Sleep is a vital part of our daily routine, essential for our overall health and wellbeing. However, for many people, getting a good night’s sleep can be a challenge. Insomnia, a sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, can cause difficulty falling and staying asleep, leaving individuals feeling tired, irritable, and unable to function during the day. Despite its prevalence, insomnia can be a perplexing and complex condition, with a variety of causes and treatment options available. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for insomnia, as well as how individuals can manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Causes of Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that affects numerous individuals. Understanding the causes of insomnia can be complex since various factors associated with lifestyle, medical conditions, mental health, and circadian rhythm disorders could lead to sleep disruptions. In this section, we will discuss the diverse contributing factors of insomnia and how each one can disrupt one’s sleeping patterns.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors can have a significant impact on sleep patterns and can contribute to the development of insomnia. These factors are often modifiable and can be addressed through changes in daily routines and behaviors.
- Shift work: People who work non-traditional hours such as overnight shifts or rotating shifts may experience disrupted sleep patterns due to changes in the body’s natural circadian rhythms.
- Excessive caffeine intake: Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with sleep if consumed in large amounts or later in the day. It is important to limit caffeine intake, especially in the afternoon and evening hours.
- Alcohol consumption: While alcohol may initially make an individual feel drowsy or relaxed, excessive consumption can lead to disrupted sleep patterns and frequent awakenings throughout the night.
- Irregular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at different times each day can cause the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle to become disrupted, leading to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to insomnia. It is important to engage in regular physical activity, but avoid vigorous exercise right before bed.
- Poor sleep environment: A comfortable sleep environment is essential for good-quality sleep. A room that is too hot, too cold, or noisy can lead to difficulty falling and staying asleep.
Addressing these lifestyle factors through changes in daily routine and behaviors can help improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of developing insomnia. Adopting healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, limiting caffeine intake, engaging in regular physical activity, and creating a comfortable sleep environment, can help promote restful sleep.
Medical Conditions and Medications
There are several medical conditions and medications that can contribute to Insomnia. Let’s take a closer look at some of them:
| Medical Conditions | Medications |
|---|---|
| Chronic Pain: conditions such as arthritis can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. Pain medications can also cause Insomnia. | Stimulants: medications used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and certain antidepressants can interfere with sleep. |
| Respiratory Problems: conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can cause nighttime breathing difficulties that disrupt sleep. | Corticosteroids: these medications, often used to treat inflammation, can cause insomnia as a side effect. |
| Endocrine Disorders: conditions such as hyperthyroidism and diabetes can disrupt sleep patterns. | Some Blood Pressure Medications: beta blockers and some other blood pressure medications can cause Insomnia or make it worse. |
| Gastrointestinal Problems: acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and other gastrointestinal issues can interfere with sleep. | Some Weight Loss Products: certain weight loss drugs can cause insomnia as a side effect. |
If you’re experiencing Insomnia and you’re taking medication or have a medical condition that may be contributing to your Insomnia, it’s important to talk to your doctor. They may be able to adjust your medication or recommend other treatments to help you get a better night’s sleep.
Mental Health Conditions
Mental Health Conditions
Mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can all contribute to insomnia. These conditions can cause racing thoughts, worry, and emotional distress, making it difficult for individuals to relax and fall asleep. Additionally, individuals with mental health conditions may experience nightmares or intrusive thoughts during the night, further disrupting their sleep.
Insomnia can also be a symptom of certain mental health conditions, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Individuals with these conditions may experience episodes of mania or psychosis that disrupt their sleep patterns.
In some cases, medications used to treat mental health conditions can also contribute to insomnia. For example, certain antidepressants and stimulants can interfere with sleep.
It is important for individuals with mental health conditions to discuss any sleep disturbances with their healthcare provider. Treating the underlying mental health condition may help improve insomnia symptoms.
| Mental Health Condition | Impact on Insomnia |
|---|---|
| Depression | May cause racing thoughts, worry, and emotional distress, making it difficult to fall asleep. |
| Anxiety | May cause fear, restlessness, and intrusive thoughts that disrupt sleep. |
| Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) | May cause nightmares or flashbacks during the night, making it difficult to sleep. |
| Bipolar Disorder | Episodes of mania or psychosis can disrupt sleep patterns. |
| Schizophrenia | Psychotic episodes can disrupt sleep patterns. |
| Medications used to treat mental health conditions | Certain medications, such as antidepressants and stimulants, can interfere with sleep. |
Circadian Rhythm Disorders
One potential cause of insomnia is disruptions to an individual’s circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is an internal 24-hour “clock” that regulates various bodily processes including sleep-wake cycles. The following are some examples of circadian rhythm disorders that can cause or contribute to insomnia:
- Jet Lag: This condition occurs when a person travels across multiple time zones, disrupting their circadian rhythm. The result is difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, as well as daytime fatigue and decreased performance.
- Shift Work Disorder: This disorder happens when an individual works outside of the traditional 9-to-5 schedule, often resulting in a misalignment or disruption of the circadian rhythm. People with shift work disorder may experience difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, as well as excessive sleepiness during waking hours.
- Delayed Sleep Phase Disorder: This condition occurs when an individual’s biological clock is set later than desired. People with delayed sleep phase disorder have difficulty falling asleep at a “normal” hour and may sleep in late in the morning.
- Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder: In contrast to delayed sleep phase disorder, advanced sleep phase disorder is characterized by a circadian rhythm that is set earlier than desired. People with this disorder may fall asleep earlier than desired and wake up earlier than they would like.
- Night Shift Workers: People who work night shifts may experience difficulty sleeping during the day due to the disruptions to their circadian rhythm.
Understanding the underlying cause of insomnia is important in determining the best course of treatment. If an individual’s insomnia is related to a circadian rhythm disorder, treatment and management may require adjustments to the individual’s sleep schedule or work hours. It may also require the use of certain medications or behavioral strategies to help regulate the sleep-wake cycle. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action.
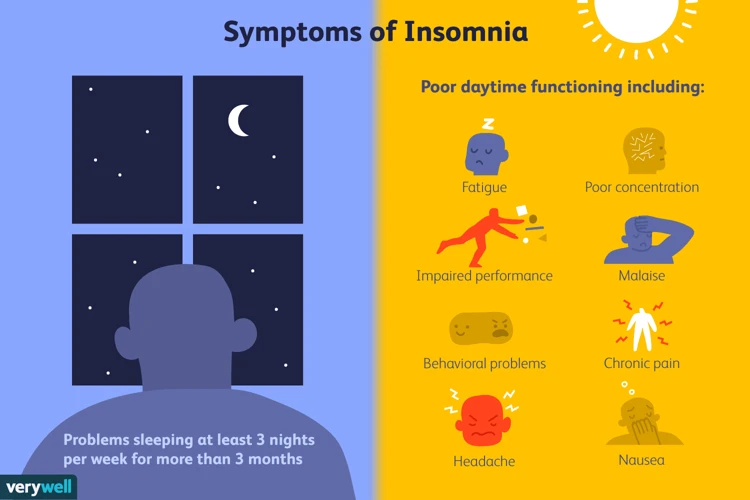
Symptoms of Insomnia

Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that can have a disruptive impact on a person’s daily life. The difficulty of falling asleep and staying asleep can lead to a host of symptoms that can affect physical and mental well-being. It is important to recognize the symptoms of insomnia and seek appropriate treatment to improve sleep quality and overall health. In this section, we will highlight the various symptoms of insomnia that people may experience.
Difficulty falling asleep
One common symptom of insomnia is difficulty falling asleep. This can manifest in a few different ways, such as taking a long time to fall asleep or feeling like you can’t fall asleep at all. Some of the potential causes of this include anxiety, stress or an overactive mind. Additionally, certain lifestyle habits or medications may contribute to difficulty falling asleep.
Factors that can contribute to difficulty falling asleep include:
- Stress and Anxiety: Feeling worried or anxious can make it difficult to relax and fall asleep. Racing thoughts and a sense of tension can keep individuals awake at night, making it challenging to wind down and fall asleep.
- Screen Time: Exposure to bright screens, such as those on smartphones or tablets, can suppress melatonin production and make it more difficult to fall asleep. This is because the blue light emitted by these devices interferes with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Caffeine: Consuming caffeine later in the day can make it difficult to fall asleep as it is a stimulant that can disrupt the natural sleep process. Drinking coffee, tea or other caffeinated beverages in the late afternoon or evening may make it hard to nod off at bedtime.
- Alcohol: Although it can make individuals feel drowsy initially, alcohol can actually interfere with restful sleep. It decreases the amount of time spent in REM sleep, which is important for proper rest and brain function.
- Medications: Certain medications may contribute to difficulty falling asleep as a side effect. For example, some antidepressants or stimulants can interfere with the natural sleep process.
If you regularly experience difficulty falling asleep, it may be worth considering changes in behavior or medication adjustments to improve your sleep quality.
Difficulty staying asleep
One common symptom of insomnia is difficulty staying asleep or waking up frequently during the night. This can cause individuals to feel fatigued and less focused during the day, affecting their overall quality of life.
There are various reasons why someone may experience difficulty staying asleep. Some of these reasons are outlined in the following table:
| Lifestyle factors | Medical conditions | Medications |
|---|---|---|
| Consuming caffeinated beverages or nicotine before bedtime | Chronic pain | Antidepressants |
| Drinking alcohol before bedtime | Respiratory conditions, such as asthma or sleep apnea | Blood pressure medications |
| Eating a heavy meal before bedtime | Neurological conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease | Stimulants, such as ADHD medication or certain asthma inhalers |
| Experiencing high levels of stress or anxiety | Endocrine disorders, such as hyperthyroidism | Corticosteroids |
Addressing the underlying cause of difficulty staying asleep is important in finding a solution. For example, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, practicing relaxation techniques, and treating underlying medical conditions may improve sleep quality. Additionally, sleep hygiene techniques such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment can also be effective in promoting better sleep. In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary to treat chronic insomnia.
Waking up too early
One of the common symptoms of insomnia is waking up too early. This means that a person wakes up earlier than they intended to and find it difficult to go back to sleep. This can result in feeling fatigued or tired throughout the day.
There can be many reasons for waking up too early, including lifestyle factors and medical conditions. Here are some possible causes:
| Lifestyle Factors | Medical Conditions |
|---|---|
|
|
If you are waking up too early on a regular basis, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause. There are several treatment options available, including:
- Lifestyle changes: focusing on good sleep hygiene, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and regular exercise can help improve sleep quality.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): this therapy involves changing negative thoughts and behaviors about sleep and improving sleep habits.
- Prescription medications: healthcare providers may prescribe sleep aids to help manage symptoms.
- Complementary treatments: some people may find relief with complementary treatments such as acupuncture or herbal supplements.
It is important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Daytime sleepiness
Daytime sleepiness is a common symptom of insomnia that can greatly impact a person’s quality of life. It can result from difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to a lack of restorative sleep. People who experience daytime sleepiness often feel fatigued, drowsy, and may have difficulty staying focused on tasks. They may also experience physical symptoms such as headaches, muscle aches, or difficulty regulating body temperature.
The impact of daytime sleepiness
Daytime sleepiness can have a significant impact on a person’s daily activities, making it hard for them to concentrate and be productive at work or school. It can also make it difficult to engage in activities they enjoy or to socialize. People who experience daytime sleepiness may also be at higher risk for accidents or errors, particularly when driving, operating heavy machinery, or engaging in other activities that require sustained attention.
Possible causes of daytime sleepiness
There are several possible causes of daytime sleepiness. Inadequate sleep, sleep fragmentation, or poor sleep quality can all result in excessive daytime sleepiness. Medical conditions such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy can also lead to daytime sleepiness. Some medications can cause drowsiness or fatigue, which can make it difficult to stay awake during the day. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, or high levels of stress can also contribute to daytime sleepiness.
How to manage daytime sleepiness
If you experience daytime sleepiness, it’s important to talk with your healthcare provider to identify any underlying conditions that may be causing or contributing to your symptoms. In some cases, simple lifestyle changes such as improving sleep habits or reducing stress can help alleviate daytime sleepiness. Treatment options for underlying medical conditions may also be necessary to improve sleep quality and reduce symptoms.
Here are some tips to manage daytime sleepiness:
| Make sleep a priority | Try to establish a regular sleep schedule and avoid electronic devices before bedtime. Create a relaxing environment that promotes sleep. |
| Stay active | Regular exercise can help improve sleep quality and reduce stress, leading to less daytime sleepiness. |
| Limit caffeine and alcohol | These substances can interfere with sleep and lead to daytime drowsiness. |
| Reduce stress | Try relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises to reduce stress and promote relaxation. |
| Talk with your doctor | If you continue to experience daytime sleepiness, talk with your healthcare provider to identify any underlying conditions that may be causing your symptoms and to explore treatment options. |
By taking steps to improve sleep quality and identify underlying conditions that may be contributing to daytime sleepiness, you can reduce symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
Irritability and mood disturbances
People who experience difficulty sleeping may also suffer from irritability and mood disturbances during the daytime. This can severely affect their daily activities and interpersonal relationships. Irritability and mood disturbances are common symptoms of insomnia that can be caused by various factors, including:
| Causes of Irritability and Mood Disturbances |
| Lack of sleep |
| Stress and anxiety |
| Depression |
| Medication side effects |
| Substance abuse |
| Health problems |
The lack of sufficient sleep can lead to irritability and mood disturbances, as it can impede the body’s ability to regulate emotions. This is often accompanied by feelings of exhaustion and lethargy, which can further exacerbate these symptoms. Stress and anxiety can also contribute to irritability and mood disturbances, as the body’s stress response can trigger changes in mood and behavior.
Depression is another common cause of irritability and mood disturbances in people with insomnia. Depression can cause changes in sleep patterns, including difficulty falling and staying asleep, which can lead to daytime symptoms such as irritability and mood disturbances.
Medication side effects can also cause irritability and mood disturbances in people who are treating other medical conditions. Substance abuse can also cause similar symptoms, as the body’s dependence on drugs or alcohol can disrupt normal sleep patterns and lead to psychological changes.
Lastly, underlying health problems such as neurological or hormonal disorders can cause irritability and mood disturbances. These conditions can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and cause symptoms such as mood swings, irritability, and depression.
Treating irritability and mood disturbances associated with insomnia usually involves addressing the root cause of the problem. This may involve a combination of lifestyle changes, natural remedies, medical interventions, and therapy. It is important to seek medical attention if your symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Difficulty concentrating and memory impairment
One of the most common symptoms of insomnia is difficulty concentrating and memory impairment, which can significantly affect a person’s daily life. Insomnia can lead to a lack of the quality sleep that is necessary for consolidation of memories and proper functioning of the brain.
People with insomnia often experience forgetfulness, difficulty with problem-solving, and a decreased ability to focus on tasks. This can be especially problematic for people who work or study, as it can impede their ability to perform optimally in these areas.
Research has shown that inadequate sleep affects the hippocampus, which is responsible for the consolidation of memories. A lack of sleep can also disrupt the functioning of the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in attention, decision-making, and behavior.
Insomnia-related difficulty concentrating and memory impairment can also affect personal relationships, as it can make it difficult for a person to remember important events or conversations. It can also lead to irritability and mood disturbances, making communication and interaction with others more challenging.
It is important for people with insomnia to address their symptoms through lifestyle changes or medical interventions to improve their quality of sleep and, in turn, improve their cognitive functioning.
| Effects of Insomnia on Concentration and Memory |
|---|
| Difficulty with problem-solving |
| Decreased ability to focus on tasks |
| Forgetfulness |
| Disrupts hippocampus functioning |
| Disrupts prefrontal cortex functioning |
| Affects personal relationships |
| Can lead to irritability and mood disturbances |
Increased accidents or errors
Individuals who suffer from insomnia may also experience increased accidents or errors during their waking hours, especially if they are operating heavy machinery or driving a vehicle. This is because sleep deprivation can impair cognitive function and response times, leading to poor judgment and decreased focus.
Some examples of potential accidents or errors due to insomnia include:
- Car accidents: Sleep deprivation is a common cause of car accidents. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, drowsy driving causes an estimated 100,000 crashes each year in the United States.
- Workplace accidents: Individuals who work in professions that require alertness, such as construction or manufacturing, are also at risk for accidents due to insomnia. A lack of sleep can impair motor function and reaction time, leading to injuries or fatalities in the workplace.
- Medication errors: Sleep deprivation can also cause cognitive impairment, leading to mistakes in medication dosages or other healthcare-related errors.
- Overall decrease in productivity: Chronic insomnia can lead to a decrease in overall productivity in various areas of life including work, school and social interactions.
It is vital for individuals with symptoms of insomnia to seek treatment to avoid not only the physical and mental health problems, but also these accidents and errors that can have serious consequences. By making lifestyle changes and working with healthcare providers, individuals with insomnia can improve their quality of life and performance in daily activities.
Treatment Options for Insomnia
For those struggling with insomnia, finding an effective treatment can be a perplexing journey. There are a plethora of different options available, ranging from natural remedies to prescription medications. It can be overwhelming to know where to start or which approach to take. However, by exploring various treatment options and working with a healthcare professional, individuals can find the right solution to improve their sleep and overall well-being. In this section, we will highlight some of the different ways to treat insomnia, including lifestyle changes, sleep hygiene techniques, natural remedies, medical interventions, cognitive behavioral therapy, prescription and over-the-counter medications, and complementary treatments.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can be an effective way to combat insomnia. The following table outlines some lifestyle changes that can help improve sleep quality:
| Lifestyle Change | Description |
|---|---|
| Stick to a sleep schedule | Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. This helps regulate the body’s internal clock and can improve sleep quality over time. |
| Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol | Caffeine and nicotine are both stimulants that can interfere with sleep. Alcohol may help you fall asleep, but can disrupt sleep later in the night. |
| Get regular exercise | Regular exercise can help improve sleep quality, but avoid exercising too close to bedtime as it can make falling asleep more difficult. |
| Avoid eating heavy meals before bed | Eating a heavy meal before bed can make it harder to fall asleep and can cause discomfort during the night. |
| Establish a relaxing bedtime routine | A relaxing routine, such as taking a warm bath or reading a book, can help signal to the body that it is time to sleep. |
| Create a sleep-conducive environment | Your sleeping environment should be cool, quiet, and dark. Use comfortable bedding and eliminate any distractions that could interfere with sleep. |
Implementing these lifestyle changes can take time, but the effort can be well worth it in terms of improved sleep quality and overall health.
Sleep Hygiene Techniques
Sleep hygiene refers to a set of practices that are believed to improve the quality of sleep. These techniques can be very effective in promoting better sleep, however, they require effort and long-term commitment. Here are some sleep hygiene techniques that can promote better sleep:
| Technique | Description |
| Avoiding caffeine | Refers to avoiding caffeine-containing beverages such as coffee, tea, and soft drinks, especially in the evening. Caffeine can stimulate the nervous system and make it difficult to sleep. |
| Avoiding alcohol | Alcohol can initially cause drowsiness, but it can disrupt later sleep stages, causing insomnia, frequent awakenings, and even nightmares. |
| Avoiding smoking and nicotine | Smoking and nicotine can have a stimulating effect similar to caffeine, they also cause disruptions in the breathing patterns that can lead to sleep disturbances. |
| Maintaining regular sleep-wake schedule | Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day including weekends, helps to set the body’s internal “clock” and promote a regular sleep pattern. |
| Creating a relaxing sleeping environment | Ensure the sleeping environment is quiet, dark, cool, and comfortable. Use earplugs, blackout curtains, white noise machines, or comfortable pillows to promote sleep. |
| Keeping a sleep diary | Keeping track of the hours slept, quality of sleep, and factors that may have contributed to sleep disruptions can help identify patterns and develop better sleep habits. |
| Avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime | Watching stimulating TV programs, using electronic devices, playing video games, or engaging in stressful activities can have a stimulating effect on the brain and make it difficult to fall asleep. |
| Relaxation techniques | Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and guided imagery can reduce stress and promote a more relaxed state that is conducive to sleep. |
| Getting regular physical exercise | Exercise helps to stimulate the production of endorphins, which can promote feelings of relaxation and happiness. However, avoid exercising within 3 hours of bedtime, as it can stimulate the body and interfere with sleep. |
These techniques are effective for individuals who have occasional trouble sleeping or those with mild insomnia. However, individuals with severe or chronic insomnia may require additional interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or medication. It’s also important to remember that sleep hygiene techniques may not work for everyone, and it may take time to see results.
Natural Remedies
There are several natural remedies that people use to treat insomnia. These remedies may not work for everyone, but they are worth trying before turning to prescription or over-the-counter medications. Here are some of the most popular natural remedies:
| Remedy | Description |
|---|---|
| Herbal Supplements | Herbs like valerian root, chamomile, and passionflower are often used as sleep aids. They may be taken in supplement form or as a tea. |
| Aromatherapy | Scents like lavender, chamomile, and vanilla have been shown to help people relax and fall asleep. Essential oils can be used in a diffuser or applied topically. |
| Exercise | Regular exercise can help improve sleep quality. However, it is important to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime. |
| Meditation and Relaxation Techniques | Practices like yoga, tai chi, and deep breathing may help calm the body and the mind, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep. |
| Dietary Changes | Avoiding stimulants like caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, especially close to bedtime, as well as eating a balanced diet can promote better sleep. |
It is important to note that natural remedies may have side effects and may interact with other medications or supplements. It is always best to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new remedy, even if it is natural.
Medical Interventions
When it comes to treating insomnia, there are a variety of medical interventions that may be used to help manage symptoms. It’s important to discuss with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for each individual case.
Some medical interventions for insomnia may include:
- Prescription Medications: There are several prescription medications that can be used to help treat insomnia. These may include sedatives, antidepressants, or antipsychotics. It’s important to note that these medications may have potential side effects and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Over-the-counter medications such as diphenhydramine or doxylamine may be used as sleep aids. However, it’s important to read labels carefully and only take as directed, as overuse or misuse may lead to negative side effects.
- Light Therapy: For individuals with circadian rhythm disorders, light therapy may be used to help regulate their sleep-wake cycle. This involves exposure to bright light during specific times of day to help reset the body’s internal clock.
- Electromagnetic Stimulation: Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive procedure that uses electromagnetic stimulation to help regulate sleep patterns. This treatment involves placing an electromagnetic coil on the scalp that sends magnetic pulses to the brain to help regulate neural activity.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): For individuals with sleep apnea, CPAP therapy may be used to help regulate their breathing during sleep. This involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers a continuous stream of air to keep the airway open.
It’s important to note that while medical interventions may be helpful for managing symptoms of insomnia, they should always be used under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare provider. It’s also important to explore other treatment options, such as lifestyle changes or cognitive-behavioral therapy, before resorting to medical interventions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a type of talk therapy that is an effective treatment for individuals with insomnia. CBT-I aims to address unhelpful thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia and replace them with more helpful ones. The following are the components of CBT-I:
- Sleep Education: Therapists provide sleep education to patients to help them understand sleep patterns, sleep hygiene, and the physical and emotional factors that affect sleep. Patients are also educated about the importance of sleep for overall health.
- Stimulus Control: Stimulus control involves identifying and eliminating environmental factors that interfere with sleep, such as noise, light, and uncomfortable bedding. This technique also involves creating a positive association between the bed and sleep by using the bed only for sleeping and sex.
- Sleep Restriction: This technique involves limiting the amount of time that a patient spends in bed to the amount of time they typically sleep. Over time, the patient’s sleep efficiency improves, and they gradually increase the time they spend in bed.
- Cognitive Therapy: This component of CBT-I helps individuals identify negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to insomnia and replace them with more rational, positive ones. Patients learn to challenge negative thoughts and change their attitudes towards sleep.
- Relaxation Techniques: Relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation and deep breathing exercises can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Patients are taught how to use these techniques to reduce stress and anxiety and improve sleep quality.
CBT-I is often more effective than medication for treating insomnia because:
- It has long-lasting effects even after treatment ends.
- It addresses the underlying causes of insomnia rather than just the symptoms.
- It has a low risk of side effects compared to medication.
If you have insomnia, consider CBT-I as a treatment option. A healthcare professional who specialized in sleep disorders can recommend CBT-I or refer you to a therapist who specializes in this approach.
Prescription Medications
Prescription medications are usually reserved for severe or chronic cases of insomnia. They are typically recommended after lifestyle changes, sleep hygiene techniques, and natural remedies have been exhausted. Prescription medications may be effective in promoting sleep, but they also have potential side effects and risks.
There are several types of prescription medications typically used to treat insomnia:
- Benzodiazepines: These drugs work by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps to calm the brain and promote sleep. Examples of benzodiazepines include diazepam (Valium) and lorazepam (Ativan).
- Nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics: Also known as z-drugs, these medications also enhance the effects of GABA, but they bind to a different site on the receptor than benzodiazepines. Examples of nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics include zolpidem (Ambien) and eszopiclone (Lunesta).
- Antidepressants: Certain types of antidepressants, such as trazodone, amitriptyline, and doxepin, may be prescribed off-label for insomnia. They work by altering the levels of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which can help regulate sleep.
It is important to note that prescription medications should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they may have potential risks and side effects. They should also be used only as a short-term solution, as long-term use can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms when discontinued. If you are considering prescription medication for your insomnia, be sure to discuss the potential risks and benefits with your doctor.
Over-the-Counter Medications
There are a variety of over-the-counter medications that can be effective in treating insomnia. However, it is important to use them cautiously and in accordance with the instructions on the packaging, as some of these medications can be habit-forming.
Here is a table outlining some common over-the-counter medications for insomnia:
| Medication | How it works | Potential side effects |
|---|---|---|
| Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) | Antihistamine with sedative effects | Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, blurred vision, constipation |
| Melatonin | Hormone that helps regulate sleep-wake cycle | Dizziness, headache, nausea, drowsiness |
| Valerian root | Herbal supplement with sedative effects | Headache, dizziness, stomach problems, dry mouth |
| Doxyalamine (Unisom) | Antihistamine with sedative effects | Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, blurred vision, constipation |
It is important to note that while these medications may be effective for short-term use, they are not intended for long-term use. If insomnia persists, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of the sleep disturbance and develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
Complementary Treatments
In addition to the more traditional methods of treating insomnia, there are also a variety of complementary treatments that may help improve sleep quality. These methods can be used in conjunction with other treatments, or on their own for those who prefer natural remedies.
One complementary treatment option is acupuncture, which involves the use of small needles inserted at specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow. This technique has been shown to be effective in improving sleep quality and duration in some individuals.
Another option is yoga, which can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. A study found that individuals who practiced yoga for eight weeks had improved sleep quality and reduced use of sleep medication.
Massage therapy is another alternative treatment that may improve sleep quality. It has been shown to decrease cortisol levels, which can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
Aromatherapy, or the use of essential oils, is also a complementary treatment option that may improve sleep quality. Lavender oil, in particular, has been shown to have a calming effect and improve sleep quality in individuals with insomnia.
Lastly, melatonin supplements may be used as a complementary treatment for insomnia. Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the body that helps regulate sleep-wake cycles. Supplementing with melatonin may help improve sleep quality and duration, particularly in individuals with circadian rhythm disorders.
While these complementary treatments may be effective for some individuals, it is important to remember that everyone experiences insomnia differently, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is also important to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any complementary treatment, to ensure safety and effectiveness.
| Complementary Treatments | Description |
|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Small needles inserted at specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow. |
| Yoga | Reduces stress and promotes relaxation, leading to improved sleep quality. |
| Massage Therapy | Decreases cortisol levels, reducing stress and promoting relaxation. |
| Aromatherapy | Use of essential oils, such as lavender, to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. |
| Melatonin Supplements | Supplementing with melatonin may help improve sleep quality and duration, particularly in individuals with circadian rhythm disorders. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, insomnia is a common sleep disorder that can have a detrimental impact on a person’s physical and mental health. The causes of insomnia can vary from lifestyle factors to medical conditions, mental health conditions, and circadian rhythm disorders. Common symptoms of insomnia include difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, waking up too early, daytime sleepiness, irritability, mood disturbances, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, and increased accidents or errors.
The treatment options for insomnia can range from lifestyle changes and sleep hygiene techniques to natural remedies, medical interventions, cognitive-behavioral therapy, prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, and complementary treatments. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any treatment for insomnia to identify the underlying cause and determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Overall, addressing and managing insomnia can improve a person’s quality of life and overall health, as well as reduce the risk for other health conditions that may arise as a result of chronic sleep deprivation. By taking steps to identify and address the underlying causes of insomnia and utilizing effective treatment options, individuals can improve their sleep quality and enjoy the many benefits that come with getting adequate rest. With proper care and attention, insomnia can be successfully managed and overcome.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that makes it difficult for a person to fall asleep or stay asleep, even when they have the opportunity to do so.
What are some common causes of insomnia?
Common causes of insomnia include lifestyle factors, medical conditions and medications, mental health conditions, and circadian rhythm disorders.
What are the symptoms of insomnia?
Symptoms of insomnia include difficulty falling asleep, difficulty staying asleep, waking up too early, daytime sleepiness, irritability and mood disturbances, difficulty concentrating and memory impairment, and increased accidents or errors.
What are some lifestyle changes that can help with insomnia?
Lifestyle changes that can help with insomnia include avoiding caffeine and alcohol, establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and getting regular exercise.
What are some natural remedies for insomnia?
Natural remedies for insomnia include herbal supplements like valerian root and chamomile, melatonin supplements, and relaxation techniques like meditation and yoga.
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a type of therapy that addresses the underlying thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia, using techniques like relaxation training and sleep hygiene education.
What are some prescription medications that can be used to treat insomnia?
Prescription medications that can be used to treat insomnia include benzodiazepines, non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, and antidepressants.
What are some over-the-counter medications that can be used to treat insomnia?
Over-the-counter medications that can be used to treat insomnia include antihistamines like diphenhydramine and doxylamine succinate.
What are some complementary treatments for insomnia?
Complementary treatments for insomnia include acupuncture, massage therapy, and aromatherapy.
Is it possible to cure insomnia completely?
While there is no guaranteed cure for insomnia, many people find that a combination of lifestyle changes, natural remedies, and medical interventions can help them manage their symptoms and improve the quality of their sleep.








