Introduction: What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where a person stops breathing for short periods while sleeping, causing disruptions in the normal sleep cycle. This disorder is often characterized by loud snoring, gasping or choking sounds, and excessive tiredness during the day.
There are two types of sleep apnea – obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. The former is caused by a partial or complete blockage of the airways during sleep, leading to breathing difficulties. The latter occurs when the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Sleep apnea has a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. Not only does it lead to daytime fatigue and drowsiness, but it can also increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. People with sleep apnea often struggle with snoring, which can cause sleep disturbances for their partners.
Fortunately, there are ways to manage and treat sleep apnea. This article will explore the impact of sleep apnea on REM sleep and dreaming, as well as provide tips on how to improve sleep quality for people with this condition.
The Four Stages of Sleep
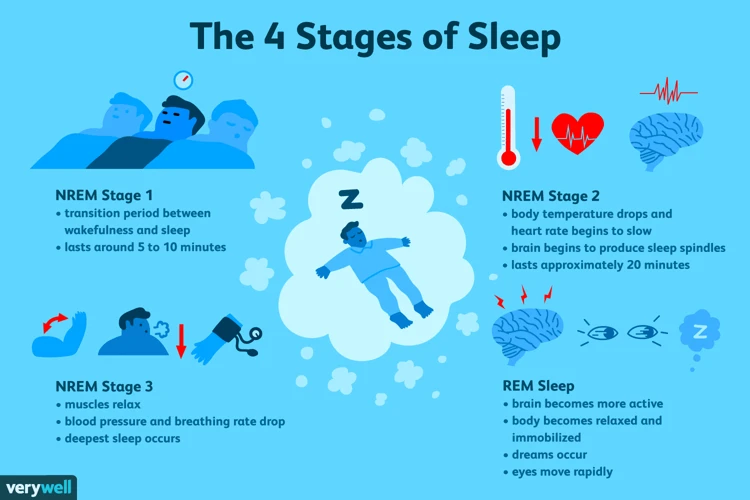
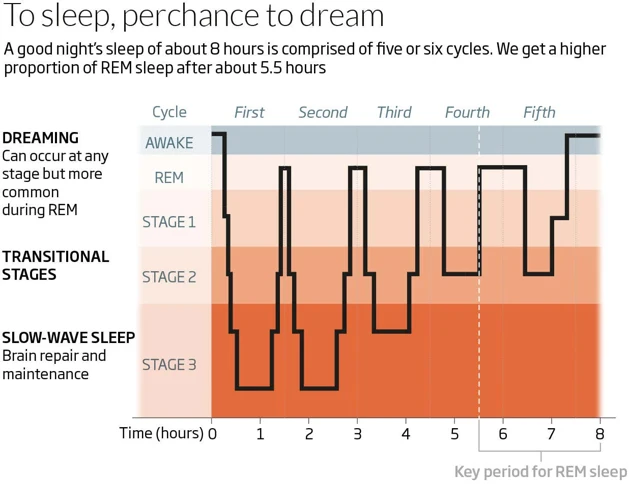
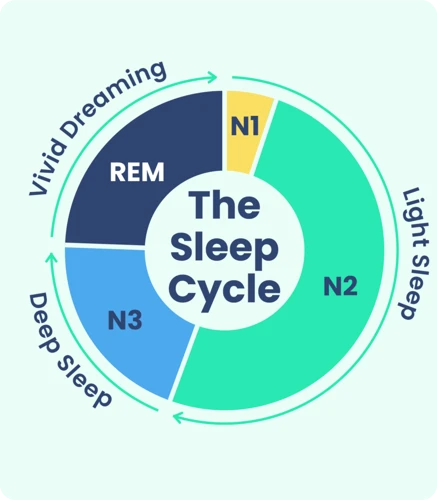
As we drift off into sleep, our bodies go through a series of distinct phases characterized by unique brain wave patterns and physiological changes. These phases, also known as sleep stages, are typically divided into four main categories: light sleep, sleep spindles, deep sleep, and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. Each stage plays a crucial role in the overall quality and restorative potential of our sleep, and disruptions to these stages can have significant impacts on our physical and mental health. In this section, we will delve deeper into each of these stages and discuss their unique characteristics and functions.
Stage 1: Light Sleep
During the first stage of sleep, also known as light sleep, it is easier to wake up as compared to other stages. This stage only comprises 5% of a person’s sleep cycle and lasts for only a few minutes. However, during this short period, a number of changes occur within the body that prepares it for deeper sleep.
What happens in Stage 1 of Sleep?
– Breathing and heart rate slow down
– Eye movement reduces
– Muscle activity slows down
During this stage, people may experience hypnagogic hallucinations, which involve vivid and often dream-like experiences. This is due to the brain’s transition from wakefulness to sleep. In some cases, people may also experience sudden muscle contractions known as myoclonic jerks, which can cause a person to wake up momentarily.
It is important for a person to go through all the stages of sleep to experience restorative sleep. Interruptions and disruptions in any stage can affect the body’s overall restorative process. Sleep apnea can have a significant impact on the quality of one’s sleep, including the amount of time spent in light sleep. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and difficulty concentrating.
Stage 2: Sleep Spindles
Stage 2 of the sleep cycle is characterized by the presence of sleep spindles that may last between 0.5 to 2 seconds each. Sleep spindles are sudden bursts of brain activity that occur in the frequency range of 11 to 16 Hz. During this stage, the body’s temperature begins to decrease, and the heart rate slows down.
The function of sleep spindles is not entirely understood, but research has suggested that they play a role in information processing and memory consolidation. They have also been linked to improvements in cognitive abilities, such as perception, attention, and problem-solving skills.
Sleep spindles are thought to originate in the thalamus of the brain and are related to the transmission of sensory information to the cortex. They are believed to help in filtering out external stimuli and preventing the sleeper from awakening to non-threatening stimuli.
Sleep spindles are also affected by certain sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea. Sleep apnea may interfere with the normal occurrence of sleep spindles, causing a reduction in their frequency and duration. This can lead to cognitive impairments, memory problems, and decreased attention span.
Stage 3: Deep Sleep
During Stage 3 of sleep, also known as deep sleep, the body and brain enter a state of relaxation and restoration. This stage is crucial for physical well-being as it allows the body to repair and regenerate tissues, boost the immune system, and release growth hormones.
Characteristics of Stage 3 Sleep:
- Delta waves, which are slow brain waves, become more prominent during this stage.
- The breathing rate, heart rate, and blood pressure drop to their lowest levels.
- Muscles relax completely, making it difficult to awaken from this stage of sleep.
- The sleeper may experience sleepwalking, night terrors, bed wetting or talking during this stage.
Interestingly, Stage 3 sleep is harder to achieve with age due to natural changes in the sleep cycle. Additionally, sleep apnea can disrupt the transition to deep sleep, preventing the body from receiving the restorative benefits it needs.
Stage 4: REM Sleep
During the final stage of sleep, known as REM sleep, the brain becomes highly active while the muscles of the body are completely relaxed. REM, which stands for Rapid Eye Movement, is the stage of sleep where dreams typically occur.
Below is a table that outlines the characteristics of REM sleep:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Brain Activity | Highly active, similar to levels during waking hours |
| Eye Movement | Rapid and constant in various directions |
| Muscle Tone | Completely relaxed |
| Breathing | Irregular and shallow |
| Duration | Increases in length throughout the night, up to an hour per cycle |
REM sleep is essential for overall health and wellbeing, allowing the brain to consolidate memories and process emotions. It is also believed to play a role in regulating mood and creativity.
However, individuals with sleep apnea often experience disruptions in their REM sleep. This can lead to a range of negative effects on both physical and mental health.
What is REM Sleep?
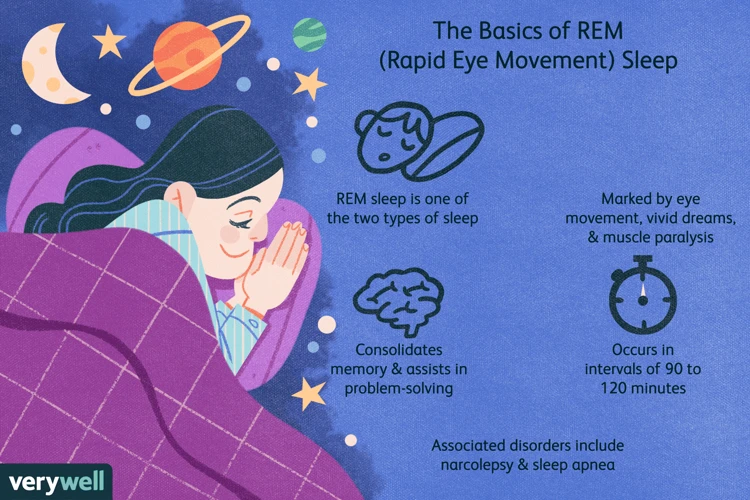
REM sleep, short for rapid eye movement sleep, is one of the four stages of sleep that occurs in cycles throughout the night. During REM sleep, the body experiences increased brain activity, which can result in vivid dreaming. The name “rapid eye movement sleep” comes from the fact that the eyes move rapidly in different directions during this stage of sleep.
While in REM sleep, the body is very relaxed, almost to the point of paralysis, and most of the body’s muscles are inactive. This state of relaxation is necessary to prevent the body from acting out dreams as they occur. Additionally, the heart rate and breathing become more irregular and there is an increase in blood flow to the brain.
REM sleep is also important for several other reasons. It is thought to play a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional regulation. It has also been suggested that REM sleep helps with creativity and problem-solving. However, the exact mechanisms and functions of REM sleep are still not fully understood.
REM sleep is an important aspect of the sleep cycle that is crucial for maintaining physical and mental health. Without enough REM sleep, individuals may experience negative effects on their mood, memory, and other cognitive functions.
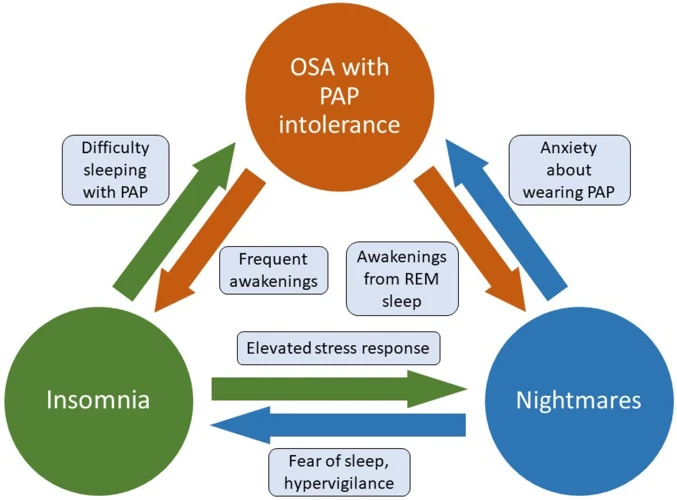
Sleep Apnea and REM Sleep

As mentioned earlier, sleep apnea is a condition that affects many individuals, causing them to experience pauses in their breathing while they sleep. This disruption to their regular breathing pattern can impact the quality of their sleep and affect the different stages of sleep, including REM sleep. REM sleep is a crucial part of the sleep cycle as it is the stage when most of our dreaming occurs. In this section, we explore how sleep apnea affects REM sleep and the relationship between this disorder and dreaming.
How Sleep Apnea Impacts REM Sleep
Sleep apnea can have severe impacts on a person’s overall sleep quality, especially when it comes to Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. During REM sleep, the body is in its deepest stage of sleep, and the brain is highly active. Below are some ways in which sleep apnea interferes with REM sleep.
1. Fragmented Sleep: Sleep apnea can cause frequent interruptions in breathing, leading to the body interrupting the REM sleep stage to restart breathing. This constant interruption leads to fragmented sleep, resulting in an insufficient amount of REM sleep during the night.
2. Oxygen Deprivation: During sleep apnea, the body experiences a lack of oxygen due to blocked airways. The brain then sends signals to the body to wake up to start breathing again, which further affects REM sleep, causing it to be insufficient.
3. Decreased Duration: Dreams typically occur during REM sleep, but when sleep is fragmented, there is a decreased duration of REM sleep. This decrease leads to a lack of dreaming and consequent side effects on the mind and body.
4. Decreased Quality: When sleep apnea interrupts REM sleep, the quality of the sleep is also affected. Even if the person reaches the REM sleep stage, the constant interruption leads to a lower quality of their sleep.
Sleep apnea’s impact on REM sleep is significant, leading to much negative impact on overall sleep quality, including a decrease in the amount and quality of dreaming.
The Relationship Between Sleep Apnea and Dreaming
Sleep apnea can significantly impact the quality of dreaming. Research suggests that individuals with sleep apnea tend to have fewer vivid dreams, and their dreams tend to be less emotionally intense compared to individuals without sleep apnea. This is because sleep apnea can disrupt the normal sleep architecture, particularly during the REM stage of sleep, which is when most dreaming occurs.
In one study, individuals with severe sleep apnea spent less time in the REM stage of sleep, and this reduction in REM time was associated with a decrease in dream content complexity and vividness. Individuals with sleep apnea may experience more negative dream themes, such as suffocation or drowning, reflecting their struggle to breathe during sleep.
It is also important to note that the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, which is often used to treat sleep apnea, may impact dreaming in a positive way. Studies have shown that CPAP therapy can improve REM sleep and dream content, leading to more vivid and positive dreams.
The relationship between sleep apnea and dreaming is complex and multifaceted. While sleep apnea can have negative effects on the quality of dreaming, treatment options such as CPAP therapy can significantly improve dreaming and overall sleep quality.
| Sleep Apnea and Dreaming: | |
|---|---|
| Sleep apnea can disrupt normal sleep architecture, particularly during the REM stage when most dreaming occurs. | Less vivid dreams and less emotionally intense dreams |
| Individuals with severe sleep apnea spend less time in the REM stage, which results in a reduction in dream content complexity and vividness. | More negative dream themes (suffocation, drowning) reflecting struggle to breathe during sleep. |
| CPAP therapy can improve REM sleep and dream content, leading to more vivid and positive dreams. |
The Importance of Dreaming
Dreaming is a crucial component of a healthy sleep cycle. During REM sleep, the brain is incredibly active and engages in important cognitive processes such as memory consolidation and emotional regulation. In fact, studies have shown that dreaming plays a significant role in memory consolidation, allowing the brain to connect new information with pre-existing knowledge and solidify those connections.
Dreaming can also promote creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. It is believed that during REM sleep, the brain is able to explore new ideas and consider different perspectives, leading to greater creativity and enhanced problem-solving abilities. It is suggested that dreaming allows the brain to process and regulate emotions, helping individuals to manage stress and maintain emotional balance.
However, when individuals suffer from sleep apnea, their ability to experience these benefits of dreaming is compromised. Interruptions in sleep caused by apnea episodes can significantly reduce the amount of REM sleep experienced each night, leading to a reduction in the cognitive and emotional benefits associated with this stage of sleep. The negative effects of sleep apnea on overall sleep quality can also impact the ability to dream, as individuals may not reach the necessary stages of sleep required for dreaming to occur.
Given the importance of dreaming for overall cognitive and emotional health, it is essential to address sleep apnea to ensure that individuals are able to regularly experience this vital stage of sleep. By seeking treatment for sleep apnea and making lifestyle changes to improve overall sleep quality, individuals can ensure that they are able to receive the full benefits of dreaming and maintain optimal cognitive and emotional health.
The Negative Effects of Sleep Apnea on Dreaming
Sleep apnea can have a negative impact on an individual’s quality of dreaming. When someone suffers from sleep apnea, they experience interruptions in their sleep cycle, which prevent them from entering deep and uninterrupted sleep. As a result, their time in REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, also known as the dream stage, is significantly decreased.
REM sleep is crucial for the brain’s cognitive functions, and a lack of it can lead to memory problems, decreased cognitive abilities, and even depression. Without enough time in REM sleep, an individual may have fewer dreams or shorter dreams that lack vividness and clarity.
Sleep apnea can cause an increase in the frequency and intensity of nightmares. When someone with sleep apnea experiences an episode of apnea, their body’s oxygen levels decrease, and their brain goes into a state of arousal to wake them up to resume breathing. This can result in a state of panic, fear, or anxiety, which may manifest as nightmares during REM sleep.
The negative effects of sleep apnea on dreaming can also lead to feelings of fatigue and grogginess despite getting enough hours of sleep. These feelings can impact an individual’s day-to-day life, making it difficult to concentrate, stay focused on tasks, and make decisions.
It is important to note that not everyone with sleep apnea experiences negative effects on their dreaming. However, for those who do, it is crucial to address their sleep apnea and take steps towards improving their quality of sleep.
Addressing sleep apnea can improve not only the quality of one’s dreaming but also their overall well-being, cognitive abilities, and mental health. There are numerous options for treating sleep apnea, including lifestyle changes, positional therapy, oral appliances, and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for individual needs.
In addition to seeking treatment for sleep apnea, there are other steps individuals can take to improve their quality of sleep and dreaming, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, and practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga.
It is important to also be aware that there are various other sleep disorders that can affect dreaming, including insomnia, narcolepsy, and REM sleep behavior disorder. Anyone experiencing abnormal dreaming or disrupted sleep should speak with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan.
Sleep apnea can negatively impact an individual’s quality of dreaming, leading to reduced cognitive function, nightmares, and feelings of fatigue. Addressing sleep apnea through various treatment options can lead to improved dreaming, overall health, and well-being.
How to Improve Dreaming with Sleep Apnea

For those who suffer from sleep apnea, the negative impact on sleep quality can extend beyond snoring, fatigue, and daytime sleepiness. The disorder can also significantly affect the quality and frequency of one’s dreams, leaving individuals feeling even more unrefreshed upon waking. Thankfully, there are steps that can be taken to improve dreaming with sleep apnea, including both medical interventions and lifestyle changes. Let’s take a closer look at some options to enhance the dream experience for those with sleep apnea.
Treating Sleep Apnea
One of the most common methods of treating sleep apnea is with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. This involves wearing a mask over the nose and/or mouth during sleep, which is connected to a machine that delivers a constant flow of air to keep the airways open. CPAP therapy is highly effective in reducing the number of apnea episodes during the night and improving overall sleep quality.
Another treatment option for sleep apnea is oral appliance therapy. This involves wearing a custom-fitted device in the mouth, similar to a mouthguard, that helps to keep the airways open. Oral appliances may be recommended for those with mild to moderate sleep apnea, or for those who are unable to use CPAP therapy.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat sleep apnea. This may involve removing excess tissue from the back of the throat or correcting structural abnormalities in the airways. Surgical options are typically reserved for those with severe cases of sleep apnea, or for those who have not had success with other treatment options.
In addition to these medical treatments, there are also lifestyle changes that can be made to improve sleep quality and reduce the severity of sleep apnea. These include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, and sleeping on one’s side rather than on the back. Lifestyle changes can be especially helpful for those with mild cases of sleep apnea, and may also be recommended in conjunction with other treatment options.
It’s important to seek treatment for sleep apnea, as untreated sleep apnea can lead to a variety of health problems, including increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. By treating sleep apnea, not only can one improve their overall health, but they may also experience improved dreaming and better sleep quality.
Other Tips for Improving Sleep Quality
There are several tips that can improve sleep quality for individuals with sleep apnea. Here are some of them:
- Avoid alcohol and sedatives: Alcohol and sedatives can relax the muscles in the throat and make sleep apnea worse. It is recommended to avoid them before bedtime.
- Keep a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can help regulate the body’s internal clock and improve sleep quality.
- Use a humidifier: A humidifier can add moisture to the air and reduce nasal congestion, which can make breathing easier for individuals with sleep apnea.
- Elevate the head: Elevating the head while sleeping can help keep the airway open and reduce snoring.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can improve overall health and help with weight loss, both of which can reduce the severity of sleep apnea.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for sleep apnea. Losing weight through diet and exercise can improve symptoms and reduce the risk of other health problems.
By incorporating these tips into their daily routines, individuals with sleep apnea can improve their sleep quality and reduce the negative effects of the disorder on their health and wellbeing.
Other Sleep Disorders That Affect Dreaming
There are several other sleep disorders that can also impact dreaming. One such disorder is known as narcolepsy, a neurological condition that causes individuals to have overwhelming daytime sleepiness, and can also cause sudden and uncontrollable sleep attacks. People with narcolepsy often experience vivid and intense dreams during both REM and non-REM sleep stages.
Another sleep disorder that can affect dreaming is called restless leg syndrome (RLS). This condition is characterized by an overwhelming urge to move the legs or other parts of the body, particularly during periods of inactivity or sleep. This can interfere with sleep quality, including the amount of time spent in REM sleep, and consequently, the amount and quality of dreaming that occurs.
Finally, insomnia, or the inability to fall asleep or stay asleep, can also affect dreaming. Insomnia can lead to fragmented sleep, which can interfere with the amount of time spent in REM sleep and result in a decrease in dreaming.
It is important to note that these sleep disorders can also co-occur with sleep apnea, leading to a compounding of negative effects on sleep quality and dreaming. It is important to seek proper diagnosis and treatment for any and all sleep disorders in order to promote healthy sleep and dreaming.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that sleep apnea has a significant impact on REM sleep and dreaming. This breathing disorder affects the quality and quantity of sleep, leading to a disturbance in the natural sleep cycle.
Without adequate REM sleep, the brain is unable to fully process and consolidate memories, and the emotional regulation becomes impaired. This can result in mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
It is crucial to address sleep apnea to prevent these negative effects on overall health and wellbeing. Treatment options, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, can improve the quality of sleep and increase the amount of REM sleep obtained each night.
Furthermore, making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, and establishing a regular sleep routine, can also enhance sleep quality.
It is essential to recognize that sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, can impact various aspects of life, including mental health, work performance, and relationships. Seeking professional help and following the appropriate treatment and lifestyle recommendations can significantly improve the quality of life for those struggling with sleep apnea and related sleep disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the causes of sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea can be caused by multiple factors, including obesity, smoking, alcohol consumption, aging, and genetics.
Can sleep apnea be treated?
Yes, there are various treatments for sleep apnea, including lifestyle changes, breathing devices, surgery, and medication.
What are the symptoms of sleep apnea?
The symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, gasping or choking during sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, and difficulty concentrating.
How is sleep apnea diagnosed?
Sleep apnea is typically diagnosed through a sleep study, which involves monitoring a person’s breathing and other physical functions while they sleep.
What is the relationship between sleep apnea and heart disease?
Sleep apnea has been linked to an increased risk of high blood pressure, heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
Can children have sleep apnea?
Yes, sleep apnea can affect children as well as adults. Common symptoms in children include snoring, restless sleep, and trouble paying attention during the day.
What are the long-term effects of untreated sleep apnea?
Untreated sleep apnea can lead to chronic fatigue, depression, cognitive decline, and other serious health problems.
Are there natural remedies for sleep apnea?
While natural remedies may provide some relief, they are not considered a substitute for medical treatment. Some natural remedies include weight loss, exercise, and avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime.
What is the relationship between sleep apnea and weight?
There is a strong correlation between sleep apnea and obesity. Losing weight can often improve symptoms of sleep apnea and may even cure the condition in some cases.
Can sleep apnea go away on its own?
No, sleep apnea typically does not go away on its own. However, with the right treatment, it can be effectively managed and symptoms can be greatly reduced.