As we all know, sleep is an essential part of our lives. It helps us regenerate and prepares us for the upcoming day. However, sometimes our sleep can be interrupted by a strange phenomenon called sleep paralysis. For those who have experienced it, sleep paralysis can be a perplexing and even frightening experience. In this article, we will dive into the understanding of sleep paralysis, learn about its different types, explore ways to deal with it, and discuss when to seek professional help. So grab a cup of tea, sit back, and let’s explore the mysteries of sleep paralysis together.
Understanding Sleep Paralysis

Sleep paralysis can be a puzzling and distressing experience for those who have encountered it. It can feel like an otherworldly phenomenon, with a temporary inability to move, speak, or even open one’s eyes. For someone who has never experienced sleep paralysis before, it may be hard to comprehend and understand what’s happening. In this section, we will delve into the details of sleep paralysis – what it is, what causes it, and what the common symptoms are. Let’s explore the mysteries behind this perplexing occurrence.
The Definition of Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis, as defined by medical professionals, is a temporary inability to move or speak, which typically lasts from a few seconds to a few minutes, that happens when a person is waking up or falling asleep. During an episode of sleep paralysis, the person is fully conscious but unable to move their body or limbs.
There are two primary types of sleep paralysis: hypnagogic and hypnopompic. Hypnagogic sleep paralysis happens as a person is falling asleep, while hypnopompic sleep paralysis happens as a person is waking up.
Sleep paralysis can be a frightening and distressing experience for those who suffer from it, as they may feel a sense of pressure on their chest, difficulty breathing, or even hallucinations. It is also commonly associated with other sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy and sleep apnea.
It is important to note that while sleep paralysis can be unsettling, it is generally not considered a serious medical condition. However, if it interferes with a person’s ability to sleep or causes significant distress, they should seek professional help.
What Causes Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a frightening experience that can be caused by a range of factors, from stress to underlying medical conditions. Below are some of the most common causes of sleep paralysis:
- Disruption of REM Sleep: Sleep paralysis is typically associated with Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep, which is the stage of sleep in which the most vivid dreams occur. When a person experiences REM sleep disruption, they are more likely to experience sleep paralysis.
- Sleeping Position: Sleeping on your back can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis, as this position makes it more difficult for the body to breathe normally during sleep.
- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of sleep or poor quality sleep can lead to sleep paralysis. If the body and brain are not receiving enough restful sleep, they may be more prone to experiencing disruptions in the sleep cycle.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety can trigger sleep paralysis in some individuals by disrupting the normal sleep cycle.
- Narcolepsy: Sleep paralysis is a common symptom of Narcolepsy, a neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Individuals with Obstructive Sleep Apnea may also experience sleep paralysis as a result of disrupted sleep patterns.
- Medications or Substance Use: Certain medications or substances, such as antidepressants or illicit drugs, can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
It’s important to note that the exact causes of sleep paralysis are not fully understood and may vary from person to person. However, by understanding the common factors that can contribute to sleep paralysis, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of experiencing this frightening phenomenon.
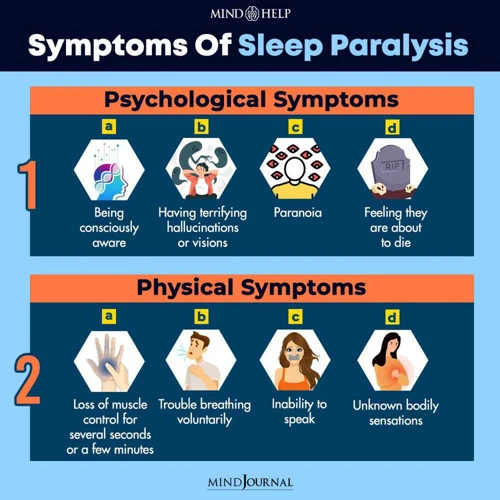
What are the Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis can be a frightening experience, especially for those who experience it for the first time. Here are some common symptoms of sleep paralysis:
- A feeling of being trapped: A person with sleep paralysis might feel like they cannot move or speak, even though they are fully aware of their surroundings.
- Hallucinations: It is not uncommon for people experiencing sleep paralysis to perceive the presence of a threat, such as a person or an animal on or near their bed, even though there is no one there.
- A sense of pressure: Some people describe the feeling of being held down, as if someone or something is sitting on their chest or abdomen.
- Difficulty breathing: The sensation of not being able to move can cause a person to feel as if they cannot take deep breaths.
- Fear: It is common for people experiencing sleep paralysis to feel intense fear, anxiety, or panic, especially if they do not understand what is happening to them.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences sleep paralysis will have all of these symptoms. Additionally, the severity of the symptoms can vary from person to person and from episode to episode. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
5 Different Types of Sleep Paralysis

As if dealing with one type of sleep paralysis wasn’t enough, there are actually five distinct types of this phenomenon. Each type varies in its frequency, duration, and accompanying symptoms. Understanding the unique features of each type can help you identify which one you are experiencing and how to best manage it. Let’s take a closer look at these different types of sleep paralysis.
Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis
Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis is a common type of sleep paralysis that occurs as a person is falling asleep. It is a state of paralysis that affects the muscles of the body and can make it difficult to move or speak. Here are some key characteristics of Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis:
- Occurs at the Onset of Sleep: Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis happens as an individual is transitioning from wakefulness to sleep. This type of Sleep Paralysis can occur even if a person is not trying to fall asleep.
- Accompanied by Vivid Hallucinations: Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis is often accompanied by intense, vivid hallucinations that can be very disturbing. These hallucinations can be visual, auditory, or even tactile in nature.
- Causes of Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis: Some potential causes of Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis include sleep deprivation, disrupted sleep schedule, and stress. Certain medications and medical conditions can also contribute to the onset of Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis.
- Treatment: Treatment for Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis typically involves improving sleep hygiene, adopting relaxation techniques, and medication therapy under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Hypnagogic Sleep Paralysis can be a distressing experience for those who suffer from it, but there are ways to manage it and minimize its impact on one’s daily life. Being aware of the potential triggers and causes of this type of sleep disorder can help individuals take proactive steps towards better sleep health.
Hypnopompic Sleep Paralysis
Hypnopompic sleep paralysis, also known as postdormital sleep paralysis, is a type of sleep paralysis that occurs when a person wakes up from sleep. This type of sleep paralysis is less common than hypnagogic sleep paralysis, but it can still be quite distressing for those who experience it.
During hypnopompic sleep paralysis, a person may be unable to move or speak for a few seconds or minutes after waking up. They may also experience hallucinations, such as seeing figures in the room or feeling a presence nearby. These hallucinations can be frightening and realistic, which can further increase anxiety and distress.
Notably, hypnopompic sleep paralysis can be triggered by various factors such as sleep deprivation, sleep schedule changes, anxiety, and use of certain medications. It is important for individuals who have experienced hypnopompic sleep paralysis to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying disorders or conditions which might be contributing to their sleep issues.
Below are some common symptoms of hypnopompic sleep paralysis:
| Symptoms of Hypnopompic Sleep Paralysis |
|---|
| Inability to move or speak |
| Hallucinations (visual, auditory, and tactile) |
| Feeling of pressure or weight on the chest |
| Feeling of a presence or someone watching over you |
If you experience hypnopompic sleep paralysis, there are some steps you can take to reduce the frequency and intensity of your episodes. These include:
– Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
– Reducing stress and anxiety through relaxation techniques or therapy
– Avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and certain medications that can disrupt sleep
– Practicing good sleep hygiene habits, such as avoiding screens and bright lights before bed
– Seeking medical advice if sleep paralysis is a recurring issue
Hypnopompic sleep paralysis can be a frightening and disruptive experience, but it is manageable with the right treatment and support.
Nocturnal Sleep Paralysis
Nocturnal Sleep Paralysis is one of the five different types of sleep paralysis. It is also referred to as sleep-onset paralysis since it happens when a person is about to sleep or is waking up from sleep. This type of sleep paralysis typically lasts from a few seconds up to a few minutes.
Below is a table that outlines the characteristics of Nocturnal Sleep Paralysis:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Timing | Occurs when a person is about to sleep or is waking up from sleep |
| Duration | Lasts from a few seconds up to a few minutes |
| Symptoms | Sensation of being unable to move, speak, or breathe; feeling of pressure on chest; hallucinations |
| Triggers | Irregular sleep schedule, sleep deprivation, anxiety, and stress |
| Treatment | Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), medication, and therapy |
During Nocturnal Sleep Paralysis, a person may experience a sensation of being unable to move, speak, or breathe. They may also feel a pressure on their chest and have hallucinations. This can be an extremely distressing experience and can lead to anxiety about going to sleep.
Nocturnal Sleep Paralysis can be triggered by an irregular sleep schedule, sleep deprivation, anxiety, and stress. It is important to establish a regular sleep routine and try to reduce stress and anxiety in order to prevent this type of sleep paralysis from occurring.
In terms of treatment, Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy can be effective for those who experience breathing difficulties during Nocturnal Sleep Paralysis. Medication and therapy can also be options for those who experience this type of sleep paralysis frequently or have severe symptoms.
It’s important to note that while Nocturnal Sleep Paralysis can be a frightening experience, it is generally not harmful and does not require medical attention. However, if a person experiences this type of sleep paralysis frequently and it starts to interfere with their daily life, they should seek professional help.
Isolated Sleep Paralysis
Isolated Sleep Paralysis (ISP) is a type of sleep disorder that can be extremely distressing for those who experience it. It is characterized by the inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up, along with vivid hallucinations and a feeling of pressure on the chest.
Causes: Although the exact cause is unknown, ISP is believed to be associated with irregular sleep patterns, a disrupted sleep-wake cycle, and stress or anxiety. It is also more common in individuals with a history of narcolepsy or other sleep disorders.
Symptoms: The symptoms of ISP are similar to those of other types of sleep paralysis, with the key difference being that it occurs sporadically, rather than along with other sleep disorders. Episodes of ISP can be infrequent or occur more frequently, sometimes several times a week.
Diagnosis: ISP is typically diagnosed based on the presence of symptoms and a thorough examination of sleep patterns.
Treatment: There is no specific treatment for ISP, but lifestyle changes, such as practicing good sleep hygiene, reducing stress and anxiety, and keeping a regular sleep schedule, can help prevent episodes from occurring. Additionally, treating any underlying sleep disorders may also help alleviate symptoms. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help regulate the sleep-wake cycle and reduce the occurrence of ISP episodes.
ISP can be a difficult condition to manage, but taking steps to improve sleep and reduce stress can help provide relief and improve overall quality of life.
| Causes | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irregular sleep patterns Disrupted sleep-wake cycle Stress or anxiety History of narcolepsy or other sleep disorders |
Inability to move or speak Vivid hallucinations Feeling of pressure on the chest Episodes occur sporadically |
Diagnosed based on symptoms and sleep patterns | Lifestyle changes such as good sleep hygiene, reducing stress and anxiety, and keeping a regular sleep schedule Treating underlying sleep disorders Medications to regulate sleep-wake cycle |
Recurrent Isolated Sleep Paralysis
Recurrent Isolated Sleep Paralysis is a type of sleep paralysis that occurs repeatedly in a person’s life. This type of sleep paralysis is characterized by the individual experiencing frequent episodes of sleep paralysis, often several times a week.
Causes: The exact cause of recurrent isolated sleep paralysis is unknown. However, it may be linked to other underlying sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea. Additionally, high levels of stress, anxiety, and sleep deprivation can trigger recurring episodes of sleep paralysis.
Symptoms: The symptoms of recurrent isolated sleep paralysis are similar to other types of sleep paralysis. The individual may experience a feeling of being awake but unable to move or speak. They may also experience hallucinations and intense feelings of fear or dread. In some cases, the individual may also experience physical sensations such as pressure on the chest or difficulty breathing.
Treatment: There are several ways to manage recurrent isolated sleep paralysis, including improving sleep hygiene and seeking professional help. Improving sleep hygiene includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, and minimizing exposure to electronic devices. Seeking professional help may involve getting treatment for underlying sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea. Additionally, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may be helpful in managing anxiety and stress-related to sleep paralysis.
Prevention: While there is no guaranteed way to prevent recurrent isolated sleep paralysis, there are several ways to reduce the likelihood of experiencing an episode. This includes prioritizing sleep, managing stress levels, and avoiding substances that interfere with sleep quality, such as caffeine and tobacco.
Recurrent Isolated Sleep Paralysis can be a frustrating and frightening experience for those who suffer from it. However, by seeking professional help, managing stress levels, and practicing healthy sleep habits, it is possible to manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency of episodes.
How to Deal with Sleep Paralysis
Overcoming sleep paralysis can be a daunting task for those who experience it. It’s important to understand that there are a variety of ways to manage this condition, and what works for one person may not work for another. With determination and some lifestyle changes, it’s possible to reduce the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes. In this section, we will explore some strategies and tips for dealing with sleep paralysis, ranging from establishing a healthy sleep schedule to considering medication and supplements. By following these steps, you may be able to regain control of your sleep and wake up feeling rested and refreshed.
Keeping a Sleep Schedule
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is crucial when dealing with sleep paralysis. Individuals who suffer from sleep paralysis should establish a sleep routine that they can stick to. Here are some tips to help establish a healthy sleep schedule:
- Set a consistent bedtime: It’s crucial to go to bed at the same time every night, even on weekends.
- Avoid naps: Napping during the day can disrupt your nighttime sleep pattern and lead to sleep paralysis.
- Avoid stimulants: Consuming caffeine or nicotine close to bedtime can make it difficult to fall asleep.
- Eliminate distractions: Keep your bedroom quiet, dark, and cool to create an optimal sleep environment.
- Develop a relaxing bedtime routine: Engage in relaxing activities like reading or taking a warm bath to prepare your body for sleep.
By regulating your sleep schedule, you can help reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis episodes. Stick to your schedule even on weekends and holidays to help keep your body on track.
Reducing Stress and Anxiety
One of the main triggers of sleep paralysis is stress and anxiety. Excessive stress can cause disruptions to sleep patterns, which can lead to various sleep disorders such as sleep paralysis. Anxiety can cause the mind to become hyperactive, leading to increased chances of sleep paralysis episodes.
It is important to take steps in reducing stress and anxiety to prevent the occurrence of sleep paralysis. Here are some tips that can help:
| Tips for Reducing Stress and Anxiety to Prevent Sleep Paralysis |
|---|
|
1. Practice Relaxation Techniques Engage in relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. These can help calm the mind and reduce stress and anxiety. |
|
2. Exercise Regularly Physical activity promotes the production of endorphins, which help to combat stress and anxiety. Find an exercise routine that works for you and stick to it. |
|
3. Maintain a Healthy Diet Eating a well-balanced diet can help reduce stress and anxiety. Avoid consuming products high in caffeine or sugar, as these can interfere with restful sleep. |
|
4. Practice Good Sleep Hygiene Establish a relaxing bedtime routine, ensure your sleep environment is comfortable, and get at least 7-8 hours of sleep each night to help reduce stress and anxiety. |
|
5. Limit Exposure to Stressors If possible, limit exposure to stressful situations – this could mean taking a break from work, reducing time spent on social media or other negative triggers, and seeking out activities that bring you joy. |
While it may not be possible to completely eliminate stress and anxiety from our lives, incorporating these tips can certainly help reduce their impact and prevent the occurrence of sleep paralysis. Remember to practice good self-care and seek professional help if needed.
Treating Underlying Sleep Disorders
Addressing underlying sleep disorders is a crucial step in dealing with sleep paralysis. Sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and restless leg syndrome are some of the common sleep disorders that can cause or exacerbate sleep paralysis. Treating the underlying sleep disorder can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes.
Here are some treatment options for underlying sleep disorders:
- Sleep apnea: Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is the most common treatment for sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth while sleeping, which delivers a steady flow of air to keep the airways open. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct structural abnormalities that contribute to sleep apnea.
- Narcolepsy: Stimulants, such as modafinil and armodafinil, are often prescribed to manage excessive daytime sleepiness in people with narcolepsy. Other medications, such as sodium oxybate and antidepressants, may also be used to manage other symptoms, such as cataplexy or hallucinations.
- Restless leg syndrome: Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, reducing caffeine and alcohol consumption, and maintaining a regular sleep schedule, may help reduce symptoms of restless leg syndrome. In some cases, medications such as dopamine agonists and anticonvulsants may be used to manage symptoms.
It’s important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment for any underlying sleep disorder. Proper treatment can improve the quality of sleep and reduce the risk of sleep paralysis.
Building Healthy Sleep Habits
When it comes to dealing with sleep paralysis, one of the most effective methods is to build healthy sleep habits. Here are some ways you can do so:
- Stick to a sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can help regulate your body’s sleep-wake cycle and promote healthier sleep.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Engage in activities that help you unwind and relax before going to bed, such as taking a hot bath or shower, reading a book, or practicing breathing exercises.
- Create a sleep-conducive environment: Ensure that your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs or a white noise machine to block out any distractions that could disrupt your sleep.
- Avoid stimulants: Avoid substances such as caffeine and nicotine, especially in the evening hours, as they can interfere with your ability to fall and stay asleep.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve the quality of your sleep, but make sure to finish moderate to intense workouts at least a few hours before bedtime to allow your body time to wind down.
- Avoid napping: Napping during the day can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to fall asleep at night. If you must nap, limit it to 20 to 30 minutes and do so in the early afternoon.
- Limit screen time: The blue light emitted by electronic devices such as smartphones, computers, and televisions can interfere with your body’s production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Try to avoid using these devices in the hour leading up to bedtime.
By incorporating these habits into your life, you may be able to reduce your risk of experiencing sleep paralysis and improve the overall quality of your sleep.
Exploring Medications and Supplements
When dealing with sleep paralysis, exploring different medications and supplements can be a helpful step towards finding relief. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new medication or supplement.
Medications:
– Antidepressants: These medications can help regulate sleep and reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis episodes.
– Benzodiazepines: These medications can help relax the body and promote sleep.
– Narcolepsy medications: For individuals with underlying narcolepsy, medications such as modafinil can be prescribed to improve daytime alertness and reduce episodes of sleep paralysis.
Supplements:
– Magnesium: This mineral can help relax the muscles and promote sleep.
– Melatonin: This hormone can regulate the sleep-wake cycle and improve sleep quality.
– Valerian root: This herbal supplement has a calming effect and can promote relaxation.
It is important to note that while medications and supplements may be helpful in managing sleep paralysis, they should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It is also important to address any underlying sleep disorders or lifestyle factors contributing to sleep paralysis in conjunction with medication and supplement use.
When to Seek Professional Help
Sleep paralysis can be a distressing experience, and in some cases, it can interfere with an individual’s daily life. While it is a common phenomenon experienced by many people, it is important to know when to seek professional help for it.
One of the primary reasons to seek professional help is if you experience extreme fear, anxiety or depression directly linked to sleep paralysis. This can be an indication of a more significant underlying mental health issue that requires immediate attention. These emotions may also negatively impact your sleep quality, potentially worsening your sleep paralysis, and leading to a vicious cycle.
If you have difficulty sleeping, experience excessive daytime sleepiness, or snore loudly, you may want to consider seeing a doctor for a sleep evaluation. In some cases, sleep paralysis can be a sign of underlying sleep disorders such as sleep apnea or narcolepsy. A sleep evaluation may help to rule out the presence of any serious underlying conditions and provide you with a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
If your sleep paralysis episodes are accompanied by other medical symptoms such as seizures, fainting or irregular heartbeats, you should seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms could be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires prompt attention.
Ultimately, if you find that your sleep paralysis is affecting your quality of life, it is essential to seek professional help. A mental health professional or sleep specialist can help you explore ways to manage your symptoms and improve your overall sleep health. They may recommend therapy, medication, or a combination of both to help reduce the frequency and severity of your sleep paralysis episodes.
If you experience extreme fear, anxiety or depression directly linked to sleep paralysis, difficulty sleeping, excessive daytime sleepiness, snoring loudly or if your sleep paralysis episodes are accompanied by other medical symptoms such as seizures or irregular heartbeats, it is important to seek professional help to achieve a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep paralysis can be a frightening and unsettling experience for those who suffer from it. However, understanding the phenomenon and identifying the specific type of sleep paralysis one is experiencing can provide some relief and help in finding effective solutions to prevent or alleviate the episodes.
It is crucial to make lifestyle changes, such as developing a consistent sleep routine, managing stress levels, and building healthy sleep habits, to reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Additionally, treating any underlying sleep disorders that may contribute to episodes of sleep paralysis and exploring medication and supplements options can also be beneficial.
If episodes of sleep paralysis persist despite making lifestyle changes and utilizing precautions, seeking professional help may be necessary to address any underlying medical conditions or psychological issues that may be causing the episodes.
Remember, sleep paralysis may be unsettling, but it is a relatively common phenomenon, and there are solutions available to help manage or prevent the episodes. By taking the steps outlined in this article, one can rest easier and enjoy a more restful and rejuvenating sleep experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a feeling of being conscious but unable to move, often accompanied by terrifying hallucinations.
How common is sleep paralysis?
It is estimated that about 8% of people experience sleep paralysis at some point in their lives.
What causes sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis can be caused by various factors, such as irregular sleep patterns, stress, sleep disorders, and some medications.
What are the symptoms of sleep paralysis?
The symptoms can include a feeling of pressure on the chest, inability to move or speak, hallucinations, and an overwhelming sense of fear.
Can sleep paralysis be treated?
Yes, there are various treatments available for sleep paralysis, such as establishing a regular sleep pattern, reducing stress, and seeking professional help.
What is the difference between hypnagogic and hypnopompic sleep paralysis?
Hypnagogic sleep paralysis occurs when falling asleep, while hypnopompic sleep paralysis occurs when waking up.
What is nocturnal sleep paralysis?
Nocturnal sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that occurs during the REM stage of sleep, where the body is temporarily paralyzed to prevent acting out dreams.
What is isolated sleep paralysis?
Isolated sleep paralysis is a one-time experience of sleep paralysis, often caused by irregular sleep patterns or stress.
What is recurrent isolated sleep paralysis?
Recurrent isolated sleep paralysis is a recurring type of sleep paralysis that can be caused by various factors, such as sleep disorders, medications, and neurological conditions.
Can sleep paralysis be dangerous?
While sleep paralysis itself is not dangerous, it can be a symptom of an underlying sleep disorder or mental health condition, which may require professional help.








