Have you ever woken up from sleep, unable to move or speak, as if your body is temporarily paralyzed? This phenomenon is known as sleep paralysis and is often accompanied by vivid hallucinations and a sense of dread. On the other hand, have you ever had a dream in which you were fully aware that you were dreaming and could even control the variables within it? This phenomenon is called lucid dreaming, and many people strive to achieve this state in order to explore their subconscious mind or fulfill their wildest fantasies. But did you know that there is a strong link between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming? In this article, we will delve into the science behind these two phenomena and explore techniques for inducing lucid dreaming through sleep paralysis. We will also cover strategies for coping with sleep paralysis, so that you can harness its power to achieve lucid dreams without the fear and anxiety associated with the experience.
What is Sleep Paralysis?
Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night, completely paralyzed and unable to move, despite being fully awake? This is a terrifying experience known as sleep paralysis. During this state, your mind is fully conscious, but your body is in a state of temporary paralysis, leaving you feeling vulnerable and helpless. It typically lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes, but the experience can feel much longer. Sleep paralysis is a perplexing phenomenon that affects many people and can be both scary and confusing. Let’s dive deeper into this topic and uncover what causes it.
What is Lucid Dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is a state in which a person is aware that they are dreaming and can actively participate and control the dream. During a lucid dream, the dreamer can alter the dream’s plot, setting, and characters. This type of dream allows individuals to explore their imagination and creativity and can lead to a transformative experience.
There are several characteristics of lucid dreaming that differentiate it from other types of dreaming. The following table outlines the common features of lucid dreaming:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Awareness | The individual is aware that they are dreaming |
| Control | The individual can exert a significant amount of control over the dream’s content |
| Memory | The individual can recall the events of the lucid dream with clarity |
| Sensory experience | The individual can experience sensations such as taste, touch, and smell within the dream |
| Duration | Lucid dreams can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes |
Lucid dreaming has been associated with several benefits, including increased creativity, problem-solving abilities, and decreased nightmares. Some individuals may use lucid dreaming as a tool for personal growth or to overcome anxiety and phobias. However, like any dream state, it is important to explore lucid dreaming with caution and seek guidance if it is causing distress or interfering with sleep quality.
What is the Connection Between Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming?
During sleep paralysis, a person is unable to move their body despite being fully conscious. This experience has been linked with lucid dreaming, which is a state in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and may have some control over the dream narrative. But what is the connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming?
The connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming lies in the fact that both happen during REM sleep. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is a stage of sleep when the brain is highly active, and dreaming is most likely to occur. During this stage, the body is typically in a state of paralysis, which is thought to prevent the dreamer from acting out their dreams and potentially harming themselves in real life.
While sleep paralysis is typically seen as a negative experience due to the associated feelings of fear and helplessness, it can also be seen as an opportunity for lucid dreaming. When experiencing sleep paralysis, the dreamer may be able to remain conscious while their body remains paralyzed, allowing them to enter a lucid dream state.
Lucid dreaming during sleep paralysis can also provide a unique opportunity for dream control and exploration. With the ability to control the dream narrative, dreamers can turn the negative experience of sleep paralysis into a positive and potentially transformative experience.
In summary, the connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming lies in their occurrence during REM sleep, the body’s natural paralysis during this stage, and the potential for using sleep paralysis as a gateway to lucid dreaming, offering opportunities for dream exploration and control.
The Science Behind Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming
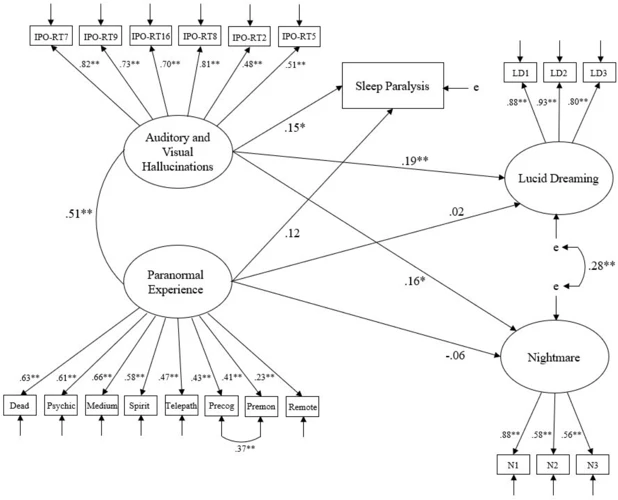
As we delve into the connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, it’s important to first understand the science behind these two phenomena. By examining the stages of sleep, the neural mechanisms of sleep paralysis, and the cognitive processes of lucid dreaming, we can unravel the intricate link between the two. So, let’s explore the scientific basis of sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, and how they work together to create a unique and often surreal experience for those who engage in it.
The Stages of Sleep
During sleep, our brain goes through different stages of activity. These stages are essential for the body to rest and repair, as well as for the mind to process and consolidate memories. There are five stages of sleep, each with distinct characteristics that differentiate them from the others.
Stage 1: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) Sleep is the transition period from wakefulness to sleep, and it lasts for about 5-10 minutes. During this stage, the brain produces slower alpha and theta waves, and muscle activity slows down.
Stage 2: NREM Sleep lasts for about 20 minutes and is characterized by the presence of sleep spindles and K-complexes. These are brief surges of brain activity that help protect and preserve sleep. During this stage, the body temperature drops, the heart rate slows down, and breathing becomes more regular.
Stage 3: NREM Sleep is also called Slow Wave Sleep (SWS) or deep sleep. It usually occurs in the first half of the night and lasts for about 30 minutes. During this stage, delta waves, which are low-frequency and high-amplitude, dominate the brain’s electrical activity. The body is completely relaxed, and it’s difficult to awaken someone from this stage.
Stage 4: NREM Sleep is the deepest stage of sleep and only lasts for a few minutes. During this stage, the brain produces mostly delta waves, and it’s challenging to wake up the sleeper.
Stage 5: Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep is when most of our dreaming occurs. It begins about 90 minutes after sleep onset and repeats every 90 minutes throughout the night. During this stage, the brain is highly active, and the eyes move back and forth rapidly. The muscles become paralyzed, except for the ones responsible for eye movements and breathing.
By understanding the stages of sleep, we can better comprehend the relationship between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming. The transitions between these stages are crucial for our body and mind to rest and rejuvenate. However, disturbances in these transitions can lead to sleep disorders, like sleep paralysis.
The Science Behind Sleep Paralysis
During sleep, our body goes through several stages, including the rapid eye movement (REM) stage. REM sleep is when we are most likely to dream, and our bodies essentially become paralyzed to prevent us from acting out our dreams. Sleep paralysis occurs when this paralysis persists even after the REM stage ends and we wake up. This state can be **terrifying** because we cannot move our bodies but are fully conscious, leading to **intense feelings of panic and terror**.
Sleep paralysis is believed to be caused by a disruption in the normal sleep cycle, specifically in the transition between REM and non-REM sleep. **During REM sleep, the brainstem sends a signal to disable the muscles that control movements, essentially putting the body in a state of paralysis.** This state is called REM Atonia. When we wake up during REM atonia, we are conscious but fully paralyzed, which can be disorienting and distressing.
There are several factors that can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis, including **sleep deprivation, an irregular sleep schedule, stress, anxiety, and sleep disorders such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea**. However, sleep paralysis can also occur without any underlying condition or trigger.
While sleep paralysis can be a distressing experience, it is generally considered a benign condition that does not require treatment. However, for those who experience frequent or severe episodes, there are techniques that can be used to reduce their occurrence, including improving sleep hygiene and reducing stress levels.
The Science Behind Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming is a state in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and can often control the dream’s outcome. It occurs during the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) stage of sleep, which typically occurs in cycles throughout the night. Here are some important points to consider when understanding the science behind lucid dreaming:
- Activation of the Pre-Frontal Cortex: The pre-frontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making, attention, and self-awareness, is more active during lucid dreaming. This increased activity is associated with the realization that one is dreaming and the ability to control the dream.
- REM Sleep: Lucid dreaming typically occurs during REM sleep, which is characterized by rapid, irregular eye movements, high brain activity, and muscle paralysis. During this stage of sleep, the brain is very active, and the body is largely immobilized to prevent acting out dreams.
- Gamma Waves: Gamma waves, which are associated with higher levels of consciousness and cognitive processing, are more present during lucid dreaming. This suggests that lucid dreaming may be an elevated state of consciousness.
- Precursors to Lucid Dreaming: Certain substances, such as galantamine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, and melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep, have been shown to increase the likelihood of having lucid dreams. Additionally, certain practices, such as meditation and reality checks, can increase one’s chances of becoming aware they are dreaming and enter a state of lucid dreaming.
Lucid dreaming is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs during the REM stage of sleep and is characterized by increased activity in the pre-frontal cortex and gamma waves. Certain substances and practices can increase the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams, opening up opportunities for those interested in exploring the limits of their consciousness during sleep.
How to Use Sleep Paralysis to Achieve Lucid Dreaming

For those who are interested in exploring the world of lucid dreaming, sleep paralysis can be an avenue worth exploring. While this experience can be unsettling and frightening, some have found that with the right techniques and mindset, it can be a gateway to achieving lucidity in their dreams. In this section of the article, we will delve into different strategies for inducing sleep paralysis and converting it into lucid dreams, so you can begin your journey towards more vivid and controllable dream experiences.
Techniques for Inducing Sleep Paralysis
There are a number of techniques that individuals can use to induce sleep paralysis. Some of the most effective techniques are:
| 1. Hypnagogic Imagery: | This technique involves lying in bed with your eyes closed and focusing on hypnagogic imagery, which are the colorful patterns and shapes that people often see in their mind’s eye as they fall asleep. By focusing on this imagery and allowing yourself to drift into a semi-conscious state, you may be able to transition into sleep paralysis. |
| 2. Wake-Back-to-Bed: | This technique involves setting your alarm for several hours earlier than you would typically wake up. When the alarm goes off, get up and engage in a quiet activity for about 30 minutes. Then, go back to bed and lie still, while trying to keep your mind alert. This technique can help trigger sleep paralysis. |
| 3. Sensory Deprivation: | Sensory deprivation is a process of removing all external stimuli, such as light and sound, which can help you enter a state of deep relaxation. By depriving your senses of external stimulation, you may be able to enter a semi-conscious state in which sleep paralysis can occur. |
| 4. Focusing on the Breath: | This technique involves lying in bed with your eyes closed and focusing on your breathing. By concentrating on the rhythm of your breath, you may be able to enter a meditative state that can help you transition into sleep paralysis. |
It is important to note that inducing sleep paralysis can be a difficult process and may not work for everyone. It is also important to remain safe and comfortable while attempting to induce sleep paralysis. Individuals should exercise caution and avoid trying to induce sleep paralysis while alone or in an unfamiliar environment.
Techniques for Converting Sleep Paralysis into a Lucid Dream
Once you have mastered the techniques for inducing sleep paralysis, the next step is to learn how to convert it into a lucid dream. This requires a specific set of techniques and strategies that can help you take control of your dreams and turn them into vivid and exhilarating experiences.
Technique | Description
— | —
Reality Checking | This technique involves performing regular reality checks during the day, such as counting your fingers or checking a clock, to increase awareness and help you recognize when you are dreaming. When you experience sleep paralysis, perform a reality check to confirm that you are in fact in a dream state.
Visualization | This technique involves visualizing yourself entering a lucid dream state before falling asleep. Picture yourself becoming aware of your dream state while in sleep paralysis, and focus on taking control of your dream.
Meditation | Meditation can help calm your mind and enhance your ability to recognize when you are in a dream state. Practicing meditation regularly can improve your chances of achieving lucid dreams during sleep paralysis.
Wake-Back-to-Bed | This technique involves waking up after a few hours of sleep, staying awake for a short period of time, and then going back to sleep. When you fall back asleep, you are more likely to enter a lucid dream state during sleep paralysis.
WILD Technique | The WILD (Wake-Induced Lucid Dream) technique involves staying conscious while your body falls asleep, and then entering a lucid dream state while in sleep paralysis. This technique requires a great deal of focus and practice, but can be highly effective.
By experimenting with different techniques and strategies, you can improve your ability to convert sleep paralysis into lucid dreams. Keep in mind that this process may take time and practice, and it is important to remain patient and persistent in your efforts. With dedication and practice, you can unlock the link between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, and experience the thrill of taking control of your dreams.
Strategies for Coping with Sleep Paralysis
For those who experience sleep paralysis, it can be a frightening and overwhelming experience. Fortunately, there are a number of strategies that can help individuals cope and manage their symptoms. By implementing certain relaxation techniques and improving their sleep hygiene habits, individuals can work towards minimizing the severity and frequency of their sleep paralysis episodes. Additionally, speaking with a sleep specialist can provide further support and guidance on coping with this condition. Let’s explore some effective strategies for managing sleep paralysis.
Relaxation Techniques
One strategy for coping with sleep paralysis is to use relaxation techniques. Relaxation techniques can help to calm your mind and body, making it easier to fall asleep and reducing the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Here are a few relaxation techniques you can try:
- Deep breathing: Slow, deep breathing can help to reduce stress and promote relaxation. Try inhaling for a count of four, holding for seven, and exhaling for eight. Repeat this pattern a few times until you feel more relaxed.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Tense your muscles one at a time, holding the tension for several seconds, then releasing. Start with your toes and work your way up to your head.
- Meditation: Meditation involves focusing your attention on an object, sound, or mantra, and letting go of distracting thoughts. There are many different forms of meditation, so you may need to experiment to find one that works for you.
- Visualization: Imagine yourself in a peaceful, relaxing environment. Focus on the sights, sounds, and smells around you as vividly as possible.
Remember that it may take some time and practice to find a relaxation technique that works for you. Don’t get discouraged if the first technique you try doesn’t work – just try another one until you find what works best for you. With practice, you may find that you’re able to fall asleep more easily and experience fewer episodes of sleep paralysis.
Sleep Hygiene Strategies
Good sleep hygiene practices can help reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. By promoting healthy and consistent sleep patterns, individuals may be able to prevent or lessen the severity of this phenomenon. Here are some recommended sleep hygiene strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Avoiding caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol | These substances can disrupt the sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. It is important to avoid consuming them several hours before bedtime. |
| Establishing a regular sleep schedule | Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can help regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle and reduce the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. |
| Maintaining a relaxing bedtime routine | Engaging in calming activities before bed, such as taking a warm bath or reading a book, can help prepare the body and mind for restful sleep. |
| Creating a comfortable sleep environment | Ensuring that the bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet can help promote restful sleep. |
| Avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime | Activities such as watching TV or using electronic devices can interfere with sleep quality and increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. |
| Managing stress and anxiety | Stress and anxiety can disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, or therapy may be helpful in managing stress levels. |
By implementing these strategies, individuals can improve their overall sleep hygiene and potentially reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis. However, it is important to note that these strategies may not work for everyone and it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional if sleep paralysis is causing significant distress or impairment in daily life.
Talking to a Sleep Specialist
If you are experiencing frequent or severe sleep paralysis, it may be beneficial to speak with a sleep specialist. A sleep specialist is a medical professional who specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders related to sleep. They can help you understand what causes your sleep paralysis, and provide guidance on how to prevent or manage the episodes.
Here are some steps you can take when talking to a sleep specialist:
- Describe your symptoms: When speaking with a sleep specialist, be sure to provide as much detail as possible about your sleep paralysis episodes. Describe how often they occur, how long they last, and any physical or emotional sensations you experience.
- Discuss your sleep habits: It’s important to talk with your sleep specialist about your overall sleep habits. Share any medications you take, how much caffeine you consume, and your typical sleep schedule.
- Consider undergoing a sleep study: A sleep study can help identify any underlying sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or narcolepsy, which may contribute to your sleep paralysis.
- Explore treatment options: Once you have a better understanding of what may be causing your sleep paralysis, a sleep specialist can recommend treatment options. This may include medications or changes to your sleep environment or habits.
- Ask questions: Don’t be afraid to ask questions or seek clarification during your appointment. Your sleep specialist is there to help you, and the more you understand about your condition, the better equipped you’ll be to manage it.
Remember, sleep paralysis can be a frightening experience, but it’s important to understand that it’s a relatively common phenomenon. By taking steps to better understand your condition and working with a sleep specialist to identify potential treatments, you can reduce the frequency and severity of your sleep paralysis episodes and achieve more restful sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, utilizing the connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming can provide a unique opportunity for individuals to explore the depths of their subconscious mind. However, it is important to do so in a safe and responsible manner.
Sleep paralysis is a common phenomenon that occurs when the body transitions between different stages of sleep. This can sometimes result in a feeling of being unable to move, and may be accompanied by hallucinations. While it can be a frightening experience, there are techniques that can be used to induce and manage sleep paralysis safely.
Lucid dreaming, on the other hand, involves becoming aware within a dream that one is dreaming, and being able to control the dream’s outcome. This can be a powerful tool for self-exploration and personal growth.
The science behind both sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is still being studied, but we do know that they are both related to the sleep cycle and the REM stage of sleep.
To use sleep paralysis to achieve lucid dreaming, it is important to practice certain techniques for inducing and converting sleep paralysis into a lucid dream. However, it is equally important to take steps to cope with sleep paralysis in case it occurs unexpectedly.
Some strategies for coping with sleep paralysis include relaxation techniques, maintaining good sleep hygiene, and seeking the guidance of a sleep specialist if necessary. By staying informed and practicing responsible sleep habits, individuals can safely unlock the link between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming to enhance their understanding of themselves and their subconscious mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming?
Sleep paralysis is a state of temporary paralysis experienced during the transition between sleep and wakefulness, while lucid dreaming is the ability to consciously control your dream while you are still asleep.
Is it possible to induce sleep paralysis?
Yes, there are techniques that can be used to induce sleep paralysis. These include the “wake back to bed” method and the “gently falling asleep” method.
What are some techniques for converting sleep paralysis into a lucid dream?
Common techniques for converting sleep paralysis into a lucid dream include trying to “roll over” out of your body or simply visualizing your desired dream environment before you fall back asleep.
Is it safe to induce sleep paralysis?
Inducing sleep paralysis is generally considered safe, but it’s important to note that some people may find the experience uncomfortable or frightening. It’s also crucial to practice good sleep hygiene techniques when experimenting with sleep paralysis induction, as a lack of quality sleep can have negative effects on your mental and physical health.
What are some common symptoms of sleep paralysis?
Common symptoms of sleep paralysis include the inability to move, a feeling of pressure on the chest, and hallucinations.
Can you experience sleep paralysis if you don’t have a history of lucid dreaming?
Yes, sleep paralysis can occur in people who have never experienced lucid dreaming before.
What are some relaxation techniques that can help with coping with sleep paralysis?
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can be effective in reducing the stress and anxiety associated with sleep paralysis.
What is sleep hygiene?
Sleep hygiene refers to a set of practices and habits that are conducive to a good night’s sleep. These may include things like avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime, establishing a regular sleep schedule, and creating a comfortable sleeping environment.
What are some potential negative impacts of poor sleep hygiene?
Poor sleep hygiene can have a variety of negative impacts on your physical and mental health, including fatigue, mood swings, increased risk of illness, and impaired cognitive function.
When should you talk to a sleep specialist about sleep paralysis?
If you are experiencing frequent episodes of sleep paralysis that are impacting your quality of life, it is advisable to speak with a sleep specialist. Additionally, if you are experiencing other symptoms such as loud snoring or interruptions in breathing during sleep, this may be a sign of a more serious underlying sleep disorder that requires medical attention.








