Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night, only to find yourself completely paralyzed? Your mind is awake, but your body refuses to move, and you feel an immense pressure on your chest as if something is weighing you down. This phenomenon is known as Sleep Paralysis, and it can be a truly terrifying experience. Many people who have gone through it are left wondering what caused it and if there is any way to prevent it from happening again. In this article, we will dive deep into the science behind Sleep Paralysis, from the symptoms and types to the causes, diagnosis and treatment. Let’s explore this intriguing and sometimes haunting phenomenon together.
What is Sleep Paralysis?

Have you ever woken up unable to move or speak? This terrifying experience is known as sleep paralysis, where the body remains temporarily paralyzed during the transition between sleep and wakefulness. It can occur to anyone and is more common in people with certain sleep disorders or those who experience high levels of stress and anxiety. Understanding sleep paralysis is essential in managing and overcoming this unusual phenomenon. Let’s dive deeper into this intriguing yet mysterious topic.
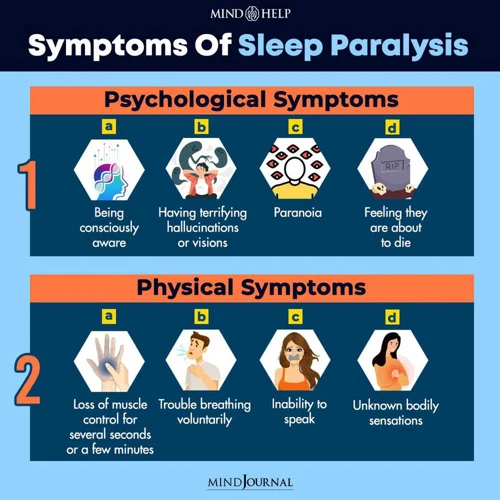
Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis
Sleep Paralysis is a sleep disorder that causes a person to be temporarily unable to move or speak when they wake up or when they are falling asleep. Here are some common symptoms that people experience during Sleep Paralysis:
| SYMPTOMS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Inability to move or speak | A person with Sleep Paralysis is unable to move their body or speak, which can be a frightening experience. |
| Sensation of pressure and weight on chest | Some people with Sleep Paralysis report feeling a sensation of pressure on their chest, as if something heavy is sitting on top of them. |
| Hallucinations | People with Sleep Paralysis often report vivid, often frightening, hallucinations. These can include seeing or feeling the presence of a person or creature in the room. |
| Feeling of suffocation | Some people with Sleep Paralysis report feeling like they are suffocating or having difficulty breathing, due to the sensation of pressure on their chest. |
| Panic attacks and anxiety | Sleep Paralysis can be a frightening experience, and people who experience it may develop anxiety or panic attacks as a result. |
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences Sleep Paralysis will have all of these symptoms, and some may have additional symptoms. Additionally, the intensity and duration of these symptoms can vary between individuals. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to speak to a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis can be a frightening experience. There are two main types of sleep paralysis: isolated sleep paralysis and familial sleep paralysis.
Isolated Sleep Paralysis: This is the most common form of sleep paralysis which occurs without any other associated medical condition. During isolated sleep paralysis, a person may experience the inability to move or speak for a few seconds or minutes, usually at the onset of sleep or during arousal from sleep. This type of sleep paralysis occurs without any underlying medical condition and is not caused by a mental health disorder.
Familial Sleep Paralysis: Unlike isolated sleep paralysis, familial sleep paralysis run in families and is inherited. This type of sleep paralysis has a strong genetic basis and is seen in several family members. The symptoms of familial sleep paralysis are similar to those of isolated sleep paralysis. However, familial sleep paralysis occurs more frequently and can be severe.
In rare cases, sleep paralysis can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition such as narcolepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden falls. In some individuals, it may also be a symptom of other sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or periodic limb movement disorder.
It is important to note that while sleep paralysis can be distressing, it is not dangerous and typically does not require medical treatment. However, if you experience frequent episodes of sleep paralysis or it significantly affects your quality of life, it is important to discuss it with your doctor.
Science behind Sleep Paralysis

As we delve into the world of sleep paralysis, we can’t help but marvel at the science behind it. This state of temporary paralysis during sleep has perplexed scientists and researchers for decades. Understanding the underlying science behind this phenomenon is crucial in order to prevent and treat it effectively. So let’s take a deep breath and explore the mystery of what really happens during sleep paralysis.
REM Sleep and Sleep Cycles
During REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, our brains are highly active while our bodies remain still. This stage of sleep is important for processing and consolidating memories, regulating emotions, and restoring energy. It is also the stage of sleep in which sleep paralysis can occur.
REM sleep occurs in cycles throughout the night, with each cycle lasting about 90-120 minutes. During these cycles, the brain goes through stages of light and deep sleep, and then enters REM sleep. It is typically during the REM stage of the sleep cycle that sleep paralysis occurs.
To better understand this, let’s take a look at the different stages of sleep and the approximate amount of time spent in each stage during a typical night’s sleep:
| Stage | Description | Approximate Time Spent |
| Stage 1 | Light sleep, easily awakened | 5% |
| Stage 2 | Deeper sleep, body temperature drops | 45-50% |
| Stage 3 | Deep sleep, difficult to awaken | 10-15% |
| REM | Brain activity increases, dreaming occurs, muscles paralyzed | 20-25% |
As you can see, REM sleep comprises roughly 20-25% of a typical sleep cycle. During this stage, brain activity increases significantly, and we experience vivid dreams. At the same time, however, our muscles are essentially paralyzed, a natural protective mechanism to prevent us from acting out our dreams and potentially injuring ourselves.
It is during this muscle paralysis that sleep paralysis can occur, as our consciousness becomes alert but our muscles remain immobile. This experience can be frightening for those who suffer from it, as it can feel as though you are unable to move or breathe. By understanding the different stages of sleep and the role of REM sleep, however, we can gain insight into the science behind sleep paralysis and work towards solutions for prevention and treatment.
Brain Activity during Sleep Paralysis
When it comes to understanding the science behind sleep paralysis, it’s important to examine the brain activity that occurs during this phenomenon. During sleep paralysis, the brain remains in a state of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep while the body is temporarily paralyzed. This can lead to vivid hallucinations and a feeling of being trapped or unable to move.
| Brainwaves | Description |
| Theta Waves | These brainwaves are associated with drowsiness and the onset of sleep. They can also contribute to the hallucinations experienced during sleep paralysis. |
| Gamma Waves | These brainwaves are associated with heightened sensory perception and can contribute to the feeling of being watched or accompanied during sleep paralysis. |
| REM Sleep | This stage of sleep is when most dreaming occurs. During sleep paralysis, the brain remains in this stage while the body is unable to move, leading to vivid and often frightening hallucinations. |
The combination of these brainwaves and the continued activity of the brain during sleep paralysis can be unsettling and leave individuals feeling anxious or afraid. It’s important to understand that these experiences are a natural occurrence and do not pose any serious threat to an individual’s health.
Causes of Sleep Paralysis

As research continues to delve deeper into the mysteries of sleep paralysis, the underlying causes of this baffling condition are becoming more apparent. It’s evident that sleep paralysis is not caused by a single factor, but rather a combination of several elements that impact the body and mind during sleep. Let’s explore some of these factors that contribute to the development of sleep paralysis.
Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders are a common cause of sleep paralysis. They can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to disruptions in REM sleep and potentially triggering sleep paralysis episodes. There are several sleep disorders that have been linked to sleep paralysis, as shown in the table below:
| Sleep Disorder | Definition |
|---|---|
| Narcolepsy | A neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks. |
| Obstructive Sleep Apnea | A disorder in which breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep, leading to reduced oxygen levels and disrupted sleep. |
| Insomnia | A sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep. |
| Restless Leg Syndrome | A neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. |
If you have any of these sleep disorders, you may be more likely to experience sleep paralysis. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about any sleep-related issues you may be experiencing, as they can recommend appropriate treatment options to manage these conditions and potentially reduce the risk of sleep paralysis.
Genetics and Family History
Family history and genetics can play a role in the development of sleep paralysis. Studies have shown that people with a family history of sleep paralysis are more likely to experience it themselves. This suggests that there may be genetic factors involved in the development of the condition.
Additionally, certain genes have been identified that may be associated with sleep paralysis. One study found that individuals with a certain variant of the gene HTR2A were more likely to experience sleep paralysis. However, more research is needed to fully understand the link between genetics and sleep paralysis.
It’s important to note that while genetics may increase the likelihood of developing sleep paralysis, it is not the sole determining factor. Environmental and lifestyle factors also play a significant role in the development of the condition.
Factors that may increase the risk of developing sleep paralysis include:
- Irregular sleep schedule
- Stress and anxiety
- Sleeping on your back
- Using certain medications
- Having other sleep disorders such as narcolepsy
If you have a family history of sleep paralysis or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional. They can help determine if genetics may be a factor and provide guidance on appropriate treatment options.
Risk Factors of Sleep Paralysis
There are various factors that may increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Certain aspects of a person’s life can contribute to this uncomfortable and distressing condition. Identifying these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps towards preventing sleep paralysis. It’s important to understand that while some of these risk factors are within our control, others may not be as easily managed. Let’s dive into the science behind these risk factors and explore how they can impact sleep paralysis.
Age and Gender
Age and gender are two common risk factors associated with sleep paralysis. Let’s take a closer look at how each of them can impact the likelihood of experiencing this phenomenon.
Age:
– Sleep paralysis can happen to anyone, but it’s most common among teenagers and young adults.
– Studies suggest that the prevalence of sleep paralysis decreases with age. People over the age of 50 are less likely to experience it compared to those in their 20s and 30s.
– One possible explanation for this age-related trend is that sleep patterns change as we age. As we get older, we tend to spend less time in REM sleep, which is the stage when sleep paralysis is most likely to occur.
Gender:
– Sleep paralysis affects people of all genders, but some studies suggest that women may be slightly more likely to experience it than men.
– Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle may play a role in this disparity, as some women report an increase in sleep paralysis symptoms during certain phases.
– However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between gender and sleep paralysis.
It’s important to note that age and gender are just two of several factors that can contribute to sleep paralysis, and not everyone who falls into these categories will necessarily experience it. Additionally, sleep paralysis can occur in people outside of these categories as well. It’s crucial to consider all potential risk factors and seek medical attention if sleep paralysis becomes a recurring issue.
Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are common risk factors for experiencing sleep paralysis. When a person experiences stress or anxiety, their body may release certain chemicals that can affect their sleep patterns. This can lead to disrupted REM sleep and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Stress:
- Stressful life events, such as a job loss, breakup, or financial problems, can increase a person’s chances of developing sleep paralysis.
- Chronic stress can lead to sleep disorders, such as insomnia, which can make it harder to get the recommended amount of sleep each night. This can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Stress can also cause muscle tension and contribute to feelings of anxiety, which can make it more difficult to fall asleep and enter into the proper sleep stages.
Anxiety:
- Anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder, can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- People with anxiety may find it difficult to relax or shut off their thoughts at night, which can disrupt their sleep patterns and increase the chances of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Anxiety can also cause physical symptoms, such as rapid heart rate and shallow breathing, which can make it more difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
It’s important for individuals experiencing high levels of stress and anxiety to seek treatment and develop stress management techniques to decrease their risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. This can include practices such as meditation, yoga, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Sleep Schedule and Habits
Sleep schedule and habits are crucial factors that can contribute to the development of sleep paralysis. Irregular sleep schedules or poor sleep hygiene can disrupt the normal sleep architecture and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis episodes. Below is a table that highlights some of the unhealthy sleep habits that can increase the risk of sleep paralysis:
| Unhealthy Sleep Habits | Description |
|---|---|
| Irregular sleep schedule | Going to bed and waking up at different times can disrupt the body’s circadian rhythm and affect the quality of sleep. |
| Sleep deprivation | Not getting enough sleep can increase sleepiness during the day and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. |
| Excessive alcohol consumption | Alcohol can affect the quality of sleep and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. |
| Sleeping on one’s back | Sleeping on the back can lead to increased episodes of sleep paralysis due to the increased likelihood of breathing difficulties and disrupted sleep patterns. |
| Stressful or traumatic events | Stressful or traumatic events can lead to disturbed sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis episodes. |
It is important to establish a regular sleep schedule that allows for adequate sleep duration and quality. Avoiding alcohol consumption close to bedtime and sleeping on the side can also help reduce the risk of sleep paralysis. Additionally, managing stress and addressing any underlying sleep disorders can also be beneficial in preventing sleep paralysis episodes.
Diagnosis of Sleep Paralysis
When experiencing episodes of sleep paralysis, it is crucial to seek proper medical diagnosis to ensure that there are no underlying health concerns. Through the use of various diagnostic tests, healthcare professionals can help identify and understand the factors that contribute to sleep paralysis. In this section, we will explore the different diagnostic methods used to determine the root cause of sleep paralysis.
Medical History and Physical Exam
When diagnosing sleep paralysis, a doctor will typically begin with a medical history and physical exam. This process involves a series of questions and tests to understand the individual’s health history and the symptoms they are experiencing.
Medical History:
During the medical history portion of the exam, the doctor will ask about any previous sleep issues or related medical conditions. This could include questions about sleep apnea, insomnia, or narcolepsy. The doctor may also ask if the individual has a history of anxiety or depression, as these conditions have been linked to an increased risk of sleep paralysis.
Physical Exam:
The physical exam portion of the diagnosis process involves a thorough review of the individual’s overall health. The doctor may check for any physical symptoms that could be contributing to the sleep paralysis, such as irregular breathing patterns or muscle weakness. They may also review any medications the individual is taking, as certain medications have been linked to sleep paralysis.
Other Diagnostic Tests:
In some cases, the doctor may recommend additional tests to help diagnose sleep paralysis. These could include a sleep study, which involves overnight monitoring of the individual’s sleep patterns and brainwave activity. This can help identify any underlying sleep disorders or abnormalities that could be contributing to the sleep paralysis.
The medical history and physical exam are important steps in diagnosing sleep paralysis. By understanding the individual’s overall health and history, and ruling out any other underlying conditions, the doctor can create an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Sleep Study
Diagnosing sleep paralysis can involve a sleep study, also known as a polysomnogram. During this study, a patient’s sleep patterns and brain activity are monitored through the use of sensors attached to their scalp and body. The data collected during the study is used to identify any underlying sleep disorders or abnormalities that may be contributing to the patient’s episodes of sleep paralysis.
The sleep study typically involves the following:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The patient arrives at a sleep center or hospital where the study will be performed |
| 2 | The patient is given time to get comfortable in a private room designed for sleep studies |
| 3 | Sensors are attached to the patient’s scalp, face, chest, legs and other areas of the body. These sensors record brain activity, heart rate, muscle activity and breathing patterns during sleep. |
| 4 | The patient is allowed to sleep while the sensors collect data throughout the night. |
| 5 | The data collected during the study is analyzed to determine if the patient has any underlying sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome, that may be contributing to their sleep paralysis. |
A sleep study is a safe and non-invasive way to diagnose sleep paralysis and other sleep disorders. It is typically conducted in a comfortable environment and patients are closely monitored throughout the entire process to ensure that they are safe and comfortable. If sleep paralysis is diagnosed as a result of a sleep study, treatment options can then be explored to help manage the symptoms and improve overall sleep quality.
Treatment for Sleep Paralysis

For individuals who experience the unsettling effects of sleep paralysis, seeking treatment can provide much-needed relief. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating this condition, there are several different options available to individuals who are struggling with sleep paralysis. In this section of the article, we will explore some of the most effective treatment methods for addressing sleep paralysis, including lifestyle changes, medications, and therapy. By understanding the various treatment options available, individuals can take steps towards achieving a more restful, less disruptive sleep experience.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on reducing the frequency and severity of sleep paralysis episodes. Here are some tips to make lifestyle changes:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Improving sleep hygiene | Promoting good sleep hygiene such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and sleeping in a comfortable and cool environment help improve sleep quality. |
| Reducing stress and anxiety | Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and anxiety, contributing to better sleep quality. |
| Avoiding stimulants | Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, and other stimulants before bed can help regulate sleep and minimize the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. |
| Improving diet and exercise | A healthy diet and regular exercise can improve overall health and quality of life, resulting in better sleep hygiene and a reduction in sleep paralysis. |
| Changing sleep position | Sleeping on your back is associated with a higher likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis, so sleeping on your side or stomach may be helpful in reducing episodes. |
By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of sleep paralysis symptoms and improve their overall sleep quality. However, it is important to note that these changes may not completely eliminate the occurrence of sleep paralysis and medical treatment may still be necessary.
Medications
There are several medications that can be used to treat sleep paralysis if lifestyle changes aren’t effective. These medications can help improve the quality of sleep and reduce the frequency and severity of incidents. Here are some medications that are commonly used to treat sleep paralysis, along with their benefits and potential side effects:
| Medication | Benefits | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Antidepressants can be helpful in treating sleep paralysis as they can reduce depression and anxiety, which are common triggers for sleep paralysis. They can also improve the quality of sleep. | Side effects may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight gain, low blood pressure, and sexual dysfunction. |
| Benzodiazepines | Benzodiazepines are sedative drugs that can help calm the mind and promote relaxation. They can help reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis by helping to regulate sleep cycles. | Side effects may include dizziness, confusion, memory impairment, and dependence. |
| Stimulants | Stimulant medications can be used to treat sleep paralysis by improving alertness and reducing the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. They can also help improve the quality of sleep. | Side effects may include insomnia, nervousness, agitation, and heart palpitations. |
| Narcolepsy Medications | Narcolepsy medications like modafinil and armodafinil can be helpful in treating sleep paralysis by promoting wakefulness during the day and improving the quality of sleep at night. | Side effects may include headache, nausea, dizziness, and insomnia. |
It’s important to note that medications should only be used under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. They should also be taken as directed and never exceeded their prescribed dosage.
Therapy
Psychotherapy can be a helpful treatment option for managing sleep paralysis. The type of therapy used may vary based on the underlying cause of the sleep disorder. Here are some examples:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This form of therapy aims to change negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to anxiety and stress. CBT may be helpful for individuals experiencing sleep paralysis as a result of anxiety or panic disorder.
- Somatic Therapy: This type of therapy focuses on the physical sensations and experiences of the body. It can be helpful for those who have experienced trauma or have developed somatic symptoms related to anxiety or stress.
- Hypnotherapy: Hypnotherapy involves using guided relaxation techniques to help individuals enter a state of deep relaxation. It may be helpful for those with sleep disorders as well as anxiety and stress.
It is important to note that therapy may not be a standalone treatment for sleep paralysis but can be used in combination with other forms of treatment such as lifestyle modifications and medications. It is also important to seek out licensed and qualified mental health professionals who specialize in the treatment of sleep disorders.
Preventing Sleep Paralysis
One of the ways to prevent sleep paralysis is by ensuring that one gets enough quality sleep. This means going to bed at a regular time every night and waking up at the same time every morning. It is also important to create a relaxing sleep environment by keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Avoiding large meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bedtime can also help.
In addition to making changes to one’s sleep habits, reducing stress and anxiety levels can help prevent sleep paralysis. This can involve practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or yoga. It may also be helpful to talk to a therapist or counselor about any sources of stress or anxiety in one’s life.
Another way to prevent sleep paralysis is by treating any underlying sleep disorders that may be contributing to its occurrence. Sleep disorders such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Treating these conditions may help reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
Finally, it is important to maintain good overall health by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis, as well as improve overall sleep quality and physical health.
While it may not be possible to completely prevent sleep paralysis, making lifestyle changes and seeking appropriate treatment for underlying conditions can help reduce its occurrence and improve overall sleep quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep paralysis is a terrifying experience that can leave individuals feeling helpless and afraid. However, understanding the science behind sleep paralysis can help demystify the experience.
During sleep paralysis, the brain is essentially awake while the body is still in a state of paralysis that normally occurs during REM sleep. This can lead to vivid hallucinations and terrifying experiences.
Sleep disorders and genetic factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis, while age, stress, and sleep habits can also play a role.
Diagnosis of sleep paralysis typically involves a medical history and physical exam, as well as a sleep study to monitor brain activity during sleep.
Treatment options for sleep paralysis may involve lifestyle changes, medications, and therapy.
Preventative measures, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and managing stress levels, can also help reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Overall, while sleep paralysis can be a frightening experience, there are measures that can be taken to manage and prevent it. By understanding the underlying causes and seeking proper treatment, individuals can take control of their sleep and reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between sleep paralysis and night terrors?
Sleep paralysis occurs when the body is unable to move during REM sleep, while night terrors involve intense fear and screaming during deep sleep.
Can you die from sleep paralysis?
No, sleep paralysis is not fatal, but it can be a symptom of other underlying sleep disorders.
Is sleep paralysis a sign of a mental illness?
No, sleep paralysis is not a mental illness, but it can be associated with anxiety and other mental health conditions.
Can medication cause sleep paralysis?
Yes, certain medications such as antidepressants and antipsychotics can increase the risk of sleep paralysis.
Is sleep paralysis more common in certain cultures?
Yes, sleep paralysis has been reported in many cultures throughout history, but it appears to be more common in African American and Caribbean populations.
Can changing my sleep schedule prevent sleep paralysis?
Yes, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and getting enough sleep can reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Can sleep paralysis be inherited?
There may be a genetic component to sleep paralysis, as it tends to run in families.
Do all people with sleep paralysis experience visual hallucinations?
No, while visual hallucinations are common during sleep paralysis, not everyone experiences them.
How can a sleep study diagnose sleep paralysis?
A sleep study can help diagnose sleep disorders that may be causing sleep paralysis by monitoring brain activity, heart rate, breathing, and other bodily functions during sleep.
Can therapy help treat sleep paralysis?
Yes, therapy can be an effective treatment for sleep paralysis by addressing underlying anxiety or other mental health concerns.








