Sleep paralysis can be a terrifying experience that leaves one feeling helpless and vulnerable. It is a state of temporary immobility that happens when you are waking up or falling asleep. While the exact causes of sleep paralysis are still not fully understood, it is known to be closely linked with stress and anxiety. Many people who experience sleep paralysis often report feeling anxious or stressed before it occurs. In this article, we will explore how stress and anxiety can trigger sleep paralysis and what you can do to prevent it.
What is Stress?

Stress is a common experience that affects everyone at some point in their lives. It’s a natural response to challenging situations, and it can motivate us to take action and solve problems. However, excessive or prolonged stress can have damaging effects on both mental and physical health. In this section, we will explore different causes and symptoms of stress, as well as its impact on sleep.
Causes of Stress
Stress can be caused by a multitude of factors, both external and internal. These causes may vary from person to person and can differ in intensity and duration. There are several key causes of stress, which are detailed in the table below:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Work-related stress | Excessive workloads, long hours, workplace conflict or harassment, lack of support or resources, and job insecurity can all contribute to work-related stress. |
| Financial stress | Struggling to make ends meet, debt, unemployment or underemployment, and unexpected expenses can all cause financial stress. |
| Personal relationships | Difficult or strained personal relationships, such as marriage problems or conflict with family members, can contribute to stress. |
| Life changes | Major life changes or transitions, such as moving, divorce, or the death of a loved one, can cause significant stress. |
| Health problems | Serious or chronic health problems, as well as caregiving responsibilities for someone with a health issue, can cause stress. |
| Internal stressors | Self-imposed pressure, perfectionism, negative self-talk, and unrealistic expectations can all contribute to stress levels. |
Identifying the sources of stress can be the first step towards addressing and managing it effectively. Being aware of the different causes and how they may impact our lives can help us find healthy coping mechanisms and solutions for reducing stress levels.
Symptoms of Stress
Stress can affect our body and mind in different ways, leading to a number of symptoms that can have a negative impact on our overall well-being. Some common symptoms of stress are:
| Physical Symptoms | Emotional Symptoms |
| Headaches | Anxiety |
| Muscle tension or pain | Frustration |
| Fatigue | Irritability |
| Digestive problems | Sadness |
| Sleep problems | Mood swings |
| Appetite changes | Lack of motivation |
| Increased heart rate | Lack of focus |
| Sweating or feeling hot | Overwhelm |
| Shallow breathing | Low self-esteem |
It’s essential to pay attention to these symptoms because prolonged or severe stress can lead to more serious health issues. In addition to physical and emotional symptoms, stress can also impact our sleep and trigger sleep paralysis.
The Impact of Stress on Sleep Cycles
When experiencing stress, the body releases adrenaline and cortisol hormones, which can lead to disrupted sleep patterns. Below are the potential impacts of stress on sleep cycles:
- Difficulty falling asleep: Stress can cause preoccupation and worrying thoughts, which can make it difficult to fall asleep. This can lead to a vicious cycle where the more you worry, the harder it gets to fall asleep.
- Light sleep: Stress can cause lighter sleep, leading to more frequent awakenings throughout the night. This means you may wake up feeling more tired and less rested.
- REM sleep: Stress can impact Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, the stage of the sleep cycle where most dreaming occurs. This stage is important for processing emotions and memories, so if it’s disrupted it can contribute to increased stress and anxiety.
- Nightmares: Stress can also cause an increase in vivid and disturbing dreams, which can lead to nightmares and further sleep disruption.
It’s important to take steps to manage stress and minimize its impact on sleep. This can include engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation or yoga, creating a bedtime routine, avoiding technology before bed, and making healthy lifestyle choices such as regular exercise and a balanced diet. By doing so, you can improve the quality of your sleep and reduce the chances of experiencing sleeping disorders such as sleep paralysis.
What is Anxiety?

Anxiety is a feeling of unease or worry about something uncertain. It is a common human emotion experienced by people of all ages and backgrounds. Everyone feels anxious at some point in their life, whether it’s related to work, school, relationships or financial issues. Anxiety can manifest in physical and emotional sensations, such as a racing heartbeat, sweating, restlessness, and a sense of impending doom. These sensations can be overwhelming and debilitating, and can impact a person’s everyday life. Understanding the causes, symptoms and connection between anxiety and sleep paralysis is crucial to managing and preventing the condition.
Causes of Anxiety
Anxiety is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. There are many potential causes of anxiety, including:
1. Genetics: Research has suggested that some people may be predisposed to anxiety due to genetic factors. If someone in your family has a history of anxiety or other mental health disorders, you may be more likely to experience anxiety yourself.
2. Trauma: Experiencing a traumatic event, such as abuse, violence, or a natural disaster, can trigger anxiety symptoms. Unresolved past traumas can also contribute to ongoing anxiety.
3. Brain Chemistry: Chemical imbalances in the brain may contribute to the development of anxiety. Specifically, imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine have been linked to anxiety disorders.
4. Stress: High levels of stress or chronic stress can contribute to the development of anxiety. When the body is under stress, it releases cortisol, which can trigger feelings of anxiety and nervousness.
5. Substance Use: Using drugs or alcohol can cause or exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Substance use disorders and anxiety often co-occur and can create a vicious cycle of dependence.
6. Chronic Medical Conditions: Living with a chronic illness or health condition can be stressful and trigger anxiety. This is especially true if the condition is painful, debilitating, or potentially life-threatening.
The causes of anxiety are multifaceted and can be different for each individual. Both genetic predisposition and environmental factors seem to play a role, and identifying the underlying causes of anxiety is an essential step in finding effective treatment and management strategies.
Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety can manifest itself in a variety of symptoms which can be physical, emotional, or psychological in nature. Some common physical symptoms of anxiety include fatigue, headaches, muscle tension, and restlessness. These symptoms are often accompanied by emotional and psychological symptoms such as feelings of fear, worry, apprehension, and irritability.
People experiencing anxiety may also exhibit behavioral symptoms such as avoidance of certain situations, compulsive behaviors, and restlessness. Additionally, anxiety can also lead to cognitive symptoms such as difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and negative thoughts.
Anxiety can have a significant impact on an individual’s physical health, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, digestive problems, difficulty sleeping or insomnia, and weakened immune system. These symptoms, if left untreated, can worsen over time and lead to a more severe form of anxiety disorder, such as panic or social anxiety disorder.
It is important to recognize and seek treatment for anxiety symptoms as it can significantly impair an individual’s daily functioning and overall quality of life.
The Connection between Anxiety and Sleep Paralysis
It is observed that anxiety can increase the chances of experiencing sleep paralysis. This is because anxiety can disrupt sleep patterns by causing the brain to stay in a state of hyperarousal, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep.
During sleep, the body goes through different stages, including Rapid Eye Movement (REM) and non-REM sleep. REM sleep is the stage of sleep where dreaming occurs, and the body is mostly paralyzed to prevent physical movement during dreams. It is during REM sleep that sleep paralysis occurs, as the body is still paralyzed, but the mind is conscious.
Anxiety and stress can cause disruptions in the sleep cycle, which can lead to more frequent occurrences of sleep paralysis. When the body is in a constant state of stress, it is more difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. This can lead to sleep deprivation, which can make sleep paralysis more likely to occur.
Additionally, anxiety can cause the brain to be more alert during sleep, making it easier for someone to wake up during REM sleep and experience sleep paralysis. Anxiety can also cause hyperventilation and changes in heart rate, which can increase the intensity of sleep paralysis.
It is important to address anxiety and stress to reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. By managing anxiety and stress levels, individuals can improve their sleep quality and reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
What is Sleep Paralysis?
Have you ever found yourself fully conscious, yet unable to move or speak, almost as if you were frozen in time? This perplexing phenomenon is known as sleep paralysis. It can be a frightening experience and may leave individuals feeling confused and helpless. Sleep paralysis is not an uncommon occurrence, with many people experiencing it at some point in their lives. In this section, we will delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, and relationship between sleep paralysis and mental health.
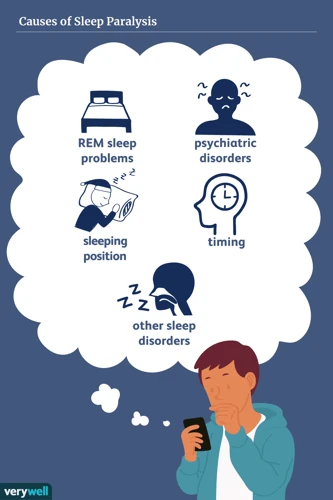
Causes of Sleep Paralysis
There is no known singular cause of sleep paralysis, but rather a multitude of factors that can contribute to the experience. Here are a few key causes worth considering:
- Disruptions to the sleep cycle: Sleep paralysis is often associated with a disruption or irregularity in the sleep cycle. This can include things like staying up late, shift work, or hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness during the day).
- Stress and anxiety: As mentioned earlier, stress and anxiety can play a significant role in sleep paralysis. These emotions can trigger an increase in cortisol levels, making it difficult for the body to relax and creating a physical response such as sleep paralysis.
- Genetics: Although it is unclear what genetic factors may cause sleep paralysis, studies have shown that it can run in families, suggesting that there may be a link.
- Sleep disorders: Certain sleep disorders like narcolepsy and sleep apnea are often associated with episodes of sleep paralysis.
- Substance use: Using certain substances like alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine before bed can disrupt the sleep cycle and increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
While these factors can contribute to sleep paralysis, it is important to note that not everyone who experiences them will necessarily experience the phenomenon. It is also possible to experience sleep paralysis without any identifiable cause, making it a complex and often perplexing experience.
Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a condition that affects one’s ability to move or speak when transitioning between sleep and wakefulness. It is a type of parasomnia, or unwanted behavior during sleep. Here are some symptoms that may indicate you are experiencing sleep paralysis:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Feeling of pressure on the chest | The individual may feel a sensation of weight on their chest or an inability to breathe deeply. |
| Seeing or hearing things that aren’t there | Individuals may experience vivid hallucinations, such as seeing shadowy figures or hearing unexplained sounds, as if they were present in the room. |
| Paralysis | As the name suggests, individuals with sleep paralysis are unable to move or speak. While they may be aware of their surroundings, they cannot respond or shift position. |
| Feeling of fear or panic | Because the experience can be so disorienting, individuals may feel extreme fear and panic during episodes of sleep paralysis. This reaction can exacerbate or prolong the symptoms. |
| Difficulty sleeping | If episodes of sleep paralysis are frequent, individuals may develop anxiety about sleeping, leading to insomnia or other sleep disorders. |
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences sleep paralysis will have every one of these symptoms, and additional symptoms may be present. Additionally, some individuals may have only one episode of sleep paralysis, while others may experience it on a regular basis. If you are experiencing symptoms of sleep paralysis, it is important to speak with a doctor or mental health professional.
The Relationship between Sleep Paralysis and Mental Health
Sleep paralysis is a condition that is often associated with mental health concerns, particularly anxiety and depression. The experience of waking up unable to move or speak can be terrifying and can trigger intense feelings of fear and anxiety. This can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health and wellbeing, particularly if it happens regularly.
Studies have found a strong relationship between sleep paralysis and mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression. In fact, individuals who experience frequent sleep paralysis are more likely to report symptoms of anxiety and depression than those who do not.
There are also suggestions that sleep paralysis may be more common in individuals with certain mental health conditions. For example, research has found that individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may be more likely to experience sleep paralysis.
Experts believe that there may be a cyclical relationship between sleep paralysis and mental health. That is, sleep paralysis may be a symptom of an existing mental health condition, but it can also exacerbate and prolong symptoms of these conditions. This may be because the fear and anxiety associated with sleep paralysis can lead to a vicious cycle of poor sleep and heightened mental health symptoms.
The following table summarises the relationship between sleep paralysis and mental health:
Sleep Paralysis and Mental Health
| Relationship | Explanation |
|————–|————-|
| Strong | There is a strong relationship between sleep paralysis and mental health conditions, particularly anxiety and depression. |
| Cyclical | There is a cyclical relationship between sleep paralysis and mental health, where sleep paralysis can both be a symptom of and exacerbate existing mental health conditions. |
| Comorbidity | Sleep paralysis is more common in individuals with certain mental health conditions, such as PTSD. |
| Impact | Sleep paralysis can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health and wellbeing, particularly if it happens regularly. |
It is clear that the relationship between sleep paralysis and mental health is complex. However, it is important for individuals who experience sleep paralysis to be aware of this relationship and to seek appropriate support for any underlying mental health conditions.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention
Now that we have explored the interconnections between stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis, it is important to understand how to diagnose, treat, and prevent these conditions. Seeking professional help and addressing the underlying causes of stress and anxiety can greatly improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. Let’s dive deeper into the steps you can take to manage these conditions and improve your overall well-being.
Diagnosing Stress, Anxiety, and Sleep Paralysis
Diagnosing stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis can be a complex process that typically involve a combination of medical examinations, psychological evaluations, and sleep studies. Effective diagnosis is crucial to ensuring appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Medical Examinations: In order to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be causing symptoms of stress, anxiety, or sleep paralysis, a healthcare provider may conduct a physical examination, which may include blood tests, thyroid function tests, and electroencephalogram (EEG) to test for any neurological conditions.
Psychological Evaluations: A licensed mental health professional may evaluate a patient’s mental health by conducting interviews or administering questionnaires to assess symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Sleep Studies: Sleep studies, such as a polysomnography, may be used to diagnose sleep disorders like sleep apnea, which may contribute to the development of sleep paralysis.
It is essential to communicate openly and honestly with healthcare providers about symptoms, medical history, and any medications or substances currently in use to facilitate an accurate diagnosis. A proper diagnosis can help identify the underlying cause of the symptoms and allow for effective treatment and management strategies to be implemented.
Treatment and Management of Stress, Anxiety, and Sleep Paralysis
One of the main goals of treating stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis is to manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of their occurrence. There are various treatment and management strategies available, including medication, therapy, lifestyle changes, and self-care practices.
Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage the symptoms of stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, and sleep aids may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication.
Therapy: Therapy can be very effective for managing stress and anxiety, as well as the psychological impact of sleep paralysis. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common treatment modality for stress and anxiety, and it is often used to help individuals change negative patterns of thinking and behavior. Additionally, therapy can help individuals process and cope with the fear and anxiety associated with sleep paralysis.
Lifestyle changes: Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis. For instance, practicing regular exercise, sticking to a healthy diet, and avoiding alcohol and caffeine can all help reduce symptoms. Additionally, developing a regular sleep routine and creating a relaxing nighttime routine can help improve the quality of sleep and reduce the likelihood of sleep paralysis.
Self-care practices: Practicing self-care is an essential part of managing stress and anxiety. Engaging in activities such as meditation, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques can help alleviate symptoms and promote a sense of calm. Additionally, taking breaks regularly, engaging in hobbies, and setting realistic goals can all help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
It’s important to note that treatment and management strategies may vary from person to person based on individual needs and preferences. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis.
Prevention Strategies for Stress, Anxiety, and Sleep Paralysis
Prevention strategies for stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis can help individuals reduce their risk of experiencing these conditions. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
| Regular exercise | Exercise is one of the best ways to reduce stress and anxiety. It helps release endorphins that improve mood and promote better sleep. Regular exercise can help individuals manage stress and reduce the risk of sleep paralysis. |
| Healthy Diet | Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help individuals maintain their physical and mental health. Consuming too much caffeine or alcohol can worsen anxiety and sleep problems, so it’s important to limit their intake. |
| Good Sleep Habits | Maintaining regular sleep patterns and making sleep a priority can help reduce the risk of sleep paralysis. It’s essential to create a relaxing bedtime routine and avoid activities that interfere with sleep, such as using electronic devices before bed. |
| Stress Management Techniques | Learning relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help individuals manage stress effectively. These techniques can improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of sleep paralysis. |
| Talk to a Professional | If stress or anxiety is interfering with daily life, talking to a mental health professional can provide valuable support and guidance. They can help individuals develop coping strategies, reduce stress, and improve mental health. |
By implementing these prevention strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis. However, if someone experiences symptoms of these conditions, it’s important to seek professional help to manage and treat the condition effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis have a close and complex relationship. The impact of stress and anxiety on the human body and mind can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, which in turn can trigger episodes of sleep paralysis. Sleep paralysis can be a distressing experience that can negatively impact mental health.
However, it is important to note that these conditions can be managed and treated. Seeking professional help from a healthcare provider can help diagnose and develop a treatment plan that suits the individual’s needs. Additionally, individuals can practice prevention strategies such as stress-reducing techniques, healthy sleep habits, and seeking social support.
Overall, it is essential to prioritize mental health and seek help when needed to prevent and manage stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis. By doing so, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of these conditions on their well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between stress and sleep paralysis?
Stress can trigger sleep paralysis as it disturbs the body’s sleep cycles and can lead to vivid and frightening dreams which can cause sleep paralysis episodes.
What is the impact of stress on our sleep?
Stress can lead to poor sleep quality, difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep, and can cause nightmares and night terrors.
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a feeling of unease or worry, often about future events or uncertain outcomes. It can cause physical and emotional symptoms and affect our daily lives.
What is the connection between anxiety and sleep paralysis?
Anxiety can trigger sleep paralysis as it increases the likelihood of vivid and frightening dreams, which can cause sleep paralysis episodes.
What is sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a condition where a person is temporarily unable to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up. It can be accompanied by vivid hallucinations and a feeling of pressure on the chest.
What causes sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis can be caused by disrupted sleep cycles, stress, anxiety, and certain medications. It can also be a symptom of narcolepsy or other sleep disorders.
What are the symptoms of sleep paralysis?
The main symptoms of sleep paralysis are being unable to move or speak, accompanied by vivid hallucinations and a feeling of pressure on the chest. It can also cause anxiety and a rapid heart rate.
How is stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis diagnosed?
A doctor will typically ask about your symptoms and medical history, and may conduct a physical examination, a sleep study, or refer you to a specialist for further testing.
What are some prevention strategies for stress, anxiety, and sleep paralysis?
Some prevention strategies include practicing good sleep hygiene, managing stress levels through relaxation techniques or therapy, and avoiding alcohol or drugs that can disrupt sleep cycles.
What is the treatment for sleep paralysis?
Treatment options for sleep paralysis may include adjusting sleep habits, medications to regulate sleep cycles, and therapy or other mental health treatments to reduce anxiety and stress levels.








