Nightmares can be a terrifying experience on their own, but for those living with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), they can become a chronic and debilitating part of life. Understanding the impact of PTSD-related nightmares on one’s mental and physical health is crucial in breaking the vicious cycle that accompanies them. From cognitive behavioral therapy to self-help techniques and lifestyle changes, there are various ways to manage and reduce the occurrence of PTSD nightmares. In this article, we explore the different treatment options and practical tips to help individuals break the cycle and regain their quality of life.
Understanding PTSD-Related Nightmares
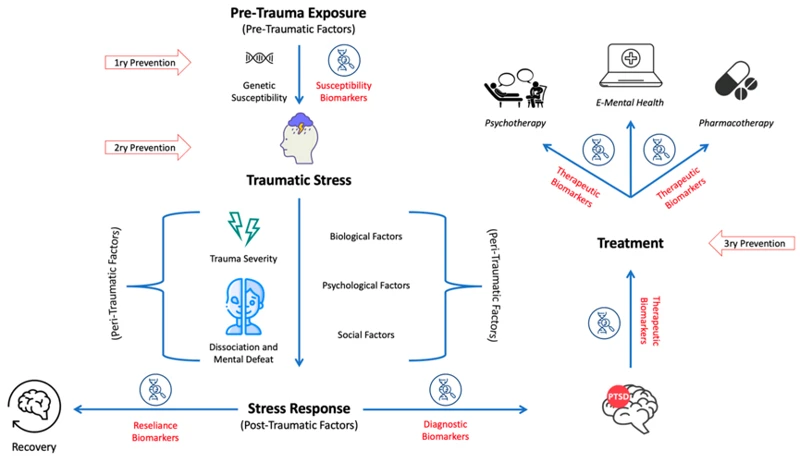
For individuals who suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), the experience can be overwhelming and consume their daily lives. One of the most common symptoms of PTSD are nightmares, which can greatly impact their ability to function and get the sleep they need. Understanding the spiral of PTSD nightmares and their impact on sleep is essential in breaking the cycle and finding effective treatment options. By delving deeper into the root causes of these nightmares, individuals can begin to take steps towards a better quality of life.
The Spiral of PTSD Nightmares
People with PTSD may experience recurrent nightmares that can disrupt their sleep and negatively impact their quality of life. These nightmares often involve re-experiencing traumatic events, leading to a vicious cycle that can be difficult to break.
The spiral of PTSD nightmares can be described in the following steps:
- Exposure to triggers: Individuals with PTSD may be exposed to triggers, such as sounds, smells, or images, that remind them of their trauma.
- Increased anxiety: Exposure to these triggers can lead to increased anxiety and a sense of impending danger.
- Difficulty falling asleep: The heightened state of anxiety can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Recurrent nightmares: When individuals do finally fall asleep, they may experience recurrent nightmares related to their traumatic experiences.
- Worsening anxiety: These nightmares can further increase anxiety and lead to a sense of ongoing danger and threat.
- More difficulty sleeping: The increased anxiety and ongoing nightmares can make it even more difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep, perpetuating the cycle.
Breaking this cycle is key to managing PTSD-related nightmares and improving overall sleep and quality of life. There are many treatment options available, including cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), exposure therapy, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR). Additionally, there are self-help techniques that individuals can use, such as relaxation techniques and imagery rehearsal therapy (IRT). Making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining healthy eating habits and regular exercise, can also help manage PTSD-related nightmares. By taking steps to manage PTSD-related nightmares, individuals with PTSD can improve their quality of life and get the restorative sleep they need.
The Impact of PTSD Nightmares on Sleep
The effects of PTSD nightmares can be far-reaching, with the most immediate impact being on sleep quality. Nightmares can cause severe sleep disruption, leading to difficulty falling and staying asleep. This disruption can result in daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and general fatigue.
The table below illustrates some impacts of PTSD nightmares on sleep:
| Impact of PTSD Nightmares on Sleep | Description |
|---|---|
| Difficulty falling asleep | PTSD nightmares can cause insomnia and make it difficult to get enough sleep. |
| Difficulty staying asleep | PTSD nightmares can cause frequent awakenings throughout the night, leaving one feeling exhausted and unrefreshed in the morning. |
| Daytime sleepiness | Individuals may feel excessively sleepy during the day, often making it difficult to concentrate and be productive. |
| Irritability and mood swings | PTSD nightmares can lead to emotional outbursts, irritability or even depression, causing significant distress in personal relationships and daily life. |
| Nightmares with flashback | PTSD nightmares can be so distressing that they can trigger a flashback of the traumatic event, making it hard to shake off the experience. |
| Impact on physical health | Chronic sleep loss from PTSD nightmares can increase the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease. |
It’s essential to acknowledge that PTSD nightmares do not just affect one’s sleep. They can lead to significant problems with daytime functioning, which can have a significant impact on someone’s quality of life. Seeking professional help is the first step in managing PTSD nightmares to improve overall sleep and mental health.
Treatment Options
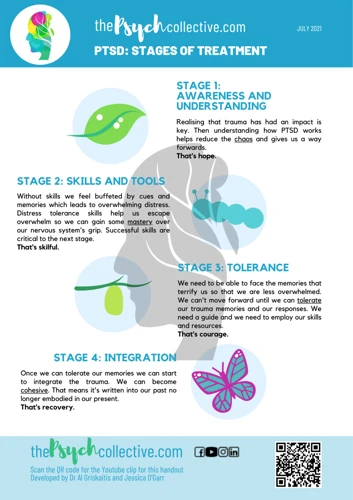
When it comes to finding a solution to PTSD nightmares, there are various treatment options available for those who need help. These treatments can range from cognitive therapies to exposure therapy and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing. Each option may work differently for each individual, and it’s important to find the right fit for you. In this section, we’ll explore the various treatment options in more detail and how they can help break the cycle of PTSD nightmares.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I):
CBT-I is a form of therapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors related to sleep. It can be effective in treating insomnia, which is a common symptom of PTSD.
Some key components of CBT-I include:
- Sleep Restriction: This involves limiting the amount of time spent in bed to increase the body’s natural drive for sleep.
- Stimulus Control: This involves creating a sleep-conducive environment and associating the bed with sleep only.
- Sleep Hygiene Education: This involves educating individuals about good sleep habits and behaviors.
- Cognitive Therapy: This involves identifying and changing negative or distorted thoughts about sleep that may be contributing to the problem.
CBT-I is typically conducted over the course of six to eight sessions, and individuals are encouraged to practice the techniques at home.
Research has shown that CBT-I can be effective in improving sleep quality and reducing insomnia symptoms in individuals with PTSD. It may also be helpful in reducing the occurrence of nightmares.
It’s important to note that CBT-I should be conducted by a licensed therapist who is trained in this type of therapy. It is not recommended to attempt CBT-I on your own without professional guidance.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure Therapy is a proven form of therapy that involves gradually exposing a person to their trauma in a safe and controlled environment. The goal is to help the person become desensitized to their triggers and reduce the intensity of their PTSD-related nightmares.
There are different approaches to exposure therapy, including imaginal exposure and in vivo exposure. Imaginal exposure involves the person mentally revisiting their trauma and describing it in detail to their therapist. In vivo exposure involves the person confronting actual situations or stimuli that trigger their PTSD symptoms, such as crowded places, loud noises, or anything that reminds them of their trauma.
Exposure therapy is usually done in conjunction with other forms of therapy, such as cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) and may include relaxation and breathing exercises to help manage anxiety and minimize the impact of any flashbacks that occur during treatment. It can be done on an individual or group basis, and the length of treatment depends on the severity of the PTSD.
While exposure therapy can be effective, it can also be emotionally challenging as it involves revisiting traumatic events. It should only be done with a trained mental health professional who specializes in treating PTSD.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
One treatment option for PTSD-related nightmares is Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR). EMDR is a technique that involves recalling distressing images while receiving a bilateral sensory input, such as eye movements or taps. This technique is believed to stimulate the brain’s natural healing process, allowing the individual to process and integrate the traumatic experience into their memory in a less distressing way.
During an EMDR session, the therapist will guide the individual through a series of eye movements or other bilateral stimuli while they recall their traumatic memory. The goal is to faciliate the processing of the traumatic memory and reduce the emotional distress associated with it. This technique has been shown to be effective in reducing the severity and frequency of nightmares in individuals with PTSD.
However, it’s important to note that EMDR is not a standalone treatment and should be used in conjunction with other therapies, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or medication. It’s also crucial to work with a licensed therapist who is trained in EMDR to ensure proper application of the technique.
Here are some key takeaways about EMDR for PTSD-related nightmares:
- EMDR is a therapy technique that involves recalling traumatic memories while receiving simultaneous bilateral sensory input, such as eye movements or taps.
- This technique stimulates the brain’s natural healing process to facilitate processing and integration of the traumatic experience.
- EMDR has been shown to be effective in reducing the severity and frequency of nightmares in individuals with PTSD.
- It should be used in conjunction with other therapies and under the guidance of a licensed therapist trained in EMDR.
Self-Help Techniques to Cope with Nightmares

While seeking professional help is always recommended, it’s also essential to have some techniques that you can use to manage PTSD nightmares on your own. By learning and practicing self-help techniques, you can increase your sense of control over your mental health and feel empowered to cope with these distressing symptoms. Here are some ways to cope with nightmares at home that you may find helpful.
Relaxation Techniques
When it comes to managing PTSD-related nightmares, relaxation techniques can be very effective. Here are some techniques to help you relax and improve the quality of your sleep:
- Deep breathing: Deep breathing is a simple and effective relaxation technique that can help you calm down and reduce your anxiety. Find a quiet place and take deep, slow breaths. Focus on the sensation of your breath going in and out of your body. Count to three as you inhale and then exhale slowly. Repeat this exercise several times until you feel your body starting to relax.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups to release tension from your body. Start by tensing your toes for a few seconds and then relax them. Move on to your calves, thighs, buttocks, stomach, chest, arms, and shoulders, and repeat the process. Do this exercise in bed before going to sleep to loosen up the tension in your body.
- Meditation: Meditation involves sitting in a quiet place and focusing your attention on the present moment. You can focus on your breath, a word or phrase, or a visualization. The goal is to quiet your mind and let go of negative thoughts and emotions.
- Yoga: Yoga is a low-impact exercise that provides physical and mental benefits. It involves practicing different poses that stretch and strengthen your muscles, while also promoting relaxation and stress relief.
Remember that it may take some time to find the relaxation technique that works best for you. These techniques can help you calm your mind and ease into a restful night’s sleep.
Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT)
Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT) is a powerful cognitive-behavioral technique that can help break the cycle of PTSD-related nightmares. In IRT, the individual is encouraged to create a new, positive ending to the nightmare, and to rehearse this new outcome multiple times during the day. The idea is that by repeatedly imagining a different, more positive ending to the nightmare, the brain will begin to change the memory of the original trauma and replace it with the new, positive memory.
Here are some specifics about how IRT works:
Step 1: Identify the nightmare(s) that are causing the most distress. It’s important to work on one nightmare at a time, starting with the most distressing.
Step 2: Write down the nightmare in as much detail as possible. This will help you to identify the specific elements that are causing the most distress.
Step 3: Rewrite the ending of the nightmare in a positive, empowering way. Be creative and come up with an ending that feels good and brings a sense of resolution.
Step 4: Visualize the new ending multiple times throughout the day. Use vivid imagery and engage as many senses as possible. This will help to strengthen the new, positive memory.
Step 5: Before bed, spend some time rehearsing the new ending in your mind. This will help to prepare your brain for a different outcome if the nightmare does occur.
Step 6: Repeat this process for each nightmare that is causing distress.
IRT can be a useful tool for managing PTSD-related nightmares. It’s important to remember that it may take time and practice to see results, and it’s important to work with a therapist or counselor who is trained in this technique. Additionally, it’s important to use IRT in conjunction with other treatment options, such as therapy and medication, for the most effective management of PTSD symptoms.
Routine for Better Sleep
Creating a routine for better sleep is a key element in managing PTSD-related nightmares. Here are some tips to help establish a consistent routine:
- Set a consistent bedtime: Going to bed at the same time every night can help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Stick to this even on weekends or days off.
- Create a calming pre-sleep ritual: Develop a relaxing routine to do before bed such as taking a warm bath or shower, reading a book, or practicing deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid electronics before bed: The blue light and stimulation from electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops can interfere with sleep. Try to avoid using these devices for at least an hour before bed.
- Create a comfortable sleep environment: Make sure your sleep environment is dark, quiet, and cool. Use comfortable bedding and pillows to promote a restful sleep.
- Avoid stimulating substances: Alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine are stimulants that can disrupt sleep. Avoid consuming these substances, especially in the evening or close to bedtime.
Creating a consistent routine for better sleep can take time and effort, but it is an important step in managing PTSD-related nightmares. By establishing healthy sleep habits, you may find yourself waking up feeling more rested and refreshed.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage PTSD Nightmares

Recovery from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is not easy, but a combination of treatment options and self-help techniques can provide relief. Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage PTSD-related nightmares. By implementing healthy eating habits, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and certain medications, individuals can take control over their symptoms and break the cycle of nightmares. In this section, we will discuss these lifestyle changes and their potential impact on managing PTSD nightmares.
Healthy Eating Habits
Maintaining healthy eating habits is crucial for managing PTSD-related nightmares. Here are some steps individuals can take to ensure they are fueling their bodies in a healthy way:
- Focus on whole foods: Incorporating whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is important for providing the body with the necessary nutrients while avoiding highly processed, sugary foods that can increase anxiety and worsen nightmares.
- Avoid caffeine and sugary foods: Caffeine can interfere with sleep, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. Sugary foods and drinks can cause blood sugar to spike and then crash, resulting in disturbed sleep and can trigger nightmares. Avoiding caffeine and sugary foods before bedtime can help reduce nightmares.
- Consume foods rich in tryptophan: Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is converted into serotonin, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and can alleviate anxiety. Foods that are high in tryptophan include turkey, chicken, soy products, nuts, and seeds.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water throughout the day can improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of nightmares. It is recommended to drink at least 8-10 cups of water each day.
- Consider supplements: In some cases, taking supplements such as magnesium, melatonin, or omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial for reducing nightmares. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
By incorporating these healthy eating habits into their daily routine, individuals can improve their physical health and potentially reduce the frequency and severity of their PTSD-related nightmares.
Exercise
Maintaining an active lifestyle through regular exercise can greatly benefit those suffering from PTSD nightmares. Exercise helps reduce stress levels, improve mood, and promote better sleep quality, which can all help alleviate PTSD symptoms.
Here are some types of exercise that can be beneficial for individuals experiencing PTSD-related nightmares:
| Type of Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular exercise | This type of exercise gets your heart pumping and includes activities such as running, cycling, swimming, and dancing. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day. |
| Strength training | Strength training involves using weights or resistance bands to build muscle and can help improve overall physical and mental health. It can be done with weights, machines, or even bodyweight exercises such as push-ups and squats. |
| Yoga or Tai Chi | These types of exercise focus on breath control, relaxation, and gentle movements. They can help reduce stress and improve relaxation, leading to better sleep quality. |
When starting an exercise routine, it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase intensity and duration over time. It’s also important to choose activities that you enjoy and that fit your abilities and schedule.
In addition to the physical benefits, exercise can also provide a sense of accomplishment and self-confidence, which can help improve overall mood and reduce the impact of PTSD nightmares.
Remember to always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine.
Avoiding Alcohol, Drugs, and Certain Medications
It is essential to avoid alcohol, drugs, and certain medications when dealing with PTSD-related nightmares, as they can worsen the symptoms and the overall condition.
Alcohol acts as a depressant on the central nervous system, which can disrupt sleep quality, and cause nightmares, and anxiety. Drinking alcohol before bedtime can reduce REM sleep, which is critical for emotional regulation and processing. This stage of sleep is essential for managing PTSD symptoms, so alcohol consumption should be avoided by individuals who are experiencing fear and trauma during sleep.
Drugs, especially illegal or unprescribed, can interfere with the sleep cycle and cause or worsen nightmares. Stimulants such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and amphetamines can increase anxiety and cause insomnia. They can also lead to vivid nightmares, which can intensify over time. The misuse of prescription drugs such as painkillers, sedatives, or sleep aids can also affect sleep and cause nightmares.
Certain medications, such as antidepressants, can also trigger nightmares. While these medications can help manage the symptoms of PTSD, they might cause undesirable side effects. If you are experiencing nightmares or other sleep issues related to your PTSD treatment, talk to your doctor or therapist about your concern. They can help you adjust your dosage, try another medication or suggest a different approach to help you manage your symptoms.
The following table summarizes the substances that should be avoided when experiencing PTSD-related nightmares.
| Substances to Avoid | Effects on Sleep and Nightmares |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | Can disturb REM sleep, worsen anxiety and nightmares |
| Illegal or unprescribed drugs | Can interfere with sleep cycle, cause or worsen nightmares |
| Prescription drugs with side effects | May cause nightmares, talk to a doctor to adjust dosage or try another medication |
To manage PTSD-related nightmares, it is essential to avoid these substances and talk to your healthcare provider about your concerns. They can help you find a treatment plan tailored to your needs and help you improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Additional Tips for Managing PTSD-Related Nightmares
As if managing PTSD-related nightmares wasn’t already a challenging task, there are additional factors that can further exacerbate the situation. However, with the right strategies, it’s possible to limit these triggers and improve the quality of your sleep. In this section, we’ll discuss some helpful tips that you can incorporate into your routine to better manage your PTSD-related nightmares. From practicing good sleep hygiene to consulting with a medical professional about potential medication options, there are various steps you can take to successfully break the cycle of PTSD-related nightmares.
Limiting Triggers Before Bedtime
It’s essential to limit triggers that can amplify your PTSD-related nightmares before bedtime. Here are some tips to help you with it:
- Avoid TV and Video Games: Watching violent or triggering content on TV or playing video games with graphic content stimulates your brain and increases the likelihood of nightmares. It is essential to avoid them before bedtime.
- Limit Caffeine Intake: Caffeine is a stimulant that increases alertness and can interfere with your sleep quality. It is essential to avoid caffeinated beverages like tea, coffee, or soda a few hours before bedtime.
- Avoid Alcohol and Nicotine: You might feel that alcohol or nicotine relaxes you, but it can disrupt your sleep cycles and stimulate nightmares.
- Reduce Screen Time: Blue light emitted from electronic devices like smartphones, computers, or tablets suppresses melatonin production, a hormone that helps regulate sleep cycles. It is essential to limit screen time and use apps like night shift mode to reduce the blue light emitted by your devices.
- Relaxation Techniques: Engage in relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation to reduce stress and control your thoughts before bedtime.
These strategies aid in reducing the occurrence and intensity of nightmares, ensuring that you get a good night’s sleep. It’s crucial to maintain your sleep hygiene to improve your overall well-being and lessen the impact of PTSD-related nightmares.
Maintaining Good Sleep Hygiene
When it comes to managing PTSD-related nightmares, maintaining good sleep hygiene is paramount. Poor sleep hygiene not only exacerbates nightmares but also further disrupts sleep, causing a vicious cycle. Here are some tips for maintaining good sleep hygiene:
| Tip: | Description: |
| Stick to a sleep schedule | Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate the body’s internal clock, leading to better sleep. |
| Create a relaxing bedtime routine | Engage in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to soothing music. |
| Create a sleep-conducive environment | Ensure the bedroom is dark, quiet, cool, and comfortable. Use blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out light. |
| Avoid stimulating activities before bed | Avoid activities that can cause emotional arousal, such as watching violent movies or engaging in arguments with others. |
| Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine | These substances are known to disrupt sleep and should be avoided, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. |
| Avoid electronics before bedtime | The blue light emitted by electronic screens can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Avoid electronics usage at least an hour before bed. |
Maintaining good sleep hygiene can go a long way in reducing the frequency and intensity of PTSD-related nightmares. These tips are especially important for individuals with PTSD, as insomnia and nightmares are common symptoms of the disorder. By making simple changes to their sleep habits, individuals can improve the quality of their sleep and reduce the impact of nightmares on their daily life.
Using Medication (Consulting a Medical Professional First)
Using Medication (Consulting a Medical Professional First)
Medications are not typically the first line of treatment for PTSD-related nightmares but may be necessary in some cases. It is crucial to seek professional medical advice before taking any medication, as not all drugs are suitable for everyone.
Here are some medications that may be prescribed for PTSD-related nightmares along with their possible side effects:
- Alpha-agonists: These medications are usually used to treat high blood pressure or anxiety, but they are also helpful in reducing nightmares. Side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and dry mouth.
- Prazosin: This medication is commonly used to treat high blood pressure but can also be used to treat PTSD-related nightmares. It can cause drowsiness, dizziness, or lightheadedness, especially when standing up from a sitting or lying position. These effects are more common at the beginning of treatment or after an increase in the dose.
- Antidepressants: These medications can be used to treat PTSD-related nightmares, particularly those that co-occur with depression. Side effects of antidepressants vary widely, but common ones include drowsiness, nausea, dry mouth, blurred vision, and weight gain.
- Benzodiazepines: These medications are usually prescribed to treat anxiety, insomnia, and muscle spasms. They have sedative effects that can help reduce nightmares, but they can be habit-forming and have potentially dangerous side effects, such as respiratory depression, particularly when combined with alcohol or other depressants. They should only be used under close medical supervision.
Remember, medication should not be the only form of treatment for PTSD-related nightmares. It should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may involve therapy, lifestyle changes, and self-help techniques.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while PTSD-related nightmares can be a challenging and debilitating symptom, there are a variety of treatment options and self-help techniques available to manage them. It’s important to understand that breaking the cycle of PTSD nightmares is not a quick fix, but rather a process that may require ongoing effort and patience.
For those seeking professional help, cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), exposure therapy, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) have shown promise in reducing the frequency and intensity of PTSD nightmares. It’s important to find a therapist who is trained in working with trauma survivors and who can provide a safe and supportive environment.
Self-help techniques, such as relaxation techniques and imagery rehearsal therapy (IRT), can also be effective in managing nightmares. Establishing a routine for better sleep and making lifestyle changes, such as adopting healthy eating habits and increasing physical activity, can further improve sleep quality.
It’s essential to limit triggers before bedtime, maintain good sleep hygiene, and avoid alcohol, drugs, and certain medications that can worsen symptoms. If medication is necessary, it’s crucial to consult with a medical professional first.
Remember that managing PTSD nightmares is a journey, and it’s essential to be patient and compassionate with yourself throughout the process. By seeking appropriate treatment and implementing effective self-help techniques, it’s possible to break the cycle of PTSD nightmares and improve overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can PTSD cause nightmares?
Yes, PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder) can cause nightmares or distressful dreams which can often be recurrent and disturbing.
How do PTSD-related nightmares impact sleep?
PTSD-related nightmares can impact sleep by causing insomnia, fatigue, and disrupted sleep patterns. It can also trigger fear and anxiety in the person, making it difficult to fall and stay asleep.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a therapy that aims to change negative thinking and behavior patterns around sleep. It includes techniques such as sleep restriction, stimulus control, and relaxation training.
What is exposure therapy for PTSD?
Exposure therapy for PTSD is a therapy that involves gradually exposing the person to the fearful or triggering situation or memory in a controlled environment. The aim is to help the person face and overcome their fear and anxiety around the traumatic event.
What is EMDR therapy?
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a therapy that uses eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation to help the person process traumatic memories and reduce their emotional response to them.
What is imagery rehearsal therapy?
Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT) is a technique that involves rehearsing new and positive endings to the person’s recurrent nightmares. By changing the ending of the dream, it can help reduce the distress and fear associated with the nightmare.
How can exercise help manage PTSD-related nightmares?
Exercise can help manage PTSD-related nightmares by reducing stress and anxiety, promoting better sleep, and improving mood and overall well-being.
What are some healthy eating habits to manage PTSD-related nightmares?
Some healthy eating habits to manage PTSD-related nightmares include avoiding foods high in sugar and caffeine, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and staying hydrated.
What are some lifestyle changes that can help manage PTSD-related nightmares?
Some lifestyle changes that can help manage PTSD-related nightmares include avoiding alcohol, drugs, and certain medications, establishing a regular sleep routine, and limiting triggers before bedtime.
When should one consult a medical professional regarding medication for nightmares?
One should consult a medical professional regarding medication for nightmares if self-help techniques and therapy have not been effective in managing nightmares, the nightmares are causing severe distress or impact daily functioning, or if other mental health concerns are present that may require medication.








