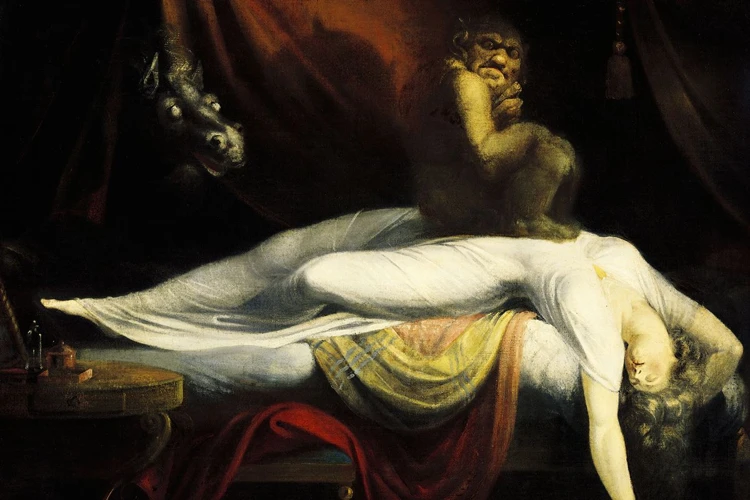
The human body is an incredibly complex machine that requires rest and recuperation to function properly. However, for some people, sleep can be a source of anxiety and discomfort instead of an escape from the stresses of the day. One particular condition that can cause distress during sleep is sleep paralysis. This phenomenon is characterized by the inability to move, speak, or react while asleep or upon waking up. The experience can be terrifying, often accompanied by hallucinations and a feeling of suffocation. In this article, we will delve deeper into the link between sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders, explore the causes and symptoms of this condition, and provide management strategies for those who suffer from it.
What is Sleep Paralysis?
When it comes to sleep disorders, one of the most perplexing and frightening experiences is sleep paralysis. This phenomena occurs when a person is either falling asleep or waking up and they find themselves unable to move or speak. Instead, they feel as though they are paralyzed and unable to escape the sensations that accompany this condition. The experience of sleep paralysis can be extremely distressing, leading to feelings of terror and a sense of being trapped. Understanding the causes and symptoms of this disorder is an important step towards managing and treating it effectively.
Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis
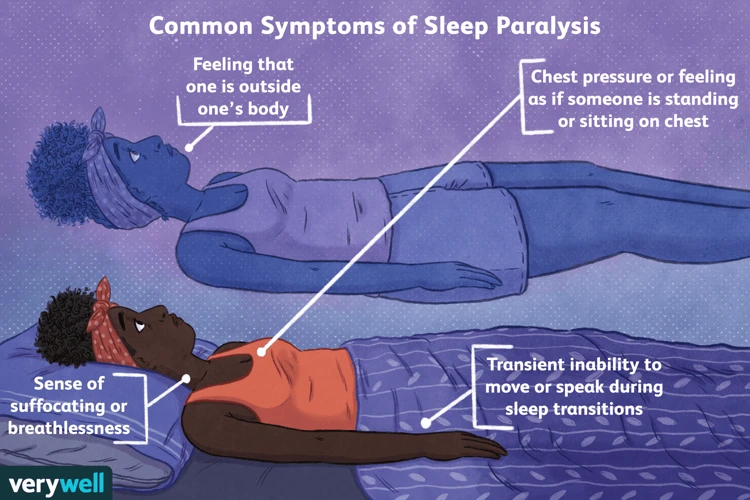
During sleep paralysis, an individual is unable to move or speak even though they are conscious. This experience can be terrifying and is often accompanied by various symptoms including:
| Hallucinations | Individuals experiencing sleep paralysis may also experience vivid hallucinations. These can be auditory, visual, or tactile in nature. |
| Inability to Move | The most common symptom of sleep paralysis is the inability to move. Individuals may feel as though they are paralyzed and unable to even move their eyelids or fingers. |
| Feeling of Pressure | People with sleep paralysis often report feeling a pressure or weight on their chest. This sensation can be incredibly frightening and add to the feeling of being trapped in one’s own body. |
| Distorted Perception of Reality | During sleep paralysis, individuals may also experience a distorted perception of reality. They may feel as though they are floating, spinning, or moving (as if they were on a roller-coaster). This can cause intense feelings of anxiety and fear. |
| Difficulty Breathing | Some individuals with sleep paralysis may experience difficulty breathing, which can further escalate feelings of panic and anxiety. |
It is important to note that sleep paralysis is a relatively common occurrence, with one study reporting that 8% of the general population experiences it at least once in their lifetime. However, for individuals with anxiety disorders, sleep paralysis can occur more frequently and be more severe.
Causes of Sleep Paralysis
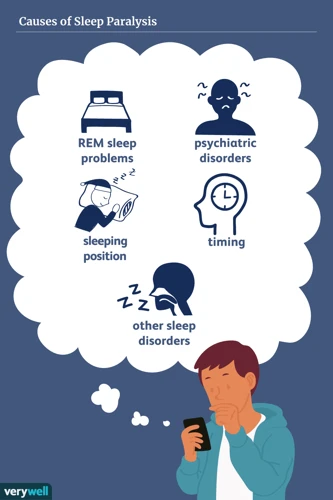
Various factors contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis. Some of these factors are biological, while others are environmental or situational. The following table summarizes the main causes of sleep paralysis:
| Heredity | Genetic factors may make one more susceptible to sleep paralysis. Some research suggests that the condition may run in families. |
| Sleep Deprivation | Insufficient sleep or irregular sleep patterns can lead to episodes of sleep paralysis. This is because sleep deprivation affects the natural sleep-wake cycle and disrupts the timing of REM sleep. |
| Stress and Anxiety | Stressful events or anxieties can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Studies have found that people with anxiety disorders have higher rates of sleep paralysis than those without such conditions. |
| Irregular Sleep Schedule | Changes in sleep schedule or disruptions in the circadian rhythm can trigger sleep paralysis. |
| Narcolepsy | Sleep paralysis is a frequent symptom of narcolepsy, a neurological sleep disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of falling asleep. |
| REM Sleep Disorders | REM sleep disorders, such as REM behavior disorder, can increase the occurrence of sleep paralysis. These disorders involve the disruption of the normal muscle paralysis during REM sleep. |
It is important to note that these causes may not be exclusive or exhaustive, and sleep paralysis may be the result of a combination of factors. Understanding the underlying causes of sleep paralysis can help individuals take steps to manage and prevent its occurrence.
When Does Sleep Paralysis Occur?
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that can occur to anyone, regardless of age or gender. However, it is more commonly seen in young adults and those who have existing sleep disorders such as narcolepsy. Sleep paralysis usually occurs during the following times:
| Time of day | Probability of Occurrence |
|---|---|
| Morning | High |
| Afternoon | Low |
| Evening | Low |
| Night | High |
As seen in the table above, sleep paralysis is more likely to occur during the morning and night times. The reason for this is due to the body’s circadian rhythm, which controls our sleep-wake cycle. During the night, our body goes through different stages of sleep, and it is during the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) stage that we experience vivid dreaming. It is also during this stage that our muscles are temporarily paralyzed to prevent us from acting out our dreams. However, in cases of sleep paralysis, this paralysis continues into the waking state, causing the individual to experience sensations of being unable to move or speak.
Sleep paralysis can also occur more frequently when an individual is experiencing high levels of stress, anxiety, or depression. This is because these emotional states can disrupt our sleep patterns, causing us to wake up more frequently during the night and increasing the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
The occurrence of sleep paralysis is dependent on both our natural sleep-wake cycle and our emotional states. Understanding these factors can help individuals better manage and prevent episodes of sleep paralysis.
The Connection to Anxiety Disorders

It’s often said that the mind and body are interconnected, and it’s no different when it comes to sleep paralysis. This terrifying condition can be linked to a variety of anxiety disorders, leaving sufferers feeling helpless and afraid. But what exactly is the connection between sleep paralysis and anxiety? Recent research has shed light on this topic, revealing that certain types of anxiety disorders may be more likely to lead to sleep paralysis. Despite the perplexity of this issue, there are steps that can be taken to manage both sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders. Let’s dive into this topic and explore the link between these two conditions.
Research Findings
Several studies have investigated the relationship between sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders. One study found that individuals who experience sleep paralysis are more likely to have symptoms of anxiety and depression compared to those who do not experience sleep paralysis. Another study suggested that sleep paralysis may be a risk factor for developing anxiety disorders later in life.
Research findings also indicate that specific types of anxiety disorders are more commonly associated with sleep paralysis. For example, one study found that individuals with panic disorder were more likely to experience sleep paralysis compared to those without panic disorder. Another study reported a link between sleep paralysis and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
Furthermore, research has also shown that reducing anxiety levels can improve sleep paralysis symptoms. One study tested an intervention that focused on reducing anxiety in individuals experiencing sleep paralysis. This intervention resulted in a significant reduction in the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes.
Overall, the research findings suggest that there is a strong link between sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders. Identifying and treating underlying anxiety disorders can help manage and reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
| Study | Findings |
|---|---|
| Study 1 | Individuals with sleep paralysis more likely to have symptoms of anxiety and depression |
| Study 2 | Sleep paralysis may be a risk factor for developing anxiety disorders later in life |
| Study 3 | Individuals with panic disorder more likely to experience sleep paralysis |
| Study 4 | Link between sleep paralysis and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) |
| Study 5 | Intervention aimed at reducing anxiety resulted in a significant reduction in frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes |
Types of Anxiety Disorders Linked to Sleep Paralysis
Recent research has linked sleep paralysis with several types of anxiety disorders. Here are some of the anxiety disorders that have been found to be linked with sleep paralysis:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): GAD is a mental disorder characterized by excessive and persistent worry about everyday things. People with GAD may experience intense fear and apprehension, which can lead to physical symptoms like heart palpitations and sweating. Studies have found that individuals with GAD are more likely to experience sleep paralysis than those without the disorder.
- Panic Disorder: Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by sudden and unexpected panic attacks. These attacks can be accompanied by symptoms like shortness of breath, trembling, and rapid heartbeat. Individuals with panic disorder may be more likely to experience sleep paralysis, and the fear of experiencing sleep paralysis can also trigger panic attacks.
- Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD): SAD is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by excessive fear and avoidance of social situations. Studies have found that individuals with SAD are more likely to experience sleep paralysis than individuals without the disorder. This may be because the fear and anxiety associated with social situations can trigger sleep paralysis.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): PTSD is a mental disorder that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. People with PTSD may experience flashbacks, nightmares, and intrusive thoughts related to the trauma. Studies have found that individuals with PTSD are more likely to experience sleep paralysis than those without the disorder. This may be because the trauma-related stress can disrupt sleep and lead to sleep paralysis.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): OCD is a mental disorder characterized by unwanted and intrusive thoughts, images, or impulses (obsessions) that are followed by repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions). Studies have found that individuals with OCD are more likely to experience sleep paralysis than those without the disorder. This may be because the obsessive thoughts can lead to sleep disturbance and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
It’s important to note that just because someone experiences sleep paralysis does not necessarily mean they have an anxiety disorder. However, if sleep paralysis is accompanied by symptoms of anxiety or a preexisting anxiety disorder, it may be worth seeking professional help.
Other Factors that Influence Sleep Paralysis
As if sleep paralysis isn’t already perplexing enough, there are other factors that can contribute to its onset. Understanding these factors is crucial to properly managing and preventing sleep paralysis. In this section, we will delve into various influences on sleep paralysis including sleep deprivation, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and substance abuse. By understanding the link between these factors and sleep paralysis, we can take steps towards improving our sleep and overall well-being.
Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation is one of the most common causes of sleep paralysis. When a person doesn’t get enough sleep, it can affect their brain function and make them more susceptible to experiencing sleep paralysis episodes. According to the National Sleep Foundation, adults need between seven and nine hours of sleep per night to function at their best.
Sleep deprivation can cause a variety of symptoms, including difficulty concentrating, fatigue, irritability, and memory problems. It can also weaken the immune system, making it easier for a person to get sick.
Research has also shown that sleep deprivation can worsen anxiety disorders, making a person more likely to experience sleep paralysis. The relationship between sleep deprivation and anxiety is complex, but it’s clear that getting enough sleep is crucial for managing anxiety symptoms.
To combat sleep deprivation, it’s important to establish healthy sleep habits. This includes going to bed at a consistent time every night, limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, and creating a relaxing sleep environment free of distractions such as screens or bright lights. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing can help reduce feelings of anxiety, which in turn can improve sleep quality and decrease the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
It’s important to note that while improving sleep hygiene can help manage sleep paralysis, it’s not a guaranteed solution. In cases where sleep paralysis is severe or accompanied by other symptoms, seeking professional help is necessary.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
One of the factors that can influence sleep paralysis is post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). PTSD is a mental health disorder triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It can cause disturbing and intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and nightmares. This condition can lead to sleep disturbances, including sleep paralysis.
There are a number of possible reasons for the link between PTSD and sleep paralysis, such as the effects of stress and anxiety on the body, sleep disruptions, and changes in neurotransmitters. Sleep paralysis can also be a symptom of PTSD, a sign that the traumatic experience is still affecting the individual.
PTSD is a complex disorder and should be treated by a mental health professional. If you think you may have PTSD, don’t hesitate to seek help. Some options for treating PTSD include psychotherapy, medication, or a combination of both.
It’s important to remember that getting enough sleep is crucial for managing PTSD and other anxiety disorders. Sleep hygiene practices such as setting a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can help prevent sleep disturbances and improve overall sleep quality.
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse is another factor that can influence the occurrence of sleep paralysis. According to research studies, individuals who abuse drugs or alcohol are more likely to experience sleep paralysis.
How Substance Abuse Affects Sleep
Substance abuse can disrupt the sleep cycle and affect the quality of sleep. Alcohol and drugs such as cocaine, amphetamines, and marijuana can interfere with REM sleep, which is the stage where most of our dreams occur. When the REM stage is interrupted, the body may experience a rebound effect, meaning that it tries to catch up on lost REM sleep. This can cause intense and vivid dreams, including nightmares and sleep paralysis.
The Connection between Substance Abuse and Sleep Paralysis
Many substances can cause or exacerbate anxiety or panic attacks, which can trigger sleep paralysis. The use of stimulants, such as cocaine and amphetamines, can increase levels of anxiety and make it more difficult to fall asleep, which can lead to sleep deprivation and sleep paralysis.
Substance abuse can also lead to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety disorders, which are already linked to sleep paralysis.
Managing Sleep Paralysis and Substance Abuse
It is essential to seek professional help if you struggle with substance abuse and sleep paralysis. Overcoming addiction can be a complex process, and it is important to seek the guidance of a licensed professional.
Some methods that can help manage substance abuse and sleep paralysis include:
| Method | Description |
| Detoxification | This process aims to eliminate toxins from your body and restore its natural balance. |
| Therapy | Individual or group therapy can help you address the root causes of substance abuse and develop coping mechanisms to manage anxiety and reduce the likelihood of sleep paralysis. |
| Medications | Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) can help reduce the physical and psychological symptoms of withdrawal and increase the chances of successful recovery. |
| Self-Care | Practicing self-care techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and exercise can help reduce anxiety and improve overall sleep quality. |
Substance abuse can increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis by affecting REM sleep and causing anxiety and panic attacks. Seeking professional help and developing healthy coping mechanisms can help manage substance abuse and reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
How to Manage Sleep Paralysis and Anxiety Disorders
Managing sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders can be overwhelming, especially since these conditions can often occur together. However, there are various approaches that one can try to alleviate the symptoms and improve overall well-being. It is important to seek professional help and make lifestyle changes that may contribute to better sleep patterns. Additionally, therapeutic interventions and techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and sleep hygiene practices can help in managing and reducing the instances of sleep paralysis and anxiety. In this section of the article, we will discuss these different management strategies in detail.
Seek Professional Help
Professional help can be beneficial in managing sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders. Here are some options to consider:
- Counseling: A counselor or therapist can help you identify triggers and develop coping strategies to manage anxiety and prevent sleep paralysis episodes. They may use cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help you change negative thought patterns and behaviors that may contribute to anxiety and sleep disturbances.
- Medication: Certain antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications may help manage anxiety and prevent sleep paralysis episodes. However, medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare provider.
- Sleep Specialist: A sleep specialist can help diagnose and treat sleep disorders, including sleep paralysis. They may suggest lifestyle changes or prescribe medication to improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis episodes.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can connect you with others who are experiencing sleep paralysis and anxiety. This can provide a sense of community and support, and help you feel less alone in your struggles.
Ultimately, seeking professional help can be an important step in managing sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders. A qualified healthcare provider can work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your individual needs and goals.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can be beneficial in managing both sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders. Here are some recommendations to consider:
- Regular exercise: Exercise is known to relieve stress and anxiety, as well as improve sleep quality. Aim to get at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise every day.
- Healthy diet: What you eat can affect your sleep and anxiety levels. Avoid consuming foods and drinks that contain caffeine, alcohol, and sugar, especially close to bedtime. Instead, opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Relaxation techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help reduce anxiety levels and promote a better sleep schedule.
- Good sleep hygiene: Maintaining good sleep hygiene can help reduce the likelihood of sleep paralysis occurrences. This includes sticking to a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing sleep environment, and avoiding electronics before bedtime.
Remember, making lifestyle changes requires patience and consistency. It can take some time to see the benefits, so don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately.
Therapies and Treatment
When it comes to managing sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders, therapy and treatment can be incredibly beneficial. There are several options available which can be used alone or in combination to improve the symptoms a person may be experiencing.
Therapy for anxiety disorders is typically rooted in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy(CBT). This approach focuses on teaching individuals techniques to change their negative thought patterns and behaviors, which can contribute to anxiety and exacerbate sleep paralysis symptoms. CBT has been shown to be effective in managing anxiety disorders linked to sleep paralysis.
Another type of therapy that may help is Exposure Therapy. This technique gradually exposes the individual to their fears, helping them become more comfortable with them over time. It can be helpful for those with sleep paralysis, who may fear experiencing the symptoms again.
Medications may also be prescribed by a doctor or mental health professional to help manage anxiety and symptoms of sleep paralysis. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and sleep aids may all be used.
For those who experience sleep paralysis due to sleep disorders like narcolepsy or sleep apnea, treatment for these conditions may also help alleviate symptoms. For example, continuous positive airway pressure(CPAP) for sleep apnea can improve breathing during sleep and lead to fewer episodes of sleep paralysis.
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, and meditation can also be helpful for managing anxiety and improving sleep quality. These practices can help a person better cope with the feelings of fear and anxiety that come with sleep paralysis.
Therapy and treatment should be tailored to the individual, as no two people experience anxiety disorders or sleep paralysis in the same way. By working with a mental health professional, individuals can identify the best options for managing their symptoms and improving their quality of life.
| Therapies and Treatments | Description |
|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy | Focused on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to anxiety and sleep paralysis |
| Exposure Therapy | Gradual exposure to fears and anxieties to increase comfort and decrease fear of experiencing symptoms again |
| Medications | Antidepressants, anti-anxiety meds, and sleep aids may be used to manage anxiety and sleep paralysis symptoms |
| Treatment for Underlying Sleep Disorders | Treating sleep disorders like sleep apnea can improve breathing during sleep and decrease episodes of sleep paralysis |
| Relaxation Techniques | Deep breathing, yoga, and meditation can help manage anxiety and fear associated with sleep paralysis |
Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene is an essential component for managing and preventing sleep disorders like sleep paralysis, especially for those with anxiety disorders. It refers to the practices and behaviors that support good quality sleep. Here are some strategies for enhancing sleep hygiene and preventing sleep paralysis:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Avoid Stimulants | Avoiding caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can help prevent sleep disturbances and promote a sounder sleep experience. |
| Establish a Regular Sleep-Wake Schedule | Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps establish a consistent sleep-wake routine that improves overall sleep quality. |
| Relaxation Techniques | Relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation or breathing exercises can help reduce anxiety levels, which is a significant contributor to sleep paralysis. |
| Create a Comfortable Environment | A cool, dark, and noise-free bedroom, with comfortable bedding and pillows, can help promote a comfortable sleep experience. |
| Avoid Technology Before Bed | The blue light emitted from electronic devices disrupts circadian rhythms, making it harder to fall asleep. Avoiding screen time an hour before bed can help make falling asleep easier. |
By implementing simple yet effective sleep hygiene habits, individuals can improve their sleep quality and potentially prevent sleep paralysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep paralysis is a terrifying experience that can leave individuals feeling helpless and anxious. It is linked to several anxiety disorders, including panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder. While the exact cause of sleep paralysis is not fully understood, there are several factors that can contribute to its onset, including sleep deprivation, PTSD, and substance abuse.
Managing sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders can be challenging, but seeking professional help, making lifestyle changes, and participating in therapies and treatment can help individuals regain control of their lives. Additionally, practicing good sleep hygiene, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule and avoiding electronic devices before bed, can also be effective in preventing sleep paralysis.
It is important for individuals experiencing sleep paralysis to understand that they are not alone and that there are effective treatments available to help alleviate their symptoms. By taking proactive steps towards managing sleep paralysis and anxiety disorders, individuals can improve their quality of life and regain a sense of control over their sleep and mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between sleep paralysis and regular dreams?
Sleep paralysis occurs during the transition between sleep and wakefulness, whereas regular dreams occur during the REM stage of sleep.
Can sleep paralysis be dangerous?
While sleep paralysis itself is not dangerous, it can be distressing and lead to anxiety or other sleep-related issues.
Is sleep paralysis more common in certain age groups?
Sleep paralysis can occur at any age, but it is most commonly experienced by young adults and teenagers.
Can anxiety disorders cause sleep paralysis?
Research suggests that anxiety disorders can be a contributing factor to experiencing sleep paralysis.
Can medication cause sleep paralysis?
Some medications, such as those used to treat depression and ADHD, have been known to increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis.
Can lack of sleep cause sleep paralysis?
Sleep deprivation can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Is it possible to move during sleep paralysis?
While it may be difficult to move or speak during an episode of sleep paralysis, some people report being able to do so with effort.
Can sleep paralysis cause hallucinations?
It is common for people experiencing sleep paralysis to have hallucinatory experiences, such as seeing or feeling a presence in the room.
Can sleep paralysis be cured?
While there is no cure for sleep paralysis, there are ways to manage and reduce its occurrence, such as seeking professional help, making lifestyle changes, and practicing good sleep hygiene.
Is it possible to prevent sleep paralysis?
While it is not always possible to prevent sleep paralysis, reducing stress, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a regular sleep routine may help reduce the likelihood of experiencing it.








