As humans, one of the most vital parts of our routine is sleep. It allows us to recharge and prepare for the tasks ahead. Unfortunately, for some people, the ability to fall and stay asleep is a major problem. This perplexing problem is commonly known as insomnia. It’s a condition that affects almost everyone at some point in their lives. Understanding the causes of insomnia and how to deal with it can be a real challenge. In this article, we will delve into the world of insomnia and explore its causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What is Insomnia?
Sleep is crucial for our overall health and wellbeing, as it allows our bodies and minds to rest and rejuvenate. However, for some individuals, getting a restful night’s sleep can be a constant struggle. This condition is known as insomnia and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. So, what exactly is insomnia and how does it affect us? Let’s delve into the definition and types of insomnia.
Definition of Insomnia
Insomnia refers to the inability to fall asleep or to stay asleep for a sufficient amount of time to feel rested and refreshed upon waking. This condition can have various causes, including lifestyle factors, medical conditions, and mental health disorders. Some people may have occasional trouble sleeping, while others experience persistent insomnia that affects their daily functioning.
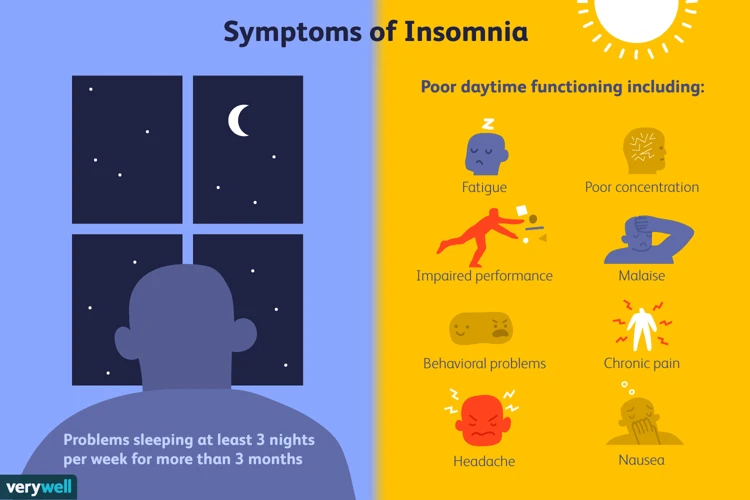
Symptoms:
- Difficulty falling asleep at night
- Waking up frequently during the night
- Waking up too early in the morning
- Feeling tired and fatigued during the day
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering things
- Increased irritability or mood swings
Duration:
Insomnia can be classified into acute or chronic depending on its duration. Acute insomnia typically lasts for a short period of time, usually a few days to a few weeks, and is often caused by stress or a change in sleep environment or routine. On the other hand, chronic insomnia lasts for longer periods, typically lasting for three or more nights a week for a month or more without any obvious cause.
Risk Factors:
Many factors can increase the risk of developing insomnia, including:
- Age – insomnia is more common in adults over 60 years old
- Gender – women are more likely to experience insomnia than men
- Medical conditions – such as chronic pain, asthma, allergies, and neurological disorders
- Shift work or irregular work hours
- Stressful life events – such as job loss, divorce, or the death of a loved one
- Use of certain medications – such as antidepressants, stimulants, and blood pressure medications
- Substance abuse – alcohol and drug abuse can lead to sleeping problems
It’s important to seek treatment for insomnia if it persists and affects your daily life.
Types of Insomnia
There are two types of insomnia: primary and secondary. Each type of insomnia has a different set of causes and treatments.
Primary Insomnia: This type of insomnia is not caused by any medical or psychiatric condition, but rather by poor sleep habits, stress, and other lifestyle factors. It is also commonly referred to as psychophysiological insomnia.
Secondary Insomnia: This type of insomnia is caused by an underlying medical or psychiatric condition, or by medications that are being taken to treat a medical condition. Some medical conditions that can cause secondary insomnia include asthma, arthritis, cancer, heartburn, and Parkinson’s disease. Psychiatric conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder can also cause secondary insomnia.
Having trouble sleeping occasionally is not necessarily a sign of an underlying problem. However, if you experience difficulty sleeping on a regular basis it is important to seek treatment. Both types of insomnia can have a negative impact on your overall health and well-being if left untreated.
Causes of Insomnia

Insomnia can be caused by a variety of complex factors that disrupt our natural sleep patterns. Understanding the underlying causes of insomnia can help in finding the right treatment and prevention methods. Let’s take a closer look at some of the factors that can contribute to the development of insomnia. From our lifestyle choices to medical conditions, these factors can significantly impact our sleep quality and quantity.
Lifestyle Factors
Various lifestyle factors can contribute to the development of insomnia. These include:
| Lifestyle Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Irregular Sleep Schedule | Going to bed and waking up at different times each day can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and make it harder to fall asleep at night. |
| Napping | While napping can be beneficial for some people, excessive and prolonged napping during the day can make it harder to fall asleep at night. |
| Poor Sleep Environment | Having a bedroom that is too hot, too cold, too noisy, or too bright can interfere with the quality of sleep. |
| Caffeine, Alcohol, and Nicotine | Caffeine and nicotine are stimulants that can interfere with sleep, while alcohol can disrupt the natural sleep cycle and cause frequent awakenings during the night. |
| Technology Use | The use of electronic devices before bedtime can disrupt the production of the sleep hormone melatonin and interfere with the sleep-wake cycle. |
| Stress | Stressful events and situations can lead to racing thoughts and anxiety, making it difficult to fall asleep. |
| Sedentary Lifestyle | Lack of physical activity during the day can lead to decreased quality of sleep at night. |
Identifying and addressing these lifestyle factors can be an important step in managing insomnia. Simple changes such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol in the evening, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and engaging in regular physical activity can help improve the quality of sleep and overall health.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Many medical conditions and medications can disrupt our sleep patterns and cause insomnia. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Chronic Pain: Conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and back pain can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. The pain not only wakes us up but also makes it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position.
- Respiratory Problems: Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory disorders can cause shortness of breath and coughing, making it difficult to sleep peacefully through the night.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: Acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and other gastrointestinal disorders can cause discomfort and pain that make it difficult to get a good night’s rest.
- Endocrine Problems: Hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and other endocrine disorders can cause hormonal imbalances that disrupt our sleep patterns.
- Neurological Problems: Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurological disorders can cause sleep disturbances, including insomnia.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Heart failure, heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems can cause shortness of breath and other symptoms that make it difficult to sleep through the night.
- Medications: Many medications, including antidepressants, antihistamines, and blood pressure medications, can cause insomnia as a side effect. Over-the-counter medications like caffeine-containing pain relievers and decongestants can also disrupt sleep.
It’s important to talk to your doctor if you suspect that a medical condition or medication is causing your insomnia. Your doctor may be able to adjust your medication or recommend other treatments to help you sleep better. It’s essential to follow their advice to get the best possible outcome.
Mental Health Disorders
Mental health disorders can be a significant cause of insomnia. Individuals suffering from anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia, for instance, often experience sleep disruptions. The following are some of the most common sleep disorders associated with mental health issues:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Individuals with GAD may have persistent, excessive worry that can interfere with sleep. They may experience difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, often waking up in the middle of the night worrying about the future.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Those who have experienced trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse or violence, may have frequent nightmares or flashbacks, leading to difficulty sleeping.
- Bipolar Disorder: People who suffer from bipolar disorder may experience mania, which can lead to difficulty getting enough sleep due to increased energy levels, and depression, which can cause excessive sleepiness and fatigue.
- Depression: Individuals with depression may experience insomnia or hypersomnia, persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness that interfere with sleep patterns.
- Schizophrenia: Those with schizophrenia may experience difficulty in regulating their sleep and are often more likely to have sleep disorders.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to speak to a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment plan. Seeking treatment for the underlying mental health disorder can help to alleviate insomnia and ultimately improve overall health and wellbeing.
Effects of Insomnia
Insomnia can have a serious impact on a person’s physical and mental health. A lack of quality sleep can result in daytime fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and mood swings, which can affect all aspects of a person’s life, including work and relationships.
Additionally, chronic insomnia can increase the risk of developing conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. This is due in part to the fact that lack of sleep can lead to disruptions in the body’s natural hormone levels, which help regulate important bodily functions such as appetite and metabolism.
People who suffer from insomnia are at a higher risk of experiencing accidents or injuries due to drowsiness and impaired cognitive function. This can be especially dangerous for those who work in industries such as transportation or manufacturing that require focus and attention to detail.
Finally, insomnia can exacerbate underlying mental health conditions, such as anxiety or depression, and can lead to a worsening of symptoms. For some individuals, insomnia may even be a contributing factor to the development of these conditions.
It is clear that the effects of insomnia can be far-reaching and serious. Addressing the underlying causes of insomnia and seeking treatment is crucial in order to mitigate these negative effects and improve overall health and well-being.
Diagnosis of Insomnia

For those who struggle with sleepless nights, getting a proper diagnosis is essential in finding effective treatment. However, diagnosing insomnia is not always straightforward as there are various factors and potential underlying causes to consider. Patients may feel uncertain about what to expect during the diagnostic process and what tests may be involved. In this section, we will explore the steps involved in diagnosing insomnia, including medical history and exams, sleep diaries and tests, and what patients can do to prepare for these assessments.
Medical History and Exam
When diagnosing insomnia, a medical history and exam are important steps to take. Here is what might happen during this process:
1. Discussion of symptoms: The healthcare provider will ask you about your sleep habits and symptoms. Be prepared to describe what it feels like to have trouble sleeping, how long it has been going on, and how frequently it occurs.
2. Medical history: Your doctor or nurse may ask questions about your medical history, such as if you have any medical conditions which may affect your sleep, including sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or if you have had any traumatic experiences that cause anxiety or nightmares.
3. Medication history: The use of certain medications can cause or contribute to the development of insomnia. Your healthcare provider may review any medications or supplements that you are currently taking or have taken in the past.
4. Lifestyle factors: Lifestyle factors can play a big role in the development of insomnia. Your healthcare provider might ask about things like caffeine or alcohol intake, work schedule, or recent changes in your life that may be causing stress.
5. Physical exam: A physical exam can find any underlying medical conditions that might be causing your sleep problems. Your doctor will check for signs of conditions such as thyroid disease, heart disease, or other conditions that can affect sleep.
After this initial discussion, the healthcare provider may recommend a sleep diary or additional testing, such as a sleep study, to help provide a more detailed picture of your sleep patterns. Using all of this information, they will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options to help you manage your insomnia.
Sleep Diary and Tests
A sleep diary is a helpful tool for diagnosing insomnia. It involves keeping track of your sleep patterns for at least two weeks. Each night, you would document the time you went to bed and the time you woke up, as well as any times you woke up during the night. Additionally, you would record any medications or substances you consumed before bed, such as caffeine or alcohol. This will help your doctor understand your overall sleep pattern and assess whether any external factors may be affecting your sleep quality.
There are also a number of tests that can be conducted to diagnose insomnia. One commonly used test is called a polysomnography, which is an overnight sleep study that tracks brain activity, eye movement, heart rate, and breathing. This can help identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to insomnia, such as sleep apnea.
Another test that may be used is called a multiple sleep latency test, which measures how quickly you fall asleep during a series of daytime naps. This test helps assess the severity of insomnia and can also help diagnose other sleep disorders.
It is important to note that a combination of a sleep diary and tests may be necessary in order to accurately diagnose insomnia. By working with your doctor to identify the underlying cause of your insomnia, you can begin to develop a personalized treatment plan to improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Treatment of Insomnia

As treating insomnia can be a complicated process, it’s important to understand the options available to those who are struggling to get a good night’s rest. From lifestyle changes to medication and therapy, there are several approaches that can be taken to address this condition. Let’s explore some of these options in detail.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can greatly improve your chances for getting better sleep if you are suffering from insomnia. Here are some lifestyle changes you can make to improve your sleep quality:
| Change | Description |
|---|---|
| Stick to a sleep schedule | Establish a regular bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s clock and establish a regular sleep pattern. |
| Reduce caffeine intake | Avoid consuming caffeine in the late afternoon or evening. Caffeine can interfere with sleep and stay in your system for hours. |
| Avoid consuming alcohol and nicotine | Both alcohol and nicotine can interfere with sleep quality, so avoid consuming them before bedtime. |
| Make your bedroom a comfortable sleep environment | Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in comfortable bedding and pillows, and remove any distractions from the room. |
| Establish a relaxing bedtime routine | Engage in activities that help you unwind and relax before bed, such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music. |
| Avoid napping during the day | If possible, avoid taking naps during the day as they can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night. |
| Exercise regularly | Regular exercise can improve sleep quality, but avoid exercising close to bedtime as the stimulation can interfere with your ability to fall asleep. |
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can significantly improve your chances of getting the restful sleep your body needs to stay healthy and alert.
Sleep Medications
When other treatments and lifestyle changes fail to improve insomnia symptoms, doctors may prescribe sleep medications to help patients get better sleep. Different types of sleep medications work in different ways, so it is important to discuss the options with a doctor.
Prescription Sleep Medications: There are different types of prescription sleep medications, some of which are listed below:
| Medication | How it works | Potential side effects |
|---|---|---|
| Benzodiazepines (such as Valium, Ativan) | Increases drowsiness by slowing down brain activity | Dizziness, headaches, grogginess, habit-forming |
| Non-Benzodiazepine sedatives (such as Ambien, Lunesta) | Mimics the effects of benzodiazepines without the same level of dependency risk | Dizziness, dry mouth, grogginess, sleepwalking |
| Ramelteon (brand name Roxyd) | Targets the sleep-wake cycle by mimicking melatonin, a natural hormone that helps regulate sleep | Dizziness, headaches, daytime sleepiness |
Over-the-Counter Sleep Aids: These are medications that can be purchased without a prescription, such as Unisom, Tylenol PM, and Nyquil. However, they can still have potential side effects and should be used with caution. Some common side effects include dizziness, nausea, and grogginess.
It is important to note that while sleep medications can be effective in the short-term, they should not be relied upon as a long-term solution. Dependence on sleep medications can develop, and they can also mask an underlying sleep disorder or health condition. It is crucial to consult with a doctor regarding the use of sleep medications and to follow the prescribed dosage and usage instructions carefully.
Therapy and Counseling
Therapy and counseling are effective treatments for insomnia, especially when the underlying cause is related to mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression or PTSD. In these cases, therapy can help individuals identify and manage the root cause of their insomnia. Here are some common types of therapy that can be beneficial for treating insomnia:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – This type of therapy focuses on identifying negative patterns of behavior and thought that may be contributing to sleep problems. CBT helps individuals create new patterns of behavior and thought that promote better sleep habits.
- Relaxation Therapy – Relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce anxiety and promote better sleep.
- Stimulus Control Therapy – This type of therapy involves making changes to the sleep environment and routine to promote better sleep. For example, only using the bed for sleep and sex, avoiding screens before bed and establishing a regular sleep schedule.
- Sleep Restriction Therapy – This therapy limits the amount of time an individual spends in bed, which can help to normalize sleep patterns and increase sleep efficiency.
- Group Therapy – Participating in group therapy sessions with others who have similar sleep problems can provide support, education and practical advice for better sleep hygiene.
It is important to note that therapy and counseling may take time to produce noticeable results, and individuals may need to pursue multiple therapy sessions before seeing improvements in their sleep quality. However, therapy can be a valuable tool for individuals who want to address the root cause of their insomnia and improve their overall quality of life.
Alternative Treatments
For those seeking non-medication options for insomnia treatment, there are several alternative treatments available. While some of these treatments may lack scientific evidence to support their effectiveness, many individuals report that they find them helpful. Some alternative treatments for insomnia are listed below:
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Its proponents believe that acupuncture can help to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. |
| Meditation and Mindfulness | Meditation and mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and guided imagery, can promote relaxation and calmness. Some people find that these techniques help them to fall asleep more quickly and sleep more soundly. |
| Herbal Remedies | Several herbs, such as valerian root and chamomile, have been traditionally used to aid with sleep. These herbs can be consumed as teas, capsules, or extracts. However, it is important to note that some herbs may interact with medications and have potential side effects. |
| Aromatherapy | Essential oils from plants, such as lavender or bergamot, can be used in aromatherapy to promote relaxation and sleep. These oils can be used in diffusers or added to baths. |
| Yoga | The practice of yoga involves stretching, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques. Many individuals find that regular yoga practice promotes better sleep and helps them feel more rested upon waking. |
| Massage Therapy | Massage therapy involves the manipulation of soft tissues to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and alleviate pain. Some people find that regular massage helps to improve their sleep quality. |
It is important to note that alternative treatments may not be suitable for everyone and may have potential side effects. It is always recommended to talk with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or supplement.
Prevention of Insomnia

It’s no secret that getting a good night’s sleep is essential to our overall health and well-being. For those who suffer from insomnia, ensuring that they establish good sleep habits is crucial to prevent the onset of sleepless nights. Fortunately, there are a variety of effective strategies that can be employed to prevent insomnia and help maintain healthy sleep patterns. Let’s explore some of the ways to prevent insomnia and promote healthy sleep.
Healthy Sleep Habits
Good sleep hygiene or having healthy sleep habits is an essential factor in treating and preventing insomnia. Here are some of the healthy sleep habits that you can incorporate into your daily routine.
| Healthy Sleep Habits |
|---|
| Establish a regular sleep schedule – Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends to regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. |
| Avoid naps – Napping during the day can confuse your internal clock, making it difficult to fall asleep at night. |
| Create a relaxing bedtime routine – Develop a calming routine before bedtime such as taking a warm bath or reading a book that can signal your brain that it’s time to sleep. |
| Make your bedroom sleep-friendly – Use comfortable bedding, maintain an ideal temperature, and block out noise and light that can disrupt your sleep. |
| Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol – Avoid consuming caffeinated drinks, smoking, and drinking alcohol at least 4-6 hours before bedtime, as these substances can interfere with your sleep. |
| Exercise regularly – Regular physical exercise can help regulate your sleep cycle and improve the quality of your sleep. However, strenuous exercise should be avoided close to bedtime. |
| Limit screen time before bed – Using electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones, or watching TV can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating sleep. |
| Manage stress – Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help alleviate stress and promote better sleep. |
By making these healthy lifestyle changes, you can improve the quality of your sleep, prevent insomnia, and promote overall well-being. However, if your insomnia persists, it’s essential to seek medical attention to identify the underlying causes of your sleep disturbances and receive appropriate treatment.
Stress Management
Stress is one of the leading causes of insomnia, and managing stress is essential for improving sleep. Here are some stress management techniques that can help:
- Deep breathing: Practice deep breathing exercises to help you relax and reduce stress. Focus on inhaling slowly through your nose, holding your breath for a few seconds, and then exhaling slowly through your mouth.
- Meditation: Meditation is a great way to clear your mind and reduce stress. Try to sit quietly in a comfortable position and focus on your breathing or repeat a calming phrase or word.
- Yoga: Yoga is a combination of physical poses, breathing techniques, and meditation that can help reduce stress and improve sleep. Find a yoga class or try a beginner’s yoga video.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce stress and improve sleep quality. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Relaxation techniques: Try different relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery, to help you relax and reduce stress.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It can be helpful for managing stress and improving sleep.
By incorporating these stress management techniques into your daily routine, you may be able to reduce stress and improve your chances of getting a good night’s sleep.
Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical exercise can play a crucial role in preventing insomnia. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help provide the body with necessary nutrients while avoiding foods high in sugar, caffeine, and alcohol. Regular exercise, particularly aerobic exercise, can help regulate the sleep-wake cycle by promoting daytime alertness and better, more restful sleep at night.
Some tips for incorporating diet and exercise into your routine include:
- Choose lean protein sources like chicken, fish, and beans. Avoid excessive amounts of red meat and processed foods.
- Incorporate whole grains like brown rice and quinoa into your diet.
- Avoid consuming excessive amounts of caffeine and alcohol, particularly in the afternoon and evening.
- Choose fruits and vegetables that are high in fiber and vitamins.
- Try engaging in regular physical exercise, such as brisk walking, running, or swimming, for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Consider incorporating relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, into your exercise routine to help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
A healthy diet and regular exercise can not only improve sleep quality, but overall physical and mental health as well. However, it is important to consult a healthcare provider before making any major changes to your diet or exercise routine, particularly if you have any underlying medical conditions.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to seek medical attention if insomnia is persistent and affecting your daily life. Chronic insomnia can lead to serious health issues and worsen existing medical conditions. Here are some signs that indicate the need to see a doctor:
Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep for several nights a week for more than a month. This can lead to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating during the day.
Worsening of existing medical conditions. Insomnia can exacerbate conditions such as heart disease, depression, and chronic pain.
Use of sleep aids for an extended period of time. Sleep aids can help in the short term, but if they are used for an extended period of time, they can lead to dependency and cause other health problems.
Increased consumption of drugs or alcohol. Substance abuse can worsen insomnia and lead to other health issues.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the underlying cause of your insomnia and recommend appropriate treatment. Remember, getting adequate sleep is essential for your overall health and well-being, so don’t hesitate to seek help if you are struggling with insomnia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, insomnia is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including lifestyle habits, medical conditions, and mental health disorders. Additionally, untreated insomnia can lead to a myriad of negative effects on both physical and mental health.
Fortunately, there are various options available to help manage and treat insomnia. Lifestyle changes, such as creating a regular sleep schedule and avoiding stimulants, can greatly improve sleep quality. In addition, sleep medication and therapy or counseling can also be effective treatments. It is important to note that alternative treatments, such as herbal remedies, should be approached with caution and always discussed with a healthcare professional.
Prevention of insomnia involves adopting healthy sleep habits, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet and exercise routine. These preventative measures can help reduce the risk of developing insomnia and improve overall health and wellbeing.
If you are struggling with sleep, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
In summary, understanding the causes and effects of insomnia is crucial in identifying and treating this common sleep disorder. By making lifestyle changes, seeking proper treatment, and adopting preventative measures, better sleep and overall health can be achieved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary symptoms of insomnia?
The primary symptoms of insomnia include difficulty falling or staying asleep, waking too early in the morning, and feeling tired upon waking.
What are some common lifestyle factors that contribute to insomnia?
Some common lifestyle factors that can contribute to insomnia include caffeine intake, alcohol and drug use, irregular sleep schedules, and stress.
What medical conditions can cause insomnia?
Medical conditions like chronic pain, breathing problems, and neurodegenerative diseases can cause insomnia.
Can certain medications cause insomnia?
Yes, medications like antidepressants, stimulants, and blood pressure medications can cause insomnia as a side effect.
Can mental health disorders contribute to insomnia?
Yes, mental health disorders like anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can contribute to insomnia.
What are the potential effects of chronic insomnia?
Chronic insomnia can lead to mood changes, difficulty concentrating, fatigue, weakened immune system, and an increased risk of accidents and injuries.
What is the first step in diagnosing insomnia?
The first step in diagnosing insomnia is taking a thorough medical history and physical exam.
What types of treatment are available for insomnia?
Treatment options for insomnia include lifestyle changes, sleep medications, therapy/counseling, and alternative treatments like acupuncture.
What are some healthy sleep habits that can help prevent insomnia?
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and keeping the bedroom cool and dark can all help prevent insomnia.
When should someone see a doctor for insomnia?
If insomnia is impacting daily life and it persists for more than a few weeks, it may be time to consult a doctor.








