There’s no denying that sleep is an essential part of our lives, affecting everything from our physical health to our mental wellbeing. However, the science of sleep is still largely unexplored territory for many people, and the different stages of sleep and their impact on dreaming can be particularly puzzling. What happens in our brains when we fall asleep and dream, and why is it so important? In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of sleep science and explore everything you need to know about the different stages of sleep and their impact on dreaming. So grab a cup of tea, get comfy, and let’s explore this mysterious world together.
The Science of Sleep
Sleep is a complex and fascinating biological phenomenon that still holds many mysteries for scientists to unravel. It is a vital process that affects every aspect of our physical, mental, and emotional well-being. From repairing and rejuvenating our bodies to processing and consolidating memories, sleep plays a crucial role in our daily lives. In this section, we will explore the different stages of sleep and the science behind what happens in our bodies during each stage.
What are the Sleep Stages?
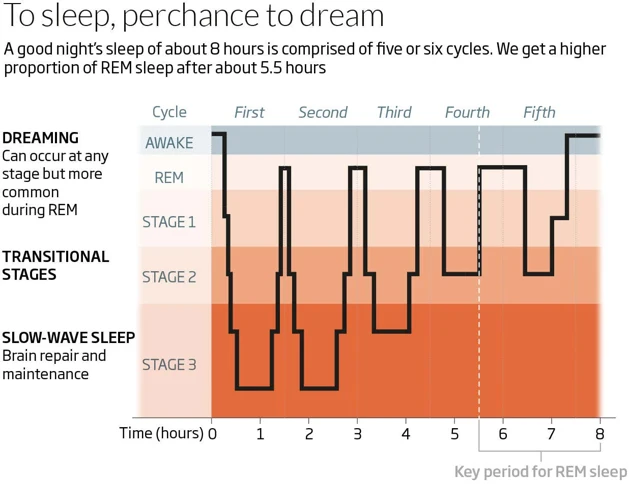
Sleep is a complex process that can be divided into different stages. During a typical night’s sleep, an individual will go through several sleep stages, each of which is characterized by specific patterns of brain activity and physiological changes. Understanding these stages is important for assessing the quality and quantity of sleep an individual is getting each night.
The different sleep stages include:
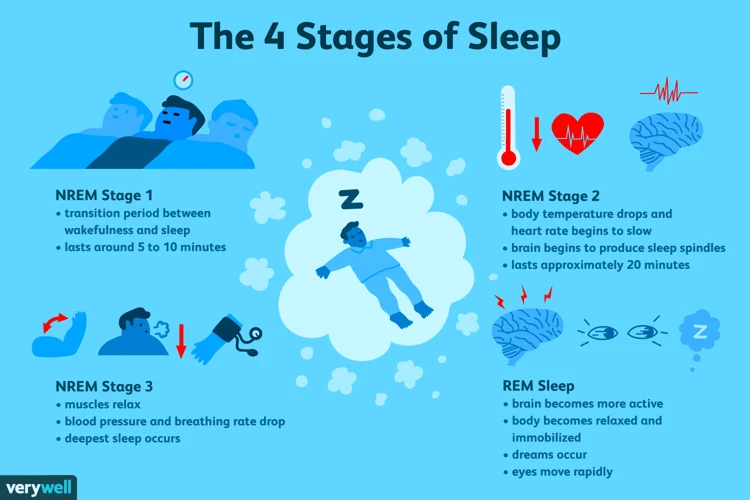
- Stage 1 NREM Sleep: This is the lightest stage of sleep, characterized by a transition from wakefulness to sleep. During this stage, the body begins to relax, and brain activity starts to slow down. It is common for people to experience sudden muscle contractions during this stage, which can cause a sensation of falling or jerking. This stage usually lasts for about 5% of the total sleep time.
- Stage 2 NREM Sleep: This is a deeper stage of sleep, characterized by a further decrease in brain activity and relaxation of the muscles. During this stage, brain activity consists of short bursts of electrical activity called sleep spindles and slow-wave activity. The body temperature also decreases, and heart rate and breathing become more regular. This stage typically lasts for about 45-50% of the total sleep time.
- Stage 3 NREM Sleep: This is the deepest stage of sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep. During this stage, the brain produces slow, high-amplitude waves, and the body’s metabolism and heart rate slow down significantly. It is difficult to wake someone up during this stage, and people who are awakened may feel groggy and disoriented. This stage makes up about 15-20% of the total sleep time.
- REM Sleep: During this stage, the brain is highly active, and rapid eye movements (REM) occur. This stage is also known as paradoxical sleep because, despite the increased brain activity, the body’s muscles are relaxed and essentially paralyzed. During REM sleep, people often dream and experience vivid sensory experiences. This stage typically occurs about 20-25% of the total sleep time and tends to increase in duration as the night progresses.
It’s important to note that the sleep cycle is not linear and goes through several NREM and REM cycles throughout the night. The cycles typically last between 90-120 minutes and repeat four to six times throughout the night. By understanding the different sleep stages, individuals can assess their sleep quality and identify any potential sleep disorders.
The Importance of Sleep Stages
One important aspect of sleep is the different stages that we pass through during the night. Each stage has its own characteristics and serves a specific purpose in maintaining our overall health and well-being. It’s crucial to have a healthy balance of these stages, as each one plays an essential role in different areas of our mental and physical health. Here are some of the reasons why each of the sleep stages is vital:
- NREM Stage 1: This stage is the transition between being awake and falling asleep. During this period, your brain activity slows down, and your muscles begin to relax. This stage is essential for the restoration and repair of your body, as well as the preparation for deeper sleep stages.
- NREM Stage 2: During this stage, your brain waves slow down even further, and your body temperature and heart rate decrease. This stage is important for the brain to consolidate memories and skills learned during the day and prepare for more profound sleep stages.
- NREM Stage 3: Also known as slow-wave sleep, this stage is crucial for physical restoration and growth, including muscle and tissue repair. It’s also an essential time for the consolidation of memories and learning that happened during the day.
- REM Stage: During this stage, your brain activity increases, and your muscles become paralyzed, preventing you from acting out your dreams. REM sleep is crucial for cognitive restoration and emotional regulation. It is also the stage where most dreaming occurs, and it has been linked to processes such as problem-solving, creativity, and emotional regulation.
These different stages help keep our bodies and minds healthy and functioning correctly. They play a crucial role in everything from memory consolidation to physical restoration. Understanding and valuing the importance of each stage can lead to better sleep habits and overall health.
The Different Sleep Stages and Dreaming
As we close our eyes at night, we enter a mysterious world of dreams. But what many people do not realize is that our sleep is not a monolithic state; instead, it consists of different stages with unique characteristics. Understanding these stages is crucial in understanding the nature of dreams that we experience each night. In this section, we will explore the different sleep stages, their impact on dreaming, and how they can affect the quality of our sleep.
NREM Sleep
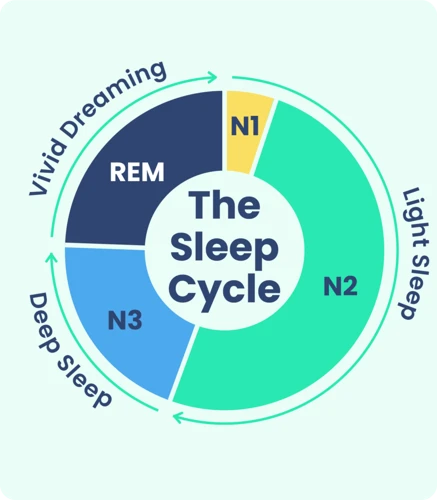
During NREM sleep, also known as non-rapid eye movement sleep, our muscles relax and brain activity slows down. This type of sleep can be further broken down into three stages, with each stage deeper than the previous one.
The three stages of NREM sleep are:
- Stage 1: This stage is considered the transition from wakefulness to sleep. During this stage, we may experience random thoughts or images and our muscles may twitch. This stage generally lasts for only a few minutes.
- Stage 2: During this stage, our body temperature drops and our heart rate slows down. We spend the majority of our sleep time in this stage, which lasts for around 20 minutes.
- Stage 3: This stage is also called slow-wave sleep or deep sleep. Our brain waves slow down significantly, and it becomes difficult to wake us up. During this stage, our body undergoes several restorative processes such as tissue repair and hormone regulation. We also experience our most vivid dreams during this stage.
While NREM sleep may not be associated with the intense dream activity of REM sleep, it is still crucial for our overall health and well-being. Our bodies undergo crucial restorative processes during this stage, such as repairing tissues and cells, strengthening the immune system, and consolidating memories. Getting enough deep sleep is especially important for those with physically demanding jobs or athletes who need to recover from intense physical activity.
Additionally, disruptions to NREM sleep can have negative impacts on our health. Chronic sleep deprivation can increase the risk of developing various health problems, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. It is important to prioritize getting enough NREM sleep in order to live a healthy life.
REM Sleep
During REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, the brain is highly active and the body is deeply relaxed. This stage of sleep is commonly associated with dreaming, which is thought to play a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional processing. Let’s dive deeper into the characteristics of REM sleep in the table below:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid Eye Movement (REM) | During this stage, the eyes move rapidly, and the brainwave patterns are similar to when a person is awake |
| Muscle Paralysis | The body’s voluntary muscles are paralyzed during REM sleep, which is thought to be a protective mechanism to prevent people from acting out their dreams |
| Dreaming | The majority of vivid, story-like dreams occur during REM sleep. These dreams can be associated with past experiences or random thoughts and emotions |
| Memory Consolidation | REM sleep is believed to play a critical role in consolidating memories and processing emotions. It allows the brain to integrate new information with prior experiences and knowledge, leading to better long-term retention of memories |
| Emotional Regulation | REM sleep helps regulate emotions by processing and integrating emotional experiences that occurred during the day. People who frequently experience REM sleep deprivation may be more susceptible to mood swings, anxiety, and depression |
It’s important to note that REM sleep occurs multiple times per night, becoming longer as the night progresses. A lack of REM sleep has been linked to memory impairment, emotional instability, and cognitive impairment. The exact function of REM sleep is still being researched, but it is clear that it is an essential stage of the sleep cycle.
The Role of Dreams in Sleep Stages
During sleep, our brain goes through different stages, each with a unique set of characteristics and functions. Dreams are closely interconnected with these stages, and they can provide insight into our emotional and psychological state. Let’s take a closer look at the role of dreams in different sleep stages:
| Sleep Stage | Description | Role of Dreams |
|---|---|---|
| NREM Stage 1 | Light sleep, drifting in and out of sleep, muscle relaxation, slowed eye movement. | During this stage, we may experience fragmented and fleeting images, sometimes called hypnagogic hallucinations. These hallucinations are usually brief and quickly forgotten. |
| NREM Stage 2 | Deeper sleep, eye movement stops, increased relaxation of muscles, occasional burst of brain activity. | Dreams during this stage tend to be more vivid and longer than those in stage 1. They may involve sensory experiences, emotions, and memories. The content of these dreams is usually more coherent and understandable. |
| NREM Stage 3 | Deep sleep, slower brain waves, physical restoration and repair, difficult to awake. | Dreams during this stage are less common, and less vivid. If present, they tend to involve simple, repetitive thoughts or actions, rather than complex stories or scenarios. |
| REM Sleep | Highly active brain, rapid eye movement, muscle paralysis, increased heart rate and breathing. | Dreams during REM sleep tend to be more emotional, complex, and strange. They often involve vivid sensory experiences, strong emotions, and bizarre scenarios. REM dreams may be connected to memory consolidation and emotional processing. |
Dreams may serve many different functions, such as processing emotions, consolidating memories, or problem-solving. By understanding the different sleep stages and their impact on dreaming, we can gain insight into the workings of our minds and promote better sleep and mental health.
How to Improve Your Sleep and Dreams
After learning about the different stages of sleep and their impact on dreaming, it’s important to understand how to improve your sleep habits and enhance your dream experience. Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for overall well-being and can affect various aspects of life, such as productivity, mood, and creativity. In this section, we will discuss effective strategies for achieving better quality sleep and ways to enhance your dream life. Let’s dive in and explore how you can improve your sleep and dreams.
Healthy Sleep Habits
Developing healthy sleep habits can greatly improve the quality of your sleep and the vividness of your dreams. Here are some tips for creating a healthy sleep environment:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, including on weekends and holidays, can help regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Set aside a regular time before bed to wind down and relax through activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or meditating.
- Avoid stimulating activities before bed: Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol before bed, as well as electronic devices that emit blue light, which can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
- Make your sleeping environment comfortable: Your bedroom should be cool, dark, and quiet, with comfortable bedding and a supportive mattress to promote restful sleep.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity during the day can help you fall asleep more easily and improve the quality of your sleep.
In addition to these healthy sleep habits, it’s important to address any underlying sleep disorders that may be impacting your sleep and dreams. If you are consistently having trouble falling or staying asleep, experience frequent nightmares, or have other concerning symptoms, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about potential diagnosis and treatment options. Taking steps to improve your sleep and dreaming can have many benefits, including improving your overall health, mood, and productivity.
Sleep Disorders and Treatments
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on the quality of sleep and overall health. Here are some common sleep disorders and treatments that can improve the quality of sleep and overall well-being:
- Insomnia: Insomnia is a sleep disorder that makes it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. It can be caused by various factors, such as stress, anxiety, depression or medical conditions. Treatments for insomnia include sleep aids, therapy, and making lifestyle changes such as avoiding caffeine and establishing a regular sleep schedule.
- Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is a condition where a person’s breathing is interrupted during sleep. This can result in loud snoring, choking or gasping during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. Treatment options for sleep apnea may include lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and avoiding alcohol, as well as using mouthpieces, breathing devices, and surgery.
- Restless Leg Syndrome: Restless leg syndrome is a condition characterized by an overwhelming urge to move one’s legs, especially during periods of inactivity or before bedtime. The cause of this condition is not completely understood, but it can be managed with medications and lifestyle changes such as exercise and avoiding caffeine and tobacco.
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that affects the ability to control sleep and wake cycles. It may lead to excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden bouts of sleep. Treatment for narcolepsy typically includes medication and lifestyle changes, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule and taking short naps during the day.
- Restless Sleep: Restless sleep is often caused by anxiety or stress. Treatment options might include stress management strategies, therapy and relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises to calm the mind and body before bedtime.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing persistent and disruptive sleep disorders. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to improve the quality of sleep and overall well-being.
The Benefits of Good Sleep
Getting a good night’s sleep is important for both physical and mental health. Here are some benefits of good sleep:
- Improved mood: Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating our emotions. Without enough sleep, we may feel irritable, impatient, and even depressed.
- Increased cognitive function: Good sleep is essential for optimal cognitive function, including memory consolidation, problem solving, and decision making.
- Reduced stress: Sleep is an important factor in reducing stress levels. Lack of sleep has been shown to increase cortisol, a stress hormone, in our bodies.
- Lower risk of chronic diseases: A lack of sleep has been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. On the other hand, good quality sleep has been shown to improve overall health.
- Improved physical performance: Sleep is essential for physical recovery and restoration. Getting enough sleep has been shown to enhance physical performance, including reaction time, speed, and accuracy.
In short, good sleep is essential for overall wellbeing. By practicing healthy sleep habits and seeking treatment for sleep disorders, we can ensure that we reap the many benefits of a good night’s sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different stages of sleep and their impact on dreaming is crucial for achieving a good night’s rest and overall health. It is important to prioritize healthy sleep habits, such as creating a relaxing sleep environment and establishing a consistent sleep schedule. Additionally, seeking treatment for any sleep disorders can greatly improve one’s quality of life.
While NREM sleep is the stage where the body is able to rest and repair itself, REM sleep is when the brain is most active and dreaming occurs. Dreams can provide insight into our subconscious thoughts and can even assist in problem-solving. However, disturbed sleep due to sleep disorders can lead to negative impacts on both physical and mental health.
By recognizing the importance of sleep stages and developing habits to improve them, individuals can reap the benefits of good sleep, such as increased productivity, better mood, and improved cognitive function. It’s crucial to prioritize sleep and seek help when necessary in order to achieve optimal overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes dreaming?
The exact cause of dreaming is not fully understood, but it is believed to be linked to the different stages of sleep and the brain’s processing of memories and emotions.
Can we dream during NREM sleep?
Yes, we can still dream during NREM sleep, but the dreams tend to be less vivid and memorable than those experienced during REM sleep.
Why do we sometimes remember our dreams and sometimes not?
There are many factors that can affect our ability to remember dreams, such as the stage of sleep we are in, the level of brain activity, and our overall sleep quality. Stress, medication, and alcohol consumption can also impact dream recall.
Is it normal to have nightmares?
Yes, it is normal to have occasional nightmares. However, if nightmares become frequent or start to affect your daily life, it may be a sign of a sleep disorder or underlying mental health issue and you should consult a healthcare professional.
What is lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is the ability to become aware that you are dreaming and to control your actions within the dream. It is a skill that can be developed with practice.
Can certain foods affect our dreams?
Yes, certain foods, particularly those high in tryptophan such as cheese and turkey, can promote vivid dreaming due to their impact on serotonin levels in the brain.
Can sleep deprivation affect our dreams?
Yes, sleep deprivation can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and impact the quality and content of our dreams. It can also lead to an increase in nightmares and sleep paralysis.
What is sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up, often accompanied by vivid and frightening hallucinations. It is a common experience and usually not a cause for concern, but if it becomes frequent or disturbing it may be a sign of a sleep disorder.
Can meditation improve dream recall?
Yes, meditation has been shown to improve dream recall by increasing mindfulness and self-awareness. It can also promote relaxation and better sleep quality.
Do all animals dream?
While it is difficult to study the dreaming patterns of animals, it is believed that many mammals, including dogs, cats, and even rats, experience some form of dreaming during sleep.