The Science of Dreaming and Sleep Deprivation
As humans, we spend almost one-third of our lives sleeping. During sleep, our brains go through a series of complex processes that help us recharge, recover, and prepare for the day ahead. One of the most fascinating aspects of sleep is dreaming, a phenomenon that still puzzles scientists and researchers to this day.
What Happens to the Brain During Sleep Deprivation?
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on the brain’s ability to function properly. Studies have shown that when we don’t get enough sleep, our brain cells can become overworked, leading to cognitive deficits, disorders, and mood swings. The longer we go without sleep, the more severe these effects can become.
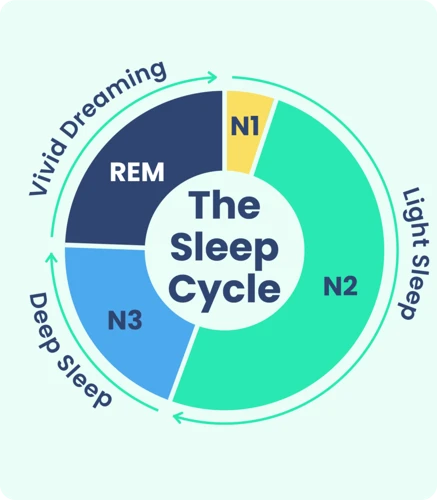
One of the most noticeable impacts of sleep deprivation is on the brain’s ability to enter REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, the stage of sleep where most of our dreaming occurs. REM sleep is crucial for our overall health and well-being, as it is during this stage that the brain consolidates memories, regulates emotions, and performs crucial restorative functions.
REM Sleep Deprivation and Dreaming
As mentioned earlier, most of our dreaming occurs during the REM stage of sleep. When we are sleep-deprived, our brains have a harder time entering this stage, which can result in vivid and intense dreams when we finally do manage to fall asleep. This is because our brains are essentially “catching up” on the REM sleep that we missed, leading to longer and more vivid dream experiences.
Why Dreaming While Sleep Deprived Can Be More Vivid
The vividness and intensity of dreams during sleep deprivation can be attributed to a few different factors. Firstly, when we are sleep-deprived, our brain cells become hyperactive, which can result in more vivid sensory experiences during dreaming. Secondly, we tend to spend more time in the REM stage of sleep when we are sleep-deprived, leading to longer and more detailed dream experiences. Lastly, when we finally do get to sleep after a period of sleep deprivation, our brains release a surge of neurotransmitters, which can heighten the emotional intensity of our dreams.
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on our ability to enter the REM stage of sleep, which can lead to more vivid and intense dreams when we finally do manage to fall asleep. Understanding these processes can help us better understand the impact of sleep deprivation on our overall health and well-being.
What Happens to the Brain During Sleep Deprivation?
As we all know, sleep is essential for the proper functioning of our bodies and minds. However, what happens when we deprive ourselves of this crucial need? The effects of sleep deprivation on the brain are numerous and complex, with various implications for our cognitive abilities and emotional well-being. In this section, we will explore the intricate ways in which sleep deprivation impacts the brain, providing a comprehensive understanding of the consequences of inadequate sleep.
REM Sleep Deprivation and Dreaming
During the REM sleep, which stands for rapid eye movement, we experience the most vivid and memorable dreaming. However, when sleep-deprived, our REM cycles can become disrupted, leading to a variety of effects on our dreams and overall mentation.
Studies have shown that sleep deprivation can lead to a REM sleep rebound effect, where the brain tries to compensate for the lost REM sleep by increasing the amount and intensity of REM activity. This can result in more frequent and vivid REM dreams, often associated with more intense emotions.
On the other hand, lack of REM sleep can cause dream deprivation, leading to a decrease in the number and quality of dreams. This can result in poor memory consolidation and affect our mood, motivation, and mental health.
Additionally, REM sleep deprivation has been found to increase sleep onset dreams, which are brief and often nonsensical dreams that occur during the transition from wakefulness to sleep. These types of dreams can be especially perplexing and disorienting, contributing to sleep disturbances and lower overall sleep quality.
Overall, REM sleep deprivation has a complex and significant impact on our dreaming experiences, potentially leading to more intense and emotional dreams, decreased dream recall, and subtype shifts in dream content.
Why Dreaming While Sleep Deprived Can Be More Vivid
When we don’t get enough sleep, our dreams can become more vivid and intense. This is because sleep deprivation can cause a rebound effect in the brain’s Rapid Eye Movement (REM) stage of sleep. Here are some reasons for why this phenomenon occurs:
- Increased brain activity: During REM sleep, the brain becomes more active, and this activity is necessary for the consolidation of memories and emotions. When we are sleep deprived, our brains try to compensate for the lost rest by increasing the time we spend in REM sleep, leading to more intense and vivid dreams.
- Heightened emotional state: Sleep deprivation can cause heightened emotional states, which can result in more intense and emotionally charged dreams. This is because our dreams are a reflection of our waking emotional state, and when we’re sleep deprived, we may be more prone to emotional extremes.
- Disrupted sleep cycles: Sleep deprivation can also disrupt our sleep cycles, causing us to wake up more frequently throughout the night. When we wake up during REM sleep, we are more likely to remember our dreams, which may contribute to the feeling that our dreams are more vivid.
It’s important to note that while more vivid dreams can be interesting, they can also contribute to feelings of grogginess and fatigue when we wake up. So, it’s essential to prioritize getting enough sleep to avoid these negative effects on both our dreaming and waking states.
The Effects on Dream Recall
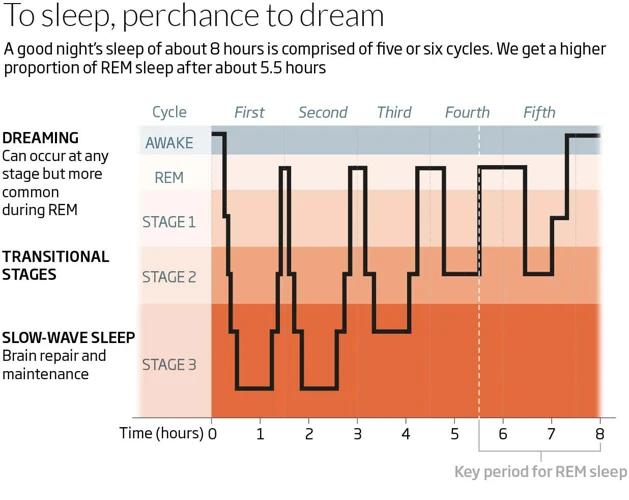
For those who prioritize their sleep, remembering their dreams can be an exciting and insightful experience. However, when experiencing sleep deprivation, dream recall can become a challenge. The effects of sleep deprivation on dream recall can vary, including difficulty remembering dreams, fragmented memories, or even a complete lack of recollection. Let’s dive deeper into the science behind the impact of sleep deprivation on dream recall and explore some ways to enhance our dream memory despite lack of quality sleep.
How Sleep Deprivation Can Impact Recall Ability
Sleep deprivation has a significant impact on dream recall ability, and this can have a considerable effect on the way individuals experience dreams. Here are some ways in which sleep deprivation can impact dream recall:
- Reduced Attention Span: Sleep deprivation can lead to a reduced attention span, making it difficult for an individual to focus and remember their dreams.
- Disruption of Brain Waves: REM sleep is critical for dream recall as it is the stage in which most dreaming occurs. Sleep deprivation can cause disruptions in REM sleep, making it more challenging for an individual to recall their dreams.
- Memory Consolidation: During sleep, memories are consolidated, and this affects both the ability to remember dreams and the content of dreams. Sleep deprivation can interfere with this memory consolidation process, leading to difficulties in dream recall.
- Inability to Complete Sleep Cycles: Sleep deprivation can prevent an individual from completing all stages of the sleep cycle, which can also impact dream recall. The interruption of the sleep cycle disrupts the continuity of the dream, making it hard for an individual to remember it.
These factors can lead to a reduction in dream recall ability, which can affect an individual’s ability to analyze and understand the significance of their dreams. It is essential to find ways to improve dream recall, even when dealing with sleep deprivation.
Ways to Improve Dream Recall Despite Sleep Deprivation
Even though sleep deprivation can negatively impact dream recall, there are still some ways to improve it. Here are a few tips to help you remember your dreams despite lack of sleep:
- Set the intention to remember: Before you go to bed, tell yourself that you want to remember your dreams. This helps your brain prioritize dream recall and can make it more likely that you will remember your dreams upon waking up.
- Wake up slowly: When you wake up, try to stay in bed for a few moments and focus on any lingering dream fragments or emotions. This can help bring your dream into your conscious awareness and increase your chances of remembering it.
- Keep a dream journal: Write down any dreams you remember as soon as you wake up. Even if you can only recall a small fragment, jot it down. Over time, this practice can help improve your dream recall and give you a better understanding of your dream patterns.
- Develop a bedtime routine: Going to bed at the same time every night and engaging in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading or meditating, can help improve the quality of your sleep and make it easier to remember your dreams.
- Avoid alcohol and drugs: Alcohol and drugs can negatively impact the quality of your sleep and make it harder to remember your dreams. Avoiding these substances can help improve dream recall.
- Use affirmations: Repeating positive affirmations, such as “I will remember my dreams,” before bed can help program your mind to prioritize dream recall and make it easier to remember your dreams.
By using these techniques, you can improve your ability to remember your dreams despite sleep deprivation. Keep in mind that it may take time and consistency to see results, so don’t get discouraged if you don’t see improvement right away.
The Impact on Dream Content

As sleep deprivation affects the brain’s ability to enter different stages of sleep, it also impacts the content of our dreams. The lack of proper rest not only alters the frequency and vividness of dreams, but it can also influence the themes and emotions present in them. Understanding how sleep deprivation affects dream content can provide valuable insight into our mental and emotional well-being. In this section, we’ll explore the impact of sleep deprivation on dream content and delve into the common themes that emerge in sleep-deprived dreams.
Common Themes in Sleep Deprivation Dreams
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on the content of our dreams, often resulting in common themes that reflect the tired and overwhelmed state of our minds. Some of the most common themes in sleep deprivation dreams include:
| Theme | Description |
|---|---|
| Being chased | One of the most common themes in sleep deprivation dreams is being chased. This may be reflective of the feeling of being pursued by the demands of everyday life and the need to keep up with a fast-paced world. |
| Falling | Another common theme is falling. This may represent a feeling of failure or inability to keep up, as well as a sense of losing control. |
| Lost or stuck | Feeling lost or stuck is also a common theme in sleep deprivation dreams. This can reflect a sense of uncertainty and confusion in one’s waking life. |
| Exams or tests | Many people report dreaming about exams or tests when sleep deprived. This may reflect a sense of pressure to perform and meet expectations in their waking life. |
| Unpreparedness | Feeling unprepared for a situation is also a common theme. This may reflect a fear of being unable to meet expectations or a sense of inadequacy in one’s abilities. |
| Disorientation | Finally, feeling disoriented or overwhelmed is a frequent theme in sleep deprivation dreams. This may reflect the intense sensory and cognitive overload that often accompanies sleep deprivation. |
It’s important to note that while these themes are common, not everyone will experience them in their sleep deprivation dreams. Dream content can vary greatly depending on the individual’s experiences and personal worries. However, recognizing these common themes can help individuals understand and process the effects of sleep deprivation on their dreams.
The Relationship Between Sleep Deprivation Dreams and Mental Health
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on mental health, and this extends to the types of dreams experienced during periods of sleep deprivation. Here are some of the ways in which sleep deprivation can affect mental health:
- Increased anxiety: Research has shown that sleep deprivation can increase anxiety levels, and this can spill over into dreams. Dreams may become more vivid and unsettling, and they may be more likely to feature themes related to stress and anxiety.
- Greater risk of depression: Sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of depression, which can have a profound impact on the content of dreams. People experiencing depression may be more likely to have dreams that are sad, lonely, or bleak.
- Impaired emotional regulation: Sleep is critical for emotional regulation, and when we don’t get enough sleep, it can be challenging to manage our emotions effectively. This can result in more intense dreams and nightmares.
- Inability to cope with stress: A lack of sleep can make it difficult to deal with stressors in our waking lives, and this can carry over into our dreams. People who are sleep-deprived may be more likely to have dreams that involve failing at tasks or feeling overwhelmed by difficult situations.
It is worth noting that the relationship between sleep deprivation dreams and mental health is complex and multifaceted. While poor sleep can negatively impact mental health, the reverse is also true – mental health conditions can interfere with sleep quality and lead to a cycle of poor sleep and poor mental health. It is essential to take steps to improve both sleep habits and mental health to break this cycle and ensure overall wellbeing.
Strategies for Better Sleep and Dreaming
Now that we have explored the effects of sleep deprivation on dreaming, it’s important to address strategies that can help promote better sleep and more positive dream experiences. Improving sleep hygiene, incorporating dream journaling and therapy, and knowing when to seek professional help can all play a critical role in enhancing sleep quality and dream content. Let’s delve into these strategies further.
Sleep Hygiene Tips
Maintaining good sleep hygiene is essential for promoting restful sleep and preventing sleep deprivation. Here are some tips to help you develop better sleep hygiene habits:
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Develop a soothing routine before bed that can help calm your mind and prepare your body for sleep. This could include taking a warm bath or shower, reading a book, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Create a sleep-conducive environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in comfortable bedding and pillows, and remove all electronics, including TVs, computers, tablets, and phones.
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine: These substances can interfere with the quality of your sleep and disrupt your natural sleep patterns.
- Avoid large meals and excessive fluids: Going to bed either hungry or too full can disturb your sleep, as can drinking too much fluid before bed, which can lead to frequent trips to the bathroom during the night.
- Get regular exercise: Regular physical activity during the day can help promote restful sleep at night, but be sure to avoid exercising too close to bedtime.
- Avoid napping during the day: While a short nap can be refreshing, taking long or frequent naps during the day can disrupt your natural sleep rhythms and contribute to sleep deprivation.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can develop better sleep hygiene habits that can help you get the restful sleep you need for optimal health and wellbeing.
Dream Journaling and Therapy
Keeping a dream journal can be a helpful tool for those experiencing sleep deprivation dreams. Dream journaling involves writing down the details of your dreams upon waking up. By recording your dreams, you can better understand your subconscious and any underlying emotions or stresses that may be contributing to the vividness and intensity of your dreams.
Additionally, seeking out therapy can also be beneficial for managing sleep deprivation and associated dreaming. Cognitive-behavioral therapy is often used to address issues causing sleep loss, like anxiety or depression. Therapy can also help individuals process and manage any disturbing or distressing dreams that may be negatively impacting their mental health.
When keeping a dream journal or engaging in therapy, it’s important to remain patient and consistent. While these methods may not provide an immediate solution to sleep deprivation dreams, with time and effort, they can help improve overall sleep and mental health.
When to Consult a Professional
If you are experiencing persistent sleep deprivation and it is affecting your quality of life, it is important to consider seeking professional help. Below are some signs that you may need to consult a professional:
1. Chronic insomnia: If you find yourself consistently struggling to fall or stay asleep for a month or longer, despite practicing proper sleep hygiene and making lifestyle changes, it may be time to see a sleep specialist.
2. Excessive daytime sleepiness: If you are consistently feeling tired and sluggish during the day despite getting what you believe to be enough sleep, it could be indicative of a larger issue.
3. Nightmares or night terrors: If you are experiencing frequent and distressing nightmares or night terrors, it could be a sign that you are not getting enough restful sleep.
4. Sleepwalking or other parasomnias: If you are engaging in any disruptive behaviors during sleep, such as sleepwalking, talking, or eating, it is a good idea to consult a professional.
5. Chronic snoring or sleep apnea: If you or your sleeping partner have noticed that you snore loudly or stop breathing during the night, it could be a sign of sleep apnea, a serious condition that requires medical attention.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider as soon as possible. A sleep specialist may recommend further evaluation and testing to determine the underlying cause of your sleep issues and develop a tailored treatment plan. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if sleep deprivation is impacting your daily life.
Conclusion
After understanding the science behind dreaming and sleep deprivation, it’s clear to see that the lack of sleep can have significant impacts on one’s dreams. Sleep deprivation can alter our brain activity during REM sleep, causing more intense dreams and vivid imagery. Additionally, it can affect our ability to recall our dreams and potentially even impact the content of them.
However, there are ways to combat the negative effects of sleep deprivation on dreaming. Practicing good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing sleep environment, can help improve the quality of our sleep and subsequently, our dream experiences. Keeping a dream journal and talking with a therapist can also aid in recalling and interpreting dreams.
It’s important to note that if sleep deprivation persists and begins to affect daily life, it’s crucial to consult a medical professional. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to a host of health issues, including anxiety and depression.
In conclusion, while sleep deprivation can impact our dreams in various ways, there are measures we can take to improve our dream experiences and ensure we’re getting the necessary amount of rest for our overall well-being. By prioritizing our sleep health, we can foster a more fulfilling and enriching dream life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the recommended amount of sleep for adults?
The National Sleep Foundation recommends adults get between 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
Can you make up for lost sleep on the weekends?
While it may help temporarily, it’s not a sustainable solution. Your body works best on a consistent sleep schedule.
What is REM sleep and why is it important?
REM sleep is the stage of sleep where dreaming occurs and is necessary for consolidating memories and learning.
What are some common causes of sleep deprivation?
Some common causes of sleep deprivation include stress, anxiety, medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle choices.
Can sleep deprivation affect your physical health?
Yes, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to a variety of physical health problems including obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
How does caffeine affect sleep?
Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with sleep by making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep.
What is dream recall?
Dream recall is the ability to remember the content of your dreams.
How can you improve dream recall?
Keeping a dream journal, practicing visualization techniques, and getting enough sleep can all help improve dream recall.
Can sleep deprivation affect mental health?
Yes, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to increased risk of mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression.
When should you consult a professional for sleep and dream issues?
If sleep and dream issues are affecting your daily life and ability to function, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare professional.








