Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night, unable to move or speak? Have you felt an unexplainable sense of fear or a presence in the room? You’re not alone. Many people have experienced these frightening episodes known as sleep paralysis. Sleep paralysis can occur when the brain wakes up, but the body remains paralyzed, causing the individual to feel trapped in their own body. While this phenomenon is not uncommon, it is still shrouded in mystery. However, recent research has shed some light on the link between sleep deprivation and sleep paralysis, and it’s time to explore this connection in greater detail.
What is Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep Paralysis is a strange and often unsettling phenomenon that can leave individuals feeling confused and frightened. It is a condition where a person is unable to move or speak for a brief period, usually lasting a few seconds to a few minutes. During this time, the individual is fully aware of their surroundings but unable to control their body. Sleep Paralysis has been a topic of interest for centuries with many theories and beliefs surrounding its cause and origin. For those who experience it, the feeling of helplessness and confusion can be disorienting and even traumatic. Let’s dive deeper into what Sleep Paralysis is, what causes it, and its symptoms.
Causes of Sleep Paralysis
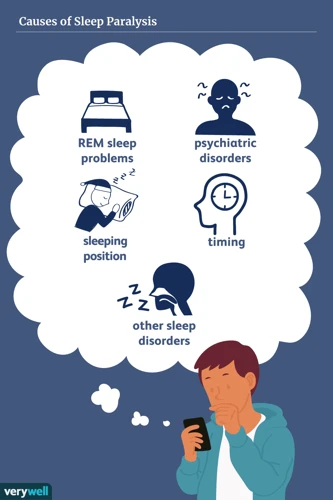
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that can be a frightening experience. It is often caused by an interruption in the normal sleep cycle. Here are some of the most common causes of sleep paralysis:
- Disruption of Sleep Cycle: Sleep paralysis can occur when the normal sleep cycle is interrupted. This can happen due to various reasons such as staying up late, changes in sleep schedule or an irregular sleep pattern.
- REM Sleep: Rapid Eye Movement (REM) is a stage of sleep where the brain is most active and dreams occur. During this stage, the muscles in our body become paralyzed. If we wake up during this stage, we may experience sleep paralysis.
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that affects the control of sleep and wakefulness. People with this condition may experience sleep attacks during the day and may also have episodes of sleep paralysis.
- Stress and Anxiety: Stress and anxiety can contribute to sleep paralysis. When we are stressed or anxious, our body releases hormones that can interrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic component to sleep paralysis. People with a family history of sleep paralysis are more likely to experience it.
- Other Sleep Disorders: Sleep disorders such as sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome are also associated with sleep paralysis.
Understanding the causes of sleep paralysis can help identify ways to prevent it from happening. It is important to maintain a regular sleep schedule and practice good sleep hygiene in order to reduce the risk of sleep paralysis.
Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a condition that causes individuals to experience temporary paralysis while they are transitioning in and out of sleep. The symptoms of sleep paralysis can vary from person to person but some of the most common symptoms are:
| Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis |
|---|
| Difficulty breathing |
| Many people who experience sleep paralysis report feeling a sensation of pressure on their chest that makes it difficult to breathe or move. |
| Hallucinations |
| During sleep paralysis, it is common for individuals to experience vivid and often terrifying hallucinations. |
| Sense of danger or evil presence |
| People who suffer from sleep paralysis may feel a sense of danger, or the presence of an evil entity in the room with them. |
| Inability to move or speak |
| One of the defining characteristics of sleep paralysis is the inability to move or speak during an episode. This can be a frightening experience for those who are unaware of the condition. |
| Feeling of being held down |
| Many individuals describe feeling as though they are being held down or restrained during an episode of sleep paralysis. |
These symptoms can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes and can occur with varying frequencies for different individuals. It is important to note that while sleep paralysis can be a very frightening experience, it is not typically dangerous or harmful to one’s health. However, it can interfere with an individual’s quality of life and should be addressed with a medical professional if it becomes a frequent occurrence.
How Sleep Deprivation Increases the Risk of Sleep Paralysis

Getting enough sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy mind and body, but unfortunately, many people experience sleep deprivation regularly. Not only can sleep deprivation lead to a variety of health problems, but it can also increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis – a state where the body is temporarily paralyzed during sleep, making it difficult or impossible to move or speak. In this section, we’ll explore how sleep deprivation can increase the risk of sleep paralysis and what factors contribute to this connection.
REM Sleep and Sleep Paralysis
During REM sleep, the brain is highly active, and the body undergoes temporary paralysis to prevent physical movement that may act out dreams or cause injury. This temporary paralysis can sometimes continue into wakefulness, resulting in sleep paralysis.
Sleep paralysis can occur when a person enters REM sleep too quickly or stays in it for too long. This can happen due to irregular sleep patterns caused by shift work or other disruptions to the sleep schedule. During REM sleep, the brain is also more susceptible to stress, anxiety, and other emotional factors that can trigger an episode of sleep paralysis.
| Factors during REM Sleep that Increase Risk of Sleep Paralysis | How it Increases the Risk |
|---|---|
| Irregular sleep patterns | Disrupts the normal cycle of REM and non-REM sleep |
| Stress and anxiety | Increases physiological activity during REM sleep |
| Substance use | Alters neurotransmitter function during REM sleep |
It’s important to note that experiencing sleep paralysis does not necessarily indicate a disorder, as it may occur occasionally in healthy individuals. However, chronic or distressing sleep paralysis may be a symptom of an underlying sleep disorder and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Irregular Sleep Patterns and Sleep Paralysis
Individuals who have irregular sleep patterns are also at higher risk for experiencing sleep paralysis. Circadian rhythm is the internal, biological process that regulates an individual’s sleep-wake cycles. When the circadian rhythm is disrupted due to irregular sleep patterns, it can lead to a higher likelihood of sleep paralysis.
People who suffer from insomnia may experience irregular sleeping patterns since they have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Individuals who work night shifts and experience jet lag due to frequent travel across time zones can also have inconsistent sleep patterns.
An irregular sleep pattern disrupts the normal REM sleep cycle, which is when most episodes of sleep paralysis occur. When an individual’s REM sleep cycle is irregular, they may experience changes in the amount and timing of their dream sleep. Additionally, the body may not fully relax during sleep, leading to an increased risk of sleep paralysis.
To reduce the risk of sleep paralysis caused by irregular sleep patterns, it is important to maintain a consistent sleep schedule. This means going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, even on weekends. Avoiding naps during the day can also promote a regular sleep schedule.
| Irregular Sleep Patterns and Sleep Paralysis |
|---|
| Circadian rhythm disruption can lead to a higher likelihood of sleep paralysis. |
| Insomnia and night shift work are two causes of irregular sleep patterns. |
| An irregular sleep pattern disrupts the normal REM sleep cycle where most episodes of sleep paralysis occur. |
| A consistent sleep schedule, including avoiding naps during the day, can reduce the risk of sleep paralysis caused by irregular sleep patterns. |
Stress and Sleep Paralysis
Stress is another factor that can increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. When the body is under stress, the release of cortisol, a stress hormone, can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, particularly the REM stage of sleep where dreams occur. As a result, individuals who experience high levels of stress may have a greater likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Here are some ways in which stress can contribute to sleep paralysis:
- Increased muscle tension: Stress can cause the muscles to tighten up, which can make it more difficult to relax and fall asleep. This tension can also make it more likely for an individual to experience sleep paralysis, as the muscles may not fully relax during the REM stage of sleep.
- Heightened anxiety: High levels of stress can cause feelings of anxiety and panic, which can contribute to the development of sleep paralysis. Anxiety and panic can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, making it more difficult to fall asleep and increasing the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis during the night.
- Negative thoughts and beliefs: Stressful situations can lead to negative thoughts and beliefs, which can also contribute to the development of sleep paralysis. Believing that sleep paralysis is a dangerous or harmful event can make it more likely for an individual to experience the condition, as the fear and anxiety associated with it can disrupt their sleep cycle.
To reduce the impact of stress on sleep paralysis, individuals can try the following:
- Meditation or relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, to reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation.
- Talking to a therapist or counselor to address underlying stress and anxiety.
- Avoiding stressful or anxiety-inducing activities before bedtime.
- Establishing a relaxing bedtime routine to help reduce stress and promote better sleep habits.
Preventing Sleep Paralysis
Now that we have explored the causes and symptoms of sleep paralysis as well as its link to sleep deprivation, the next step is to delve into how to prevent it. Sleep paralysis can be distressing and disruptive to one’s sleep, so it is important to take proactive measures to reduce its occurrence. In this section, we will discuss several strategies that can help prevent sleep paralysis, ranging from maintaining regular sleep schedules to improving the sleeping environment. By implementing these techniques, individuals can minimize the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis and enjoy a more restful night’s sleep.
Maintaining a Regular Sleep Schedule
One of the most effective ways to prevent sleep paralysis is by maintaining a regular sleep schedule. This means going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Here’s a table with some tips on how to create and maintain a regular sleep schedule:
| What to do | Why it’s important | |
|---|---|---|
| Create a sleep schedule | Pick a bedtime and wake-up time that works for you and stick to it every day. | Helps regulate your body’s internal clock and makes it easier to fall asleep and wake up. |
| Avoid napping | Avoid taking naps during the day or limit them to 20-30 minutes. | Can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night and disrupt your sleep schedule. |
| Avoid sleeping in | Try not to sleep in on the weekends or have a different schedule on different days. | Throws off your body’s internal clock and can make it harder to fall asleep and wake up on other days. |
| Establish a bedtime routine | Create a relaxing pre-sleep routine that helps you unwind and stick to it every night. | Signals to your body that it’s time to sleep and can help you fall asleep faster. |
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule can be challenging, especially if you work different shifts or have other obligations that interfere with your sleep. However, sticking to a consistent sleep routine as much as possible can help reduce your risk of sleep paralysis, as well as other sleep-related disorders.
Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Reducing stress and anxiety can also help prevent sleep paralysis. Stress and anxiety often lead to disrupted sleep, which can increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. Here are some ways to reduce stress and anxiety:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Engage in activities that help reduce stress and anxiety such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. These techniques can help calm the mind and promote relaxation before bedtime.
- Identify and address the source of stress: Identify the source of stress and try to address it. This can involve talking to a trusted friend, seeking the help of a mental health professional, or finding ways to manage the stressor.
- Establish pre-sleep routine: Develop a pre-sleep routine that involves relaxing activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath or listening to calming music. The routine can help signal to the body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
- Avoid stressful activities before bedtime: Try to avoid engaging in stressful activities or watching or reading anything that might cause anxiety before bedtime. This can help reduce the chance of experiencing disrupted sleep due to stress and anxiety.
By implementing these techniques, individuals can reduce their stress and anxiety levels and improve their sleep quality, ultimately reducing their risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Avoiding Stimulants Before Bedtime
The consumption of stimulants before bedtime can disrupt sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Stimulants such as caffeine and nicotine are commonly found in our daily routines and can negatively impact our ability to maintain healthy sleep patterns.
Caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant found in coffee, tea, and many popular soft drinks. It is a commonly used drug to help improve alertness and increase energy levels. However, consuming caffeine before bed can interfere with the brain’s ability to fall asleep or to enter into REM sleep, which is a critical sleep phase for the body’s restoration process. REM sleep cycles are characterized by an increased level of brain activity, which can lead to vivid dreams and potentially trigger a sleep paralysis episode. If you must consume caffeine, it is recommended to limit its consumption or to avoid it altogether in the late afternoon and evening hours.
Nicotine: Nicotine is a stimulant commonly found in cigarettes and other tobacco products. The use of these products can negatively impact sleep quality, as nicotine causes an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, which can make it difficult to fall asleep. Additionally, studies have shown that individuals who smoke cigarettes are more likely to experience sleep disturbances and have a higher risk of developing sleep paralysis. If you use nicotine products, it’s advised to quit or gradually reduce the consumption before bedtime.
Avoiding these stimulants before bedtime is vital to maintaining a healthy sleep routine and reducing the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. The following table summarizes the negative effects of caffeine and nicotine on sleep quality:
| Caffeine | Nicotine | |
|---|---|---|
| Negative Effects | Interference with sleep onset Disrupts REM sleep cycles Potentially triggers sleep paralysis episodes |
Increase in heart rate and blood pressure Difficulty falling asleep Higher risk of sleep disturbances and sleep paralysis |
| Recommendations | Limit consumption and avoid in late afternoon and evenings | Quit or gradually reduce use before bedtime |
Improving Sleeping Environment
Creating a comfortable and conducive sleeping environment is essential in preventing sleep paralysis. Here are some tips to improve your sleeping environment:
- Eliminate Noise: Unwanted noise can disrupt sleep and increase the risk of sleep paralysis. Consider using earplugs or a white noise machine to block out any distractions.
- Control Room Temperature: The temperature of your room can affect your sleep quality. It is recommended to keep your room cool and comfortable to promote better sleep. The ideal temperature for sleeping is around 60-67°F.
- Reduce Light Exposure: Exposure to light can disrupt sleep and affect the natural sleep-wake cycle. Consider using curtains or blinds to block out any unwanted light or wearing a sleep mask to create a dark sleeping environment.
- Choose a Comfortable Mattress and Pillow: A comfortable mattress and pillow can make a huge difference in your sleep quality. Choose a mattress and pillow that are comfortable and provide adequate support for your body.
- Create a Relaxing Atmosphere: A relaxing atmosphere can help promote better sleep. Consider using aromatherapy, such as lavender or chamomile, or playing calming music to help you relax and fall asleep easier.
- Remove Electronic Devices from Bedroom: Electronic devices such as TVs, laptops, and smartphones emit blue light that can interfere with melatonin production and disrupt sleep. It is recommended to remove all electronic devices from the bedroom to create a relaxing and distraction-free sleeping environment.
By making these changes in your sleeping environment, you can significantly reduce the risk of sleep paralysis and improve the quality of your sleep.
Practicing Good Sleep Hygiene
Practicing good sleep hygiene is crucial for preventing sleep paralysis. Sleep hygiene refers to a set of practices and habits that promote quality and healthy sleeping patterns. Here are some tips on how to improve your sleep hygiene and reduce the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis:
| Sleep Hygiene Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Avoid eating heavy meals before bedtime. | Heavy or spicy meals can cause discomfort and affect sleep quality. |
| Establish a relaxing bedtime routine. | A relaxing routine can help signal your brain that it’s time to sleep. For example, you can take a warm bath or read a book before bed. |
| Avoid using electronic devices before bedtime. | Electronic devices emit blue light that can suppress melatonin production and affect sleep quality. |
| Create a comfortable sleeping environment. | Your sleeping environment should be quiet, cool, and comfortable to promote relaxation and quality sleep. Use comfortable pillows and a supportive mattress. |
| Limit caffeine intake. | Caffeine is a stimulant that can affect sleep quality. Avoid consuming caffeine-containing beverages or foods before bedtime. |
| Exercise regularly. | Physical activity can help reduce stress and promote quality sleep, but avoid exercising too close to bedtime as it can stimulate the body. |
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can improve your sleep hygiene and reduce the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. Remember that sleep hygiene is an important aspect of overall health and wellbeing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep paralysis is a distressing and often scary experience that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It occurs when a person is either falling asleep or waking up and is unable to move or speak.
While the exact causes of sleep paralysis are not fully understood, there is evidence that sleep deprivation can increase the risk of experiencing it. This is because sleep deprivation can disrupt the normal sleep patterns that are important for regulating REM sleep, which is when sleep paralysis occurs.
Fortunately, there are several steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of sleep paralysis. These include maintaining a regular sleep schedule, reducing stress and anxiety, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, improving the sleeping environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene.
It is important to note that while sleep paralysis can be frightening, it is not typically a sign of a serious underlying medical condition. However, if an individual is experiencing frequent episodes of sleep paralysis that are interfering with their daily life, they should speak with a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying health issues and discuss possible treatment options. Overall, by prioritizing good sleep habits and addressing any underlying issues, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing sleep paralysis and enjoy better sleep and overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can sleep paralysis be dangerous?
Sleep paralysis itself is not dangerous. However, the hallucinations that often accompany it can be scary and cause anxiety.
How common is sleep paralysis?
About 8% of the general population experiences sleep paralysis. It’s more common in individuals who have a history of anxiety disorders or family members who have experienced it.
Can medication cause sleep paralysis?
Some medications, such as antidepressants or medications used to treat ADHD, can indirectly affect sleep patterns and potentially lead to sleep paralysis. However, it’s not always the case.
Does sleep paralysis only occur during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep?
Yes, sleep paralysis typically occurs during the REM stage of sleep when the body is prepped for dreaming. The brainstem shuts down muscle function for safety during dreams, but sometimes this muscle atonia lasts beyond the dream.
Is it possible to move during a sleep paralysis episode?
It is difficult to move during a sleep paralysis episode because the body is usually still under the effects of REM atonia, but some people can make small movements, such as blinking or wiggling their toes, to help break the paralysis.
Can sleep paralysis be genetic?
There is currently no specific gene known to be responsible for sleep paralysis, but it may have a genetic basis as it is known to run in families.
Are there any treatments for sleep paralysis?
While there is no cure for sleep paralysis, various techniques and strategies can help prevent or minimize its occurrence, such as improving sleep hygiene or seeking therapy to manage anxiety or underlying mental health issues.
Can sleep paralysis cause hallucinations?
Yes, sleep paralysis episodes are often accompanied by vivid hallucinations, which can be visually, auditory, or sensory in nature. These hallucinations are often frightening and unsettling.
Can sleep paralysis occur in children?
Yes, sleep paralysis can occur in children, but it’s less common than in adults. Children who experience sleep paralysis are more likely to have a family history of the condition or underlying medical disorders.
Does sleep paralysis indicate an underlying sleep disorder?
Sleep paralysis is not necessarily indicative of an underlying sleep disorder, but it can be linked to certain conditions, such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea. If sleep paralysis is persistent or significantly affects daily life, it’s important to discuss it with a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying medical issues.








