experiences can offer valuable insights into our emotional well-being and serve as a key tool for unlocking the mysteries of our psyche. Let’s delve deeper into this intriguing link between dreaming and emotional processing.
Why We Dream About Emotional Events
Dreams often play out as a series of emotional events that may be confusing or even distressing. So, why do we dream about emotional experiences? The answer lies in the role of dreams in emotional regulation.
1. Memory consolidation: One reason we dream about emotional events is to consolidate our memories. Our brains process emotional memories differently than neutral memories, which can make them more difficult to store and retrieve. Dreaming about emotional events can help our brains encode and consolidate these memories for long-term storage.
2. Emotional processing: Dreams also provide a safe space for our brains to process and regulate emotions. During sleep, our brains can work through complex emotions without the interference of our conscious minds. For example, if you have a fight with a loved one, you may dream about the event as a way to work through your feelings of anger, hurt, or sadness.
3. Problem-solving and creativity: Dreams can also be a source of creative problem-solving. Our brains are still active during sleep, and can use this time to work through problems or issues we may be struggling with. You may find that you wake up with a new idea or solution after dreaming about a problem you’ve been trying to solve.
However, it’s important to note that not all dreams are the same. Some dreams may be more distressing than others, and may indicate underlying emotional issues that need to be addressed. It’s important to pay attention to your dreams and the emotions they evoke, and seek help if needed.
The Impact of Dream Content on Emotions
The content of our dreams can significantly impact our emotions. During REM sleep, the brain processes emotional experiences and memories, which can manifest in dreams. These dreams can evoke strong emotional responses, such as fear, sadness, or happiness. However, the way we interpret and integrate these emotions into our waking life can depend on various factors.
One factor is our individual disposition. For example, a person who is generally more anxious may have more fearful or unsettling dreams. Additionally, our coping mechanisms can influence how we process and react to dream content. Someone who tends to avoid or suppress unpleasant emotions may struggle with integrating the emotions evoked by their dreams.
Another factor is the type of dream content we experience. Dreams that involve unresolved conflicts, traumatic experiences, or overwhelming stress can be particularly impactful on our emotions. These dreams may cause us to ruminate on negative feelings, leading to increased anxiety or depression.
Conversely, positive dream content can have a beneficial impact on our emotions. Dreams that involve feelings of love, comfort, or achievement can leave us feeling more content and motivated. However, it is important to note that the nature of our dreams and how we interpret them can be highly personal.
The impact of dream content on our emotions can be significant, and it is important to consider how we process and integrate these experiences into our waking life.
Sleep Deprivation and Emotional Instability
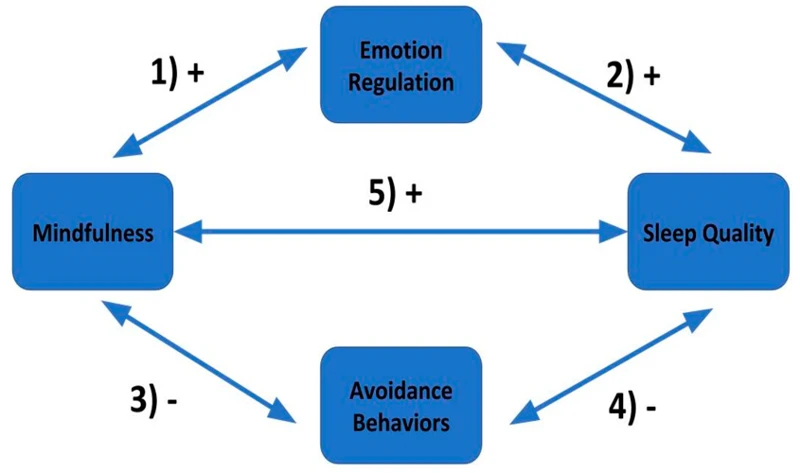
Lack of sufficient sleep is often linked to emotional instability and loss of emotional control. When we don’t get enough sleep, our brain’s capacity to regulate our emotions effectively is impaired. This means we may be more prone to emotional outbursts and experiencing negative emotions.
Sleep deprivation can also lead to cognitive impairment, which makes it harder for us to manage our emotions. We may find it difficult to think rationally and be more susceptible to irrational thinking.
Sleep-deprived individuals often have elevated levels of stress hormones such as cortisol, which can further contribute to emotional instability. This can result in symptoms such as anxiety and irritability.
Several studies demonstrate that inadequate sleep has a significant impact on moods and emotions. One such study found that sleep-deprived individuals were more likely to experience negative emotions such as irritability, anger, and frustration compared to those who had adequate sleep.
Another study concluded that sleep-deprived individuals were more susceptible to emotional exhaustion, which can lead to a decline in overall emotional well-being.
It is important to understand that sleep deprivation can negatively impact various aspects of our lives, including our mental health. It is crucial to make sleep a priority and ensure we are getting enough quality sleep each night in order to maintain emotional stability and overall well-being.
How to Improve Sleep for Better Emotional Health
Ensuring quality sleep is essential for maintaining emotional stability and promoting overall well-being. Yet, many individuals struggle to achieve restful sleep on a regular basis. Poor sleep can lead to increased stress and anxiety, difficulty processing emotions, and even physical health issues. Fortunately, there are strategies and habits that can be adopted to improve sleep quality and promote emotional health. By prioritizing sleep hygiene, managing stress and anxiety, and seeking professional help when necessary, individuals can enhance their emotional regulation abilities and enjoy more restful, rejuvenating sleep. Let’s explore some ways that one can improve their sleep for better emotional health.
Sleep Hygiene Habits
One of the most important ways to improve the quality of your sleep and enhance your emotional regulation is to establish good sleep hygiene habits. These habits can help you fall asleep faster, stay asleep longer, and experience deeper, more restful sleep. Here are some key sleep hygiene habits to incorporate into your nighttime routine:
| Sleep Hygiene Habits | Description |
|---|---|
| Stick to a regular sleep schedule | Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends or when you’re traveling. This helps regulate your body’s clock and could help you fall asleep and stay asleep for the night. |
| Create a relaxing bedtime routine | Do the same relaxing things each night to tell your body it’s time to wind down. This could include taking a warm bath or shower, reading a book, or listening to calming music. |
| Limit exposure to screens before bedtime | The blue light emitted by screens on smartphones, tablets, computers, and TVs suppresses the production of melatonin, the hormone that controls your sleep/wake cycle. So, try to avoid screens for at least an hour before bedtime. |
| Create a comfortable sleep environment | Your bedroom should be cool, quiet, and dark. Consider using blackout curtains, eye shades, earplugs, or a white noise machine to create an ideal sleep environment. |
| Limit caffeine and alcohol intake | Both caffeine and alcohol can interfere with sleep. So, avoid drinking caffeine in the afternoon and evening, and limit alcohol consumption to one or two drinks per day. |
| Exercise regularly | Regular exercise can help you fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it can make it harder to fall asleep. |
By incorporating these sleep hygiene habits into your nightly routine, you can improve your sleep quality and enhance your emotional regulation.
Managing Stress and Anxiety Before Bedtime
Managing stress and anxiety is crucial for achieving quality sleep and improving emotional health. Here are some tips to alleviate stress before bedtime:
| Tip 1: Practice relaxation techniques | Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help relieve stress and reduce anxiety before bedtime. Find a quiet and comfortable place to practice these techniques, and try to incorporate them into your bedtime routine. |
| Tip 2: Avoid electronics before bedtime | Electronic devices emit blue light that can suppress the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep. Avoid using electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops before bedtime to prevent the interference of blue light and improve your quality of sleep. |
| Tip 3: Establish a bedtime routine | Establishing a bedtime routine can help signal your body that it’s time for sleep. Try to create a calming and soothing routine that suits your preference. This could include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music. |
| Tip 4: Write down your worries | If you find yourself unable to turn off your racing thoughts before bedtime, it may be helpful to write down your worries in a journal. This can help you unload your thoughts and reduce the anxiety that keeps you up at night. |
| Tip 5: Seek professional help | If your stress and anxiety are persistent and affecting your quality of life, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. Therapy or counseling can help you identify the root causes of your stress and develop strategies to manage it effectively. |
By implementing these tips into your routine, you can effectively manage stress and anxiety before bedtime, leading to better sleep and improved emotional well-being.
Seeking Professional Help for Sleep Issues
If you have been consistently experiencing sleep issues and they are impacting your emotional health, it may be time to seek professional help. Here are some options to consider:
- Talk to your doctor: Your primary care physician can be a good starting point for addressing sleep concerns. They may be able to provide resources for managing stress and anxiety, as well as refer you to a specialist if necessary.
- Consult a sleep specialist: If your sleep issues are chronic or severe, a sleep specialist can provide a more in-depth evaluation and treatment plan. They may recommend lifestyle changes, medication, or cognitive-behavioral therapy to improve your sleep.
- Consider therapy: If stress or anxiety is causing your sleep issues, therapy can be a helpful way to address these underlying concerns. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, in particular, has been shown to be effective in treating insomnia.
- Explore alternative therapies: In addition to traditional medical approaches, alternative therapies like acupuncture, aromatherapy, or meditation may also be helpful in improving sleep quality and managing emotions.
Remember, sleep is essential for emotional well-being, and seeking help for sleep issues is a proactive step towards improving your overall health.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Sleep for Emotional Well-Being
After delving into the intricate relationship between sleep and emotional regulation, it’s clear that making sleep a priority is crucial for maintaining one’s emotional well-being. As we’ve seen, consistent sleep allows the brain to effectively process and regulate emotions, reducing the likelihood of feeling overwhelmed or reactive to emotional stimuli.
To achieve quality sleep, it’s important to establish healthy sleep habits, starting with creating a relaxing sleep environment that is conducive to rest. This may include making sure the room is dark, quiet, and cool, and avoiding the use of electronics before bedtime.
In addition to optimizing sleep hygiene, it’s important to manage stress and anxiety before bedtime. This may include engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation, or engaging in calming activities like reading or taking a warm bath.
If you find that despite taking these measures, you are still experiencing sleep difficulties or emotional instability, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. A healthcare provider or therapist can provide individualized recommendations and support to address underlying issues that may be impacting both sleep and emotional regulation.
Prioritizing sleep is essential for emotional well-being. By implementing healthy sleep habits, taking steps to manage stress and anxiety, and seeking professional help if needed, individuals can support their brain’s ability to effectively regulate emotions and maintain a positive mental and emotional state.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between sleep and emotional regulation?
Sleep plays a crucial role in emotional regulation, allowing us to process and regulate our emotions effectively.
What is REM sleep and how does it affect emotional memory processing?
REM sleep is a stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movement and intense brain activity, during which emotional memory processing occurs.
Why do we dream about emotional events?
We dream about emotional events because our brain is trying to process and make sense of these experiences, allowing us to regulate our emotions and consolidate memories.
How does dream content impact our emotions?
Dream content can have a significant impact on our emotions, as it allows us to process and regulate emotions related to real-life events, leading to emotional stability and well-being.
What are the consequences of sleep deprivation on emotional stability?
Sleep deprivation can lead to emotional instability, mood swings, and poor emotional regulation, increasing the risk of mental health problems and impacting overall well-being.
What can we do to improve our sleep for better emotional health?
We can improve our sleep for better emotional health by adopting good sleep hygiene habits, managing stress and anxiety before bedtime, and seeking professional help for sleep issues.
What are some effective sleep hygiene habits?
Some effective sleep hygiene habits include establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing sleep environment, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and limiting screen time before bed.
How can we manage stress and anxiety before bedtime?
We can manage stress and anxiety before bedtime by practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, and avoiding stimulating activities such as work or intense exercise.
When should we seek professional help for sleep issues?
We should seek professional help for sleep issues if we experience persistent sleep problems such as insomnia, sleep apnea, or restless leg syndrome, impacting our daily life and emotional well-being.
Why is prioritizing sleep essential for emotional well-being?
Prioritizing sleep is essential for emotional well-being because it allows our brain to process and regulate emotions effectively, leading to emotional stability, improved mood, and overall better mental health.








