As we rest our weary minds each night, the world of dreams unfolds before us, offering glimpses into our deepest desires, fears and aspirations. Despite the fact that everyone dreams, many remain perplexed by this elusive realm of the mind. However, the link between dreams and sleep is well-documented, with scientific research having shed light on the importance of Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep and the correlation it has with dreaming. By unlocking the mysteries behind this connection, we gain insight into a world of wonder and possibility that exists just beyond the veil of our consciousness.
Understanding Sleep
Sleep is a fascinating and complex phenomenon of the body and mind, leaving humans and animals alike perplexed with its mysteries. We spend approximately one-third of our lives asleep, yet there is still so much we do not understand about this essential process. Through the years, scientists and researchers have been tirelessly studying and unraveling the intricacies of sleep, leading to a better understanding of the stages of sleep, including REM sleep, and how it affects our physical and mental health. Let us delve deeper into the world of sleep and uncover the link between dreams and REM sleep.
Stages of Sleep
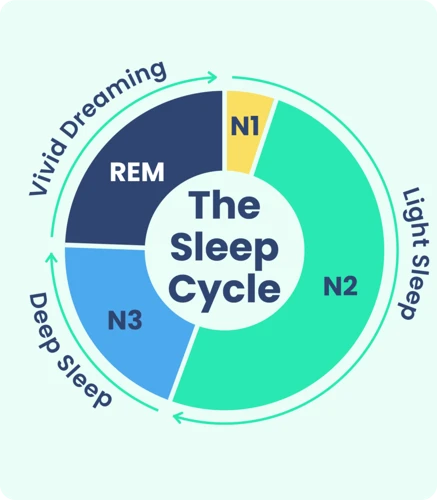
During sleep, the body goes through several stages, each of which has a different level of brain activity and physical responses. These stages are divided into two main categories, REM sleep and non-REM sleep.
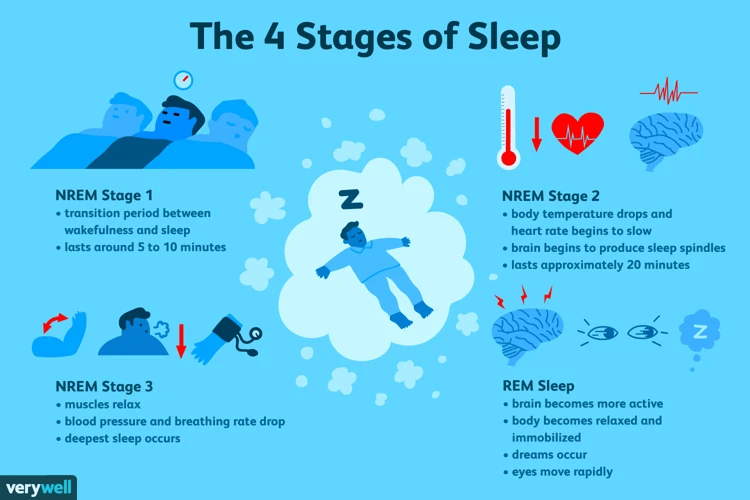
Non-REM sleep is composed of three distinct stages. The first stage is a period of light sleep, during which the body begins to relax and slow down. This stage usually lasts for only a few minutes. The second stage is a period of deeper sleep, during which the body’s temperature, heart rate, and breathing slow down even further. This stage usually lasts for around 20-30 minutes. Finally, the third stage is the deepest stage of sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS). It is during this stage that the body undergoes the most restorative processes, such as muscle repair and growth hormone release.
REM sleep, on the other hand, is characterized by rapid eye movement and vivid dreaming. This stage usually occurs about 90 minutes after falling asleep and is repeated in cycles throughout the night. During REM sleep, the brain is highly active, yet the body is completely relaxed, which is why it is also known as paradoxical sleep. This is the stage where most dreams occur and when the brain processes and consolidates memories.
It’s important to note that these stages of sleep do not occur in a linear fashion throughout the night. Instead, the body goes through several cycles of non-REM and REM sleep, each lasting approximately 90 minutes. As the night progresses, the amount of time spent in REM sleep increases, while the amount of time spent in non-REM sleep decreases. This is why most deep sleep occurs during the first half of the night, while the latter half is characterized by more vivid and memorable dreams.
REM Sleep Definition
REM sleep, also known as Rapid Eye Movement sleep, is one of the stages of sleep that occur throughout the night. During REM sleep, our brains are highly active, and this is when we are most likely to experience vivid dreams. Here are some key features of REM sleep that you should be aware of:
- Rapid Eye Movement: As the name suggests, during REM sleep, our eyes move rapidly from side to side. This is because our brains are processing the visual information generated by our dreams.
- Muscle Paralysis: One of the most interesting things about REM sleep is that our bodies are almost completely paralyzed during this stage. This is believed to be a protective measure that prevents us from acting out our dreams in real life.
- Increased Brain Activity: During REM sleep, our brains are highly active and our neural activity is similar to when we are awake. This is why we might wake up feeling like we’ve been thinking all night.
- Irregular Breathing: Our breathing patterns during REM sleep are often irregular and can even vary from shallow to deep breaths. This can sometimes cause people to snore or gasp for air while they are sleeping.
While you might think of sleep as a quiet, peaceful state, REM sleep is actually a fascinating and dynamic stage that is characterized by heightened brain activity, vivid dreams, and temporary muscle paralysis.
REM vs. Non-REM Sleep
In order to understand the link between dreams and sleep, it’s important to first understand the different stages of sleep. There are two main categories of sleep: REM (rapid eye movement) and non-REM sleep.
Non-REM sleep is further broken down into three stages:
- Stage 1: This is the transitional stage between being awake and asleep. During this stage, you may experience muscle twitches or sudden jerks, and you may still be somewhat aware of your surroundings.
- Stage 2: This is a deeper stage of sleep, during which your heart rate and breathing slow down and your body temperature drops. Your brain waves also slow down, and you become less aware of your surroundings.
- Stage 3: This is the deepest stage of non-REM sleep, also known as slow wave sleep. Your brain waves are at their slowest during this stage, and it’s difficult to rouse someone from this stage of sleep.
REM sleep is the stage of sleep during which most dreaming occurs. During REM sleep, your brain waves become more active, and your eyes move back and forth rapidly. This is also the stage of sleep when your body becomes very relaxed and muscles become temporarily paralyzed, preventing you from acting out your dreams.
While non-REM sleep is important for physical restoration and repair, REM sleep is believed to be important for cognitive function and emotional regulation. A healthy sleep cycle involves cycling through both REM and non-REM sleep stages throughout the night.
Understanding the differences between REM and non-REM sleep is important when it comes to interpreting and analyzing dreams, as different stages of sleep may be associated with different types of dreams or dream themes.
Dreaming During REM Sleep
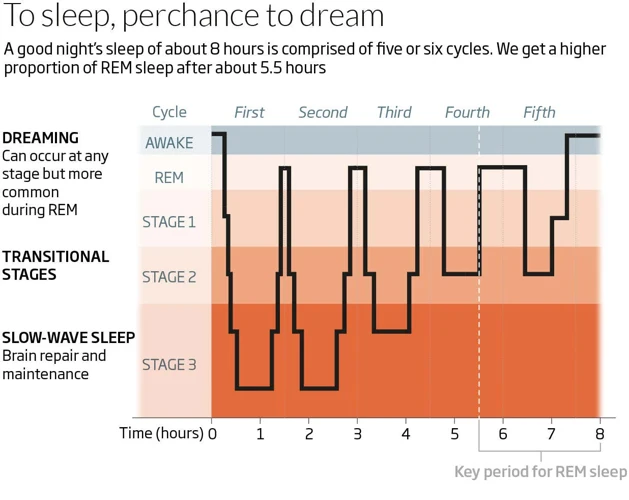
As we lay in bed each night, we often find ourselves drifting into a world of dreams. But what exactly is the connection between our dreams and the state of sleep we are in? It turns out that the answer lies in a specific stage of sleep known as REM sleep. During this stage, our brains are highly active and it’s when many of our most vivid dreams occur. In this section, we’ll explore the fascinating link between dreaming and REM sleep, and delve into some of the science and theories behind the phenomenon.
Why Do We Dream?
Have you ever woken up from a dream and wondered, “why do we dream?” The exact purpose of dreaming is still unclear to scientists, but there are several theories that attempt to explain this enigmatic phenomenon. Here are some possible explanations:
- Memory consolidation: One theory is that dreaming helps consolidate our memories from the day. During REM sleep, the brain selectively strengthens certain memories and discards unnecessary ones. Dreams may be a byproduct of this process, as the brain tries to make sense of what memories to keep and what to let go.
- Emotional regulation: Another theory suggests that dreaming is a way for the brain to process and regulate our emotions. Dreams provide a safe space for us to explore and confront our deepest fears, desires, and conflicts. By doing so, we can better manage our emotional responses in waking life.
- Creative thinking: Dreams may also help facilitate creative thinking and problem-solving. When we dream, our brains are free to make new connections and associations between ideas that may not be possible while awake. This can lead to innovative solutions and ideas that we may not have come up with otherwise.
- Evolutionary adaptation: Some researchers argue that dreaming has an evolutionary advantage, such as practicing threat recognition or improving social cognition. By dreaming about potential dangers or social scenarios, our brains can better prepare us for those situations in waking life.
These are just a few of the many hypotheses that attempt to explain the purpose of dreams. Regardless of the exact reason, one thing is clear: dreams are a fundamental aspect of the human experience, and they continue to intrigue and fascinate us.
Brain Activity During REM Sleep
During Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, the brain is highly active, and several areas in the brain show unique patterns of activity. Here are some interesting facts to enlighten you on the brain activity that occurs during REM sleep.
The Cerebral Cortex:
During REM sleep, the cerebral cortex, responsible for cognitive, sensory, and perceptual processes, is active. The brainstem sends signals to the cerebral cortex, causing it to become highly active, leading to the vivid and often bizarre dreams that occur during this stage.
The Limbic System:
The limbic system, responsible for regulating emotions, is also highly active during REM sleep. This activity is crucial in understanding why dreams are frequently associated with the emotional state of the individual. Studies have confirmed that, during this stage, the amygdala, a structure in the limbic system associated with emotion, is more active than during non-REM stages.
The Thalamus:
The thalamus, responsible for regulating sensory input, relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex responsible for perception. During the REM stage, the thalamus modulates gating sensory information, allowing the brain to create an imaginative world perceived through all sensory modalities.
Other Areas:
Other areas of the brain, including the hippocampus associated with memory formation, and the basal ganglia responsible for motor control, are also active during REM sleep.
Understanding the brain activity during REM sleep is essential in unlocking the mysteries of dreaming. The unique pattern of brain activity during this stage explains why dreams are often vivid, imaginative, and loaded with emotion. Additionally, scientists believe that decoding these patterns may lead to better understanding and treatment of sleep and neuropsychiatric disorders.
The Science of Dreams
Dreams have fascinated scientists, psychologists, and philosophers for centuries. Although we still don’t fully understand the purpose and mechanism of dreaming, there have been numerous theories and studies conducted to shed light on this mysterious phenomenon.
Some of the key findings from the science of dreams include:
- Activation-Synthesis Hypothesis: proposed by psychiatrist J. Allan Hobson and Robert McCarley, this hypothesis suggests that dreams are essentially the result of random electrical activity that occurs in the brain during REM sleep. According to this theory, the brain tries to make sense of this activity by constructing a narrative or storyline, which becomes the dream.
- Threat Simulation Theory: this theory suggests that dreaming is essentially a way for our brains to prepare for potential threats in our waking lives. By simulating different scenarios in our dreams, we are able to rehearse and improve our responses to threatening situations.
- Memory Consolidation Theory: studies have shown that sleep plays a crucial role in consolidating memories and processing new information. During REM sleep, the brain may be consolidating and integrating new memories into existing knowledge.
Despite these and other theories, the exact purpose and mechanism of dreaming remain somewhat of a mystery. It’s clear, however, that dreams can have a significant impact on our emotions, behaviors, and overall well-being. By better understanding the science of dreams, we may be able to unlock some of the secrets of this intriguing and often perplexing phenomenon.
Common Dream Themes and Interpretations

Dreams are mysterious and often confusing experiences that can leave us wondering about their meaning or significance. Many people have similar dream experiences, and these common dream themes have given insight into possible interpretations. Nightmares are a common dream theme, where the dreamer experiences intense fear or anxiety. They are often linked to a traumatic experience or unresolved emotional issues. Similarly, flying dreams are common and can symbolize a sense of freedom or control, but they can also indicate a desire to escape from something in real life.
Another common dream theme is falling, which can be interpreted as a feeling of instability or loss of control. Dreams about teeth falling out are also common, and they may be related to an insecurity in the dreamer’s appearance or a feeling of powerlessness. Being chased in a dream can represent feeling threatened or pursued in real life. Nudity dreams, where the dreamer is naked or exposed, can indicate vulnerability or shame.
On the other hand, sex dreams can be interpreted in many ways, ranging from a desire for emotional intimacy to the fulfillment of physical desires. Death dreams are also common, and they can represent a significant life change or a fear of the unknown. Dreams about animals, such as snakes or spiders, can be interpreted as a fear of something unknown or a representation of aspects of oneself that are not fully understood.
It’s important to remember that dream interpretation is highly individualized and should be approached with an open mind. Dreams can have multiple interpretations and can be influenced by personal experiences and cultural beliefs. Seeking the guidance of a therapist or dream analyst can help provide a deeper understanding of recurring dream themes and their significance.
The Significance of Dreams
The significance of dreams has been a topic of fascination and debate for centuries. While some consider dreams to be mere random brain activity, others believe that dreams hold a deeper meaning and can provide insight into our subconscious thoughts and desires.
In psychoanalysis, dreams are seen as a method of accessing the unconscious mind. According to Sigmund Freud, dreams are a means of wish-fulfillment, allowing individuals to act out repressed desires and emotions. Other psychologists, such as Carl Jung, viewed dreams as a way to access the collective unconscious and connect with universal symbols and archetypes.
Dreams can also have significant cultural and personal significance. In many indigenous cultures, dreams are considered a way to communicate with ancestors or receive guidance from the spirit world. In modern Western culture, dreams are often seen as a reflection of one’s current emotional state or a manifestation of anxiety.
One of the most intriguing aspects of dreams is their ability to provide insight into our subconscious thoughts and feelings. Dreams can sometimes reveal hidden fears, desires, and conflicts that we may not be aware of in our waking life. Analyzing and interpreting our dreams can help us gain a better understanding of our true selves and our deepest motivations.
Additionally, some researchers believe that dreams play a vital role in memory consolidation and learning. During sleep, the brain processes and consolidates memories from the day, helping to strengthen and solidify them for long-term storage.
The significance of dreams remains a subject of much debate and study in the field of psychology. While some see dreams as purely random and meaningless, others believe that they hold a deeper symbolic and psychological meaning. Regardless, exploring and analyzing our dreams can offer valuable insights into our subconscious thoughts and emotions, and ultimately lead to greater personal growth and self-awareness.
Lucid Dreaming
Have you ever been in a dream and suddenly realized that you’re dreaming? You’re not alone. Many people have experienced this phenomenon known as lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming is a state where the dreamer is aware that they are in a dream and can even control their actions within the dream. This concept has fascinated people for centuries, but it has only been in recent years that scientists have started to study it. What causes lucid dreaming? Can we learn to control our dreams and improve our mental health? Let’s explore the mystery of lucid dreaming.
Definition and Studies on Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming is a state where the person is aware that they are dreaming, giving them the ability to control their dreams. In a study conducted in 1980, lucid dreaming was coined by the Dutch psychiatrist and writer Frederik van Eeden. He defined it as “the phenomenon in which an individual has a dream, and is aware that they are dreaming, while the dream is still in progress.” Since then, many researchers have studied this phenomenon.
One study found that 51% of participants had experienced at least one lucid dream in their lifetime. Another study found that people who frequently have lucid dreams tend to have better problem-solving skills and are more creative. Lucid dreaming has also been used in therapy as a tool for treating nightmares, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Lucid dreaming occurs during the REM stage of sleep, and certain techniques can increase the likelihood of experiencing it. These include keeping a dream journal, performing reality checks throughout the day, and using mnemonic induction of lucid dreams (MILD) before bed.
Although lucid dreaming can be a fun and useful practice, some individuals may experience negative effects such as sleep disturbances or confusion between dreams and reality. It is important to approach lucid dreaming with caution and to stop if any negative effects occur.
Controlling and Remembering Your Dreams
Controlling and Remembering Your Dreams is an essential part of lucid dreaming. Lucid dreaming is an experience where the sleeper is aware that they are dreaming and can control the dream’s content. Here are some techniques for improving your ability to control and remember your dreams:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Mnemonic Induction of Lucid Dreams (MILD) | This technique involves setting an intention to remember your dreams and become lucid. Before going to bed, repeat the phrase “I will remember my dreams” and visualize yourself becoming lucid in your dream. When you wake up, focus on recalling your dreams and write them down immediately. |
| Reality Testing | Throughout the day, perform reality tests to determine whether you are awake or dreaming. This habit can carry over into your dreams, making it more likely that you will realize when you are dreaming. Tests might include looking at a clock twice to see if the time changes or trying to push your finger through your palm. |
| Wake-Back-to-Bed (WBTB) | Set an alarm for roughly four to five hours after you fall asleep. When the alarm goes off, get up and stay awake for 30 to 60 minutes. During this time, engage in a relaxing activity and consider your intention to remember your dreams and become lucid. Return to bed and focus on your intention as you fall asleep. |
| Dream Journaling | Keep a journal near your bed and write down your dreams immediately upon waking up. Refrain from analyzing or interpreting your dreams until you have a significant record of dream content. The more you practice dream journaling, the better your dream recall will become. |
By combining these techniques and practicing them consistently, you can improve your ability to control and remember your dreams. Once you can control your dreams, the possibilities are endless.
Causes of Dreaming and REM Sleep Disturbances
As fascinating as dreams may be, some individuals experience disturbances in their REM sleep and struggle with frequent nightmares or other unpleasant dream-related events. These disturbances can be caused by a variety of factors, leaving individuals feeling exhausted and drained the following day. It is important to understand the potential causes of these disturbances, as well as how they can be managed and treated to help individuals get the restful and restorative sleep they need. Let’s delve into this topic further and explore the potential causes of REM sleep disturbances and their impact on our overall health and well-being.
Sleep Disorders Linked to REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
When it comes to sleep disorders, REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a condition that stands out. This type of disorder is characterized by the loss of muscle atonia during REM sleep, which leads to physical movements and vocalizations during sleep. RBD most commonly affects men over the age of 50, but can occur in women and younger individuals as well.
According to research, RBD is linked to a higher risk of developing neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and dementia. In fact, studies show that up to 80% of individuals with RBD will develop Parkinson’s disease or a related disorder later in life.
Other sleep disorders have also been linked to RBD, including obstructive sleep apnea and narcolepsy. It’s important for individuals suffering from RBD or any sleep disorder to seek medical attention and treatment to address their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Treatment options for RBD may include medications to improve sleep quality and reduce movement during sleep, as well as lifestyle changes such as avoiding alcohol and caffeine before bedtime. For those with associated neurological disorders, treating the underlying condition may also help manage symptoms of RBD.
It’s important to address sleep disorders as they can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. Seeking help from a healthcare professional and following a treatment plan can make all the difference in improving sleep quality and reducing the risk of developing related disorders.
| Sleep Disorders | Linked to REM Sleep Behavior Disorder |
|---|---|
| Parkinson’s disease | Yes |
| Dementia | Yes |
| Obstructive Sleep Apnea | Yes |
| Narcolepsy | Yes |
Managing and Treating Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders that affect REM sleep can be debilitating and have a lasting effect on an individual’s overall health and well-being. It is essential to manage and treat these disorders with care and caution to ensure quality sleep is achieved. Here are some ways to manage and treat sleep disorders:
1. Medications: Certain medications like melatonin, clonazepam, and other sedative-hypnotic drugs can help regulate sleep.
2. Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle changes like avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and reducing stress can improve sleep quality.
3. Therapy: Therapy options like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and relaxation techniques can help alleviate stress and anxiety that may cause sleep disturbances.
4. Sleep Environment: Creating a conducive sleep environment with a comfortable bed, cool temperature, and minimal noise and light can aid in uninterrupted sleep.
5. Medical Procedures: In rare cases, medical procedures like Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, which helps regulate breathing during sleep, may be necessary.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for sleep disorders affecting REM sleep. With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can experience improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
Interpretation and Analysis
One of the most intriguing aspects of dreaming is the meanings and messages behind them. Dreams are often enigmatic and can leave us feeling uncertain or confused. Understanding and interpreting our dreams can provide us with important insights into our subconscious mind and emotional well-being. In this section, we will explore the importance of interpreting and analyzing our dreams, including the benefits of keeping a dream journal and utilizing tools for understanding dream symbols and themes. So, let’s dive deeper into the mysteries of our dreams and learn how to decode their hidden meanings.
Benefits of Recording Your Dreams
Recording your dreams can have a number of benefits – both for your mental wellbeing and personal growth. Here are a few reasons why keeping a dream journal can be a valuable practice:
- Improve Dream Recall: Recording your dreams regularly can actually help you remember them better. As you get in the habit of writing down your dreams, you may find that you start to remember more of them.
- Discover Patterns and Themes: By looking back over your recorded dreams, you may begin to see patterns or recurring themes. This can help you gain insight into your subconscious mind and identify areas of your life that might need attention or exploration.
- Process Emotions and Trauma: Dreams can often be a way for your mind to process strong emotions or traumatic experiences. Recording your dreams can help you make sense of these experiences and work through any lingering emotions that may be affecting your waking life.
- Inspiration and Creativity: Dreams can be a source of inspiration for artists, writers, and other creatives. Recording your dreams can help you capture these ideas and use them in your creative work.
- Increased Self-Awareness: By analyzing your dreams and uncovering their underlying meanings, you can gain a deeper understanding of yourself and your motivations. This can help you make more conscious choices in your waking life.
By making a habit of recording your dreams and reflecting on their deeper meanings, you can gain a greater understanding of your mind and your life. So grab a notebook and pen, and start writing down your dreams today!
Tools for Analyzing and Understanding Dreams
Analyzing and interpreting dreams is a complex task that requires the use of various tools and techniques. Here are some examples of tools that can help you understand and make sense of your dreams:
- Dream journal: Keeping a dream journal can help you remember your dreams more vividly and analyze them more effectively. Make sure to write down every detail you remember, including people, places, emotions, and any recurring themes.
- Dream dictionaries: Dream dictionaries can provide insights into the symbolism and meaning of different dream elements. However, it’s important to remember that the interpretation of dreams is highly personal and subjective, so it’s best to use dream dictionaries as a starting point rather than a definitive guide.
- Talking to a therapist: A trained therapist can help you explore the deeper meanings and themes of your dreams, and provide guidance on how to integrate these insights into your waking life.
- Online dream analysis tools: There are many online tools and resources that can help you analyze and interpret your dreams, such as dream analysis websites, forums, and chat rooms. However, it’s important to be cautious when using these tools, as they may not always provide accurate or reliable information.
Using one or more of these tools can help you gain a deeper understanding of your dreams and unlock their hidden meanings. However, it’s important to recognize that the interpretation of dreams is a highly personal and subjective process, and ultimately, only you can truly understand the significance of your own dreams.
Conclusion
After delving into the world of dreaming and REM sleep, it’s clear that there is still much to be understood and discovered. However, the link between these two phenomena is undeniable. As we sleep, our brains go through different stages of sleep, with REM sleep being the most prominent stage for dreaming.
The importance of dreaming and its purpose is a topic of ongoing research and debate. It’s been suggested that dreaming facilitates memory processing, emotional regulation, problem-solving, and creativity. Dreams can also provide insight into our subconscious thoughts, feelings, and fears.
Lucid dreaming, the ability to control and remember dreams, has fascinated people for years. While some research suggests that it can be beneficial for improving skills and reducing nightmares, more studies are needed to fully understand it.
Sleep disorders such as REM Sleep Behavior Disorder can cause disruptions in dreaming and lead to physical harm. It’s essential to manage and treat these conditions to ensure a good night’s sleep.
Recording and analyzing dreams can provide valuable insight into our psyche and can aid in personal growth and self-discovery. Tools such as dream journals and dream analysis websites can help with this process.
In conclusion, the link between dreams and REM sleep is a fascinating and complex topic that requires more research and investigation. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of dreaming, we can gain a better understanding of our minds and ourselves.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens during REM sleep?
During REM sleep, brain activity increases, and we experience vivid dreams while our eyes move rapidly behind our closed eyelids.
What is the significance of dreams?
Dreams can provide insight into our emotions and experiences and can even help us problem-solve and process memories.
What is lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is when someone becomes aware that they are dreaming and can often control their dream experiences.
What causes nightmares?
Nightmares can be caused by stress, anxiety, traumatic experiences, medications, and even sleep disorders like sleep apnea.
How can I improve my dream recall?
Keeping a dream journal and consistently writing down your dreams upon waking can help improve dream recall significantly.
What is the relationship between sleep disorders and REM sleep?
Many sleep disorders, such as REM sleep behavior disorder, are linked to disturbances during REM sleep.
What is sleep hygiene?
Sleep hygiene refers to healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a sleep-conducive environment.
What is the best way to manage sleep disturbances?
Consulting with a healthcare professional and following recommended treatment plans can often be the most effective way to manage sleep disturbances.
How can analyzing dreams benefit my mental health?
Examining the patterns and themes in your dreams can provide insight into your thoughts, emotions, and experiences and can improve self-awareness and mental health.
What is the scientific explanation for why we dream?
There is no one definitive answer, but theories suggest that dreaming may help with memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and problem-solving.








